Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Uploaded by
Benin06Copyright:
Available Formats
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Uploaded by
Benin06Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
Uploaded by
Benin06Copyright:
Available Formats
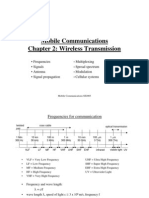
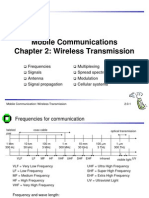
Mobile Communications
Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
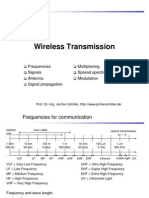
Frequencies Multiplexing
Signals Spread spectrum
Antenna Modulation
Signal propagation Cellular systems
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.1
Frequencies for communication
twisted coax cable optical transmission
pair
1 Mm 10 km 100 m 1m 10 mm 100 m 1 m
300 Hz 30 kHz 3 MHz 300 MHz 30 GHz 3 THz 300 THz
VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF infrared visible light UV
VLF = Very Low Frequency UHF = Ultra High Frequency
LF = Low Frequency SHF = Super High Frequency
MF = Medium Frequency EHF = Extra High Frequency
HF = High Frequency UV = Ultraviolet Light
VHF = Very High Frequency
Frequency and wave length:
= c/f
wave length , speed of light c 3x108m/s, frequency f
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.2
Frequencies for mobile communication
VHF-/UHF-ranges for mobile radio
simple, small antenna for cars
deterministic propagation characteristics, reliable connections
SHF and higher for directed radio links, satellite communication
small antenna, focusing
large bandwidth available
Wireless LANs use frequencies in UHF to SHF spectrum
some systems planned up to EHF
limitations due to absorption by water and oxygen molecules
(resonance frequencies)
weather dependent fading, signal loss caused by heavy rainfall etc.
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.3
Frequencies and regulations
ITU-R holds auctions for new frequencies, manages frequency bands
worldwide (WRC, World Radio Conferences)
Europe USA Japan
Cellular GSM 450-457, 479- AMPS, TDMA, CDMA PDC
Phones 486/460-467,489- 824-849, 810-826,
496, 890-915/935- 869-894 940-956,
960, TDMA, CDMA, GSM 1429-1465,
1710-1785/1805- 1850-1910, 1477-1513
1880 1930-1990
UMTS (FDD) 1920-
1980, 2110-2190
UMTS (TDD) 1900-
1920, 2020-2025
Cordless CT1+ 885-887, 930- PACS 1850-1910, 1930- PHS
Phones 932 1990 1895-1918
CT2 PACS-UB 1910-1930 JCT
864-868 254-380
DECT
1880-1900
Wireless IEEE 802.11 902-928 IEEE 802.11
LANs 2400-2483 IEEE 802.11 2471-2497
HIPERLAN 2 2400-2483 5150-5250
5150-5350, 5470- 5150-5350, 5725-5825
5725
Others RF-Control RF-Control RF-Control
27, 128, 418, 433, 315, 915 426, 868
868
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.4
Signals I
physical representation of data
function of time and location
signal parameters: parameters representing the value of data
classification
continuous time/discrete time
continuous values/discrete values
analog signal = continuous time and continuous values
digital signal = discrete time and discrete values
signal parameters of periodic signals:
period T, frequency f=1/T, amplitude A, phase shift
sine wave as special periodic signal for a carrier:
s(t) = At sin(2 ft t + t)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.5
Fourier representation of periodic signals
1
g (t ) c an sin( 2nft ) bn cos( 2nft )
2 n 1 n 1
1 1
0 0
t t
ideal periodic signal real composition
(based on harmonics)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.6
Signals II
Different representations of signals
amplitude (amplitude domain)
frequency spectrum (frequency domain)
phase state diagram (amplitude M and phase in polar coordinates)
A [V] A [V] Q = M sin
t[s]
I= M cos
f [Hz]
Composed signals transferred into frequency domain using Fourier
transformation
Digital signals need
infinite frequencies for perfect transmission
