TOPIC 12 RBC INDICES.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes160 views
This document defines red blood cell indices and explains how they are used to help diagnose anemia. It describes that red blood cell indices are calculated from a complete blood count test and include the mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). Each of these indices provides information about the average size, hemoglobin content, and hemoglobin concentration of red blood cells, which can indicate if cells are macrocytic, microcytic, hypochromic, or hyperchromic. Normal ranges for each index are provided.
1 of 14
Download to read offline












Recommended
Coombs test



Coombs testManoj Mahato This document provides information about the Coombs test, which is used to detect antibody or complement coating of red blood cells. It describes the history and principles of the test, as well as the direct and indirect Coombs test procedures. The direct Coombs test detects in vivo coating of red blood cells and is used to diagnose conditions like hemolytic disease of the newborn. The indirect Coombs test detects in vitro coating of red cells and is used for compatibility testing and antibody screening. Factors affecting the tests and causes of false positive and negative results are also outlined.
CBC Part 2 - WBC Differential & Morphology.pdf



CBC Part 2 - WBC Differential & Morphology.pdfssuser75fd45 This document provides instructions for a multi-part study exercise on the complete blood cell count (CBC). It focuses on the second part which covers the white blood cell (WBC) differential count and morphology. A peripheral blood smear stained with Wright's stain is used for microscopic examination to identify and classify WBCs, including immature and abnormal cell types. Performing a WBC differential count provides information on the frequency distribution of different WBC lineages and can help identify diseases.
Platelet



PlateletBhaikaka University This document discusses platelets, including their structure, function, production, and methods for detection. Key points include:
- Platelets are non-nucleated blood cells that help form blood clots and repair damaged blood vessels.
- They are produced from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and have an average lifespan of 10 days.
- Platelet functions include initiating blood clotting and wound healing through the release of chemical signals.
- Platelet counts can be measured using a hemocytometer to manually count platelets in a diluted blood sample under a microscope.
Pleural fluid



Pleural fluidBhaikaka University It is fluid which is present in the pleural cavity of
lungs b/w parietal pleura n visceral pleura.
The pleural cavity is a potential space lined by
mesothelium of the visceral n parietal pleura.
Romanowsky stain



Romanowsky stainsandeep singh This document provides information on staining blood films and smears. It discusses the different types of stains used including Romanowsky stains like Leishman stain, Giemsa stain, Wright stain, and Field stain. Specimens should be collected in EDTA and smears prepared within an hour then fixed in methanol or ethanol to preserve cell morphology before staining. Romanowsky stains use methylene blue and eosin dyes to reveal subtle differences in cell structures and components.
Peritonial fluid



Peritonial fluidBhaikaka University It is fluid which is present in
the abdominal cavity.
The peritoneal cavity is a potential
space lined by mesothelium of the
visceral n parietal peritoneum.
Rbc counting unopette



Rbc counting unopetteShabab Ali This document describes the procedure for determining red blood cell (RBC) count using the Unopette system. Whole blood is added to an isotonic saline solution in a Unopette reservoir to preserve RBCs without lysis. This provides a 1:200 dilution ratio of sample to total volume. The diluted blood is then charged to a hematocytometer and counted under a microscope. The total RBC count per cubic millimeter is calculated based on the cell counts. Normal RBC counts in adults range from 4.2-6.1 million per cubic millimeter. Potential sources of error include issues with the apparatus or technique.
Urine analysis microscopic examination



Urine analysis microscopic examinationAarthiKB This document provides details on microscopic examination of urine sediment. Key points include:
- Urine sample collection and preparation for examination under microscope by centrifuging and examining the sediment.
- Classification of findings as organised or unorganised substances, and types of cells, casts, crystals and other formed elements that may be observed.
- Significance of various normal and abnormal findings in identifying renal and other diseases. Detailed morphology of different cell types, casts, crystals and other structures are described.
Pleural fluid examination



Pleural fluid examinationNasir Nazeer Pleural fluid is the fluid found between the membranes lining the thoracic cavity. An excess amount is called a pleural effusion, which can be caused by conditions like heart failure, pneumonia, or rheumatoid arthritis. A sample of pleural fluid is removed through thoracentesis and analyzed to determine if it is a transudate or exudate and diagnose the cause. A transudate is caused by pressure imbalances while an exudate results from inflammation or injury, requiring additional testing to identify conditions like infection, bleeding disorders, or cancer. Test results provide information on the fluid's characteristics, protein levels, and microscopic examination of cells to diagnose the pleural effusion's underlying cause.
Quality-Control-in-Blood-Bank.pptx



Quality-Control-in-Blood-Bank.pptxDhanrajKcity This document discusses quality control in blood banks. It defines quality assurance and quality control, and describes the types of internal and external quality control. It emphasizes the importance of quality control in blood transfusion to ensure safe blood products. It outlines the key steps and parameters involved in quality control for blood collection, testing, component preparation, storage and transportation. These include controls for reagents, equipment, facilities and processes to minimize risks to donors and patients.
Synovial fluid



Synovial fluidBhaikaka University It is fluid which is viscous found in the cavity of movable joints,
b/w Sub-intima n Intima synovium.
APHERESIS METHODS AND TYPES APERESIS.ppt



APHERESIS METHODS AND TYPES APERESIS.pptItsMe468321 Apheresis is a technique where whole blood is collected from a donor or patient and separated into its components. The desired component is retained while the remaining constituents are returned. It is used to collect blood components for transfusion or remove pathological components. There are two main types of apheresis machines - intermittent flow centrifugation and continuous flow centrifugation. The process involves drawing blood, separating components via centrifugation, and collecting the desired component while returning the rest. Complications can include citrate toxicity, allergic reactions, and hypotension. Apheresis provides benefits over regular blood donation such as less HLA sensitization and lower risk of transfusion-transmitted infections.
Cerebrospinal fluid



Cerebrospinal fluidSanjeev Kumar Analysis of CSF, Gucose, Protien, Albumin, Globulin, Function of CSF, Secretion of CSF, Absorption of CSF, Bacterial Infection, Clinical Significance, Normal Composition of CSF, Microscopic examination of CSF, COOMASSIE BRILLIANT BLUE(CBB), REVERSE BIURET METHOD
Automation in hematology



Automation in hematologyDr Siddartha Automation In Haematology.
Dept Of Lab Medicine
Basavatarakam Indo American Hospital And Research Institute
Anticoagulant



