0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
382 viewsPopulation Distribution Density
Population Distribution Density
Uploaded by
api-261914272Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Population Distribution Density
Population Distribution Density
Uploaded by
api-2619142720 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
382 views7 pagesOriginal Title
population distribution density
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
382 views7 pagesPopulation Distribution Density
Population Distribution Density
Uploaded by
api-261914272Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
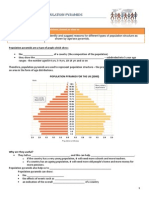
IGCSE GEOGRAPHY
Population Dynamics: Population Density & Distribution
POPULATION & SETTLEMENT Candidates should be able to:
Population Dynamics Describe the factors influencing the density and distribution of population and
population migration.
Population distribution means the pattern of where people live. World population distribution is uneven.
Places which are __________ populated
contain few people. Places which are
____________ populated contain many
people.
Sparsely populated places tend to be
difficult places to live. These are usually
places with ______environments e.g.
Antarctica. Places which are densely
populated are ________ environments
e.g. Europe.
Population distribution is usually shown
by a _______ map.
Population density is a measurement of the ________________________. It is an ____________ number.
Population density is calculated _________
___________________________________
Population density is usually shown as the
__________________________________.
Kenya = 47 people/km
2
Singapore = 6389 people/km
2
Shown by a _____________________ map
darker = more dense population
lighter = less dense population
Places with a high concentration of people = densely populated.
Places with a low concentration of people = sparsely
populated.
ECONOMIC
Ports and good infrastructure (railways, roads,
airports) e.g. Sydney
CLIMATE
evenly distributed rainfall, no extreme temperatures
e.g. North West Europe
NATURAL ROUTES
confluence of rivers, gaps through mountains e.g.
Rhine Valley
VEGETATION
forest (e.g. Amazon)
POLITICAL
lack of government investment, depopulation of
rural and old industrial areas, loss of land through
deforestation and soil erosion
SOCIAL
better housing opportunities e.g. Arizona,
education, health facilities e.g. Milan, good
entertainment, retirement areas e.g. Spanish Coasts
FACTORS
CLIMATE
Extremely high or low temperatures, high humidity,
unreliable rainfall (e.g. Sahara desert)
RELIEF
high, rugged mountains (e.g. Andes)
NATURAL RESOURCES
lacking in minerals, fossil fuels e.g. Ethiopia
SOIL
Thin soils in mountainous areas (e.g. Northern
Scandinavia)
soils lacking in humus (e.g. Sahel) or affected by
leaching (e.g. Rainforests)
WATER SUPPLY
unreliable sources e.g. Afghanistan
ECONOMIC
limited facilities and poor transport links e.g. Sudan
NATURAL ROUTES
mountain barriers e.g. Himalayas
POLITICAL
Government investment, new towns, reclamation of
land
RELIEF
Flat plain and low lying areas (e.g Bangladesh),
broad river valleys (e.g. Ganges)
SOCIAL
Poor housing opportunities, little entertainment,
poor facilities for retirement
NATURAL RESOURCES
minerals, fossil fuels or other energy sources e.g.
Rhone Valley
SOIL
Deep fertile soils, left by rivers e.g. Nile Valley
Volcanic soils e.g. Etna
VEGETATION
grasslands which are easy to clear and farm (e.g.
Paris Basin)
WATER SUPPLY
Reliable sources e.g. North West Europe
ECONOMIC
Well-developed industrial areas e.g. Rhur
money available for new high tech industries e.g.
California
CLIMATE
Extremely high or low temperatures, high humidity,
unreliable rainfall (e.g. Sahara desert)
CLIMATE
seasonal rainfall for agriculture e.g. Bangladesh
ECONOMIC
Development of tourism e.g. Banff (Canada)
SOCIAL
limited education e.g. Rwanda, fewer health
facilities, poor facilities for retirement
ECONOMIC
lack of development of both industry and tourism,
lack of money for new investments
CLIMATE
Areas with high sunshine or snowfall for tourism e.g.
