0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views8254 Timer
8254 Timer
Uploaded by
Yosef KirosThe 8253/54 is a programmable interval timer chip used in PCs to generate precise timing and frequency signals. It contains 3 independent timers that can be programmed to different modes and divisors using an 8-bit control word. The 8254 is an enhanced version that supports higher clock frequencies up to 10MHz. Initialization involves sending control words and divisors to each timer register to set the desired timing parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
8254 Timer
8254 Timer
Uploaded by
Yosef Kiros0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views19 pagesThe 8253/54 is a programmable interval timer chip used in PCs to generate precise timing and frequency signals. It contains 3 independent timers that can be programmed to different modes and divisors using an 8-bit control word. The 8254 is an enhanced version that supports higher clock frequencies up to 10MHz. Initialization involves sending control words and divisors to each timer register to set the desired timing parameters.
Original Description:
8254-timer
Original Title
8254-timer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The 8253/54 is a programmable interval timer chip used in PCs to generate precise timing and frequency signals. It contains 3 independent timers that can be programmed to different modes and divisors using an 8-bit control word. The 8254 is an enhanced version that supports higher clock frequencies up to 10MHz. Initialization involves sending control words and divisors to each timer register to set the desired timing parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views19 pages8254 Timer
8254 Timer
Uploaded by
Yosef KirosThe 8253/54 is a programmable interval timer chip used in PCs to generate precise timing and frequency signals. It contains 3 independent timers that can be programmed to different modes and divisors using an 8-bit control word. The 8254 is an enhanced version that supports higher clock frequencies up to 10MHz. Initialization involves sending control words and divisors to each timer register to set the desired timing parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
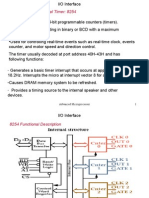
8253/54 Timer
8253/54 Timer Description and Initialization
• PTI (programmable Interval Timer)
• The 8253 chip was used in the IBM PC/XT, but starting with
the IBM PC/AT, the 8254 replaced the 8253.
• 8253 and 8254 have exactly the same pinout.
• 8254 is a superset of the 8253.
Programmable Interval Timer - 8254
Pin Description of 8253/54
A0, A1, and CS
• Inside the 8253/54 timer, there
are 3 counters.
• Each timer works independently
and programmed separately.
• Each counter is assigned an
individual port address.
• The control register common to
all 3 counters and has its own
port.
CLK
• CLK is the input clock frequency, which can range between 0 and 2
MHz for the 8253.
• For input frequencies higher than 2 MHz, the 8254 must be used.
• The 8254 can go as high as 8 MHz, and 8254-2 can go 10 MHz.
OUT
• Can have square-wave, one-shot, and other square-shape waves for
various duty cycles but no sine-wave or saw-tooth shapes.
Gate
• This pin is used to enable or disable the counter.
D0-D7
• The D0-D7 data bus of the 8253/54 is a bidirectional bus
connected to D0-D7 of the system data bus.
• RD and WR are connected to IOR and IOW control signals of the
system bus.
Initialization of the 8253/54
• Each of the three counters of the 8253/54 must be programmed
separately.
• The 8253/54 must be initialized before it is used.
Control word
The figure shows the one-byte control word of the 8253/54.
• D0 chooses between a binary number divisor of 0000 to
FFFFH or a BCD divisor of 0000 to 9999H.
• The highest number is 216 for binary and 104 for BCD.
• To get the highest count, the counter is loaded with zeros.
• D1, D2, and D3 are for mode selection.
• D4 and D5 are for RL0 and RL1
• RL0 and RL1 are used to indicate the size of the divisor, and have
3 options:
1. Read/write MSB only
2. Read/write LSB only
3. Read/write LSB first followed immediately by the MSB.
Operation Modes
Mode 0 Interrupt on terminal count
Mode 1 Programmable one-shot
Mode 2 Rate Generator
Mode 3 Square wave rate generator
Mode 4 Software triggered strobe
Mode 5 Hardware trigger strobe
• All counters are down counters.
• D6 and D7 are used to select the 3 counters, counter 0, counter
1, or counter 2, is to be initialized by the control byte.
• To program a given counter of the 8253/54 to divide the CLK
input frequency one must send the divisor to that specific
counter’s reg.