AnticoagulantWani Insha The document discusses different types of anticoagulants that are commonly used in hematology. The top five anticoagulants listed are double oxalate, EDTA, heparin, sodium citrate, and sodium fluoride. EDTA is the most commonly used anticoagulant for complete blood count testing as it prevents clotting by chelating calcium ions while maintaining cell morphology. Sodium citrate is used for coagulation testing as it prevents clotting through precipitation of calcium ions. Heparin prevents clotting by inhibiting thrombin.
BONE MARROW SMEAR .pptx



BONE MARROW SMEAR .pptxabdiasis omar mohamed Bone marrow examination is used to diagnose conditions like leukemia, multiple myeloma, and anemia. Bone marrow samples are obtained through aspiration or biopsy of the sternum, iliac crest, or tibia. Samples are prepared as bone marrow films which are stained and examined under a microscope. The cellularity, myeloid to erythroid ratio, and differential count of cell types in the bone marrow are assessed to evaluate for conditions like aplastic anemia or myeloproliferative disorders.
Reticulocyte count



Reticulocyte countSUNIL KUMAR PEDDANA Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that contain RNA and cytoplasmic remnants from earlier stages of development. A reticulocyte count provides information about bone marrow response and red blood cell production. There are four stages of reticulocyte maturation defined by their morphological appearance after staining. A reticulocyte count can be performed manually using supravital staining or automatically using flow cytometry to measure RNA levels. An increased reticulocyte count indicates bone marrow response to anemia while a decreased count suggests impaired red blood cell production.
CRP & ASO 



CRP & ASO P.B.PRAVEEN KUMAR This document provides instructions for performing qualitative and semi-quantitative tests to detect C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Anti-Streptolysin O (ASO) using latex agglutination. For both tests, the specimen is mixed with latex particles coated with the target protein and agglutination within 2 minutes indicates a positive result. For semi-quantitative tests, serial dilutions of the specimen are made and the highest dilution showing agglutination is used to calculate the approximate concentration of CRP or ASO.
Osmotic fragility test



Osmotic fragility testfateh11 The osmotic fragility test is used to diagnose different types of anemia by examining how red blood cells react in solutions of different tonicity. Red blood cells will swell and rupture in hypotonic solutions like distilled water due to excess water entering the cell. They will shrink and rupture in hypertonic solutions with high salt content due to water leaving the cell. In a normal saline solution that is isotonic, the red blood cells will remain intact. The test involves adding blood to solutions of varying tonicity, then centrifuging and observing if the fluid portion becomes colored, indicating red blood cell rupture.
CSF BIOCHEMICAL EXAMINATION



CSF BIOCHEMICAL EXAMINATIONHussein Al-tameemi The document discusses biochemical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in medical laboratories. Routinely tested parameters in CSF include glucose, protein, electrolytes, lactate, and enzymes. Proper handling and centrifugation of CSF samples is important to avoid contamination. Abnormal levels of glucose, protein, lactate and enzymes can indicate conditions like meningitis or tumors. The Pandy's test and Biuret method are described for measuring CSF protein levels, along with normal ranges. Spectrophotometry is used to analyze results from colorimetric assays.
Compatability testing.pptx



Compatability testing.pptxD. JASMINE PRIYA The Compatibility can be determined by matching the different blood group systems, such as ABO and Rh system, and/or by directly testing for the presence of antibodies against a sample of donor tissues or blood.
The main purpose of this test is to distinguish the appearance of antibodies in the recipient against the red blood cells of the donor. These antibodies can be found on the surface of red blood cells of the donor after transfusion.
Reticulocyte



ReticulocyteBhaikaka University An immature red blood cell without a nucleus, having a granular or reticulated appearance when suitably stained.
Reticulocytes are the immature RBC that contain nucleus.
They are originally seen at the site of their formation i.e. bone marrow. They take 2-3 (lays for maturation only about 1-2% of circulating RBCs are Reticulocytes.
Peripheral blood Smear Preparation



Peripheral blood Smear Preparationraihan6112 This document provides information about preparing and examining peripheral blood smears. It discusses how to make a good blood smear by ensuring the smear is evenly spread and covers most of the slide. The document also describes staining blood smears using the Leishman's stain method and examining smears under a microscope. Key things to observe during examination include the different types of white blood cells, red blood cell morphology, and any abnormal findings. Performing a manual differential count involves identifying 100 white blood cells and categorizing them by type.
Pcv



PcvRandhirsinghbisht This document discusses the determination of red blood cell indices including packed cell volume (PCV), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It describes the macrohematocrit or Wintrobe tube method for determining PCV which involves centrifuging a blood sample and measuring the ratio of packed red cells to total blood volume. Formulas are provided for calculating MCV from PCV and RBC count, MCH from hemoglobin and RBC count, and MCHC from hemoglobin and PCV. Normal ranges are listed for each index.
Hematological stains



Hematological stainsAkash Dhiman made from the latest information and dacie and lewis and wintrobes latest edition. A very precise and to the point presentation
Automation in haematology bernard



Automation in haematology bernardBosco Mbonimpa Automated cell counters provide several advantages over manual cell counting including objectivity, elimination of errors, higher precision, and ability to measure more parameters. They work using principles of impedance, optical light scattering, or both. Quality control and daily maintenance are important to ensure accurate results. While automated counts are precise, manual review of films is still needed when results are abnormal. Newer automated hematology analyzers can measure over 30 parameters using technologies like flow cytometry.
Peripheral Blood Smear



Peripheral Blood SmearAnwar Siddiqui The document describes the key parts and functions of a compound microscope used to examine peripheral blood smears. It outlines the proper procedure for making blood films, including using a spreader slide to create a thin, even smear. An ideal blood smear is translucent and uniformly thick. The process of fixing blood films with Leishman's stain and identifying features of a well-stained smear is also detailed. The major blood cell types—red blood cells, white blood cells including granulocytes and agranulocytes—are defined based on their appearance under different microscope magnifications.
RBC Indices and Their Role in Differential Diagnosis of different types of An...



