Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Uploaded by
dinohrawrCopyright:
Available Formats
Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Uploaded by
dinohrawrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Useful Inequalities: V0.26a April 26, 2014
Uploaded by
dinohrawrCopyright:
Available Formats
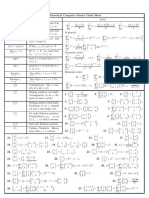
Useful Inequalities
{x2
0}
n k
k
binomial
v0.26a April 26, 2014
xi y i
Cauchy-Schwarz
i=1
n
Minkowski
i=1
|xi + yi
|xi yi |
x)r
(1 +
i=1
n
i=1
|xi
i=1
(1 +
nx)n+1
(1 +
1+
|yi
for p 1.
1/q
|yi |q
for p, q > 1,
1
p
1
q
(1 + (n +
for x [1,
1)x)n
x q
q
1+
1
),
r1
= 1.
2 x+12 x <
e
means
min{xi }
for x R, n N.
for a, b 0, n N.
for (i) x > 0, p > q > 0,
power means
(iv) q < 0 < p , q > x > 0, (v) q < 0 < p , p < x < 0.
x n
n
ex 1 +
e x xe
1
2x
1
<
1+
xn
n!
for x R, and
ex 1 + x +
ex
1 + x,
xx
x
2
<
x2
2
x n
n
x2
n
ex 1
+ 1 ex 1 +
x n+x/2
n
x+1
2x
x y
y
yx
ex
> 1 and
> 1+
>e
x
2
for x [0, 1].
x2 1
x2 +1
x1
x
2x
2+x
ln(1 + x)
x
x+1
1
n
ln(n + 1) < ln(n) +
ln(1 + x) x
x2
2
ln(1 x) x
x3
2
trigonometric
hyperbolic
x cos x
2
x
x2 1
2x
ln(x)
x
2
x cos x
x3
sinh2 x
x
2
x cos x
1x2 /3
x cos2 (x/2) sin x (x cos x + 2x)/3
cosh(x) + sinh(x) ex(+x/2)
x+ y
2
for x R, [1, 1].
1
4n
(1 9n ).
n
|w i ,
x1 < 2 x2 x1
n!
1i1 <<ik n
n n 1/12n
e
e
2n
xi
1
n
wi |xi |p
1/p
for x 1.
x2
,
sinh x
n n
e
en
xi 2 max{xi }
, wi 0,
wi = 1.
for p q, wi 0.
x+y
2
x+ y
2
x+y
2
for x, y > 0.
for x, y > 0, [0, 1].
Sk
(k+1)
ai 1 ai 2 aik ,
pi (xi )
1
n
xy
ln(x)ln(y)
and
d 0.
M = mini {xi }, M = maxi {xi }.
wi |xi |q
for n d 0.
1
for (0, 2 ).
1/n
xi
2n
n
Sk+1
and
where pi 0,
for 1 k < n,
ai 0.
pi = 1, and convex.
f (ai )g(bi )pi
f (ai )pi
i=1
i=1
g(bi )pi
f (ai )g(bni+1 )pi
i=1
for a1 an , b1 bn and f, g nondecreasing, pi 0,
sin x,
x1 y +x y 1
2
p i xi
for n > k > 0.
H(x) = log2 (xx (1x)1x ).
2n
n
2
for
x+1
(xy) 4
all for x 0,
1.
wi |xi |q1
n
k
2n
Alternatively: (E [X]) E [(X)]. For concave the reverse holds.
Alternatively: E f (X)g(X) E f (X) E g(X) .
for x [0, 0.43], reverse elsewhere.
tan x
xy
i=1
x 3 cos x x x3 /6 x cos
Sk 2 Sk1 Sk+1
for x [0, 0.45], reverse elsewhere.
x3
3
wi |xi |
Jensen
<
p1
Heinz
Chebyshev
ln(n) + 1
sin x x cos(x/2) x x +
wi |xi |p
xy
Sk =
for x, y R.
n
d
i=0 i
and
i |xi
x 1, ln(x) n(x n 1) for x, n > 0.
n
1
i=1 i
x3
4
for x 0, reverse for x (1, 0].
Lehmer
for x, y > 0.
