Common Source Amplifier Experiment
Uploaded by
appuamreddyCommon Source Amplifier Experiment
Uploaded by
appuamreddyExperiment No. 2.
COMMON SOURCE AMPLIFIER
I. AIM:
To plot the frequency response of the FET amplifier and to calculate the mid frequency gain and bandwidth
II. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS:
i. Apparatus:
1. Regulated power supply 0-30 v/1 Amp - 1
2. Function generator - 1
3. CRO 1
4. Multimeter 1
5. Digital Multimeter
ii. Components:
1. FET BFW 10/11
2. Bread board, wires and probes
3. Resistors 1K-3, 10M-1, 2.2K
4. Capacitors 10 f 3, 0.01f-1
iii. Specifications:
BFW11 BFW10
IDSS 4-10 mA 8-20 mA
VGS 2-4 v 4-8 v
gm 3.9 mA/V 3.2 mA/v
III. THEORY:-
In a FET, the conduction of current through the device is controlled by the electric field between the gate and the conducting channel of
the device. The output current is controlled by the input voltage. Thus, FET is basically a voltage controlled device.
In common source JFET amplifier there is phase displacement of 180 degrees between the output and input voltage the mid
frequency voltage gain of the amplifier is given by A = gm x Rd The voltage gain and phase angular are constant in mid frequency range.
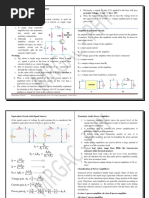
Design:
Self Bias Method:
Capacitor C1, C2 are open circuited and the resistor RG acts as short circuit, since IG=0. Therefore VRG=IG RG=0V
The gate voltage is zero and the current through RS is equal to the drain current. i.e.
IS =ID
RS = VRS = ID RS
Applying KVL to the gate source loop we obtain,
-VGS ID RS = 0
VGS = -VRS = -ID RS
Where VGS is used to the output current ID and not fixed in the magnitude. The value of output drain current ID can be calculated using
equation as.
2
P
S D
DSS
2
P
GS
DSS D
V
V V
- 1 I
V
V
- 1 I I
|
|
.
|
\
| +
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
Summing the voltage drop across RD and applying KVL to output loop
VDD-ID RD VDS ID RS = 0
VDS =VDD ID (RS +RD)
Since the gate current is practically zero, the drain resistance RD is given by
|
|
.
|
\
| +
= =
D
RS DS
D
D
D
I
V V - VDD
I
R
V
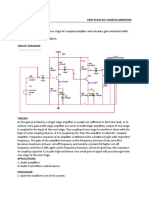
IV. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
V. PROCEDURE:
1. Make the circuit connections as shown in the figure.
2 Set Vin= 50mv from the signal generator.
3. Keeping the input voltage constant, vary the frequency from 50 HZ to 1 MHZ in regular steps and note down the
corresponding output voltage.
4. Plot the graph of gain v/s frequency.
5. Find the bandwidth.
PROGRAM
*FET AMPLIFIER
VDD 5 0 DC 12V
VS 1 0 AC 50MV
R6 1 2 1K
C1 2 3 10UF
R7 3 0 10MEGA
RS 6 0 1K
CS 6 0 10UF
R3 5 4 5K
C3 4 7 10UF
R5 7 0 1K
C4 7 0 0.01UF
J 4 3 6 BFW10
.MODEL BFW10 NJF(BETA=1E-1)
.AC DEC 10 10HZ 10MEGAHZ
.PRINT AC V(7)
.PLOT AC V(7)
.PROBE
.OP
.END
VI. OBSERVATIONS:
Sl.No. Frequency Output voltage Vo Voltage gain Av =
Vo/Vi
Voltage gain Av dB =
20 log Vo/Vi
1 50Hz
2 100Hz
3 200Hz
4 ....
