Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
ruguCopyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
ruguOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
ruguCopyright:
Available Formats
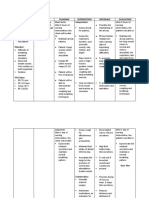
Assessment
Nursing diagnosis
Scientific Explanatio n exposure to triggers the bronchi (large airways) contract into spasm Inflammati on narrowing of the airways excessive mucus production coughing breathing difficulties
Planning
Nursing Intervention Establish rapport to patient and SO. Auscultate chest, noting presence/chara cter of breath sounds, presence of secretions. Note rate and depth of respirations Review Laboratory data. Administer O2 indicated for underlying pulmonary condition Elevate HOB as appropriate. Maintain a calm attitude while dealing with client and SO.
Rationale To gain trust and have a better NPI. To identify etiology/ precipitati ng factors.
Evaluation
Subjective Data: medyo nahihirapan akong huminga Objective data: Looks pale Restlessn ess Fatigue Use accessory muscles when breathing (+) wheezes With productive cough On high back rest Profound breathing pattern Vital
Ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchosp asm 2 BAiAE
Short term: After 3-4 hrs of effective nursing intervention the patient will established a normaleffective respiratory pattern AEB: (-) Restlessness (-)fatigue (-)Use accessory muscles when breathing With productive cough On moderate high back rest Regular breathing pattern Vital signs: T-36 P-78 R-2224 BP-100/60mmHg
To provide relief .
To promote physiologic/ psychologic ease of maximal inspiration To limit level of
Short term: Goal met as evidenced by: (-) Restlessnes s (-)fatigue (-)Use accessory muscles when breathing With productive cough On moderate high back rest Regular breathing pattern Vital signs: T-36 P-78 R23 BP100/60mmHg Long term
signs: T-36 P-78 R28 BP100/60mmHg
Long term: During the whole duration of hospitalization the patient can/will: Verbalize awareness of causative factors. Initiate needed lifestyle changes Demonstra te appropriate coping behaviors. Maintained normal/sta ble Vital signs Experience d free from signs of hypoxia.
Assist client in the use of relaxation technique. Assist and demonstrate deep breathing and coughing exercise. Encourage position of comfort. Reposition every 2 hrs. . Health teachings: Review etiology and possible coping behaviors Teach conscious control of RR as appropriate. Recommend energy conservation techniques
anxiety.
To assist client in taking control of the situation .
Goal met as evidenced by: able to Verbali ze awaren ess of causati ve factors. Initiate neede d lifestyl e change s Demon strate approp riate coping behavi ors. Maintai ned normal /stable Vital signs Experi enced free
and pacing of activities. Encouraged adequate rest periods between activities Collaborative: Nebuliz ation as ordered Admini ster hydroc ortison e as ordered .
To limit fatigue.
from cyanos is and other signs of hypoxi a.
> To decreased secretions and allow ease from maximal inspiration
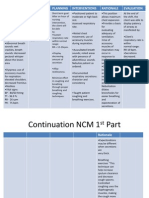
Assessment Subjective Data: medyo nahihirapan akong huminga Objective data: Looks pale Restlessnes s Fatigue Use accessory muscles when breathing (+) wheezes With productive cough On high back rest Profound breathing pattern Vital signs: T-36 P-78 R28 BP100/60mmHg
Nursing diagnosis Ineffective breathing pattern related to bronchospasm 2 BAiAE
Planning Short term: After 3-4 hrs of effective nursing intervention the patient will established a normal-effective respiratory pattern AEB: (-) Restlessness (-)fatigue (-)Use accessory muscles when breathing With productive cough On moderate high back rest Regular breathing pattern Vital signs: T-36 P-78 R-22-24 BP-100/60mmHg Long term: During the whole duration of hospitalization the patient can/will: Verbalize awareness of
Nursing Intervention Establish rapport to patient and SO. Auscultate chest, noting presence/character of breath sounds, presence of secretions. Note rate and depth of respirations Review Laboratory data. Administer O2 indicated for underlying pulmonary condition Elevate HOB as appropriate. Maintain a calm attitude while dealing with client and SO. Assist client in the use of relaxation technique. Assist and demonstrate deep breathing and coughing exercise. Encourage position of comfort. Reposition every 2 hrs. . Health teachings: Review etiology and possible coping behaviors
Evaluation Short term: Goal met as evidenced by: (-) Restlessness (-)fatigue (-)Use accessory muscles when breathing With productive cough On moderate high back rest Regular breathing pattern Vital signs: T-36 P-78 R-23 BP-100/60mmHg Long term Goal met as evidenced by: able to Verbalize awareness of causative factors. Initiate needed lifestyle changes Demonstrate appropriate coping
causative factors. Initiate needed lifestyle changes Demonstrate appropriate coping behaviors. Maintained normal/stable Vital signs Experienced free from signs of hypoxia.