RBC Indices and Their Role in Differential Diagnosis of different types of An...meducationdotnet A complete blood count provides essential information about red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and cell indices. Red blood cell indices like mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration quantify characteristics of red blood cells like size, hemoglobin content, and concentration. These indices help identify different types of anemia based on whether red blood cells appear normal sized, large, or small and normally or abnormally colored. Evaluating red blood cell indices is important for diagnosing anemia and guiding appropriate treatment.
Physiology Presentation: RBC Indices 



Physiology Presentation: RBC Indices KemUnited A presentation on RBC indices and their role in differential diagnosis of different types of anemias, presented by M. Mohsin, Ahsan Iqbal, Basit Ali, Muhammad Ali and Irfan Kaleem from 1st Year MBBS.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Urine analysis microscopic examination



Urine analysis microscopic examinationAarthiKB This document provides details on microscopic examination of urine sediment. Key points include:
- Urine sample collection and preparation for examination under microscope by centrifuging and examining the sediment.
- Classification of findings as organised or unorganised substances, and types of cells, casts, crystals and other formed elements that may be observed.
- Significance of various normal and abnormal findings in identifying renal and other diseases. Detailed morphology of different cell types, casts, crystals and other structures are described.
Pleural fluid examination



Pleural fluid examinationNasir Nazeer Pleural fluid is the fluid found between the membranes lining the thoracic cavity. An excess amount is called a pleural effusion, which can be caused by conditions like heart failure, pneumonia, or rheumatoid arthritis. A sample of pleural fluid is removed through thoracentesis and analyzed to determine if it is a transudate or exudate and diagnose the cause. A transudate is caused by pressure imbalances while an exudate results from inflammation or injury, requiring additional testing to identify conditions like infection, bleeding disorders, or cancer. Test results provide information on the fluid's characteristics, protein levels, and microscopic examination of cells to diagnose the pleural effusion's underlying cause.
Quality-Control-in-Blood-Bank.pptx



Quality-Control-in-Blood-Bank.pptxDhanrajKcity This document discusses quality control in blood banks. It defines quality assurance and quality control, and describes the types of internal and external quality control. It emphasizes the importance of quality control in blood transfusion to ensure safe blood products. It outlines the key steps and parameters involved in quality control for blood collection, testing, component preparation, storage and transportation. These include controls for reagents, equipment, facilities and processes to minimize risks to donors and patients.
Synovial fluid



Synovial fluidBhaikaka University It is fluid which is viscous found in the cavity of movable joints,
b/w Sub-intima n Intima synovium.
APHERESIS METHODS AND TYPES APERESIS.ppt



APHERESIS METHODS AND TYPES APERESIS.pptItsMe468321 Apheresis is a technique where whole blood is collected from a donor or patient and separated into its components. The desired component is retained while the remaining constituents are returned. It is used to collect blood components for transfusion or remove pathological components. There are two main types of apheresis machines - intermittent flow centrifugation and continuous flow centrifugation. The process involves drawing blood, separating components via centrifugation, and collecting the desired component while returning the rest. Complications can include citrate toxicity, allergic reactions, and hypotension. Apheresis provides benefits over regular blood donation such as less HLA sensitization and lower risk of transfusion-transmitted infections.
Cerebrospinal fluid



Cerebrospinal fluidSanjeev Kumar Analysis of CSF, Gucose, Protien, Albumin, Globulin, Function of CSF, Secretion of CSF, Absorption of CSF, Bacterial Infection, Clinical Significance, Normal Composition of CSF, Microscopic examination of CSF, COOMASSIE BRILLIANT BLUE(CBB), REVERSE BIURET METHOD
Automation in hematology



Automation in hematologyDr Siddartha Automation In Haematology.
Dept Of Lab Medicine
Basavatarakam Indo American Hospital And Research Institute
Anticoagulant



AnticoagulantWani Insha The document discusses different types of anticoagulants that are commonly used in hematology. The top five anticoagulants listed are double oxalate, EDTA, heparin, sodium citrate, and sodium fluoride. EDTA is the most commonly used anticoagulant for complete blood count testing as it prevents clotting by chelating calcium ions while maintaining cell morphology. Sodium citrate is used for coagulation testing as it prevents clotting through precipitation of calcium ions. Heparin prevents clotting by inhibiting thrombin.
BONE MARROW SMEAR .pptx



BONE MARROW SMEAR .pptxabdiasis omar mohamed Bone marrow examination is used to diagnose conditions like leukemia, multiple myeloma, and anemia. Bone marrow samples are obtained through aspiration or biopsy of the sternum, iliac crest, or tibia. Samples are prepared as bone marrow films which are stained and examined under a microscope. The cellularity, myeloid to erythroid ratio, and differential count of cell types in the bone marrow are assessed to evaluate for conditions like aplastic anemia or myeloproliferative disorders.
Reticulocyte count



Reticulocyte countSUNIL KUMAR PEDDANA Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells that contain RNA and cytoplasmic remnants from earlier stages of development. A reticulocyte count provides information about bone marrow response and red blood cell production. There are four stages of reticulocyte maturation defined by their morphological appearance after staining. A reticulocyte count can be performed manually using supravital staining or automatically using flow cytometry to measure RNA levels. An increased reticulocyte count indicates bone marrow response to anemia while a decreased count suggests impaired red blood cell production.
CRP & ASO 



CRP & ASO P.B.PRAVEEN KUMAR This document provides instructions for performing qualitative and semi-quantitative tests to detect C-Reactive Protein (CRP) and Anti-Streptolysin O (ASO) using latex agglutination. For both tests, the specimen is mixed with latex particles coated with the target protein and agglutination within 2 minutes indicates a positive result. For semi-quantitative tests, serial dilutions of the specimen are made and the highest dilution showing agglutination is used to calculate the approximate concentration of CRP or ASO.
Osmotic fragility test



Osmotic fragility testfateh11 The osmotic fragility test is used to diagnose different types of anemia by examining how red blood cells react in solutions of different tonicity. Red blood cells will swell and rupture in hypotonic solutions like distilled water due to excess water entering the cell. They will shrink and rupture in hypertonic solutions with high salt content due to water leaving the cell. In a normal saline solution that is isotonic, the red blood cells will remain intact. The test involves adding blood to solutions of varying tonicity, then centrifuging and observing if the fluid portion becomes colored, indicating red blood cell rupture.
CSF BIOCHEMICAL EXAMINATION



CSF BIOCHEMICAL EXAMINATIONHussein Al-tameemi The document discusses biochemical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in medical laboratories. Routinely tested parameters in CSF include glucose, protein, electrolytes, lactate, and enzymes. Proper handling and centrifugation of CSF samples is important to avoid contamination. Abnormal levels of glucose, protein, lactate and enzymes can indicate conditions like meningitis or tumors. The Pandy's test and Biuret method are described for measuring CSF protein levels, along with normal ranges. Spectrophotometry is used to analyze results from colorimetric assays.
Compatability testing.pptx