• To divide the frequency by 10000 (BCD) or 65536 (binary) we
must send in 0 for both high and low bytes.
You might also like
- Mobile Eyewear RecorderDocument7 pagesMobile Eyewear Recordergabriel01022010No ratings yet
- ICT COC Level I Exam Sheet With AnswerDocument17 pagesICT COC Level I Exam Sheet With AnswerYosef Kiros0% (1)
- Proposal ThesisDocument15 pagesProposal ThesisYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- JaspergoldDocument20 pagesJaspergoldmuripaNo ratings yet
- 8253/54 Timer: Section 5.1 8253/54 Timer Description and InitializationDocument19 pages8253/54 Timer: Section 5.1 8253/54 Timer Description and InitializationNaganarasaiah GoudNo ratings yet
- 8253 NewDocument12 pages8253 NewDevNo ratings yet
- Adc0808 and 8253Document35 pagesAdc0808 and 8253Avanish NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Adc0808 and 8253Document35 pagesAdc0808 and 8253Avanish NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer - 8254Document20 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer - 8254Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer.Document68 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer.BETHWEL KIPROTICH100% (1)
- Engineering 4862 Microprocessors: Cheng LiDocument42 pagesEngineering 4862 Microprocessors: Cheng LiriyasekaranNo ratings yet
- Engineering 4862 Microprocessors: Cheng LiDocument14 pagesEngineering 4862 Microprocessors: Cheng LiPaul Erwin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 8253 / 8254 TimerDocument22 pages8253 / 8254 Timershivam mauryaNo ratings yet
- 8254 PDFDocument14 pages8254 PDFMehul Shah100% (1)
- MicroprocessorDocument23 pagesMicroprocessorSahilPrabhakarNo ratings yet
- MP 8253,54 Timer SlidesDocument30 pagesMP 8253,54 Timer SlidesAnuj GuptaNo ratings yet
- The 8253Document29 pagesThe 8253Soumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- 8254 MICROPROCESSOR (Driste)Document13 pages8254 MICROPROCESSOR (Driste)CSE7 NDUBNo ratings yet
- 8254 ModesDocument39 pages8254 ModesVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer 8253 (PIT) : COE305 LabDocument10 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer 8253 (PIT) : COE305 LabudayNo ratings yet
- 8254-Programmable Interval TimerDocument21 pages8254-Programmable Interval TimerSanthosh SandyNo ratings yet
- EEE 311 Online Class 2Document7 pagesEEE 311 Online Class 2KhairulNo ratings yet
- 8253 54-1Document14 pages8253 54-1crsarinNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer - 8254Document35 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer - 8254Arnav BansalNo ratings yet
- Intel 8253/8254 - Programmable Interval TimerDocument15 pagesIntel 8253/8254 - Programmable Interval TimerAjnamol N RNo ratings yet
- MP Module 4 8254Document15 pagesMP Module 4 8254Lekshmi SasidharanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Interfacing ChipsDocument12 pagesModule 4 Interfacing ChipsaviralNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer 8253 or 8254Document13 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer 8253 or 8254api-3749180100% (3)
- Microprocessors & MicrocontrollersDocument20 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollersitsaartihere001No ratings yet
- Interface DAC To A PC: Engineering 4862 MicroprocessorsDocument8 pagesInterface DAC To A PC: Engineering 4862 MicroprocessorsGaneshRahulWolverineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27Document42 pagesLecture 27Archana TiwariNo ratings yet
- CS305 M6 Ktunotes - inDocument35 pagesCS305 M6 Ktunotes - inDipin Preet SinghNo ratings yet
- PIT: Programmable Interval Timer: Introduction To 8253/8254Document34 pagesPIT: Programmable Interval Timer: Introduction To 8253/8254Sayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- 8255 PpiDocument22 pages8255 PpiAswin AswinNo ratings yet
- Programmable Interval Timer 8254Document21 pagesProgrammable Interval Timer 8254Raksha ArulNo ratings yet
- MPMC_UNITDocument308 pagesMPMC_UNITkarthick058No ratings yet
- 8254 AnniDocument43 pages8254 AnniCSE7 NDUBNo ratings yet
- 825482C54Document4 pages825482C54Anonymous lubWipsrWNo ratings yet
- 8254 Micro ProcessorDocument16 pages8254 Micro Processornishukaushal100% (2)