2 y exy 1 + x y + exy , and ex x + ex
logarithm
n
x1
i
Maclaurin
xy
x+y
1
4
(1 8n )
n
2nH()
,
2n(1)
n n 1/(12n+1)
e
e
2n
log mean
for x, r 1.
xy
Mp Mq for p q, where Mp =
for x, n > 0.
for x (0, 1).
x1/r (x 1) rx(x1/r 1)
for G =
In the limit M0 =
for n > 1, |x| n.
for x 0, reverse for x 0.
for x [0, 1.59] and
x2
n n
e
nn
kk (nk)nk
for n1 k1 0, n2 k2 0.
d
en
for n d
d
n
d
d 1 + n2d+1
n
n n
1
i=0 i 12 n
Stirling
r > 1.
n
k
n k 0 and
square root
(ii) p < q < x < 0, (iii) q > p > x > 0. Reverse for:
exponential
en k
,
k
nd + 1
n
d
i=0 i
n
d
i=0 i
n
for x [1, 0], n N.
rx
1(r1)x
for
n
d
i=0 i
for x [0, 1], r R \ (0, 1).
(a + b)n an + nb(a + b)n1
x p
p
1
p
|p
n
k
nk
k!
+n
n1 n2
n1 +k 2
k1
k1 k2
2
n
G n G
2
for x 1, r R \ (0, 1). Reverse for r [0, 1].
1
1nx
(1 + x)r 1 +
n
i=1
i=1
(1 + x)r 1 + (2r 1)x
x)n
1
p
|xi |p
1 + rx
2
yi
|p
1/p
i=1
Bernoulli
1
p
|p
Hlder
o
x2
i
i=1
n
4k!
n
k
rearrangement
i=1
ai b i
i=1
ai b(i)
ai bni+1
i=1
for a1 an ,
b1 bn and a permutation of [n]. More generally:
n
i=1
fi (bi )
i=1
fi (b(i) )
fi (bni+1 )
i=1
with fi+1 (x) fi (x) nondecreasing for all 1 i < n.
pi = 1.
Weierstrass
wi
1 xi
w i xi
where xi 1, and
n
k=1
Carleman
either wi 1 (for all i) or wi 0 (for all i).
If wi [0, 1],
Young
1
( pxp
Kantorovich
Cauchy
Hermite
U
L1
xi
yi
0<m
sum-integral
1 1
)
qxq
xi
Chong
i=1
Gibbs
i
i
n
Shapiro
i=1
yi
ai log
ai
bi
bi
ai
i=1
a
b
1
q
= 1.
f (x) dx
for f nondecreasing.
ai a i
for ai > 0.
ai , b :=
Hadamard
i=1 j=1
bi .
Hilbert
where xi > 0, (xn+1 , xn+2 ) := (x1 , x2 ),
Hardy
1
n!
Schur
Mathieu
A2
ij
n
i,j=1
2
i
where A is an n n matrix.
A2
ij
k
i=1
and
di
k
i=1
Aczl
e
n
i=1
xi i
n
ai
i=1 (1 xi )
a1 b 1
given that
n
i=2
a2
1
xi + yi
Mahler
a i xi
for xi [0, 1 ], ai [0, 1],
n
2
i=1 ai (1 xi )
2
ai b i
n
i=2
>
1/n
i=1
a2
1
a2
i
n
n=1
1
c2 +1/2
Milne
b1 min
k
i=1
or
1/n
xi
b2
1
>
n
2 b2
1
i=2 ai
n
2
i=2 bi .
+
i=1
1/n
yi
i=1
n
i=1 (ai
+ bi )
i=1
(bi )
j=1 i=1
ai(j)
a1+y b1y
i
i
1+y
a1y bi
i
for a1 a2 an and b1 bn ,
1
n!
t
i=1
ai
t
i=1 bi
for all 1 t n,
xb1 xbn
(n)
(1)
m=1
n
2
i=2 bi
ai bi b1 max
k
XA
a2
m
1
2
ai bi
n
i=1 ai +bi
n
i=1
for b1 bn 0.
ai
n=1
ak
k
n 1
|X|
pp
n=1
a2
n
2n
n=1 (n2 +c2 )2
<
p
p1
1
c2
<
an p
n=1
2 2
n=1 bn
{bk },
for am , bn R.
i=0
n
i=1 bi
Ai
n
i=1
for an 0, p > 1.
for an R.
for c = 0.
for an 0, p > 1, reverse if p (0, 1).
1, A 2[n] , no set in A is subset of another set in A.