Compatability testing.pptxD. JASMINE PRIYA The Compatibility can be determined by matching the different blood group systems, such as ABO and Rh system, and/or by directly testing for the presence of antibodies against a sample of donor tissues or blood.
The main purpose of this test is to distinguish the appearance of antibodies in the recipient against the red blood cells of the donor. These antibodies can be found on the surface of red blood cells of the donor after transfusion.
Reticulocyte



ReticulocyteBhaikaka University An immature red blood cell without a nucleus, having a granular or reticulated appearance when suitably stained.
Reticulocytes are the immature RBC that contain nucleus.
They are originally seen at the site of their formation i.e. bone marrow. They take 2-3 (lays for maturation only about 1-2% of circulating RBCs are Reticulocytes.
Peripheral blood Smear Preparation



Peripheral blood Smear Preparationraihan6112 This document provides information about preparing and examining peripheral blood smears. It discusses how to make a good blood smear by ensuring the smear is evenly spread and covers most of the slide. The document also describes staining blood smears using the Leishman's stain method and examining smears under a microscope. Key things to observe during examination include the different types of white blood cells, red blood cell morphology, and any abnormal findings. Performing a manual differential count involves identifying 100 white blood cells and categorizing them by type.
Pcv



PcvRandhirsinghbisht This document discusses the determination of red blood cell indices including packed cell volume (PCV), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). It describes the macrohematocrit or Wintrobe tube method for determining PCV which involves centrifuging a blood sample and measuring the ratio of packed red cells to total blood volume. Formulas are provided for calculating MCV from PCV and RBC count, MCH from hemoglobin and RBC count, and MCHC from hemoglobin and PCV. Normal ranges are listed for each index.
Hematological stains



Hematological stainsAkash Dhiman made from the latest information and dacie and lewis and wintrobes latest edition. A very precise and to the point presentation
Automation in haematology bernard



Automation in haematology bernardBosco Mbonimpa Automated cell counters provide several advantages over manual cell counting including objectivity, elimination of errors, higher precision, and ability to measure more parameters. They work using principles of impedance, optical light scattering, or both. Quality control and daily maintenance are important to ensure accurate results. While automated counts are precise, manual review of films is still needed when results are abnormal. Newer automated hematology analyzers can measure over 30 parameters using technologies like flow cytometry.
Peripheral Blood Smear



Peripheral Blood SmearAnwar Siddiqui The document describes the key parts and functions of a compound microscope used to examine peripheral blood smears. It outlines the proper procedure for making blood films, including using a spreader slide to create a thin, even smear. An ideal blood smear is translucent and uniformly thick. The process of fixing blood films with Leishman's stain and identifying features of a well-stained smear is also detailed. The major blood cell types—red blood cells, white blood cells including granulocytes and agranulocytes—are defined based on their appearance under different microscope magnifications.
Similar to TOPIC 12 RBC INDICES.pptx (20)
RBC Indices and Their Role in Differential Diagnosis of different types of An...



RBC Indices and Their Role in Differential Diagnosis of different types of An...meducationdotnet A complete blood count provides essential information about red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and cell indices. Red blood cell indices like mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration quantify characteristics of red blood cells like size, hemoglobin content, and concentration. These indices help identify different types of anemia based on whether red blood cells appear normal sized, large, or small and normally or abnormally colored. Evaluating red blood cell indices is important for diagnosing anemia and guiding appropriate treatment.
Physiology Presentation: RBC Indices 



Physiology Presentation: RBC Indices KemUnited A presentation on RBC indices and their role in differential diagnosis of different types of anemias, presented by M. Mohsin, Ahsan Iqbal, Basit Ali, Muhammad Ali and Irfan Kaleem from 1st Year MBBS.
Hema I Chapter 11_RBC indices.ppt



Hema I Chapter 11_RBC indices.pptssuser88fb021 The red cell indices include
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
Red cell distribution width (RDW) is another important red cell parameter obtained by electronic methods
RDW measures the variation in size of the red blood cells (degree of anisocytosis)
It must be remembered that the red cell count has the greatest potential error and must be performed with extreme care preferably using an electronic counter
Hema I Chapter 11_RBC indices.ppt



Hema I Chapter 11_RBC indices.pptssuser88fb021 Normocytic anemia with ineffective erythropoiesis (reduced reticulocyte count)
May be normochromic or hypochromic
Results from
Chronic inflammation (e.g. rheumatologic disease): Cytokines released by inflammatory cells cause macrophages to accumulate iron and not transfer it to plasma or developing red cells (iron block anemia)
Renal failure (erythropoietin from kidneys)
Endocrine (e.g. hypothyroid)
Hepatic disease
Bone marrow suppression (EPO is elevated)
Calculation of red cell indices



Calculation of red cell indicesTasmiaZeb1 This document discusses the calculation of red blood cell indices, including mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). These indices are calculated using measurements of total red blood cell count, packed cell volume, and hemoglobin concentration. Formulas for calculating each index are provided, along with normal reference ranges and descriptions of how the indices are affected in different types of anemias. The document notes that MCH is more reliably calculated using automated counters while MCHC can be reliably calculated manually.
Red blood cell Indices



Red blood cell IndicesQussai Abbas Red Blood Cell (RBC) Indices: Definitions and Calculations
Mean cell (or corpuscular) volume (MCV)
Mean cell hemoglobin (MCH)
Mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
RED CELL INDICES.pdf



RED CELL INDICES.pdfNgungSamuel This document discusses red blood cell indices, which measure the size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells. The three main indices are:
1. MCV measures average red cell volume, with a normal range of 80-100 femtoliters. Low MCV indicates microcytic cells and high MCV indicates macrocytic cells.
2. MCH measures average hemoglobin content per cell in picograms, normally 27-32 pg. High MCH indicates hyperchromic cells and low indicates hypochromic cells.
3. MCHC measures hemoglobin concentration as a percentage, normally 32-36 g/dL. Low MCHC suggests iron deficiency anemia.
The document also presents
Classification of anem.JHIKUYHHKHIOUia.ppt



Classification of anem.JHIKUYHHKHIOUia.pptSARLSAICAMEDICALES There are three main classifications of anemia: functional, clinical, and quantitative. The functional classification describes the cause of reduced hematopoiesis. The clinical classification categorizes anemias based on their etiology such as blood loss, iron deficiency, or hemolysis. The quantitative classification analyzes hematocrit, hemoglobin levels, and red blood cell indices including MCV, MCH, and MCHC to help diagnose the type of anemia.
Classification of anemia123345678997.ppt