Nice and the Alps in France
FACTORS AFFECTING POPULATION DISTRIBUTION & DENSITY
DENSELY POPULATED AREAS SPARSELEY POPULATED AREAS
CASE STUDY: POPULATION DISTRIBUTION & DENSITY IN BRAZIL
You might also like
- Drains To Living Streams WORKBOOK Bodkin Park 2022 (003) - 1Document32 pagesDrains To Living Streams WORKBOOK Bodkin Park 2022 (003) - 1sponNo ratings yet
- Flooding in YorkDocument24 pagesFlooding in Yorksuejacksonthree100% (26)
- How To Enroll in Online AdaDocument8 pagesHow To Enroll in Online AdaDhey ZheNo ratings yet
- IB Geography Oceans Case StudiesDocument6 pagesIB Geography Oceans Case StudiesMarc Wierzbitzki0% (1)
- Unit 1 Going Global Revision GuideDocument37 pagesUnit 1 Going Global Revision Guideshahanaz2012100% (1)
- Earthquake Case Studies in A Ledc MedcDocument16 pagesEarthquake Case Studies in A Ledc Medcapi-301535260No ratings yet
- Hot Desert Case Study - Sahara DesertDocument1 pageHot Desert Case Study - Sahara DesertCamilleNo ratings yet
- A Level Geography GlossaryDocument17 pagesA Level Geography Glossarysteve119No ratings yet
- 197glaciation in ScotlandDocument5 pages197glaciation in Scotlandapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Losses in Fittings ReportDocument7 pagesLosses in Fittings ReportAmartya Mitra100% (1)
- Revision Booklet - PopulationDocument26 pagesRevision Booklet - PopulationYIHAN (HANNAH) XU 徐奕涵No ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Worldpopulation DensityDocument53 pages1 Intro To Worldpopulation Densityapi-29631793867% (3)
- Geo IGCSEDocument3 pagesGeo IGCSEZeynep Akı100% (1)
- Geofile Exam Techniques AsDocument4 pagesGeofile Exam Techniques AsreservoirgeogsNo ratings yet
- Geofile Contrasting Contemporary Case StudiesDocument4 pagesGeofile Contrasting Contemporary Case StudiesreservoirgeogsNo ratings yet
- Coastal FieldworkDocument4 pagesCoastal FieldworkebidNo ratings yet
- GEOACTIVE - Large Scale River Basin MGMT ColoradoDocument4 pagesGEOACTIVE - Large Scale River Basin MGMT ColoradoThaddeus NgNo ratings yet
- Field InquiryDocument44 pagesField InquiryLiliana CaughmanNo ratings yet
- Igcse Plate Tectonics 2015Document39 pagesIgcse Plate Tectonics 2015api-261914272100% (3)
- GCSE Rivers River Landforms FormationDocument48 pagesGCSE Rivers River Landforms FormationWill TeeceNo ratings yet
- Drainage BasinsDocument4 pagesDrainage BasinsDannySP10100% (1)
- What Is A Supervolcano?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Supervolcano?api-26229229No ratings yet
- IGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsDocument42 pagesIGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsxerxesNo ratings yet
- India MonsoonDocument4 pagesIndia MonsoonDannySP10No ratings yet
- Chap 04Document26 pagesChap 04api-240900456100% (1)
- Case Study Holderness CoastlineDocument1 pageCase Study Holderness Coastlinebiology111No ratings yet
- Ga251 Fieldwork For Physical Geography - Hydrological Studies - Sept 2001 Series 13 Autumn Issue Unit 251Document4 pagesGa251 Fieldwork For Physical Geography - Hydrological Studies - Sept 2001 Series 13 Autumn Issue Unit 251eeeeeksNo ratings yet
- Case Studies - China's One-Child Policy, Singapore's Dual Policy, and France's Pro-Natalist PolicyDocument3 pagesCase Studies - China's One-Child Policy, Singapore's Dual Policy, and France's Pro-Natalist PolicyAleArevaloCahuas100% (1)
- IGCSE Geography - Worksheet 2.1 PDFDocument1 pageIGCSE Geography - Worksheet 2.1 PDFebidNo ratings yet
- Rice Farming in India IGCSE Geography Case StudyDocument1 pageRice Farming in India IGCSE Geography Case StudyLuc Mvono100% (2)
- Weathering Erosion InteractiveDocument47 pagesWeathering Erosion InteractiveSunny YadavNo ratings yet
- Population PyramidsDocument19 pagesPopulation Pyramidsapi-261914272100% (1)
- IB Geography, Oceans and Their Coastal Margins, Geopolitical, Scramble For The ArcticDocument3 pagesIB Geography, Oceans and Their Coastal Margins, Geopolitical, Scramble For The ArcticHolly OliviaNo ratings yet
- Geofile Rural IssuesDocument4 pagesGeofile Rural IssuesreservoirgeogsNo ratings yet
- Global Hazards Edexcel AS RevisionDocument38 pagesGlobal Hazards Edexcel AS Revisionjoblack91% (11)
- Idoc - Pub New Complete Geography For Cambridge IgcseDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub New Complete Geography For Cambridge IgcseAshley MutangiriNo ratings yet
- GCSE Rivers Revision - The Middle CourseDocument2 pagesGCSE Rivers Revision - The Middle CoursecwnoraniNo ratings yet
- The 3 Gorges DamDocument4 pagesThe 3 Gorges Damapi-361310234No ratings yet