Teach conscious control of RR as appropriate. Recommend energy conservation techniques and pacing of activities. Encouraged adequate rest periods between activities Collaborative: Nebulization as ordered Administer hydrocortisone as ordered.
behaviors. Maintained normal/stable Vital signs Experienced free from cyanosis and other signs of hypoxia.
You might also like
- Service Manual US-S 10... SF 29-2 PDFDocument63 pagesService Manual US-S 10... SF 29-2 PDFpham quang vinh50% (2)
- Мотивационное письмо образецDocument4 pagesМотивационное письмо образецOncampus - ваш гид по образованию за рубежом75% (4)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pages1 Ineffective Breathing PatternKrisJane Ratilla Abiva100% (2)
- 6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pages6 Pleural Effusion Nursing Care PlansShaina Fe RabaneraNo ratings yet
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 pagesNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNcp-Ineffective Breathing PatternRoxanne Ganayo Claver100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 pageImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215No ratings yet
- NCP - CapDocument4 pagesNCP - CapSherryNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Impaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange R/T Ventilation-Perfusion Imbalance Care PlanCristina Centurion100% (10)
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeNedeve Ozned100% (5)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- Risk For InjuryDocument5 pagesRisk For InjuryAllene PaderangaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Difficulty of BreathingDocument2 pagesNCP - Difficulty of BreathingTarquin Tomada33% (3)
- NCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNCP For Ineffective Airway ClearanceJennelyn BayleNo ratings yet
- NCP Rds 2Document1 pageNCP Rds 2Angelokeizer Gavino0% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- NCP IcuDocument2 pagesNCP Icujennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Lung Impairment PNEUMOTHORAXMa. Elaine Carla Tating0% (2)
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobTata Wendz100% (1)
- NCP N SOPIEDocument9 pagesNCP N SOPIEDonna DavidNo ratings yet
- Asthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageAsthma Risk For Activity IntoleranceWdy Tanakht Sparrow100% (4)
- Acutepain PneumoniaDocument3 pagesAcutepain PneumoniaJoy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Alvarez - Impaired Gas ExchangeNader AbdurasadNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternChristianmel JavierNo ratings yet
- Final NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 pagesFinal NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceHazel EndayaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Disturbed SleepDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleepmawel100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionTrixie Anne GamotinNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute PainDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - Acute PainLei Ortega100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanatio Nofthe Problem Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- NCP - AnxietyDocument1 pageNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Casilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Document3 pagesCasilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Ynalie Casilan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP Baby DDocument3 pagesNCP Baby DYna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument6 pagesNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeNo ratings yet
- NCP AlteredDocument3 pagesNCP AlteredShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP LocDocument2 pagesNCP LocMel RodolfoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchangejanelee2824No ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen RegalaNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Ventilation AssistanceDocument3 pagesSubjective: Ventilation AssistanceJobelle Acena100% (2)
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocument3 pagesAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocument3 pagesNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToFrudz Orjaleza100% (2)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP Sleep DisturbanceDocument1 pageNCP Sleep DisturbanceIsrael Soria EsperoNo ratings yet
- C P P P P P P PP PP PP: Up Up UpDocument4 pagesC P P P P P P PP PP PP: Up Up UpValerie BaracaoNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentEjoy Rayos AdawagNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Course in The Ward (Intraoperative Phase)Document1 pageCourse in The Ward (Intraoperative Phase)ruguNo ratings yet
