Gear2 02a
Gear2 02a
Uploaded by
Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςCopyright:
Available Formats
Gear2 02a
Gear2 02a
Uploaded by
Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Gear2 02a
Gear2 02a
Uploaded by
Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςCopyright:
Available Formats
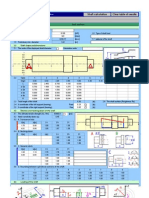
Bevel gearing
with straight,
and curved
teeth [mm/DIN]
Bevel gearing
with straight,
obliqueoblique
and curved
teeth [mm/DIN]
i
ii
Pinion
Check lines:11.7;
Project information
Gear
Author
Date
Project No.
John Doe
3/11/2014
111-111
File name
Gear2_02.xls
Project Name
Bevel Gear
Basic Info
Bevel gearing: Beta=23,31; mmn=12; b=130; z1=21; z2=52; n1=1000; n2=403,8; i=2,48; P=50 [kW]
Project Notes
Comments
?
1.0
Input section
Options of basic input parameters
1.1 Transferred power
Pw [kW]
50,000
49,325
1.2 Speed (Pinion / Gear)
n [/min]
1000,0
403,8
[/min]
1.3 Torsional moment (Pinion / Gear)
Mk [Nm]
477,50
1166,41
[Nm]
1.4 Transmission ratio / from table
2,48
1.5 Actual transmission ratio / deviation
2,4762
2.0
0,00%
Options of material, loading conditions, operational and production parameters
DIN
2.0 Material identification according standard :
2.1 Material of the pinion : A...Carbon structural steel Ck 60 (Rm=740 MPa) heat treated
2.2 Material of the gear :
A...Carbon structural steel Ck 60 (Rm=660 MPa) normalized
2.3 Loading of the gearbox, driving machine - examples
A...Continuous
2.4 Loading of gearbox, driven machine - examples
A...Continuous
2.5 Type of gearing mounting
A...Overhung both wheels - type 1
2.6 Accuracy grade - DIN3965 / ISO1328 |Ra max|v max
6 / 7....(Ra max.= 1,6 / v max.= 12)
2.7 Coefficient of one-off overloading
KAS
2,8 Desired service life
2.9 Coefficient of safety (contact/bend)
[h]
1,30
1,60
B. Helical gearing
Parameters of the tooth profile, gearing type
3.1 Guiding curve of the toothing (Type of toothing)
A,B. Straight line, type I (Standard straight and oblique toothing)
3.2 Addendum - Coefficient of the height of the tooth head
3.3 Unit head clearance
ha*
1,000
1,000
[modul]
c*
0,200
0,200
[modul]
0,293
0,293
[modul]
0,293
0,293
[modul]
3.4 Recommended coefficient of the root radius
3.5 Coefficient of the root radius
4.0
20000
SH / SF
2.10 Automatic design
3.0
2,00
Lh
rf*
Design of a module (Diametral Pitch) and geometry of toothing
4.1 Number of teeth Pinion / Gear
21
4.2 Angle of shaft axes
S
a
90
Transverseangle
pressure angle
4.3 A.Pressure
4.4 Base helix angle
bm
4.5 Direction of the teeth pitch (pinion)
52
90
[]
20,0
20,0
[]
23,3
25
[]
Left-Hand
4.6 Width of toothing to the surface straight line of the cone (b/Re)
4.7 Width of toothing to the surface straight line of the cone (b/Re)
4.8
B. Normal module (mean)
Module
4.9 Face width / max. recommendet value
4.10 Approximate weight of the gearing
4.11 Minimum coefficient of safety
Re/b
0,35
mmn
12,000
[mm]
130
m
SH / SF