- Tourism Complete Notes AQA Geography GcseDocument5 pagesTourism Complete Notes AQA Geography GcseMisterBlueSky0% (1)
- Theme 1 - Case Study BookletDocument21 pagesTheme 1 - Case Study BookletWarlinghamGeog100% (3)
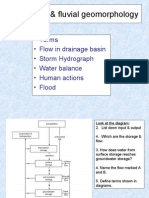
- Hydrology & Fluvial GeomorphologyDocument13 pagesHydrology & Fluvial Geomorphologylyana1234100% (1)
- GA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3Document4 pagesGA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3geoboom12No ratings yet
- Geography GCSE Revision - ALL Case StudiesDocument16 pagesGeography GCSE Revision - ALL Case StudiesAttiya50% (2)
- Geoactive 484 - The Japanese Earthquake and TsunamiDocument4 pagesGeoactive 484 - The Japanese Earthquake and Tsunamiapi-243720682100% (1)
- GEOG Year 12 INDUCTION PACKAGE 2022Document12 pagesGEOG Year 12 INDUCTION PACKAGE 2022Sophia LeiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Template 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Template 2api-366020288100% (1)
- A Case Study of A Youthful Population UgandaDocument3 pagesA Case Study of A Youthful Population Ugandafaryal khanNo ratings yet
- Geo Factsheet: How Do Countries Achieve Optimum Populations?Document3 pagesGeo Factsheet: How Do Countries Achieve Optimum Populations?Neha MishraNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Geo Case Studies (Incomplete)Document7 pagesIGCSE Geo Case Studies (Incomplete)Keyla CahyaNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Aral Sea Shrinking and What Are The EffectsDocument3 pagesWhy Is The Aral Sea Shrinking and What Are The EffectsliamblairNo ratings yet
- The Restless EarthDocument164 pagesThe Restless Earthb_osborneNo ratings yet
- Regenerating Places RevisionDocument19 pagesRegenerating Places Revisionapi-407286530No ratings yet
- Continental Drift Seafloor SpreadingDocument30 pagesContinental Drift Seafloor SpreadingRainier Magno100% (1)
- IgcsecoastsrevisionDocument18 pagesIgcsecoastsrevisionapi-232441790100% (2)
- Hazardous Environments: A Comparison of The Impacts of Tropical Storms, in An LIC and An HICDocument26 pagesHazardous Environments: A Comparison of The Impacts of Tropical Storms, in An LIC and An HICapi-232441790No ratings yet
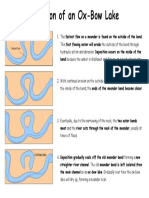
- Ox-Bow Lake Handout 1Document1 pageOx-Bow Lake Handout 1api-336814146No ratings yet
- Coasts Key Word Glossary (1) MDocument5 pagesCoasts Key Word Glossary (1) MRia PatelNo ratings yet
- Geo Textbook Geoactive Chapter 3Document22 pagesGeo Textbook Geoactive Chapter 3_Danda_No ratings yet
- GCE A LEVEL H2 GEOGRAPHY 9730 Physical Geography Lithospheric NotesDocument24 pagesGCE A LEVEL H2 GEOGRAPHY 9730 Physical Geography Lithospheric NotesWong Rong JunNo ratings yet
- Most Dangerous Deserts In The World | Deserts Of The World for Kids | Children's Explore the World BooksFrom EverandMost Dangerous Deserts In The World | Deserts Of The World for Kids | Children's Explore the World BooksNo ratings yet
- Ultimo Examen de HistoriaaaaDocument8 pagesUltimo Examen de Historiaaaalois.tb.2028No ratings yet
- Population Pt1 - Population and Population DensityDocument5 pagesPopulation Pt1 - Population and Population Densityk4mpsjn6hkNo ratings yet
- Igcse Agricultural Systems 2015Document37 pagesIgcse Agricultural Systems 2015api-261914272100% (1)
- Weather IgcseDocument23 pagesWeather Igcseapi-261914272100% (2)
- Contract Law QuestionsDocument8 pagesContract Law Questionsapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Igcse Plate Tectonics 2015Document39 pagesIgcse Plate Tectonics 2015api-261914272100% (3)
- Cold PPQ BookletDocument10 pagesCold PPQ Bookletapi-261914272No ratings yet
- As Essay StructureDocument1 pageAs Essay Structureapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Exam Question AdviceDocument3 pagesExam Question Adviceapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Short Structured Exam Question Keywords AdviceDocument4 pagesShort Structured Exam Question Keywords Adviceapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Salt Crystal GrowthDocument3 pagesSalt Crystal Growthapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Hydration and Oxidation Slide ShowDocument3 pagesHydration and Oxidation Slide Showapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Usgs LandslidesDocument4 pagesUsgs Landslidesapi-261914272100% (1)
- Smart V Hma 1975 JC 30Document5 pagesSmart V Hma 1975 JC 30api-261914272No ratings yet
