0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsPlayers in The Market
Players in The Market
Uploaded by
Harsh ThakurThe securities market consists of the equity market, debt market, and derivatives market. The debt market includes government securities, corporate debt, and money markets. The derivatives market includes options and futures markets. Each market has a primary market where new securities are issued and a secondary market where outstanding securities are traded. Key players in the primary market include merchant bankers, registrars, collecting/coordinating bankers, underwriters, brokers, printers, advertising agencies and mailing agencies. In the secondary market, important roles are played by client brokers, floor brokers, jobbers/market makers, and arbitragers. Other entities include stock exchanges, depositories, foreign institutional investors, primary dealers, mutual funds, custodians, registrars, bankers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Players in The Market
Players in The Market
Uploaded by
Harsh Thakur0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views17 pagesThe securities market consists of the equity market, debt market, and derivatives market. The debt market includes government securities, corporate debt, and money markets. The derivatives market includes options and futures markets. Each market has a primary market where new securities are issued and a secondary market where outstanding securities are traded. Key players in the primary market include merchant bankers, registrars, collecting/coordinating bankers, underwriters, brokers, printers, advertising agencies and mailing agencies. In the secondary market, important roles are played by client brokers, floor brokers, jobbers/market makers, and arbitragers. Other entities include stock exchanges, depositories, foreign institutional investors, primary dealers, mutual funds, custodians, registrars, bankers
Original Title
Players in the Market
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The securities market consists of the equity market, debt market, and derivatives market. The debt market includes government securities, corporate debt, and money markets. The derivatives market includes options and futures markets. Each market has a primary market where new securities are issued and a secondary market where outstanding securities are traded. Key players in the primary market include merchant bankers, registrars, collecting/coordinating bankers, underwriters, brokers, printers, advertising agencies and mailing agencies. In the secondary market, important roles are played by client brokers, floor brokers, jobbers/market makers, and arbitragers. Other entities include stock exchanges, depositories, foreign institutional investors, primary dealers, mutual funds, custodians, registrars, bankers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views17 pagesPlayers in The Market
Players in The Market
Uploaded by
Harsh ThakurThe securities market consists of the equity market, debt market, and derivatives market. The debt market includes government securities, corporate debt, and money markets. The derivatives market includes options and futures markets. Each market has a primary market where new securities are issued and a secondary market where outstanding securities are traded. Key players in the primary market include merchant bankers, registrars, collecting/coordinating bankers, underwriters, brokers, printers, advertising agencies and mailing agencies. In the secondary market, important roles are played by client brokers, floor brokers, jobbers/market makers, and arbitragers. Other entities include stock exchanges, depositories, foreign institutional investors, primary dealers, mutual funds, custodians, registrars, bankers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 17
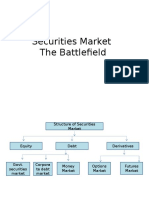
Structure of the Securities Market
• The securities market is the market for Equity, Debt
and Derivatives.
• The Debt Market, in turn, may be divided into 3 parts,
viz., The government securities market, the corporate
debt market and the money market.
• The derivatives market, in turn, may be divided into 2
parts, viz., The Options Market and the Futures
Market.
Except Derivatives market, each of the above markets
has two components, viz., The Primary Market and the
secondary market.
The market where new securities are issue is called the
primary market and the market where outstanding
securities are traded is called the secondary market.
Players in the Market
1. Merchant Bankers: Their functions &
working are very crucial to the operations
in the primary market. They are the issue
managers, lead managers, co-managers
and are responsible to the company and
SEBI.
2. Registrars:
They collect the applications for new issues, their cheques,
stock invests, etc., classify and computerized them.
They also make allotment in consultation with the regional
stock exchange regarding norms in the event of
oversubscription and before a public representative.
They have to despatch the letters of allotments, refund
orders and share certificates within the time schedules
stipulated under the companies act and observe the
guidelines of SEBI and the government and RBI.