Classification of anemia123345678997.pptddd074213 Anemia classification for undergraduate medical school students
Blood indices



Blood indicesJilsha Cecil This document discusses various red blood cell indices including mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), red cell distribution width (RDW), and color index (CI). These indices are calculated from measurements of hemoglobin, hematocrit, and red blood cell count and provide information about red blood cell size, hemoglobin content, and variation that can help classify types of anemia. The document defines each index and provides the normal ranges and clinical applications.
RBC Indices- MCV, MCH, MCHC II Blood Physiology



RBC Indices- MCV, MCH, MCHC II Blood PhysiologyHM Learnings RBC Indices- MCV, MCH, MCHC II Blood Physiology
The slide will cover the following:
1. Introduction to RBC indices
2. Mean Corpuscular volume (MCV)
3. Mean Corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)
4. Mean Corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
5. Color index (CI)
You can also watch the same topic on HM Learnings Youtube channel.
You can also follow HM Learnings on facebook, instagram and twitter for daily updates
L13-HAEMATOLOGICAL TESTS.pptx



L13-HAEMATOLOGICAL TESTS.pptxJasperOmingo This document discusses routine hematological laboratory tests, focusing on the complete blood count (CBC). It describes the CBC in detail, including that it measures white blood cell count, platelet count, red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and red blood cell indices. It explains what each component indicates and normal ranges. The document also discusses peripheral blood films and coagulation tests.
Complete blood count



Complete blood countDr Issah J.K This presentation covers on complete blood cells count and it's differentials. Starting with RBC count, WBC count and Platelets interpretation as a whole.
Laboratory hematology



Laboratory hematologyBiswa Ranjan Patra This document discusses hematological parameters analyzed in laboratory hematology. It describes the main anticoagulants used in blood collection and how they work. It also summarizes the methods used to analyze red blood cell parameters like red cell count, hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration both manually and using automated hematology analyzers. Key factors that affect the accuracy of these measurements are also highlighted.
Erythrocyte indices



Erythrocyte indicesDr. Pritika Nehra This document discusses several red blood cell indices used to characterize anemias, including mean cell volume (MCV), mean cell hemoglobin (MCH), mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and red cell distribution width (RDW). It provides details on how each index is calculated and interpreted, and examples of abnormal red blood cell morphologies seen in different types of anemias that would affect the index values.
red cell morphology indices.1.pdf



red cell morphology indices.1.pdfMohamed Alashram Red cell morphology indices are measurements derived from a complete blood count that provide information about red blood cells, including their size, shape, and color. The indices - mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, and red cell distribution width - are used alongside other tests and symptoms to diagnose blood disorders, especially anemias. Normal ranges exist for each index, but abnormalities can indicate issues like iron deficiency anemia, vitamin deficiencies, or hemolytic conditions.
RBC INDICES final.pptx



RBC INDICES final.pptxsaswati14 RBC indices like MCV, MCH, MCHC and RDW provide quantitative measurements of red blood cell size and hemoglobin content that can help diagnose different types of anemia. A low MCV and high RDW indicate iron deficiency anemia, while a high MCV and RDW suggest megaloblastic anemia. The combination of various RBC index measurements, especially with RDW, aids in the differential diagnosis of anemias. However, RBC indices alone cannot definitively diagnose disorders and require correlation with other test results.
Rbc indices



Rbc indicesManan Shah This presentation is focused on diagnostic utility of Red blood cell indices which will be very useful for undergraduate and postgraduate of medical field.
More from BainunDali (20)
TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO IMMUNOHEMATOLOGY.pptx



TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO IMMUNOHEMATOLOGY.pptxBainunDali This document provides an introduction to immunohematology and blood banking. It discusses the patterns of inheritance for blood group antigens, including that ABO antigens are inherited through co-dominant expression. The document defines key terms like genotype and phenotype. It explains that phenotype is the physical expression determined through testing, while genotype refers to the actual genes inherited which can only be inferred. Finally, it distinguishes between homozygous and heterozygous inheritance patterns.
PRINCIPLE OF ANTIGENS AND ANTIBODIES.pptx



PRINCIPLE OF ANTIGENS AND ANTIBODIES.pptxBainunDali Antigens are any substances that can induce antibody formation. Erythrocytes can be antigenic if their cell membranes contain epitopes, which are areas recognized as foreign. The immunogenicity of a substance is influenced by factors such as its foreignness, molecular weight, structural stability, complexity, and route of administration - more complex proteins administered intravenously tend to be better antigens. Antibodies are proteins called immunoglobulins that the body produces in response to antigens. The five major immunoglobulins are IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD and IgE. Blood group antibodies are usually IgG, IgM, or IgA.
CHAPTER 10- OTHER BLOOD GROUP.ppt



CHAPTER 10- OTHER BLOOD GROUP.pptBainunDali This document provides information on several minor blood group systems beyond ABO and Rh, including Kell, MNS, Duffy, Kidd, and Lutheran. It describes the antigens and genes involved in each system, how the antigens are expressed on red blood cells, and clinical significance of antibodies against antigens in these systems including their ability to cause hemolytic disease of the newborn or hemolytic transfusion reactions. The document also discusses relationships between some blood groups and disease susceptibility, such as the protective effect of the Duffy-negative blood group against malaria.
TOPIC 10 ROMANOWSKY STAINING.pptx



TOPIC 10 ROMANOWSKY STAINING.pptxBainunDali Romanowsky stains are commonly used to stain blood films. They contain basic dyes like methylene blue that stain nucleic acids blue-grey and acidic dyes like eosin that stain proteins and granules orange-red. Leishman's stain contains methylene blue and eosin in methanol and is useful for identifying cells in blood smears and genetics. The staining process involves making a blood smear, fixing it with alcohol, staining it using the Romanowsky stain followed by a rinse to differentiate cells by their staining. Care must be taken to maintain the proper pH and timing during staining.
TOPIC 8 BLOOD CELL COUNT.pptx



TOPIC 8 BLOOD CELL COUNT.pptxBainunDali This document provides instructions for performing a blood cell count using a hemocytometer. It explains that a hemocytometer is used to count blood cells and involves diluting a blood sample then counting the cells under a microscope. The key steps are filling pipettes with diluted blood and diluting fluid, charging the counting chamber, allowing cells to settle, and counting cells that touch the ruled lines. Calculations are provided to determine total red blood cell, white blood cell and platelet counts based on the number of cells counted. Precautions like cleaning equipment and ensuring no clumping or bubbles are also outlined.
TOPIC 13 HEMATOCRIT AND ITS SIGNIFICANT.pptx