modulation with a carrier frequency for transmission (analog signal!)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.7
Antennas: isotropic radiator
Radiation and reception of electromagnetic waves, coupling of
wires to space for radio transmission
Isotropic radiator: equal radiation in all directions (three
dimensional) - only a theoretical reference antenna
Real antennas always have directive effects (vertically and/or
horizontally)
Radiation pattern: measurement of radiation around an antenna
z
y z
y x ideal
x isotropic
radiator
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.8
Antennas: simple dipoles
Real antennas are not isotropic radiators but, e.g., dipoles with lengths
/4 on car roofs or /2 as Hertzian dipole
shape of antenna proportional to wavelength
/4 /2
Example: Radiation pattern of a simple Hertzian dipole
y y z
simple
x z x dipole
side view (xy-plane) side view (yz-plane) top view (xz-plane)
Gain: maximum power in the direction of the main lobe compared to
the power of an isotropic radiator (with the same average power)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.9
Antennas: directed and sectorized
Often used for microwave connections or base stations for mobile phones
(e.g., radio coverage of a valley)
y y z
directed
x z x antenna
side view (xy-plane) side view (yz-plane) top view (xz-plane)
z
z
x
sectorized
x antenna
top view, 3 sector top view, 6 sector
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.10
Antennas: diversity
Grouping of 2 or more antennas
multi-element antenna arrays
Antenna diversity
switched diversity, selection diversity
receiver chooses antenna with largest output
diversity combining
combine output power to produce gain
cophasing needed to avoid cancellation
/2 /2
/4 /2 /4 /2
+ +
ground plane
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.11
Signal propagation ranges
Transmission range
communication possible
low error rate
Detection range
detection of the signal
possible
no communication sender
possible
Interference range transmission
signal may not be distance
detected detection
signal adds to the
interference
background noise
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.12
Signal propagation
Propagation in free space always like light (straight line)
Receiving power proportional to 1/d²
(d = distance between sender and receiver)
Receiving power additionally influenced by
fading (frequency dependent)
shadowing
reflection at large obstacles
refraction depending on the density of a medium
scattering at small obstacles
diffraction at edges
shadowing reflection refraction scattering diffraction
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.13
Real world example
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.14
Multipath propagation
Signal can take many different paths between sender and receiver due to
reflection, scattering, diffraction
multipath
LOS pulses pulses
signal at sender
signal at receiver
Time dispersion: signal is dispersed over time
interference with “neighbor” symbols, Inter Symbol Interference (ISI)
The signal reaches a receiver directly and phase shifted
distorted signal depending on the phases of the different parts
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.15
Effects of mobility
Channel characteristics change over time and location
signal paths change
different delay variations of different signal parts
different phases of signal parts
quick changes in the power received (short term fading)
Additional changes in long term
power
distance to sender fading
obstacles further away
slow changes in the average power
received (long term fading)
t
short term fading
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.16
Multiplexing
Multiplexing in 4 dimensions channels ki
space (si) k1 k2 k3 k4 k5 k6
time (t)
frequency (f) c
code (c) t c
t
Goal: multiple use s1
f
of a shared medium s2
f
c
Important: guard spaces needed!
