Road Note 29 Charts
Road Note 29 Charts
Uploaded by
Midnight_dreamerCopyright:
Available Formats
Road Note 29 Charts
Road Note 29 Charts
Uploaded by
Midnight_dreamerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Road Note 29 Charts
Road Note 29 Charts
Uploaded by
Midnight_dreamerCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Flexible and Rigid Pavements
Dr Ong Ghim Ping Raymond Department of Civil Engineering National University of Singapore
IES Preparatory Course PE Exams Course 2010 CE 204 Transportation
Foster and Ahlvin Influence Chart for Vertical Stresses
z
p 100%
z a
Foster and Ahlvin Influence Chart for Vertical Deflections
Types of Axle Loads
Single axle load: wheels with distance more than 1 m apart Tandem axle load: two or more consecutive axles between 1 m to 2.44 m spacing
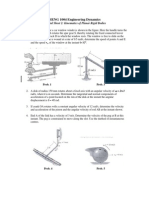
Problem: Compute the ESAL of this truck on a flexible pavement with SN=4 and terminal PSI pt = 2.5.
10 kips
32 kips
32 kips
Solution: ESAL load = 0.10 + 0.89 + 0.89 = 1.88 ESAL per truck
Flexible Pavements
Types of Axle Loads
Single axle load: wheels with distance more than 1 m apart Tandem axle load: two or more consecutive axles between 1 m to 2.44 m spacing
Problem: Compute the ESAL of this truck on a rigid pavement with D=9 in. and terminal PSI pt = 2.5.
10 kips
32 kips
32 kips
Solution: ESAL load = 0.08 + 1.49 + 1.49 = 3.06 ESAL per truck
Rigid Pavements
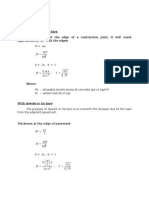
UK Road Note 29 Step 3: Determining Thickness of Sub-base Layer
UK Road Note 29 Step 4: Rolled Asphalt Roadbase: Minimum Thickness of Surfacing and Roadbase
UK Road Note 29 Dense Macadam Roadbase: Minimum Thickness of Surfacing and Roadbase
UK Road Note 29 Lean Concrete, Soil-Cement and CementBounded Granular Roadbase: Minimum Thickness of Surfacing & Roadbase
UK Road Note 29 Wet-Mix and Dry-Bound Macadam Roadbase: Minimum Thickness of Surfacing and Roadbase
10
AAHSTO Flexible Pavement Nomograph
11
UK Road Note 29: Thickness of Reinforced and Unreinforced Concrete Slabs
12
UK Road Note 29: Weight of Reinforcement Fabric and Area of Steel per Unit Width of Pavement
13
UK Road Note 29: Joint Spacing for Jointed Reinforced Concrete Pavement
14
Estimating k assuming semiinfinite subgrade depth
15
Correction of k to account for presence of rigid foundation near surface
16
Estimating Relative Damage u using slab thickness and composite k value
17
Correction of k Value due to Loss of Support
18
AASHTO Rigid Pavement Nomograph I
H. Determine Slab Thickness
Use nomograph (p. 68-69) to determine required slab thickness
19
AAHSTO Rigid Pavement Nomograph - II
20
You might also like
- Hydraulic HandbookDocument251 pagesHydraulic Handbookdwdobbs93% (27)
- 2.4 Road Note 29 (RN-29)Document33 pages2.4 Road Note 29 (RN-29)Rajesh Khadka85% (13)
- Kenya Road Design Manual Part IIIDocument198 pagesKenya Road Design Manual Part IIIGiora Rozmarin95% (20)
- RHQ-IOCL-CPMSL-2020 Rev.0 Master Supplier ListDocument224 pagesRHQ-IOCL-CPMSL-2020 Rev.0 Master Supplier ListKunal100% (1)
- Road Note 29 & 31Document12 pagesRoad Note 29 & 31Yasruddin Mt78% (9)
- 2.4 Road Note 31Document29 pages2.4 Road Note 31Rajesh Khadka100% (10)
- AFCAP MAL 016 Pavement Design Manual MalawiDocument182 pagesAFCAP MAL 016 Pavement Design Manual Malawitom shibaleNo ratings yet
- ORN - 09 - A Design Manual For Small BridgesDocument238 pagesORN - 09 - A Design Manual For Small Bridgesprc.j301100% (1)