- Studying Law at UniveristyDocument5 pagesStudying Law at Univeristyapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Global Issues Exemplar Essay QuestionsDocument8 pagesGlobal Issues Exemplar Essay Questionsapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Physical Exemplar Essay Questions UpdatedDocument6 pagesPhysical Exemplar Essay Questions Updatedapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument3 pagesLatitude and Longitudeapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Gce Geography h083 h483 Ms Jan 10Document85 pagesGce Geography h083 h483 Ms Jan 10api-261914272No ratings yet
- Coasts Past Paper QuestionsDocument6 pagesCoasts Past Paper Questionsapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Global Issues Data Response Questions AdviceDocument9 pagesGlobal Issues Data Response Questions Adviceapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Population Distribution DensityDocument31 pagesPopulation Distribution Densityapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Coasts Revision BookDocument31 pagesCoasts Revision Bookapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Igcse Migration and Gcse MigrationDocument11 pagesIgcse Migration and Gcse Migrationapi-261914272100% (2)
- Design For Longevity - A Framework To Support TheDocument10 pagesDesign For Longevity - A Framework To Support TheChetna Shetty DikkarNo ratings yet
- 2 - A Truck and Drones Model For Lastmile Delivery A Mathematical ModelDocument29 pages2 - A Truck and Drones Model For Lastmile Delivery A Mathematical ModelAndres Vega ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Quantile Regression: 40 Years On: Annual Review of EconomicsDocument24 pagesQuantile Regression: 40 Years On: Annual Review of EconomicsSrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Mysteries Story PDFDocument96 pagesMysteries Story PDFRamya SathishkumarNo ratings yet
- NEW Business Plan (Boutique)Document30 pagesNEW Business Plan (Boutique)shurahbeel75% (4)
- Chapter 6 (On Geometric Designs)Document67 pagesChapter 6 (On Geometric Designs)Joshua SumillaNo ratings yet
- The Halliburton Employment Application FormDocument4 pagesThe Halliburton Employment Application FormNur SyahimaNo ratings yet
- Java Lab InheritanceDocument6 pagesJava Lab InheritanceSantanuSarkar100% (1)
- Makita Table SawDocument4 pagesMakita Table SawIka Novianty MANo ratings yet
- Fact To Fiction - The Last Children by Gudrun PausewangDocument1 pageFact To Fiction - The Last Children by Gudrun PausewangSam MunshiNo ratings yet
- TV Ads 2013Document505 pagesTV Ads 2013Pcnhs Sal100% (1)
- Nikon Pricelist February 2009Document7 pagesNikon Pricelist February 2009longzhengNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS (Code No. 030) : RationaleDocument8 pagesECONOMICS (Code No. 030) : RationaleAshish GangwalNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing and Wireless Communications - Short Tutorial and R&D TrendsDocument36 pagesMobile Computing and Wireless Communications - Short Tutorial and R&D TrendskanjankanjanNo ratings yet
- Advent of EuropeansDocument26 pagesAdvent of EuropeansChandan TenduNo ratings yet
- Frantinco E Catalog Vinyl FlooringDocument30 pagesFrantinco E Catalog Vinyl Flooringdan diNo ratings yet
- Safety Rules For The Construction and Installation of Escalators and Passenger ConveyorsDocument64 pagesSafety Rules For The Construction and Installation of Escalators and Passenger ConveyorsLina NimriNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Model by Michael PorterDocument6 pagesFive Forces Model by Michael Portergreeshmaprakashv100% (1)
- BQ Plumbing N FittingDocument22 pagesBQ Plumbing N FittingMohd HafizNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Swing DancingDocument3 pagesA Brief History of Swing DancingKrisha loraine GapacNo ratings yet
- MOS - Plumbing and Sanitary Services Rev. 2Document4 pagesMOS - Plumbing and Sanitary Services Rev. 2KAKANo ratings yet
- 1982 Corresp Adj DAFFE-CFA-WP1 (82) 2EDocument4 pages1982 Corresp Adj DAFFE-CFA-WP1 (82) 2EHoracio VianaNo ratings yet
- Gestalt Principles For Data VisualizationDocument10 pagesGestalt Principles For Data Visualizationrehaank816No ratings yet
- 2016CompositeList Web 20Document1 page2016CompositeList Web 20AnuranjanNo ratings yet
- Quantum CryptographyDocument20 pagesQuantum CryptographyBridget Smith100% (1)
- Sustainable Development PDFDocument21 pagesSustainable Development PDFMariane Joyce MianoNo ratings yet
- Dina Food ProcessingDocument3 pagesDina Food ProcessingMeklit WorkuNo ratings yet
- Reteach 4Document97 pagesReteach 4Spring BballNo ratings yet