t
s3
f
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.17
Frequency multiplex
Separation of the whole spectrum into smaller frequency bands
A channel gets a certain band of the spectrum for the whole time
Advantages:
no dynamic coordination
necessary k1 k2 k3 k4 k5 k6
works also for analog signals
c
f
Disadvantages:
waste of bandwidth
if the traffic is
distributed unevenly
inflexible
guard spaces
t
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.18
Time multiplex
A channel gets the whole spectrum for a certain amount of time
Advantages:
only one carrier in the
medium at any time
throughput high even k1 k2 k3 k4 k5 k6
for many users
c
Disadvantages: f
precise
synchronization
necessary
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.19
Time and frequency multiplex
Combination of both methods
A channel gets a certain frequency band for a certain amount of time
Example: GSM
Advantages:
better protection against
tapping
protection against frequency
k1 k2 k3 k4 k5 k6
selective interference
higher data rates compared to c
code multiplex
f
but: precise coordination
required
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.20
Code multiplex
Each channel has a unique code
k1 k2 k3 k4 k5 k6
All channels use the same spectrum
at the same time
c
Advantages:
bandwidth efficient
no coordination and synchronization
necessary
good protection against interference and
tapping f
Disadvantages:
lower user data rates
more complex signal regeneration
Implemented using spread spectrum t
technology
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.21
Modulation
Digital modulation
digital data is translated into an analog signal (baseband)
ASK, FSK, PSK - main focus in this chapter
differences in spectral efficiency, power efficiency, robustness
Analog modulation
shifts center frequency of baseband signal up to the radio carrier
Motivation
smaller antennas (e.g., /4)
Frequency Division Multiplexing
medium characteristics
Basic schemes
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
Frequency Modulation (FM)
Phase Modulation (PM)
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.22
Modulation and demodulation
analog
baseband
digital
signal
data digital analog
101101001 modulation modulation radio transmitter
radio
carrier
analog
baseband
digital
signal
analog synchronization data
demodulation decision 101101001 radio receiver
radio
carrier
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.23
Digital modulation
Modulation of digital signals known as Shift Keying
Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK): 1 0 1
very simple
low bandwidth requirements
t
very susceptible to interference
1 0 1
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK):
needs larger bandwidth
t
Phase Shift Keying (PSK): 1 0 1
more complex
robust against interference
t
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.24
Advanced Frequency Shift Keying
bandwidth needed for FSK depends on the distance between
the carrier frequencies
special pre-computation avoids sudden phase shifts
MSK (Minimum Shift Keying)
bit separated into even and odd bits, the duration of each bit is
doubled
depending on the bit values (even, odd) the higher or lower
frequency, original or inverted is chosen
the frequency of one carrier is twice the frequency of the other
Equivalent to offset QPSK
even higher bandwidth efficiency using a Gaussian low-pass
filter GMSK (Gaussian MSK), used in GSM
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.25
Example of MSK
1 0 1 1 0 1 0
data bit
even 0101
even bits odd 0011
odd bits signal hnnh
value - - ++
low h: high frequency
frequency n: low frequency
+: original signal
-: inverted signal
high
frequency
MSK
signal
t
No phase shifts!
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.26
Advanced Phase Shift Keying
BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying): Q
bit value 0: sine wave
bit value 1: inverted sine wave I
1 0
very simple PSK
low spectral efficiency
10 Q 11
robust, used e.g. in satellite systems
QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying):
I
2 bits coded as one symbol
symbol determines shift of sine wave
needs less bandwidth compared to 00 01
BPSK A
more complex
Often also transmission of relative, not
t
absolute phase shift: DQPSK -
Differential QPSK (IS-136, PHS) 01
11 10 00
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.27
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM): combines amplitude and
phase modulation
it is possible to code n bits using one symbol
2n discrete levels, n=2 identical to QPSK
bit error rate increases with n, but less errors compared to
comparable PSK schemes
Q
0010
0001 Example: 16-QAM (4 bits = 1 symbol)
0011 0000
Symbols 0011 and 0001 have the same phase φ,
φ but different amplitude a. 0000 and 1000 have
a I different phase, but same amplitude.