- Bs 4987 2Document15 pagesBs 4987 2Hamid Naveed100% (1)
- Orn 31 PDFDocument82 pagesOrn 31 PDFRaghavNo ratings yet
- Technical Methods For Highways Sampling Methods For Roads Construction MaterialsDocument59 pagesTechnical Methods For Highways Sampling Methods For Roads Construction MaterialsPatrick Bauman100% (1)
- Cycle 091 (August 2012) Reserve Advancement ResultsDocument13 pagesCycle 091 (August 2012) Reserve Advancement ResultsMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Lta StandardDocument178 pagesLta Standardkokuei100% (5)
- BS-1377 PART-4 (R) SOIL Compaction Related TestsDocument52 pagesBS-1377 PART-4 (R) SOIL Compaction Related TestsAshraf Tomizeh100% (2)
- Road Note 29 & 31Document31 pagesRoad Note 29 & 31Shafi UllahNo ratings yet
- 1 - 827 - ORN - 40 Axle Load Surveys and Traffic Counts For Traffic LoadingDocument76 pages1 - 827 - ORN - 40 Axle Load Surveys and Traffic Counts For Traffic LoadingHendhira Astianto100% (2)
- Manual On Pavement DesignDocument31 pagesManual On Pavement DesignRietiNateNo ratings yet
- Overseas Road Note 03Document46 pagesOverseas Road Note 03Amadu FarrowNo ratings yet
- Orn 19Document94 pagesOrn 19rajithfernando50% (2)
- Overseas Road NotesDocument1,618 pagesOverseas Road NotesAndrada Ivan100% (5)
- Road Note 29: A Guide To The Structural Design of Pavements For New RoadsDocument43 pagesRoad Note 29: A Guide To The Structural Design of Pavements For New Roads7d5b3373100% (8)
- BS 4466Document25 pagesBS 4466Umange Ranasinghe100% (6)
- Design of Surface Dressing PDFDocument11 pagesDesign of Surface Dressing PDFChristian Nicolaus100% (1)
- BS 5400 Part 2Document2 pagesBS 5400 Part 2poziomka36100% (1)
- Gallivan - Pre Final Edits - Superpave Volumetric Mix DesignDocument16 pagesGallivan - Pre Final Edits - Superpave Volumetric Mix DesignWail Osman MukhtarNo ratings yet
- BS EN 12697 Part 36 2003 - Determination of The Thickness of A Bituminous Pavement PDFDocument13 pagesBS EN 12697 Part 36 2003 - Determination of The Thickness of A Bituminous Pavement PDFjerin sam kurianNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Geometric Design (With Ghanaian Considerations)Document36 pages1 - Introduction To Geometric Design (With Ghanaian Considerations)Kwasi Agyeman-Boakye100% (1)
- Low Cost Sealing of Low Volume Roads EditedDocument22 pagesLow Cost Sealing of Low Volume Roads Editedhaumbamil100% (3)
- Surface DressingDocument34 pagesSurface DressingNyangoe Joel100% (1)
- Low Volume Roads - ManualDocument191 pagesLow Volume Roads - Manualbikerkid100% (1)
- Low Volume Roads Manual: Republic of MalawiDocument312 pagesLow Volume Roads Manual: Republic of MalawiMichaelNo ratings yet
- Overseas Road Note 04 PDFDocument44 pagesOverseas Road Note 04 PDFbala subramanyamNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement Design Manual, Part I First PartDocument32 pagesFlexible Pavement Design Manual, Part I First PartSteven T Musumba82% (17)
- Bituminous Mixtures - Material Specifications: BSI Standards PublicationDocument9 pagesBituminous Mixtures - Material Specifications: BSI Standards PublicationCristián JiménezNo ratings yet
- Bs 5400 - Concrete DesignDocument1 pageBs 5400 - Concrete Designcaner_kurtoglu-1No ratings yet
- Surface DressingDocument82 pagesSurface Dressingluci99No ratings yet
- Pavement DistressesDocument45 pagesPavement DistresseswedjefdbenmcveNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Road Note No. 4-1Document40 pages3.3 Road Note No. 4-1Asad Choudhary100% (1)