Pr
ap
n
for c(i) depth of leaf i of binary tree, sum over all leaves.
|A| |str(A)|
Pr
n=1
n 2 a2
n
n
i
for A 2[n] , and
str(A) = {X [n] : X shattered by A},
Bonferroni
ai
vc(A)
Sauer-Shelah
where xi , yi > 0.
i=1
an
kn
LYM
ai = 1.
a1 +a2 ++an
n
2c(i) 1
Kraft
ai
n
i=1
am bn
n=1 m+n
i=1
Abel
a1x b1+x
i
i
xa 1 xa n
(n)
(1)
n=1
n=1
for 1 k n.
A is an n n matrix. For the second inequality A is symmetric.
n
i=1
j=1 i=1
{bi } (majorization), i.e.
m=1
1 n the eigenvalues, d1 dn the diagonal elements.
Ky Fan
(ai )
Carlson
Copson
n
i=1
aij
where a1 a2 an and b1 b2 bn and {ak }
where x, y, z 0, t > 0
(det A)2
j=1 i=1
and
With max{m, n} instead of m + n, we have 4 instead of .
n
2
ai(j)
xi 0 and the sums extend over all permutations of [n].
xt (x y)(x z) + y t (y z)(y x) + z t (z x)(z y) 0
n
for |ai |, |bi | 1.
with equality for t = n and is convex (for concave the reverse holds).
i=1
for concave, and a :=
|ai bi |
a1+x b1x
i
i
n
i=1
Karamata
for convex.
ai a(i)
n
i=1
|ak |
for 1 x y 0, and i = 1, . . . , n.
Muirhead
aij
n
k=1
where 0 ai1 aim for i = 1, . . . , n and is a permutation of [n].
and n 12 if even, n 23 if odd.
Schur
and {ai }
(a)+(b)
2
n
i=1 bi
j=1 i=1
1/k
|ai |
ai
sum-product
for ai , bi 0, or more generally:
b
a
1
p
where a < b, and convex.
(x) dx
and
xi
xi+1 +xi+2
U +1
L
f (i)
(b)
a log
for x, y 0, p, q > 0,
xi yi
n
i=1
product di.
Callebaut
U
i=L
b
a
y
q
ai
a(i)
ai
x
p
for xi , yi > 0,
A = (m + M )/2, G = mM .
M < ,
1
ba
A
G
f (b)f (a)
ba
a+b
2
xy
f (x) dx
(a)
wi 1 and xi 1, the reverse holds.
k
i=1
(1)j1 Sj
for 1 k n, k odd,
(1)j1 Sj
for 2 k n, k even.
j=1
k
Ai
j=1
Sk =
1i1 <<ik n
vc(A) = max{|X| : X str(A)}.
Pr Ai1 Aik
where Ai are events.
Bhatia-Davis
Var[X] M E[X] E[X] m
where X [m, M ].
Samuelson
n 1 xi + n 1
for i = 1, . . . , n.
xi /n , 2 =
Where =
Markov
Pr |X| a E |X| /a
Pr X E[X] t
VysochanskijPetunin-Gauss
for X [0, 1] and c 0, E[X] .
2nd
moment
Pr X > 0
(E[X])2 /(E[X 2 ])
kth
moment
Pr X t
Cherno
Pr[X t] F (a)/at
F (z) =
pk
zk
pk
exp
2
2
(1+)
pk /
k k = /(1 p), E[Xi ] = pi , X =
Azuma
Pr X E[X] 2 exp
Xi [ai , bi ] (w. prob. 1), X =
E eX exp
Pr max |Sk |
k
for Xi [0, 1] k-wise i.r.v.,
,
n
2
2(n 2 + M /3)
exp
for Xi i.r.v.,
Pr Xn X0 2 exp
n
2
i=1 ci
1
n
Var[Xi ], 0.
for martingale (Xk ) s.t.
Var[Z]
1
2
E
i=1
Z Z (i)
for Xi , Xi X i.r.v.,
Pr Z E[Z] 2 exp
2 2
n
2
i=1 ci
for Xi , Xi X i.r.v.,
Z, Z (i) as before, s.t. Z Z (i) ci for all i, and 0.
> 0.
Janson
for Xi i.r.v.,
M Pr
M =
Xi , 0.
Lovsz
a
a)2
Pr
B i M exp
(1 Pr[Bi ]), =
Bi
2 2
i=j,Bi Bj
(1 xi ) > 0
where Pr[Bi ] for all i,
Pr[Bi Bj ].
where Pr[Bi ] xi
(i,j)D
(1 xj ),
for xi [0, 1) for all i = 1, . . . , n and D the dependency graph.