1000 used in standard 9600 bit/s modems
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.28
Hierarchical Modulation
DVB-T modulates two separate data streams onto a single DVB-T stream
High Priority (HP) embedded within a Low Priority (LP) stream
Multi carrier system, about 2000 or 8000 carriers
QPSK, 16 QAM, 64QAM
Example: 64QAM
good reception: resolve the entire Q
64QAM constellation
poor reception, mobile reception:
resolve only QPSK portion
10
6 bit per QAM symbol, 2 most
I
significant determine QPSK
HP service coded in QPSK (2 bit),
LP uses remaining 4 bit
00
000010 010101
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.29
Spread spectrum technology
Problem of radio transmission: frequency dependent fading can wipe out
narrow band signals for duration of the interference
Solution: spread the narrow band signal into a broad band signal using a
special code
protection against narrow band interference
power interference spread power signal
signal
spread
detection at interference
receiver
protection againstf narrowband interference f
Side effects:
coexistence of several signals without dynamic coordination
tap-proof
Alternatives: Direct Sequence, Frequency Hopping
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.30
Effects of spreading and interference
dP/df dP/df
user signal
i) ii) broadband interference
narrowband interference
f f
sender
dP/df dP/df dP/df
iii) iv) v)
f f f
receiver
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.31
Spreading and frequency selective fading
channel
quality
1 2 5 6
narrowband channels
3
4
frequency
narrow band guard space
signal
channel
quality
2
2 spread spectrum channels
2
2
2
1
spread frequency
spectrum
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.32
DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) I
XOR of the signal with pseudo-random number (chipping sequence)
many chips per bit (e.g., 128) result in higher bandwidth of the signal
Advantages
reduces frequency selective tb
fading
user data
in cellular networks
0 1 XOR
base stations can use the
same frequency range tc
several base stations can chipping
detect and recover the signal sequence
01101010110101 =
soft handover
Disadvantages resulting
signal
precise power control necessary
01101011001010
tb: bit period
tc: chip period
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.33
DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) II
spread
spectrum transmit
user data signal signal
X modulator
chipping radio
sequence carrier
transmitter
correlator
lowpass sampled
received filtered products sums
signal signal data
demodulator X integrator decision
radio chipping
carrier sequence
receiver
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.34
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) I
Discrete changes of carrier frequency
sequence of frequency changes determined via pseudo random number
sequence
Two versions
Fast Hopping:
several frequencies per user bit
Slow Hopping:
several user bits per frequency
Advantages
frequency selective fading and interference limited to short period
simple implementation
uses only small portion of spectrum at any time
Disadvantages
not as robust as DSSS
simpler to detect
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.35
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) II
tb
user data
0 1 0 1 1 t
f
td
f3 slow
f2 hopping
(3 bits/hop)
f1
td t
f
f3 fast
f2 hopping
(3 hops/bit)
f1
tb: bit period td: dwell time
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.36
FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) III
narrowband spread
signal transmit
user data signal
modulator modulator
frequency hopping
synthesizer sequenc
transmitter e
narrowband
received signal
signal data
demodulator demodulator
hopping frequency
sequenc synthesizer
e receiver
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.37
Cell structure
Implements space division multiplex: base station covers a certain
transmission area (cell)
Mobile stations communicate only via the base station
Advantages of cell structures:
higher capacity, higher number of users
less transmission power needed
more robust, decentralized
