Work From Steam
Uploaded by
aushad3mWork From Steam
Uploaded by
aushad3mWork from Steam
Work is the expansion (or contraction) of a pressurized gas or vapor. From the
perspective of a steam cylinder, work is related to pressure P and volume ¦.
Work = F_x = .Pnet Apiston• . _¦
Apiston
. = Pnet_¦
Pnet is the net pressure di_erence across the piston. For
the atmospheric engines, the pressure di_erence across the
slow moving cylinders was equal to Patmospheric − Psaturation
which was essentially constant. Psaturation is the pressure
at which the steam condenses (or evaporates).
Work = (Patm − Psat)_¦
= (Patm − Psat)Apiston_x
The work extracted from the atmosphere could be mea-
sured by the force F exerted from the piston and the piston
displacement _x during the power stroke.
x
(1 )
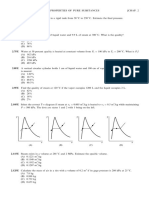
(2 )
vapor
After Evan's engine development, the work was extracted from pressurized steam
instead of the atmosphere. Thus, the net pressure di_erence, Psteam − Patm was
not constant during the power stroke and the work during a power stroke required
integration of the pressure and volume.
W=S
2
1
Pnetd¦
In addition, the speed of the engines was getting faster; too fast to watch a pressure
gauge or manometer and record the pressures as a function of piston position. Some
sort of device was needed to measure pressure and volume and correlate the two
You might also like
- physq11 05 chapter 5 energy in systems – mechanical work and efficiencyNo ratings yetphysq11 05 chapter 5 energy in systems – mechanical work and efficiency16 pages
- Work and Heat Concepts in ThermodynamicsNo ratings yetWork and Heat Concepts in Thermodynamics13 pages
- The Energy Equation: Control Volume With No Mass TransferNo ratings yetThe Energy Equation: Control Volume With No Mass Transfer39 pages
- Chapter 2 Energy Transport by Heat, Work and MassNo ratings yetChapter 2 Energy Transport by Heat, Work and Mass23 pages
- 2-CHAPTER 2-First Law of Thermodynamics-Closed System100% (1)2-CHAPTER 2-First Law of Thermodynamics-Closed System42 pages
- The First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics: Du DQ DWNo ratings yetThe First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics: Du DQ DW7 pages
- REV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic TechnologyNo ratings yetREV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic Technology73 pages
- Understanding Work, Heat, and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1: FundamentalsNo ratings yetUnderstanding Work, Heat, and The First Law of Thermodynamics 1: Fundamentals40 pages
- Chapter Five (Energy Analysis of Closed Systems)No ratings yetChapter Five (Energy Analysis of Closed Systems)31 pages
- Ideal Gas Power Cycles: 13.1 Genera) IntroductionNo ratings yetIdeal Gas Power Cycles: 13.1 Genera) Introduction5 pages
- Material Selection For Design - An IntroNo ratings yetMaterial Selection For Design - An Intro5 pages
- Question 1: Bezier Quadratic Curve Successive Linear Interpolation EquationNo ratings yetQuestion 1: Bezier Quadratic Curve Successive Linear Interpolation Equation4 pages
- Rebound Continues For The Second Straight YearNo ratings yetRebound Continues For The Second Straight Year6 pages
- Pressure Pressure - Manometry Manometry: Man Tech 4Tf3 Man Tech 4Tf3No ratings yetPressure Pressure - Manometry Manometry: Man Tech 4Tf3 Man Tech 4Tf322 pages