TOPIC 13 HEMATOCRIT AND ITS SIGNIFICANT.pptxBainunDali Hematocrit, also known as packed cell volume, is the percentage of red blood cells in blood. It is an important indicator in a complete blood count. The normal ranges are 46% for males and 38% for females. Hematocrit can be measured through microhematocrit and macrohematocrit methods. Microhematocrit involves centrifuging a blood sample in a capillary tube and reading the percentage of red blood cells. Macrohematocrit uses a Wintrobe tube and centrifugation to separate plasma from red blood cells to determine the hematocrit percentage. Precise measurement requires avoiding errors like not including the buffy coat layer or improper sealing of tubes.
TOPIC 11 AIDS.pptx



TOPIC 11 AIDS.pptxBainunDali 1. AIDS is caused by the HIV virus which weakens the immune system. HIV is transmitted through sexual contact, sharing needles, from mother to child during birth or breastfeeding.
2. The HIV lifecycle involves binding to CD4 cells, releasing its contents and integrating its DNA into the host cell. It can then lie dormant for years.
3. HIV infection progresses in three phases - acute infection, asymptomatic middle phase lasting 10-12 years, and final phase with full-blown AIDS where the CD4 count drops below 200.
4. AIDS leaves the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections like pneumonia, tuberculosis, fungal infections and cancers like Kaposi's sarcoma.
TOPIC 1 INRODUCTION TO HEMATOLOGY.pptx



TOPIC 1 INRODUCTION TO HEMATOLOGY.pptxBainunDali Serum is the pale yellow fluid remaining after blood has clotted, containing proteins, electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones, and any drugs present. The main cellular components of blood are red blood cells that carry oxygen and carbon dioxide without nuclei, white blood cells that help fight infection in two types, and platelets that help with clotting and don't have nuclei. Normal ranges are provided for counts of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO IMMUNOLOGY.pptx



TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO IMMUNOLOGY.pptxBainunDali The document provides an overview of immunology and defines key terms. It discusses the categories of the immune system as innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity is non-specific and acts rapidly through physical and chemical barriers, as well as phagocytes. Adaptive immunity is specific and works more slowly through antibodies produced by B cells and cellular responses mediated by T cells. It also describes the basis of effector molecules and development of both the humoral and cell-mediated responses in adaptive immunity.
768_Concept_of_health_and_disease.pptx



768_Concept_of_health_and_disease.pptxBainunDali This document discusses the concepts of health, disease, and well-being. It begins by exploring definitions of health, including the WHO's definition of health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. The document then examines changing models of health from the biomedical to holistic. It outlines the various dimensions of health, including physical, mental, social, emotional, and spiritual. Finally, the document defines well-being as having both objective and subjective components, and discusses indices used to measure population health and quality of life, such as the Physical Quality of Life Index, Human Development Index, and Human Poverty Index.
TOPIC 13 INTRODUCTION TO OTHER HEALTHCARE TEAM.pptx



TOPIC 13 INTRODUCTION TO OTHER HEALTHCARE TEAM.pptxBainunDali An ultrasound technician, also known as a sonographer, uses ultrasound equipment to produce images of internal organs and diagnose medical conditions. Sonographers perform ultrasound procedures, take sonograms, and work in hospitals, diagnostic labs, outpatient centers, and clinics. Other related jobs include cardiovascular technician, cytotechnologist, medical imaging technician, and nuclear medicine technologist. A radiologist is a doctor who uses medical imaging technologies like X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, PET scans, ultrasound and nuclear imaging to diagnose and treat illnesses. Radiologists may specialize in areas like angiography, fluoroscopy, mobile radiography, or trauma radiography.
TOPIC 9 INTRODUCTION TO PHARMACY.pptx



TOPIC 9 INTRODUCTION TO PHARMACY.pptxBainunDali This document provides an introduction to pharmacy, including definitions, roles, and practices. It defines pharmacy as the science of preparing and dispensing medications. Pharmacists are educated and licensed professionals who prepare, dispense, and provide drug information to the public. Pharmacist duties include interpreting prescriptions, compounding, labeling, and dispensing drugs, as well as providing patient education. There are several career paths for pharmacists in settings like communities, hospitals, industry, and academia. The document also outlines the code of ethics pharmacists must follow and good dispensing practices around labeling, storage, and maintaining a clean environment.
TOPIC 4 THERMOCHEMISTRY - Copy.pptx



TOPIC 4 THERMOCHEMISTRY - Copy.pptxBainunDali This document discusses various types of thermochemistry and enthalpy changes in chemical reactions. It begins by defining exothermic and endothermic reactions, and describes how enthalpy (ΔH) is the heat released or absorbed during a reaction. It then explains how to calculate enthalpy changes using specific heat and temperature change. The main types of enthalpy covered are heat of precipitation, neutralization, displacement, and combustion. Examples are provided for calculating enthalpy changes using thermochemical equations and experimental temperature changes. In summary, the document provides an overview of thermochemistry concepts and calculations involving enthalpy for different reaction types.
TOPIC 3 CARBON COMPOUND.pptx



TOPIC 3 CARBON COMPOUND.pptxBainunDali This document provides information about carbon compounds. It begins by defining carbon compounds as compounds that contain carbon as a constituent element. It then discusses why carbon is unique in its ability to form four covalent bonds and long chains of carbon atoms. The document separates carbon compounds into organic and inorganic compounds. It focuses on organic compounds, especially hydrocarbons. It discusses saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, including alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. The document explains how to name compounds in each homologous series and describes some of their physical and chemical properties.
TOPIC 1 RATE OF REACTION.pptx



TOPIC 1 RATE OF REACTION.pptxBainunDali The document discusses the rate of reaction in chemistry. It defines rate of reaction and explains how to calculate average and instantaneous rates. It describes four main factors that affect the rate of reaction: size of reactants, concentration, temperature, and presence of a catalyst. It introduces collision theory and activation energy to explain these factors. Students are asked to research examples of how each factor influences reaction rates and present their findings in a slideshow.
TOPIC 8 HEALTH SCREENING.pptx