base station deals with interference, transmission area etc. locally
Problems:
fixed network needed for the base stations
handover (changing from one cell to another) necessary
interference with other cells
Cell sizes from some 100 m in cities to, e.g., 35 km on the country side
(GSM) - even less for higher frequencies
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.38
Frequency planning I
Frequency reuse only with a certain distance between the base
stations
Standard model using 7 frequencies:
f3
f5 f2
f4 f6 f5
f1 f4
f3 f7 f1
f2
Fixed frequency assignment:
certain frequencies are assigned to a certain cell
problem: different traffic load in different cells
Dynamic frequency assignment:
base station chooses frequencies depending on the frequencies
already used in neighbor cells
more capacity in cells with more traffic
assignment can also be based on interference measurements
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.39
Frequency planning II
f3 f3 f3
f2 f2
f1 f1 f1 f2 f3 f7
f3 f3
f2 f2 f2
3 cell cluster f5 f2
f4 f6 f5
f1 f1 f1 f4
f3 f3 f3 f3 f7 f1
f2 f3
f6 f5 f2
7 cell cluster
f2 f2 f2
f1 f f1 f f3
h f3 h 1
3
h1 2
g2 h3
h1 2
g2 h3 g2 3 cell cluster
g1 g1 g1
g3 g3 g3 with 3 sector antennas
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.40
Cell breathing
CDM systems: cell size depends on current load
Additional traffic appears as noise to other users
If the noise level is too high users drop out of cells
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller, http://www.jochenschiller.de/ MC SS02 2.41
You might also like
- F - RST Eva Film: EP304 & EP308Document6 pagesF - RST Eva Film: EP304 & EP308Shashwata ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument41 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissiongskaswinthNo ratings yet
- 2 C02 Wireless TransmissionDocument37 pages2 C02 Wireless TransmissionpurplebrinkNo ratings yet
- c02 Wireless Transmission22Document56 pagesc02 Wireless Transmission22GDNo ratings yet
- C02-Wireless Transmission PDFDocument41 pagesC02-Wireless Transmission PDFmateuussNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument30 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionAisha RiazNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument42 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionBhanumathiNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument41 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionKevin Mauricio VelasquezNo ratings yet
- C02-Wireless TransmissionDocument45 pagesC02-Wireless Transmissionivan.nasasira067No ratings yet
- C02-Wireless TransmissionDocument41 pagesC02-Wireless TransmissionAnushka PatilNo ratings yet
- MObile 4 FinalcseDocument41 pagesMObile 4 Finalcseapi-3717234No ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument44 pagesWireless Transmissionssascw.bcaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Wireless - TransmissionDocument41 pagesLecture 2-Wireless - TransmissionNashrah AnsariNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument41 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionmanikantaNo ratings yet
- Transmission WirelessDocument86 pagesTransmission Wirelessmarwen_zNo ratings yet
- T - CS513 - 02 Wireless TransmissionDocument40 pagesT - CS513 - 02 Wireless TransmissionHeba MaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications: Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument40 pagesMobile Communications: Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionNguyễn Thanh TuyềnNo ratings yet
- Wireless & Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument74 pagesWireless & Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionMichael Derrick OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- C02 Wireless TransmissionDocument48 pagesC02 Wireless TransmissionTrần Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Physical and Link Layer OriginalDocument41 pagesChapter 2 Physical and Link Layer OriginalNilesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument147 pagesWireless Transmissionepc_kiranNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionDocument38 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless TransmissionSafura BegumNo ratings yet