1
Var[Sn ]
2
1
2
If each Bi mutually indep. of the set of all other events, exc. at most d,
Var[Xi ]
Pr[Bi ] p for all i = 1, . . . , n , then if ep(d + 1) 1 then Pr
where X1 , . . . , Xn are i.r.v., E[Xi ] = 0,
Var[Xi ] < for all i, Sk =
Xi
f : X n R, Z = f (X1 , . . . , Xn ), Z (i) = f (X1 , . . . , Xi , . . . , Xn ).
Xi .
A related lemma, assuming E[X] = 0, X [a, b] (w. prob. 1) and R:
2 (b
Pr
Xi Xi1 < ci (w. prob. 1), for i = 1, . . . , n, 0.
Efron-Stein
for R 2e ( 5.44).
2 2
n
2
i=1 (bi ai )
Var[Xi ], |Xi | M (w. prob. 1), 0,
E[Xi ] = 0, |Xi | < M (w. prob. 1) for all i, 2 =
for [0, 1).
Xi , = E[X], p =
where Xi i.r.v.,
(u) = (1 + u) log(1 + u) u.
i=1
Xi , = E[X], 0.
1
n
for martingale (Xk ) and > 0.
n 2
M
M2
n 2
exp
E[Xi ] = 0, 2 =
McDiarmid
Pr X (1 + )
Kolmogorov
i=1
Xi
for Xi {0, 1} k-wise i.r.v., E[Xi ] = p, X =
n
0.
Pr
Bernstein
2
min{2 + , 3}
exp
2
.
3
Pr max1kn |Xk | E |Xn | /
n
for X r.v., Pr[X = k] = pk ,
e
(1 )(1)
t
k
1kn
k
i=1 Xi ,
Bennett
Simpler (weaker) form: Pr X R 2R
n
k
1kn
Doob
k/2
where Xi indep. r.v. drawn from {0,1}, X =
Pr X t
if
Pr max |Sk | 3 3 max Pr |Sk |
and
e
(1 + )(1+)
Pr X (1 )
2
,
3
if
where Xi are i.r.v., Sk =
probability gen. func., and a 1.
Pr X (1 + )
Hoeding
Etemadi
for Xi [0, 1] k-wise indep. r.v.,
Xi , i = 1, . . . , n, = E[X], Ck = 2 ke1/6k 1.0004, k even.
Pr X t Ck
X=
where t > 0.
where E[X 2 ] = 0.
E (X )k
tk
nk
t2
4 2
92
8
,
3
if
2 = Var[X] < , 2 = Var[X] + (E[X] m)2 = E[(X m)2 ].
where E[X] 0.
Pr X = 0 Var[X]/(E[X 2 ])
for X 0,
Where X is a unimodal r.v. with mode m,
where t > 0.
Pr X E[X] t Var[X]/(Var[X] + t2 )
4
92
Pr X E[X]
Pr X m 1
for f 0, and f (x) s > 0 for all x S.
Var[X]/t2
Var[X]
(1 )2 (E[X])2 + Var[X]
Pr X m
where X is a random variable (r.v.), a > 0.
Pr X S] E[f (X)]/s
Pr X E[X]
Var[X] < , and (0, 1).
(xi )2 /n.
Pr X c (1 E[X])/(1 c)
Chebyshev
Paley-Zygmund
k
i=1
Xi and > 0.
Lszl Kozma latest version: http://www.Lkozma.net/inequalities_cheat_sheet
a o
B i > 0.