Besides, they also have to satisfy the listing requirements
and get them listed on one or more of the stock exchanges.
3. Collecting & Co-ordinating Bankers
• Collecting & co-ordinating bankers may be the
same or different.
• While the former collects the subscriptions in
cash, cheques, stock invest, etc., the latter
collects the information on subscription and
coordinates the collection work and monitors
the same to the registrars and merchant
bankers, who in turn keep the company
informed.
4. Underwriters & Brokers
• Underwriters may be financial institutions, banks,
mutual funds, brokers, etc., and undertake to mobilize
the subscriptions upto some limits.
• Failing to secure subscriptions as agreed to, they have
to make good the shortfalls by their own subscriptions.
• Brokers along with their network of sub-brokers
market the new issues by their own circulars, sending
the application form and follow up recommendations.
5. Printers, Advertising Agencies and Mailing Agencies
are the other organizations involved in the new issue
market operations.
Stock Market Intermediaries
1. Client Brokers: Doing simple broking
between buyers and sellers and earning only
brokerage for their services from the clients.
2. Floor Brokers: Authorized clerks and sub-
brokers who enter the trading floor and
execute orders for the clients or for
members.
3. Jobbers & Market Makers:
• Those members who are ready to buy and sell
simultaneously in selected scrips, offering bid
and offer rates for the brokers and sub-
brokers on the trading floor and earning profit
through margin between buying and selling
rates.
• Market makers undertake the work
compulsory for some companies and bank
finance is available to them.
4. Arbitragers
• Those who do inter market deals for a profit through
differences in prices as between markets, say buy in
Kolkata and sell in Mumbai and vice versa.
5. Badla Financiers: Those members who finance carry
forward deals in specified group (A Group) for a return
in the form of interest, called BADLA Rate. They lend
money or shares for the brokers who are over bought
or oversold respectively at the time of settlement.
Badla is a carry forward facility from one settlement to
another without taking a delivery upto a maximum
period of 90 days at a time, now reduced to 7 to 15
days.
Some Others Are:
Regulators: The key agencies that have a significant regulatory
influence, direct or indirect, over the securities market are currently
as follows:
• The Company Law Board (CLB) which is responsible for the
administration of the Companies Act, 1956.
• The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) which is primarily responsible, inter
alia, for the supervision of banks, money market and the
government securities market.
• The SEBI which is responsible for the regulation of the capital
market.
• The Department of Economic Affairs (DEA), an arm of government,
which, inter alia, which concern with the orderly functioning of the
financial markets as a whole.
• The Department of Company Affairs (DCA), an arm of government,
which is responsible for the administration of corporate bodies.
Stock Exchanges
• A stock exchange is an institution where
securities that have already been issued are
bought and sold.
• Presently there are 23 stock exchanges in
India, the most important ones being the NSE
and BSE.
Listed Securities
• Securities that are listed on various stock
exchanges and hence eligible for being traded
there are called listed securities.
• Presently above 10,000 securities are listed on
all the stock exchanges in India put together.
Depositories
• A Depository is an institution which
dematerializes physical certificates and effects
transfer of ownership by electronic book
entries.
• Presently there are 2 depositories in India,
viz., The National Securities Depository
Limited (NSDL) and the Central Securities
Depository Limited (CDSL).
• Brokers: They are registered members of the
stock exchanges through whom investor
transacts. There are above 10,000 brokers in
India.
• Foreign Institutional Investors: Institutional
investors from abroad who are registered with
SEBI to operate in the Indian Capital Market
are called Foreign Institutional Investors.
There are about 600 of them and they have
emerged as a major force in the Indian
Market.
• Primary Dealers: Appointed by the RBI, primary
dealers serve as underwriters in the primary
market and as market makers in the secondary
market for government securities.
• Mutual Funds: A mutual fund is a vehicle for
collective investment. It pools and manages the
fund of investors. They are more than 30 mutual
funds in India.
• Custodians: A custodian looks after the
investment back office of a mutual fund. It
receives and delivers securities, collects income,
distributes dividends, and segregates the assets
between schemes.