- Wireless Transmission Parti PDFDocument20 pagesWireless Transmission Parti PDFMarkNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument147 pagesWireless TransmissionAshraf EltholthNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Wireless TransmissionDocument74 pagesCh2 Wireless TransmissionJennifer HowellNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 & 4 - Amplitude Modulation - DoneDocument73 pagesLecture3 & 4 - Amplitude Modulation - Donerizwanahmed06100% (1)
- WNLecture 2Document6 pagesWNLecture 2sarahz_2009No ratings yet
- 1 - Basic PrinciplesDocument37 pages1 - Basic Principlessoo chiNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument56 pagesWireless Transmissionስቶፕ ጀኖሳይድNo ratings yet
- JP 1Document90 pagesJP 1yashNo ratings yet
- Cellular 7th SemDocument217 pagesCellular 7th SemKhusveen KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter-01-Introduction To MicrowaveDocument41 pagesChapter-01-Introduction To MicrowaveAbdullahi Abukar FiqiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-Basic Principles Off COmmunicationsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1-Basic Principles Off COmmunicationsDanielle TioNo ratings yet
- Lec1 WN Introduction (13!11!2018) (Dr. Rabia Riaz)Document49 pagesLec1 WN Introduction (13!11!2018) (Dr. Rabia Riaz)majid jalilNo ratings yet
- Base BandDocument110 pagesBase BandMohanNo ratings yet
- Design and Working of FM TransmitterDocument6 pagesDesign and Working of FM TransmitterliyuNo ratings yet
- Notes Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument22 pagesNotes Antennas and Wave PropagationTarun JoshiNo ratings yet
- Photonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesDocument19 pagesPhotonic Technologies For Millimeter - and Submillimeter TechnologiesSenjuti KhanraNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line TheoryDocument50 pagesTransmission Line Theorykhusnul khotimah100% (2)
- NotesDocument16 pagesNotesAviatorX JobinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chap1 MicrowaveDocument17 pagesChap1 MicrowaveVamsi Krishna Dokku100% (1)
- Orginal Seminae Cellonics Seminar ReportDocument33 pagesOrginal Seminae Cellonics Seminar Reportajmalchicku100% (2)
- Slide 1Document41 pagesSlide 1M. Dimas Aviv FahrezaNo ratings yet
- SSD07 CSP 3107 PDFDocument4 pagesSSD07 CSP 3107 PDFPABLO MAURONo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Antennas and Wave Propagation - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - Antennas and Wave Propagation - WWW - Rgpvnotes.invarun palNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document87 pagesChapter 3haileNo ratings yet
- Wave Propagation Part1 Compressed 1648408262Document102 pagesWave Propagation Part1 Compressed 1648408262nimmi chandranNo ratings yet
- Bio Accoustic 131203Document10 pagesBio Accoustic 131203Choirun Nisa Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture23 1233854096875992 3Document41 pagesLecture23 1233854096875992 3Mohammed RizwanNo ratings yet
- Use of A DRM Modulation To Study The Ionosphere G01-6Document4 pagesUse of A DRM Modulation To Study The Ionosphere G01-6philippe.malietNo ratings yet
- Effect of Radiation & HEI On Flicker Noise in 0.5 M CMOS TransistorDocument5 pagesEffect of Radiation & HEI On Flicker Noise in 0.5 M CMOS TransistorShuNo ratings yet
- SignalsDocument8 pagesSignalsaalaa hussienNo ratings yet
- Electgromagnetic Spectrum-Radio WavesDocument10 pagesElectgromagnetic Spectrum-Radio WavesMelai Rodriguez IbardalozaNo ratings yet
- Air Cadet Publication: CommunicationsDocument50 pagesAir Cadet Publication: CommunicationsMarcus DragoNo ratings yet
- Aporte - Stiven G - Step 2 - Recognize The Electrodynamic and Waves ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAporte - Stiven G - Step 2 - Recognize The Electrodynamic and Waves ApplicationsNELSON GARCIANo ratings yet
- RF BasicDocument50 pagesRF Basiciamlouise015No ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Transducers With Piezoelectric Polymer Foil: F. HarnischDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Transducers With Piezoelectric Polymer Foil: F. HarnischAmir JoonNo ratings yet