TOPIC 8 HEALTH SCREENING.pptxBainunDali Health screening involves using tests, exams, or other procedures to detect diseases in asymptomatic individuals. It aims to identify diseases early so treatment can begin sooner, outcomes can be better managed, and mortality and suffering can be reduced. Screening tests differ from diagnostic tests in that screening examines large groups of generally healthy people, uses less accurate but less expensive tests, and results are not conclusive. Common screening tests include growth charts, blood tests, blood pressure checks, and cancer screenings. Health screening can detect conditions like high cholesterol, diabetes, cancer, and other diseases.
Recently uploaded (20)
Local Rural Practices of the future. MWC



Local Rural Practices of the future. MWCJosep Vidal-Alaball At #MWC2025, we presented "Local Rural Practices of the Future", a visionary project designed to enhance healthcare access in rural areas through telemedicine, AI, telemonitoring, and point-of-care (PoC) analysis. By integrating these digital health solutions, we aim to improve patient care, reduce unnecessary travel, and support healthcare professionals in remote settings.
Medication Adherence.pptx Medication Adherence: Importance, Challenges, and S...



Medication Adherence.pptx Medication Adherence: Importance, Challenges, and S...UmeaHani This presentation explores the crucial role of medication adherence in achieving optimal health outcomes. It covers key topics such as the factors affecting adherence, common barriers faced by patients, and effective strategies to improve compliance. Learn about the impact of non-adherence on disease management, healthcare costs, and patient well-being. Ideal for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone interested in improving medication adherence.
LIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTS.pptx



LIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTS.pptxManjula N LIVER FUNCTION TEST CBME UG PRACTICLAS AND CHARTS
community mental health nursing (CMHN).pptx



community mental health nursing (CMHN).pptxshailendranakum58 Community mental health nursing is a field of nursing that focuses on promoting mental health and treating mental illness in communities.
The Impact of ADHD on Relationships and Social Skills (2).pdf



The Impact of ADHD on Relationships and Social Skills (2).pdfjohnhadson167 Anxiety is a prevalent mental disorder that touches the lives of millions of individuals globally. Although a little anxiety in everyday life is normal, excessive anxiety can easily disrupt daily activities and interpersonal relationships. Knowledge about its effects will enable individuals to approach proper care and coping mechanisms.
Ballerina for Healthcare - Code to Cloud in Mins with AI driven programming ...



Ballerina for Healthcare - Code to Cloud in Mins with AI driven programming ...Mifan Careem Ballerina is an open source, cloud native, healthcare context aware language for building general integration and healthcare backends. In addition to native support for JSON, XML, Async, GraphQL etc, it also supports FHIR, HL7, X12, EDI formats in the healthcare domain.
A Roadmap for Strengthening Health Leadership in the Western Pacific Region



A Roadmap for Strengthening Health Leadership in the Western Pacific RegionBecky Goins Strong leadership and a highly skilled health workforce are essential for achieving universal health coverage and building resilient health systems. This strategic storyboard presents a comprehensive approach to leadership development and capacity building for mid-level health professionals in the Western Pacific Region specifically, but could be applied to other geographic regions.
This deck compiles global best practices, successful case studies from various countries, and evidence-based recommendations in a digestible storyboard to build sustainable health leadership programs.
📖 Who Should Read This?
- Public health leaders, policymakers, and capacity-building professionals
- Global health consultants and leadership trainers
- Organizations looking to strengthen workforce development in health systems
Contamination OCD Treatment without medicine



Contamination OCD Treatment without medicineShyamGupta497190 Contamination OCD Treatment without medicine with CBT and ERP .pptx
SMART Practices for Responding to FDA Observational Warnings Using Generative AI



SMART Practices for Responding to FDA Observational Warnings Using Generative AIhrutikapanakrtg Pharma Now Unveils Groundbreaking Industry Insights in Latest Issue
Pharma Now is thrilled to introduce its latest feature, Navigating the Digital Frontier, a comprehensive deep dive into the latest advancements, challenges, and opportunities shaping the pharmaceutical industry. This edition provides invaluable insights for professionals in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and regulatory compliance, equipping them with the knowledge to navigate the ever-evolving landscape.
Inside This Edition:
Global Industry Trends & Insights: Explore the most significant technological innovations, regulatory changes, and market disruptions that are shaping the future of pharmaceuticals. Gain insights from industry experts on how companies can adapt and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Global Events & Conferences: A carefully curated list of the most influential upcoming pharmaceutical events, conferences, and summits worldwide, designed to foster collaboration and industry networking. Stay informed about where to find the best opportunities for learning and partnership-building.
Market Insights & Trends: Get an in-depth look at key market dynamics, investment trends, and strategic shifts in the pharmaceutical industry. Understand how companies are responding to emerging challenges and leveraging new opportunities to drive growth.
Exclusive Leadership Interview: "In Talks With Leadership"
A special feature with Dr. Ashok Kumar Bhattacharya, a distinguished industry leader, who shares his expert perspectives on the latest advancements and the future of pharmaceuticals. Gain firsthand insights into the strategic decisions shaping the industry today.
Leveraging Generative AI for Regulatory Compliance
Discover how pharmaceutical companies can integrate generative AI technologies to enhance regulatory compliance, respond efficiently to FDA warnings, and streamline operational efficiency. This feature provides an in-depth analysis of AI-driven solutions transforming the industry.
With the pharmaceutical sector constantly evolving, Navigating the Digital Frontier serves as an essential resource for industry leaders, professionals, and innovators looking to stay ahead in the digital age.
Stay informed and explore the future of pharmaceuticals with Pharma Now.
For further details, partnership inquiries, or to access the latest issue, visit
ACUTE INFLAMMATIOn PAthology ppt free download



ACUTE INFLAMMATIOn PAthology ppt free downloadjenishJebadurai1 ACUTE INFLAMMATIOn PAthology ppt free download
ABG ANALYSIS. PART-1: PRIMARY GAS EXCHANGE FUNDAMENTALS & CLINICAL IMPLICATIO...



ABG ANALYSIS. PART-1: PRIMARY GAS EXCHANGE FUNDAMENTALS & CLINICAL IMPLICATIO...Shilpasree Saha ABG Analysis :Basics
Dr Sobia Ali case ppt (BEST VITELLIFORM MACULOPATHY OSp Quetta 2024pptx.pptx



Dr Sobia Ali case ppt (BEST VITELLIFORM MACULOPATHY OSp Quetta 2024pptx.pptxSobia Ali This ppt is a case study about a rare congenital eye disease
Best VITELLIFORM MACULOPATHY (BEST Diseases)
It's an an award winning ppt
I presented this ppt during my Pg training @ OSp conference and won Gold Medal
Choosing the Right NDIS Support Coordinator: Key Factors & Expert Tips.