• Registrars: Also known as transfer agent, a registrar is
employed by a company or a mutual fund to handle all
investors related services.
• Bankers to An Issue: The bankers to an issue collect
money on behalf of the company from the applicants.
• Debenture Trustees: When debentures are issued by a
company, a debenture trustee has to be appointed to
ensure that the borrowing firms fulfills its contractual
obligations.
• Venture Capital Funds: A venture capital fund is a pool
of capital which is essentially invested in equity shares
or equity-linked instruments of unlisted companies.
• Credit Rating Agencies: A credit rating agency assigns
ratings primarily to debt securities.
You might also like
- Deccan Proposed SolutionDocument20 pagesDeccan Proposed SolutionAmigos Al CougarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Financial Accounting 6E by Libby Chapter 01Document45 pagesTest Bank Financial Accounting 6E by Libby Chapter 01Ronald James Siruno Monis100% (2)
- Securities Market The BattlefieldDocument14 pagesSecurities Market The BattlefieldJagrityTalwarNo ratings yet
- Securities Markets Structure and Participants - Part 2Document18 pagesSecurities Markets Structure and Participants - Part 2lakshaymalikk11No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Securities Operations and Risk ManagementDocument50 pagesChapter 2 Securities Operations and Risk ManagementMRIDUL GOELNo ratings yet
- Secondary MarketDocument16 pagesSecondary MarketTania GhoshNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument27 pagesIndian Financial SystemDurga Prasad DashNo ratings yet
- Investment BankingDocument64 pagesInvestment BankingSandeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Stock Market "Working of Stock Exchange & Depositary Services"Document11 pagesProject Report On Stock Market "Working of Stock Exchange & Depositary Services"Kruti NemaNo ratings yet
- Secondary Markets in IndiaDocument49 pagesSecondary Markets in Indiayashi225100% (1)
- Iii Semester Model I B Com Cbcs - MG University Core 9-Financial Market Operations 1.what Do You Mean by Financial System?Document38 pagesIii Semester Model I B Com Cbcs - MG University Core 9-Financial Market Operations 1.what Do You Mean by Financial System?Trojan riderNo ratings yet
- Understanding Securities Markets and PerformanceDocument27 pagesUnderstanding Securities Markets and PerformanceSandhya Darshan DasNo ratings yet
- Complete Financial-Capital Market - 33894813 - 2024 - 07 - 25 - 10 - 27Document25 pagesComplete Financial-Capital Market - 33894813 - 2024 - 07 - 25 - 10 - 27subhransusekharjanaNo ratings yet
- New Issue MarketDocument33 pagesNew Issue MarketParul BajajNo ratings yet
- Distributed Generation An OverviewDocument9 pagesDistributed Generation An OverviewAbhishek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Financial MarketDocument11 pagesFinancial MarketDr. Prafulla RanjanNo ratings yet
- New Issue MarketDocument31 pagesNew Issue MarketAashish AnandNo ratings yet
- Financial Services ManagementDocument43 pagesFinancial Services ManagementChandan ParsadNo ratings yet
- Newissuemarket 090919095525 Phpapp01Document31 pagesNewissuemarket 090919095525 Phpapp01vikramrajuNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vibhuti TripathiDocument39 pagesDr. Vibhuti TripathiforevermukeshNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions & Financial Markets Module - 1: by Sanjeev TamhaneDocument35 pagesFinancial Institutions & Financial Markets Module - 1: by Sanjeev TamhaneSwagatJagtapNo ratings yet
- IBE Module 6Document29 pagesIBE Module 6Prathik_Shetty_204No ratings yet
- Section 2 - Secondary MarketsDocument71 pagesSection 2 - Secondary MarketsABHINAV AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Stockbroking 101108232905 Phpapp02Document30 pagesStockbroking 101108232905 Phpapp02Kalpesh GundechaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 SecuritiesDocument12 pagesUnit 2 Securitiespranati maruNo ratings yet
- MGMT 102 - Module - 3Document13 pagesMGMT 102 - Module - 3shubhangiverma2005No ratings yet