- Cell Phone Codes For All Types of Phones - Phone Phreaking & HDocument29 pagesCell Phone Codes For All Types of Phones - Phone Phreaking & Hapi-376167950% (4)
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDocument77 pagesMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsBenin06No ratings yet
- C03 Media AccessDocument26 pagesC03 Media AccessbimalhpaNo ratings yet
- C01 IntroductionDocument33 pagesC01 IntroductionAndes HarahapNo ratings yet
- How Not To PrayDocument18 pagesHow Not To PrayBenin06100% (1)
- Esti Mystery 443 Factoring in The DiceDocument19 pagesEsti Mystery 443 Factoring in The DiceKor16No ratings yet
- DAA Lab Work BookDocument98 pagesDAA Lab Work BookKurre anuhyaNo ratings yet
- Food Allowance PolicyDocument5 pagesFood Allowance PolicyRiyas MohamedNo ratings yet
- Technical Data - Fan Model APS0562AA5/15: 1F BPF-1F-01Document2 pagesTechnical Data - Fan Model APS0562AA5/15: 1F BPF-1F-01duc minhNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Chapter 3 - Fuel - Air Cycles and Their Analysis+Document38 pagesFINAL - Chapter 3 - Fuel - Air Cycles and Their Analysis+Vishnu Vardhan Reddy PeddireddyNo ratings yet
- XLC975 BrochureDocument4 pagesXLC975 Brochurejairgonzalez31No ratings yet
- PT 100-Temperature Relay Type TR 250: Digital, 3 Sensors, 3 LimitsDocument1 pagePT 100-Temperature Relay Type TR 250: Digital, 3 Sensors, 3 LimitsGelu BordeaNo ratings yet
- Sand Cone TestDocument6 pagesSand Cone TestOl SreylinNo ratings yet
- Backward Classes & Minorities Welfare Dept.: Fresh ApplicationDocument3 pagesBackward Classes & Minorities Welfare Dept.: Fresh ApplicationManpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentmian577938No ratings yet
- Cyber Crime IncidentDocument2 pagesCyber Crime IncidentkhushankNo ratings yet
- PP CT20 - Borealis Bormod Bf970moDocument3 pagesPP CT20 - Borealis Bormod Bf970moarmandoNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Advanced Techniques Using Microsoft WordDocument28 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Advanced Techniques Using Microsoft WordKramOrtcasNo ratings yet
- Dome Roc Domestic RefrigerationDocument4 pagesDome Roc Domestic RefrigerationMañebog Dagaman MJNo ratings yet
- Me at The Zoo - WikipediaDocument17 pagesMe at The Zoo - WikipediaNishanth NishanthNo ratings yet
- Webex Video Integ Ms Teams TDMDocument59 pagesWebex Video Integ Ms Teams TDMCarlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- Bill of Materials PoolDocument1 pageBill of Materials PoolJustine Yap100% (1)
- Introduction To FlutterDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Flutterdemo workNo ratings yet
- Guardian: 4600 Series Fire Extinguisher Brackets & CoversDocument1 pageGuardian: 4600 Series Fire Extinguisher Brackets & CoversJULIO ALBANo ratings yet
- Technology Habits of Generation Z in Vietnam: AbstractDocument13 pagesTechnology Habits of Generation Z in Vietnam: AbstractUYÊN NGUYỄN THỊ PHƯƠNGNo ratings yet
- 1Z0-1060-20 - CertsOut - MansoorDocument4 pages1Z0-1060-20 - CertsOut - MansoorMansoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- MG 1705 Brochure LQ Trasmision ZF 6WG158 LiugongDocument3 pagesMG 1705 Brochure LQ Trasmision ZF 6WG158 LiugongJose Esteem M CamelNo ratings yet
- Iubirea La Timpul Prezent PDFDocument55 pagesIubirea La Timpul Prezent PDFANo ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica Detector de Gaz Metan Adresabil Cu Sirena UniPOS FD71CNGDocument2 pagesFisa Tehnica Detector de Gaz Metan Adresabil Cu Sirena UniPOS FD71CNGAugustin CatineanNo ratings yet
- Prabhakar Mishra ResumeDocument1 pagePrabhakar Mishra ResumeionigedlalajiNo ratings yet
- MCASHPOINT Know Your Customers Form-1Document1 pageMCASHPOINT Know Your Customers Form-1Sandra CristinmNo ratings yet
- CR 513 AfgjaehqqeDocument2 pagesCR 513 AfgjaehqqeSuryansah MNo ratings yet
- Upload PDF From WF To PA30Document5 pagesUpload PDF From WF To PA30gauravNo ratings yet
- EDUM 541 - Research: Ivy Leah P. Santillan - Maed IDocument27 pagesEDUM 541 - Research: Ivy Leah P. Santillan - Maed IMeriam Gornez TorresNo ratings yet