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument1 pageAdvantages and Disadvantagesrugu100% (1)
- Basic Water Rescue and Survival TrainingDocument3 pagesBasic Water Rescue and Survival Trainingrugu100% (1)
- Another Look at Roles and Functions: Has Hospital Case Management Lost Its Way?Document9 pagesAnother Look at Roles and Functions: Has Hospital Case Management Lost Its Way?ruguNo ratings yet
- DM Self AssessmentDocument6 pagesDM Self AssessmentruguNo ratings yet
- Niyog NiyoganDocument2 pagesNiyog NiyoganruguNo ratings yet
- Community Based With Chronic DseDocument9 pagesCommunity Based With Chronic DseruguNo ratings yet
- What Is AmpalayaDocument5 pagesWhat Is Ampalayarugu0% (1)
- Ebola Virus Disease: Key FactsDocument3 pagesEbola Virus Disease: Key FactsruguNo ratings yet
- Brief Summary of Peptic UlcersDocument3 pagesBrief Summary of Peptic UlcersruguNo ratings yet
- Call For Application Brazil Scholarships Program PAEC OAS GCUB 2022Document12 pagesCall For Application Brazil Scholarships Program PAEC OAS GCUB 2022Jolinx JeanNo ratings yet
- SEIPS 101 and Seven Simple SIEPS ToolDocument10 pagesSEIPS 101 and Seven Simple SIEPS Toolpaulofrosh27No ratings yet
- Preparation No. "16" "Aromatic Elixir" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsDocument5 pagesPreparation No. "16" "Aromatic Elixir" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsMEDELYN KEITH ESTANISLAONo ratings yet
- Info For AVECandidates Oct 2023Document48 pagesInfo For AVECandidates Oct 2023rainbowgraphics102No ratings yet
- Grief After Suicide - Transition Survivors From Why To What's NextDocument35 pagesGrief After Suicide - Transition Survivors From Why To What's NextAlguémNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics L6Document89 pagesPharmacokinetics L6Indira ButkoonNo ratings yet
- Manual Maxigas Multi LingualDocument480 pagesManual Maxigas Multi LingualRobert ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Kerala Panchayat Raj (Burial and Burning Grounds) Rules, 1998Document7 pagesKerala Panchayat Raj (Burial and Burning Grounds) Rules, 1998Nithin GNo ratings yet
- 7 Assessment For Development and LearningDocument38 pages7 Assessment For Development and LearningRenie FedericoNo ratings yet
- M2 - Digital CitizenshipDocument21 pagesM2 - Digital CitizenshipMuhammad Agym ArwandarosanzaNo ratings yet
- SAQ Short Form 2006Document1 pageSAQ Short Form 2006Hanan DaghashNo ratings yet
- Management of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis Through Ayurveda - A Case StudyDocument8 pagesManagement of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis Through Ayurveda - A Case Studydr amitNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument91 pagesCleft Lip and PalatedrgreeshmahariniNo ratings yet
- 17 Normal PuerperiumDocument12 pages17 Normal PuerperiumAhmed TarigNo ratings yet
- HardgainerDocument13 pagesHardgainerAnthony Pilipauskas100% (3)
- Endo Nutrient Pad SetsDocument1 pageEndo Nutrient Pad SetsLorena LópezNo ratings yet
- Project Inception Report: Adaptation Fund BoardDocument32 pagesProject Inception Report: Adaptation Fund BoardSunil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Fipronil Plus C SDS 3-12-19Document5 pagesFipronil Plus C SDS 3-12-19jpinternational81No ratings yet
- Ielts Mock 2Document21 pagesIelts Mock 2Azimov ShoxruxNo ratings yet
- Format Disability CertificateDocument6 pagesFormat Disability CertificateSachin Khandare0% (1)
- Soyamilk Class 12 ProjectDocument29 pagesSoyamilk Class 12 ProjectPrithvi BhushanNo ratings yet
- (SOP) TB Preventive Treatment - 3HR RegimenDocument27 pages(SOP) TB Preventive Treatment - 3HR RegimenJohnPhilipTiongcoNo ratings yet
- FORENSIC - Term 2 - MS'3 '26 (2023-10-02)Document51 pagesFORENSIC - Term 2 - MS'3 '26 (2023-10-02)Wajiha MughalNo ratings yet
- ADHD Handbook Revision September 20201Document37 pagesADHD Handbook Revision September 20201mason.sadeghiNo ratings yet
- Zeva 1 - MSDSDocument6 pagesZeva 1 - MSDSRowi ArifudinNo ratings yet
- Immediate and Short Term Effects of Short And.99146 PDFDocument6 pagesImmediate and Short Term Effects of Short And.99146 PDFAndy CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Superbugs 1Document7 pagesSuperbugs 1api-268405956No ratings yet
- Philippine Society of Medical Oncology (PSMO) Consensus Recommendations For Breast CancerDocument30 pagesPhilippine Society of Medical Oncology (PSMO) Consensus Recommendations For Breast Cancertiburciamd27No ratings yet