Choosing the Right NDIS Support Coordinator: Key Factors & Expert Tips.Fitnall1 Finding the right NDIS support coordinator is essential for maximizing your plan and accessing the best services. This presentation outlines the key factors to consider, including experience, communication, independence, and local knowledge. Learn where to search, the critical questions to ask, and how to make the best choice for your needs.
680128_Spiritual H and Complete Well-being.pptx



680128_Spiritual H and Complete Well-being.pptxPattie Pattie Spiritual Health and Complete Well-being, Vicharn Panich, MD
Chairman of PMAC Organizing Committee
Introductory Remark in PMAC 2025 Side Meeting “Complete Well-being in the Age of AI: The Crucial Role of Spiritual Health and Practical Strategies”, 28 January 2025, Centara Grand Hotel, Bangkok
Brain stroke: Symptoms, Classification, prevention and management .pptx



Brain stroke: Symptoms, Classification, prevention and management .pptxJoginder Singh Brain stroke, classification, Symptoms, risk factors, procedures, stroke treatment, BEFAST, neuro imaging, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke
introduction for Diabetic Mellitus - simplified



introduction for Diabetic Mellitus - simplifiedMaryGemGalvanFesalbo notes to easily understand diabetes mellitus
Tran Quoc Bao Named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam by Hosp...



Tran Quoc Bao Named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam by Hosp...Ignite Capital Tran Quoc Bao, named Best and Most Influential Hospital CEO in Vietnam 2025 by Hospital Insight Magazine, is transforming Vietnam’s healthcare landscape with his unique blend of medical expertise and financial acumen. As CEO of Prima Saigon, the country's leading international daycare and ambulatory hospital, Bao has turned the institution into a benchmark of excellence, setting new standards for innovation and patient care.
His leadership at Prima Saigon has propelled the hospital to the forefront of the Vietnamese healthcare sector, but Bao's impact goes beyond national borders. As a member of the Advisory Board for Asian Hospital & Healthcare Management, a prominent publication influencing global healthcare policy, he is helping to shape trends and set standards that extend across Asia and the world.
With nearly two decades of experience, Bao has held key positions at renowned institutions like City International Hospital, FV Hospital, TMMC Healthcare (Tam Tri Hospital Group), and Cao Tang Hospital, where he led the transformation into Vietnam’s first Joint Commission International (JCI)-accredited hospital. This milestone put Vietnam firmly on the global healthcare map, thanks to Bao’s visionary leadership.
His extensive expertise is matched by a distinguished financial background, holding elite credentials such as CFA®, CMT®, CPWA®, FMVA®, and others. Bao’s strategic approach has allowed him to lead $2 billion in healthcare M&A transactions, reshaping Vietnam’s healthcare investment landscape. His ability to blend healthcare with finance has earned him recognition as a thought leader in the field.
Bao has also contributed more than 20 articles to major outlets like Forbes, Bloomberg, and Voice of America, sharing his insights on healthcare innovation and investment. His accolades include being named Healthcare Executive of the Year – Vietnam 2019, Medical Tourism Leader of the Year 2021, and being honored as a “Doing Business 2022” Leader by the World Bank Group.
In addition, Bao's strategic expertise is sought by top global consulting firms like BCG, Bain, and McKinsey, advising on major healthcare investments and partnerships in Asia. With his visionary leadership, Tran Quoc Bao continues to drive the future of healthcare, both in Vietnam and globally.
Advances in Point of Care Diagnostics for Rapid Pathogen Detection.pptx



Advances in Point of Care Diagnostics for Rapid Pathogen Detection.pptxDr Punith Kumar This presentation explores the latest advancements in Point-of-Care (PoC) diagnostics for rapid pathogen detection, highlighting innovative technologies, emerging trends, and real-world applications. It covers biosensors, microfluidics, CRISPR-based detection, and AI-driven diagnostics, emphasizing their role in early disease detection, outbreak control, and personalized medicine. The slides provide insights into the speed, accuracy, and accessibility of modern PoC diagnostic tools, transforming healthcare by enabling on-site testing and real-time results.
TOPIC 12 RBC INDICES.pptx
- 1. BT 1103 HEMATOLOGY 1 TOPIC 12: RED BLOOD CELL INDICES
- 2. LEARNING OUTCOME Define red cell indices Identify the parameters needed for red cell indices’s calculation. Explain the purpose of red cell indices. Define MCH, MCV and MCHC. Describe the normal values and red cell indices significance.
- 3. RED BLOOD CELL INDICES Red Blood Cell indices are part of the complete blood count (CBC) test. They are used to help diagnose the cause of anemia, a condition in which there are too few red blood cell.
- 4. INDICES OF RBC Average red blood cell size (MCV) Hemoglobin amount per red blood cell (MCH) The amount of the hemoglobin relative to the size of the cell (hemoglobin concentration per red blood cell (MCHC)
- 5. MEAN CELL VOLUME (MCV) Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) is the average size of a red blood cell and is calculated by dividing the hematocrit (Hct) by the red blood cell count. Normal range: 80-100 fL To calculate the MCV, expressed in femtoliters (fl, or 10-15L), the following formula is used:
- 6. MCV Cells are macrocytic (bigger size than normal) Cells are microcytic (smaller size than normal) 80-96 fL >96 fL <80 fL
- 7. MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN (MCH) MCH measures the average amount of hemoglobin in a red blood cell. It is a calculation based on two other values measured in the CBC
- 8. MCH
- 10. Cells are hypochromic (low Hb content, pallor) Cells are hyperchromic (high Hb content, blush) 33-36 g/dL <33 g/dl >36 g/dl
- 11. MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN CONC (MCHC) The MCHC is the average concentration of hemoglobin inside a red blood cell. The MCHC is calculated using two other values in the CBC
- 12. the Hb, which measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood the hemocrit (Hct), which measures the percentage of red blood cells in a given volume of blood The MCHC = Hb/Hct.
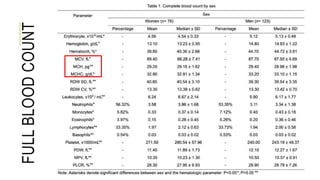
- 13. So where do we usually found these indices?
- 14. FULL BLOOD COUNT