VII. GRAPH:
VIII. CALCULATIONS:
Bandwidth = fH-fL
Mid frequency gain AVM =
IX. RESULT:
1. Frequency response curve is plotted.
2. Bandwidth is calculated.
X. INFERENCE:
1. The maximum voltage gain occurs at mid band.
2. The gain at the half power point is 3 dB less than the mid band gain.
3. The gain remains constant throughout the mid band.
4. The gain decreases both at low frequency and high frequency.
XI. PRECAUTIONS:
1. Identify the terminals of FET properly.
2. Set the function generator just below the point of distortion. So that maximum undistorted sine wave appears.
3. Adjust the oscilloscope for proper viewing.
XII. APPLICATIONS:
1. In balanced modulator
2. Multi Channel Switch driver and amplifier squences
XIII. EXTENSION:
Designing cascaded FET amplifier
XIV. TROUBLE SHOOTING:
Sl No. Fault Diagnosis
1 If there is no output Check for loose connection in the circuit
Check the CRO probes
2. If the output is distorted Check the position of operating point.
XV. QUESTIONS:
1. What is the difference between FET and BJT?
2. Explain the construction and working of JFET?
3. Briefly describe some applications of FET.
4. What is the difference JFET and MOSFET?
5. What do you mean by frequency response?
6. Why FET is called unipolar device?
7. What is the typical value for the input impedance Zi for JFET?
8. Which BJT amplifiers configuration is similar to common source amplifiers?
9. Why thermal runaway is not possible for FET?
10. What is the amplification factor for FET transistor amplifier.
You might also like
- Experiment 11 Frequency Response of CE Amplifier86% (7)Experiment 11 Frequency Response of CE Amplifier4 pages
- Pulse and Digital Circuits - Linear Wave Shaping100% (2)Pulse and Digital Circuits - Linear Wave Shaping132 pages
- Software - Experiment 5. Frequency Response of Common Source Ac Amplifier PDF100% (1)Software - Experiment 5. Frequency Response of Common Source Ac Amplifier PDF5 pages
- Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor Amplifier100% (3)Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor Amplifier7 pages
- High-Frequency Response of Common-Emitter and Common-Source CircuitsNo ratings yetHigh-Frequency Response of Common-Emitter and Common-Source Circuits22 pages
- Design An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.100% (1)Design An Inverting and Non Inverting Amplifier.8 pages
- Name: Date:: Experiment 03 Common Collector AmplifierNo ratings yetName: Date:: Experiment 03 Common Collector Amplifier3 pages
- Experiment No. 4 Design of Square Wave Generator Using Op-Amp IC 7410% (1)Experiment No. 4 Design of Square Wave Generator Using Op-Amp IC 74122 pages
- Common Collector Amplifier: Experiment No. 15100% (3)Common Collector Amplifier: Experiment No. 152 pages
- Experiment 07 Mosfet Name: Date:: Objective100% (2)Experiment 07 Mosfet Name: Date:: Objective4 pages
- MOSFET High Frequency Model and Amplifier Frequency ResponseNo ratings yetMOSFET High Frequency Model and Amplifier Frequency Response17 pages
- Class B Complementary Symmetry Power Amplifier50% (2)Class B Complementary Symmetry Power Amplifier15 pages
- Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A Differentiator100% (2)Experiment No:9: Op-Amp As A Differentiator2 pages
- (CC) Transistor Characteristics in Common Collector ConfigurationNo ratings yet(CC) Transistor Characteristics in Common Collector Configuration6 pages
- Experiment No: 4: TITLE: 4-Bit Comparator AIM: To Design 4-Bit Comparator Using IC 7485 Prior ConceptNo ratings yetExperiment No: 4: TITLE: 4-Bit Comparator AIM: To Design 4-Bit Comparator Using IC 7485 Prior Concept43 pages
- Experiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Summing Amplifire. Aim: To Design and Setup A Summing Amplifier Circuit With OP AMP100% (1)Experiment No: 04 Experiment Name: Summing Amplifire. Aim: To Design and Setup A Summing Amplifier Circuit With OP AMP4 pages
- Monostable Multivibrator Using 555 Timer Aim100% (1)Monostable Multivibrator Using 555 Timer Aim4 pages
- Experiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 ObjectiveNo ratings yetExperiment - Feedback Amplifiers: 3.2.1 Objective13 pages
- Analog Circuits frequence responce of CS ampNo ratings yetAnalog Circuits frequence responce of CS amp69 pages
- SET-1 (Analog Communications) - ECE Max. Marks: 10 M Time: 60 Min Date: Answer Any TWO Questions 2x 5 Marks 10 MarksNo ratings yetSET-1 (Analog Communications) - ECE Max. Marks: 10 M Time: 60 Min Date: Answer Any TWO Questions 2x 5 Marks 10 Marks2 pages
- Microwave Engineering R09 June July 2014No ratings yetMicrowave Engineering R09 June July 20141 page
- SET-1 (Electronics Measurements & Instrumentation) - Ece Time: 60 Min DateNo ratings yetSET-1 (Electronics Measurements & Instrumentation) - Ece Time: 60 Min Date2 pages
- Answer Any Two Questions: Symbo L Probability A e I o U ! 0.2 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.1No ratings yetAnswer Any Two Questions: Symbo L Probability A e I o U ! 0.2 0.3 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.11 page
- Food of Odisha - 17 Dishes of Odisha That You Should Not Miss!100% (2)Food of Odisha - 17 Dishes of Odisha That You Should Not Miss!1 page
- System Design Using FPGAs - Google FormsNo ratings yetSystem Design Using FPGAs - Google Forms5 pages
- ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR (OPEN ELECTIVE - III) - Google FormsNo ratings yetORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOUR (OPEN ELECTIVE - III) - Google Forms7 pages
- Actuators and Robot Systems (PE-VI) - Google FormsNo ratings yetActuators and Robot Systems (PE-VI) - Google Forms8 pages
- Performance Analysis of FIR Filter Design by Using Optimal, Blackman Window and Frequency Sampling MethodsNo ratings yetPerformance Analysis of FIR Filter Design by Using Optimal, Blackman Window and Frequency Sampling Methods6 pages
- NTE1641 Integrated Circuit: 1024 Stage BBD For Audio Signal DelaysNo ratings yetNTE1641 Integrated Circuit: 1024 Stage BBD For Audio Signal Delays3 pages
- UNIT 3 Advanced Signals & Systems Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFNo ratings yetUNIT 3 Advanced Signals & Systems Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDF5 pages
- 60-PREP-0005 Kornit Electrical Modular Curing System Site Preparation GuideNo ratings yet60-PREP-0005 Kornit Electrical Modular Curing System Site Preparation Guide20 pages
- Raypa ID Culture Incubator - User ManualNo ratings yetRaypa ID Culture Incubator - User Manual13 pages
- Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) : PHYSICS 0972/62No ratings yetCambridge IGCSE (9-1) : PHYSICS 0972/6216 pages
- Gran Mango 3.1416: Resistors Capacitors Potentiometers Parts List (Stock Big Muff)No ratings yetGran Mango 3.1416: Resistors Capacitors Potentiometers Parts List (Stock Big Muff)2 pages
- Heat Pump Mirai Split Technical Sheet GB01No ratings yetHeat Pump Mirai Split Technical Sheet GB0128 pages