You might also like
- STOR 435 Formula Sheet: BasicsDocument3 pagesSTOR 435 Formula Sheet: BasicsEricQianNo ratings yet
- Advanced QM Susskind - Ramo NotesDocument4 pagesAdvanced QM Susskind - Ramo NotesEddy R. Vélez50% (4)
- Soa Exam PDocument10 pagesSoa Exam PAnonymous ZL37my2K100% (1)
- Probability Cheat Sheet: DistributionsDocument2 pagesProbability Cheat Sheet: DistributionsVinny MalizaNo ratings yet
- Useful Inequalities: v0.20b July 22, 2013Document3 pagesUseful Inequalities: v0.20b July 22, 2013George ProtopapasNo ratings yet
- Useful Inequalities: V0.27a November 29, 2014Document3 pagesUseful Inequalities: V0.27a November 29, 2014peterNo ratings yet
- Probability FormulasDocument1 pageProbability FormulasEmily BrookNo ratings yet
- Coplex Number FormulasDocument7 pagesCoplex Number FormulasMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesTheoretical Computer Science Cheat SheetRosa GonzalezNo ratings yet
- hw3 SolDocument8 pageshw3 SolanthalyaNo ratings yet
- Expectation: Definition Expected Value of A Random Variable X Is DefinedDocument15 pagesExpectation: Definition Expected Value of A Random Variable X Is DefinedLibyaFlowerNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument2 pagesFormulaeMahatama Sharan PandeyNo ratings yet
- A NalgebraDocument3 pagesA NalgebralisoviciNo ratings yet
- FormDocument6 pagesFormBruno AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 So LNDocument10 pagesTutorial 5 So LNBobNo ratings yet
- 1 Iterative Methods For Linear Systems 2 Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument2 pages1 Iterative Methods For Linear Systems 2 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectorsbohboh1212No ratings yet
- Sol 6 Fall 04Document9 pagesSol 6 Fall 04Daniel Cervantes CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chebyshev's Inequality:: K K K KDocument12 pagesChebyshev's Inequality:: K K K KdNo ratings yet
- Tab LiceDocument2 pagesTab LiceМилован МиљковићNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- TheoreticalCS CheatsheetDocument10 pagesTheoreticalCS Cheatsheetmaile4scribdNo ratings yet
- $ Sem5 - Maths FormulaeDocument3 pages$ Sem5 - Maths FormulaeParth CholeraNo ratings yet
- Interpolation and Approximation TheoryDocument15 pagesInterpolation and Approximation TheoryFaisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 List of ExercisesDocument8 pagesCalculus 1 List of Exercisesp1tru1mariusNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Integration: 0.1.1 Trapesoid RuleDocument3 pages0.1 Integration: 0.1.1 Trapesoid RuleMing-Chien HsuNo ratings yet
- CSC 5132: Information Theory and Coding Techniques: Lecturer: Dr. P. SibandaDocument2 pagesCSC 5132: Information Theory and Coding Techniques: Lecturer: Dr. P. SibandaPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument7 pagesFormulaMàddìRèxxShìrshírNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For StatisticsDocument43 pagesFormula Sheet For StatisticsmibuhariNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Fall 2006 Math 301 Midterm Problems: N M 1 N NDocument4 pagesSolutions To Fall 2006 Math 301 Midterm Problems: N M 1 N NJacky PoNo ratings yet
- TMA4180 Optimisation I Spring 2018: Solutions To Exercise Set 7Document4 pagesTMA4180 Optimisation I Spring 2018: Solutions To Exercise Set 7Sakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Formulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDocument10 pagesFormulario: L Ogica Matem AticaDaniel ChuquipomaNo ratings yet
- Special Eigenfunctions For The Ruijsenaars Operator: Yosuke SaitoDocument24 pagesSpecial Eigenfunctions For The Ruijsenaars Operator: Yosuke Saitoapi-225890336No ratings yet
- Exam - 2013 10 30Document5 pagesExam - 2013 10 30lieth-4No ratings yet
- Lect 38Document12 pagesLect 38Mustafa KösemNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument3 pagesTrigxmikelawsonxNo ratings yet
- STAT 3008 Applied Regression Analysis Tutorial 1 - Term 2, 2019 20Document2 pagesSTAT 3008 Applied Regression Analysis Tutorial 1 - Term 2, 2019 20MingyanNo ratings yet
- Newton Iteration and Polynomial Computation:: Algorithms Professor John ReifDocument12 pagesNewton Iteration and Polynomial Computation:: Algorithms Professor John Reifraw.junkNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- 00MET03 Metric SpacesDocument5 pages00MET03 Metric SpacesAjoy SharmaNo ratings yet
- X X X F X F X F X: Likelihood FunctionDocument12 pagesX X X F X F X F X: Likelihood FunctiondNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2009-10-30. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Solutions of Real Analysis 11Document8 pagesSolutions of Real Analysis 11Kartika NugraheniNo ratings yet
- s39 57 PDFDocument23 pagess39 57 PDFBreno EnricoNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument3 pagesFormulasYamer YusufNo ratings yet
- Hw1sol PDFDocument9 pagesHw1sol PDFRohit BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument27 pagesMathematicsneilmehta87No ratings yet
- Assignment (Ch-Continuity & Differentiabilty)Document15 pagesAssignment (Ch-Continuity & Differentiabilty)sheetalNo ratings yet
- Lect 38 PDFDocument12 pagesLect 38 PDFwin alfalahNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and ApplicationsFrom EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and ApplicationsNo ratings yet