- CapitalDocument5 pagesCapitalLyn AmbrayNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System Chapter 1Document16 pagesIndian Financial System Chapter 1Rahul GhosaleNo ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial SystemDocument25 pagesOverview of Indian Financial SystemDr. Meghna DangiNo ratings yet
- Summer Placement at IFCDocument20 pagesSummer Placement at IFCCrazytoonagainNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Indian Debt MarketDocument55 pagesPresentation On Indian Debt Marketpriya_12345632369100% (9)
- Module 2 Part 2Document65 pagesModule 2 Part 2Shivam AroraNo ratings yet
- Discount MarketDocument13 pagesDiscount MarketAakanksha SanctisNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument33 pagesCapital Marketahanadgp2003No ratings yet
- PFM QBDocument22 pagesPFM QBhinowal388No ratings yet
- Merchant Banking and Financial Services Two Marks Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesMerchant Banking and Financial Services Two Marks Questions and AnswersadammurugeshNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial SystemDocument34 pagesIndian Financial SystemVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indian Money Market and Capital MarketDocument41 pagesIndian Money Market and Capital Marketsamrulezzz100% (4)
- Newissuemarket 090919095525 Phpapp01Document31 pagesNewissuemarket 090919095525 Phpapp01Dr-Afzal Basha HSNo ratings yet
- Secondary Markets in IndiaDocument16 pagesSecondary Markets in IndiaAvanishNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: - Investment Environment in India - Overview of Indian Financial System - Investment AlternativesDocument35 pagesUnit 1: - Investment Environment in India - Overview of Indian Financial System - Investment AlternativesSatya KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document18 pagesCH 5RevathyNo ratings yet
- 234presentation On Indian Debt MarketDocument57 pages234presentation On Indian Debt Marketvikasronaldo71No ratings yet
- Discount and Finance House of IndiaDocument25 pagesDiscount and Finance House of Indiavikram_bansal_5No ratings yet
- Overview of The Indian Securities MarketDocument7 pagesOverview of The Indian Securities MarketNiftyDirectNo ratings yet
- Mgt-205: Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument78 pagesMgt-205: Financial Markets and InstitutionsBishal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Money Market by MostafaDocument28 pagesMoney Market by Mostafamostafaali123No ratings yet
- SapmmDocument31 pagesSapmmmeparamtoshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Financial ManagementDocument41 pagesFundamentals of Financial Managementesshaker doubleddNo ratings yet
- Advanced Corporate FinanceDocument6 pagesAdvanced Corporate FinanceVeasna KhunNo ratings yet
- Unit III Capital MarketDocument27 pagesUnit III Capital MarketAbin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Federal Bank Training Part 2Document8 pagesFederal Bank Training Part 2Gayathry SureshNo ratings yet
- FMBODocument10 pagesFMBOHimani ChavanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument25 pagesProjectDeana PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Secondary Market: What Is It?Document6 pagesSecondary Market: What Is It?Vaibhav SinghviNo ratings yet
- Vaibhav (Banking and Insurance) - 1Document10 pagesVaibhav (Banking and Insurance) - 1Vaibhav TiwariNo ratings yet
- Indianfinancialsystem 180826104033Document29 pagesIndianfinancialsystem 180826104033Vivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- S 2 - Indian Financial SystemDocument12 pagesS 2 - Indian Financial SystemAninda DuttaNo ratings yet
- A Primer On Share MarketDocument24 pagesA Primer On Share MarketrahulunknownNo ratings yet