- 8254 Programmable Interval Timer (Andres Suarez-201210937)Document21 pages8254 Programmable Interval Timer (Andres Suarez-201210937)Andres SuarezNo ratings yet
- IC - 8253 PIT Intels Programable Interval Timer ICDocument23 pagesIC - 8253 PIT Intels Programable Interval Timer ICAsawari DudwadkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document122 pagesUnit 3sarokumaarNo ratings yet
- Dma Controller 8257Document14 pagesDma Controller 8257Sreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- Double Data Rate 3 (DDR 3)Document61 pagesDouble Data Rate 3 (DDR 3)vivek narakalaNo ratings yet
- 8253 - Timer: Features of 8253Document5 pages8253 - Timer: Features of 8253srikrishnathotaNo ratings yet
- 8254 Programmable Interval Timer: CS A1 A0 SelecetionDocument5 pages8254 Programmable Interval Timer: CS A1 A0 Selecetionabu sayedNo ratings yet
- Unit III 8254Document29 pagesUnit III 8254Sahil SinghNo ratings yet
- By K. Vijay Kumar Assistant Professor Dept. of ECEDocument31 pagesBy K. Vijay Kumar Assistant Professor Dept. of ECEsignjpcoeNo ratings yet
- The Programmable Timer 8253-8254Document19 pagesThe Programmable Timer 8253-8254atorresh090675No ratings yet
- 6.timer 8254Document15 pages6.timer 8254Akram TahaNo ratings yet
- 8254 Programmable Interval TimerDocument4 pages8254 Programmable Interval Timerapi-26100966100% (1)
- 8254 - Programmable Interval TimerDocument21 pages8254 - Programmable Interval Timeray1975507No ratings yet
- ALL Interview BasicsDocument38 pagesALL Interview BasicsgokulchandruNo ratings yet
- TimerDocument15 pagesTimerCharanjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Part2 Expr03Document10 pagesPart2 Expr03akaka1392781No ratings yet
- 8253Document17 pages8253Parv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Timer InterfaceDocument22 pagesTimer InterfacevinayNo ratings yet
- Dma Controller 8257Document28 pagesDma Controller 8257mnshraoNo ratings yet
- 8253 NotesDocument8 pages8253 NotesSushmita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Timer 8254Document20 pagesProgrammable Timer 8254Axe AxeNo ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- ESP Unit 4Document25 pagesESP Unit 4Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- ESP Unit 1-1Document38 pagesESP Unit 1-1Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- SsssDocument16 pagesSsssYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument30 pagesSwitchingYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- MCQ EspDocument34 pagesMCQ EspYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Milk Supplying in Student Cafe: 1. BackgroundDocument28 pagesMilk Supplying in Student Cafe: 1. BackgroundYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation Project Title:Automatic Room Light Controller With Bidirectional Visitor CountorDocument15 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation Project Title:Automatic Room Light Controller With Bidirectional Visitor CountorYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Final Draft 0Document47 pagesFinal Draft 0Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Ethiopian Institute of Technology-MekelleDocument34 pagesEthiopian Institute of Technology-MekelleYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Final Draft 0Document74 pagesFinal Draft 0Yosef Kiros0% (1)
- Section 2Document12 pagesSection 2Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- By: Gebremariam Fisseha Adigrat University, Ethiopia 2010E.CDocument17 pagesBy: Gebremariam Fisseha Adigrat University, Ethiopia 2010E.CYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Introduction To Information Theory and Coding: Efficient and Reliable CommunicationDocument22 pagesChapter 5: Introduction To Information Theory and Coding: Efficient and Reliable CommunicationYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgmentDocument241 pagesAcknowledgmentYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Performance Analysis of An Opticalcross Connect at DWDM SystemDocument8 pagesChapter Three Performance Analysis of An Opticalcross Connect at DWDM SystemYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- 10m Slab BridgeDocument20 pages10m Slab BridgeYosef