- Tanzania - Road Field Testing Manual - 2003Document155 pagesTanzania - Road Field Testing Manual - 2003Giora Rozmarin100% (2)
- Highway Engineering Group 2Document12 pagesHighway Engineering Group 2Christine Joyce BunyiNo ratings yet
- CTMM Standard Specification (Third Edition) 2005 PrintDocument322 pagesCTMM Standard Specification (Third Edition) 2005 PrintKubwensu Mwanshukisha MambweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Pavement Design (Flexible - JKR2013)Document28 pagesChapter 3 - Pavement Design (Flexible - JKR2013)elleyashahari100% (1)
- BS 434-1 (1984) - Specification For Bitumen Road Emulsions PDFDocument22 pagesBS 434-1 (1984) - Specification For Bitumen Road Emulsions PDFStephen Mauta KithongoNo ratings yet
- BS 5400 Part 4Document2 pagesBS 5400 Part 4ekia_my0% (2)
- British Standard Kerb and Edging TdsDocument6 pagesBritish Standard Kerb and Edging TdsNitzOONo ratings yet
- Pothole CSIR Tech GuideDocument52 pagesPothole CSIR Tech GuideMamphot100% (2)
- BS 598-104-1989Document18 pagesBS 598-104-1989hibonardo100% (2)
- Design of Rigid Pavement PDFDocument24 pagesDesign of Rigid Pavement PDFSayantan Chakraborty75% (4)
- Overseas Road Note 2Document49 pagesOverseas Road Note 2Iftikhar Kamran83% (6)
- Pavement Design ReportDocument7 pagesPavement Design ReportYaselaNo ratings yet
- BS-8006-1-2010-trang-143-167-trang-1-25-đã NénDocument25 pagesBS-8006-1-2010-trang-143-167-trang-1-25-đã NénPhan Thanh HiếuNo ratings yet
- BS en 12350-4-2000-Degree of CompactabilityDocument8 pagesBS en 12350-4-2000-Degree of CompactabilityOana CristinaNo ratings yet
- TMH-6 - ST10Document10 pagesTMH-6 - ST10ATHOLSCHWARZNo ratings yet
- Tanzania Pavement & Materials Design Manual 1999 Chapter 5 - SubgradeDocument10 pagesTanzania Pavement & Materials Design Manual 1999 Chapter 5 - SubgradeGiora Rozmarin100% (1)
- List of EstandardsDocument10 pagesList of EstandardsCharles MunetsiNo ratings yet
- Pavement Design: Highway EngineeringDocument37 pagesPavement Design: Highway Engineeringjeromefamadico100% (2)
- Rigid and Flexible Pavemment FormulasDocument13 pagesRigid and Flexible Pavemment FormulasRonald Costales100% (2)
- Study of Comosite Effect of Concrete Base in Rigid Pavement For Village Roads in Alluvial RegionDocument10 pagesStudy of Comosite Effect of Concrete Base in Rigid Pavement For Village Roads in Alluvial RegionShreyansh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Thickness of Pavement PDFDocument7 pagesThickness of Pavement PDFReech Aerol Almendral100% (1)
- ch04 RevDocument39 pagesch04 RevGlenn Midel Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement (Compatibility Mode)Document15 pagesRigid Pavement (Compatibility Mode)Mohammad Imran NewazNo ratings yet
- Transportation EngineeringDocument71 pagesTransportation EngineeringjifotNo ratings yet
- Pavement DesignDocument21 pagesPavement DesignAbinash Panda100% (4)
- 411-Design of Highway PavementsDocument41 pages411-Design of Highway PavementsnotokordNo ratings yet
- mod 4 partDocument17 pagesmod 4 partashnaabu996No ratings yet