- 850Document21 pages850Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Money Market Its InstrumentsDocument13 pagesMoney Market Its InstrumentsHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bba IV Bis Unit 4 NotesDocument12 pagesBba IV Bis Unit 4 NotesHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Fso Unit-3Document7 pagesFso Unit-3Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Mutual Funds 1Document42 pagesMutual Funds 1Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- School of Managment Sciences, Varanasi (An Autonomous College)Document2 pagesSchool of Managment Sciences, Varanasi (An Autonomous College)Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Capital Primary MarketDocument45 pagesCapital Primary MarketHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Significance of Diagrams and GraphsDocument2 pagesSignificance of Diagrams and GraphsHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3Harsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Bba IV Bis Unit 3 NotesDocument18 pagesBba IV Bis Unit 3 NotesHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Secondary MarketDocument22 pagesSecondary MarketHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- AFM Section C Group 1 Assignment CalculationsDocument12 pagesAFM Section C Group 1 Assignment CalculationsAkshitNo ratings yet
- Underwriting of SharesDocument13 pagesUnderwriting of Sharesarshia45No ratings yet
- About SebiDocument55 pagesAbout SebichaudharipravinNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Directors Loans Under FRS 102 FAQsDocument7 pagesAccounting For Directors Loans Under FRS 102 FAQswattersed1711No ratings yet
- Ipo ProjectDocument82 pagesIpo ProjectKalyani JoshiNo ratings yet
- Zacks Equity Research Report For Stanley Black & DeckerDocument8 pagesZacks Equity Research Report For Stanley Black & DeckerAnup KelkarNo ratings yet
- Mini Test 3Document14 pagesMini Test 3Quyen Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ba7202-Financial Management Notes RejinpaulDocument193 pagesBa7202-Financial Management Notes Rejinpauls.muthuNo ratings yet
- Requirements:: Intermediate Accounting 3Document7 pagesRequirements:: Intermediate Accounting 3happy240823No ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Hybrid and Derivative SecuritiesDocument70 pagesChapter 16: Hybrid and Derivative SecuritiesJoreseNo ratings yet
- Fact Erp - NG: The Next Generation ERP SoftwareDocument20 pagesFact Erp - NG: The Next Generation ERP SoftwareAbhijit BarmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document111 pagesChapter - 1Niranjan Phuyal100% (1)
- Advanced Accounting Part 2 Dayag 2015 Chapter 14Document29 pagesAdvanced Accounting Part 2 Dayag 2015 Chapter 14jayson100% (2)
- Introduction To Investment & SecurityDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Investment & Securitygitesh100% (1)
- Company Law Lecture 2 (Intro Company Law + SECP)Document34 pagesCompany Law Lecture 2 (Intro Company Law + SECP)Faheem buttNo ratings yet
- Return On AssetsDocument9 pagesReturn On AssetsKirsten MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Hareem Zoya WarsiNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Foundations of Financial Management 11th Edition by Stanley B BlockDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Foundations of Financial Management 11th Edition by Stanley B Blockulysses.padgett483No ratings yet
- Bangalore University Previous Year Question Paper AFM 2020Document3 pagesBangalore University Previous Year Question Paper AFM 2020Ramakrishna NagarajaNo ratings yet
- CFA Level II: EquityDocument185 pagesCFA Level II: EquityCrayonNo ratings yet
- Thoughtful Investors Excel ScreenerDocument21 pagesThoughtful Investors Excel ScreenermattanurmunnaNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions For Chapter 01Document15 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions For Chapter 01Minh Châu VũNo ratings yet
- If You're So Smart, Why Aren't You RichDocument297 pagesIf You're So Smart, Why Aren't You RichRixiuNo ratings yet
- AmldraftDocument249 pagesAmldraftadhavvikasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Dhaka Stock ExchangeDocument25 pagesAnalysis of Dhaka Stock ExchangeSaima Haque EmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 - Basic Financial StatementsDocument139 pagesChapter 02 - Basic Financial StatementsElio Baz100% (1)
- Introduction To Corporations: Dr. Ronnie G. Salazar, CpaDocument102 pagesIntroduction To Corporations: Dr. Ronnie G. Salazar, CpaJoshua CabinasNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles Lecture-3Document5 pagesAccounting Principles Lecture-3shivani chhipaNo ratings yet