Kiros100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Optical Transmitter and ReceiverDocument72 pagesChapter 2: Optical Transmitter and ReceiverYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Procurment and Contract ManagementDocument31 pagesChapter 4 - Procurment and Contract ManagementYosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 1Document28 pagesChapter2 1Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- BlazeVideo HDTV Player v6.0R User's Manual DTR8101Document16 pagesBlazeVideo HDTV Player v6.0R User's Manual DTR8101Oscar Dario NIño GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Panelview Plus PDFDocument244 pagesPanelview Plus PDFdilipNo ratings yet
- 【Product Spec】18.5 inch-1366×768 - DV185WHM-NM2 500nit - Rev.0 - 2019.03.25Document30 pages【Product Spec】18.5 inch-1366×768 - DV185WHM-NM2 500nit - Rev.0 - 2019.03.25MaruthiNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Fg730 Data SheetDocument2 pagesHoneywell Fg730 Data SheetAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet
- TPS61197 Single-String White-LED Driver For LCD TV: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument30 pagesTPS61197 Single-String White-LED Driver For LCD TV: 1 Features 3 DescriptionIrwantoirwanNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Diodes BYV32E, BYV32EB Series Ultrafast, Rugged: Features Symbol Quick Reference DataDocument7 pagesRectifier Diodes BYV32E, BYV32EB Series Ultrafast, Rugged: Features Symbol Quick Reference Datajose luis100% (1)
- KD Maximum Torque Angle AdjustmentDocument4 pagesKD Maximum Torque Angle AdjustmentNassar AbdulrahimanNo ratings yet
- Lab-7 VLANDocument6 pagesLab-7 VLANrobiul_hossen9911No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesComputer NetworkstrevorNo ratings yet
- 1 Futaba Denshi Singapore (S) Pte. LTDDocument65 pages1 Futaba Denshi Singapore (S) Pte. LTDShyamal BhatNo ratings yet
- 5 Channel Radio Remote Control Circuit Based of TX-2B - RX - 2B PairDocument9 pages5 Channel Radio Remote Control Circuit Based of TX-2B - RX - 2B PairSulianto BhirawaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: PNP General Purpose TransistorDocument8 pagesData Sheet: PNP General Purpose TransistorPaquito ClnNo ratings yet
- The Package The Varactors The Supply Line The Combline FilterDocument42 pagesThe Package The Varactors The Supply Line The Combline FilterGara Kodndebe GossiNo ratings yet
- Telect MIX 28Document120 pagesTelect MIX 28dasaintNo ratings yet
- EasyPact EZC - EZC400N3300Document2 pagesEasyPact EZC - EZC400N3300JessFloresBarlaanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Multistage AmplifiersDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices Multistage AmplifiersErroll FonteNo ratings yet
- Thermocouples PDFDocument16 pagesThermocouples PDFFlorin Daniel Ionut BotaNo ratings yet
- Distributed Systems: A Brief IntroductionDocument30 pagesDistributed Systems: A Brief IntroductionKarthikeyan PurusothamanNo ratings yet
- DTA144EUADocument3 pagesDTA144EUAMasUd MzNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Course FlyerDocument1 pageCognitive Course FlyergobinathNo ratings yet
- MC1.25KW Connection DiagramDocument2 pagesMC1.25KW Connection DiagramPedroLHernandezNo ratings yet
- Nokia - Cong Suat Nguon Tieu ThuDocument3 pagesNokia - Cong Suat Nguon Tieu ThuTinh DongNo ratings yet
- Multi-Purpose Self-Contained Digital Access Control Keypad: DK-9523 Programming & Installation ManualDocument10 pagesMulti-Purpose Self-Contained Digital Access Control Keypad: DK-9523 Programming & Installation ManualramedinarNo ratings yet
- CV Rifqi Amalul Ahli V3Document1 pageCV Rifqi Amalul Ahli V3Rifqi Amalul AhliNo ratings yet
- Crossconnect Multiplexer CMXC User ManualDocument156 pagesCrossconnect Multiplexer CMXC User ManualrzhevskiyNo ratings yet
- Tri LoopDocument6 pagesTri LoopFelipe Andrés Camarada SilvaNo ratings yet
- By Anusha K S: LECTURE 1 (Introduction To Automation)Document10 pagesBy Anusha K S: LECTURE 1 (Introduction To Automation)GODWIN TOMNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICADO DE CONFORMIDAD CSA - CoC - 2345436Document4 pagesCERTIFICADO DE CONFORMIDAD CSA - CoC - 2345436Ventilación Minera S.A.SNo ratings yet