- Human and The EnvironmentDocument5 pagesHuman and The EnvironmentMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Wasteguide FinalDocument53 pagesWasteguide FinalIshwar ChandraNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Design GuideDocument80 pagesWaste Management Design GuideMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- MENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics TutorialDocument3 pagesMENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics TutorialMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Case AnalysisDocument21 pagesNavigating The Case AnalysisMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- 1001 Vocabulary and Spelling QuestionsDocument160 pages1001 Vocabulary and Spelling Questionssashi01092% (12)
- Experimental Study On The Structural Behavior of Circumferentially and Diametrical Braced DomesDocument13 pagesExperimental Study On The Structural Behavior of Circumferentially and Diametrical Braced DomesHaitham HassanNo ratings yet
- Stormwater Drainage SchedulesDocument2 pagesStormwater Drainage SchedulesClement TakavarashaNo ratings yet
- Pages From Design of Fluid Systems-Hook-Ups, Spirax Sarco 4Document1 pagePages From Design of Fluid Systems-Hook-Ups, Spirax Sarco 4Ujwal KhandokarNo ratings yet
- Anticorrosion Treatment AlucoastDocument7 pagesAnticorrosion Treatment Alucoastznim04No ratings yet
- Fibrekork SpecsDocument1 pageFibrekork SpecsRonald José Zavarce FloresNo ratings yet
- Transport Processes in Petroleum Production: PETE 314Document4 pagesTransport Processes in Petroleum Production: PETE 314Bharat BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- 590 1365 1 SMDocument11 pages590 1365 1 SMzeni romdhoniNo ratings yet
- Russia StandardDocument2 pagesRussia StandardersinNo ratings yet
- Low Water FlowDocument38 pagesLow Water FlowKamaruz DanialNo ratings yet
- BS 5950-2000 Example 001Document5 pagesBS 5950-2000 Example 001Anitha Hassan KabeerNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics NotesDocument12 pagesFluid Mechanics Notessubha_aeroNo ratings yet
- Brochure - Kohler Brochure - 2020Document96 pagesBrochure - Kohler Brochure - 2020Md Omor Faruk0% (1)
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research: Guoqing Xu, Bruce R. EllingwoodDocument9 pagesJournal of Constructional Steel Research: Guoqing Xu, Bruce R. EllingwoodBayuAgungGilangWibowoNo ratings yet
- Technical Note AllpileDocument1 pageTechnical Note AllpileDavidNo ratings yet
- SST 41M 3legDocument38 pagesSST 41M 3legSemogaBeruntungNo ratings yet
- Deflection CalculationDocument6 pagesDeflection CalculationSuhas MangaloreNo ratings yet
- Highshrink PT814Document1 pageHighshrink PT814Hemant Kumar PathakNo ratings yet
- EVACHMACriteriaFinal For2012Document10 pagesEVACHMACriteriaFinal For2012Assane LeyeNo ratings yet
- Indoor Pool Design Utah Ashrae 040717Document65 pagesIndoor Pool Design Utah Ashrae 040717Réda RédaNo ratings yet
- Caisson Design Based On 2018 IBC & 2016 CBCDocument2 pagesCaisson Design Based On 2018 IBC & 2016 CBCNelson VegaNo ratings yet
- Guidance and Schedule Iccer 2016Document8 pagesGuidance and Schedule Iccer 2016Perdana Miraj SejatigunaNo ratings yet
- Safe Bearing Capacity and Settlement PresentationaDocument39 pagesSafe Bearing Capacity and Settlement PresentationaFaisal RehmanNo ratings yet
- Air Leakage of Office BuildingsDocument34 pagesAir Leakage of Office BuildingsAdrian JugariuNo ratings yet
- Return Period & Others GuidelinesDocument1 pageReturn Period & Others GuidelinesHarish Kumar Mahavar100% (1)
- VSL Data Sheets USDocument22 pagesVSL Data Sheets USLydia WangNo ratings yet
- Factors in The Choice of Mix DesignDocument31 pagesFactors in The Choice of Mix DesignMudduKrishna shettyNo ratings yet