< 0.35
< 151
256,085
1,877
300
200
100
16,984
[mm]
[kg]
-500
-400
-300
-200
-100
100
200
300
400
-100
-200
-300
5.0
Correction of toothing (Addendum modification)
5.1 Correction type
E. Curved teeth
5.2 Recommendet value
x1 / xt1
0,000
0,000
5.3 - Permissible undercutting of teeth (min. value)
x1 / x2
-0,6360
-8,1756
5.4 - Preventing undercutting of teeth (min. value)
x1 / x2
-0,4693
-8,0090
x1 / x2
xt1 / xt2
-0,3000
-0,0300
0,3000
0,0300
5.5 Pinion addendum modification coefficient setting
5.6 Addendum modification coefficient Pinion / Gear
5.7 Tooth thicknes modification coefficient
eg
5.8 Total contact ratio
2,9531
5.9 Unit tooth thickness on the tip diameter
sae*
0,7512
1,4340
5.10 Safety coefficient for surface durability
5.11 Safety coefficient for bending durability
SH
SF
2,130
16,98
1,877
18,94
21
52
Results section
6.0
Basic dimensions of gearing
6.1 Number of teeth Pinion / Gear
6.2 Transverse module (outer, midle, inner)
6.3 Normal module (outer, midle, inner)
6.4 Cone length (outer, midle, inner)
z
met,mmt,mit
15,3846
13,0665
10,7484
[mm]
men,mmn,min
14,1289
12,0000
9,8711
[mm]
Re,Rm,Ri
431,387
366,387
301,387
[mm]
d
da
df
21,9911
68,0089
[]
23,4212
70,6633
[]
18,9290
66,1705
[]
6.8 Tip diameter (outer)
dae
343,049
814,979
[mm]
6.9 Tip diameter (midle)
dam
291,359
692,181
[mm]
6.10 Tip diameter (inner)
dai
239,670
569,383
[mm]
6.11 Pitch diameter (outer)
de
323,077
800,001
[mm]
6.12 Pitch diameter (midle)
dm
274,397
679,459
[mm]
6.13 Pitch diameter (inner)
di
225,717
558,918
[mm]
6.14 Root diameter (outer)
dfe
280,281
789,631
[mm]
6.15 Root diameter (midle)
dfm
238,050
670,652
[mm]
6.16 Root diameter (inner)
dfi
qa
195,818
551,673
[mm]
1,4300
2,6545
[]
6.5 Pitch cone angle
6.6 Addendum cone angle
6.7 Dedendum cone angle
6.17 Addendum angle
qf
3,0621
1,8384
[]
hae
10,7692
20,0000
[mm]
6.20 Addendum (midle)
ha
9,1466
16,9865
[mm]
6.21 Addendum (inner)
hai
7,5239
13,9729
[mm]
6.22 Dedendum (outer)
hfe
23,0769
13,8462
[mm]
6.23 Dedendum (midle)
hf
19,5998
11,7599
[mm]
6.24 Dedendum (inner)
hfi
16,1226
9,6736
[mm]
6.18 Dedendum angle
6.19 Addendum (outer)
500
6.25 Normal pressure angle
6.26 Transverse pressure angle
6.27 Helix angle
6.28 Base helix angle
6.29 Pressure angle at the pitch cylinder
6.30 Transverse pressure angle at the pitch cylinder
6.31 Circular pitch
an
at
b
bb
awn
awt
18,4828
[]
20,0000
[]
23,31
[]
22,0425
[]
18,4828
[]
20,0000
[]
pe
44,387
[mm]
6.32 Transverse circular pitch
pte
48,332
[mm]
6.33 Tooth thickness on the pitch diameter
sne
18,6843
25,7030
[mm]
6.34 Tooth thickness on the pitch diameter
sn
15,8690
21,8301
[mm]
6.35 Tooth thickness on the pitch diameter
sni
13,0537
17,9573
[mm]
6.36 Tooth thickness on the tip diameter
sae
10,6136
20,2613
[mm]
6.37 Tooth thickness on the tip diameter
sa
9,0144
17,2084
[mm]
6.38 Tooth thickness on the tip diameter
6.39 Unit tooth thickness on the tip diameter
7.0
sai
7,4152
14,1555
[mm]
sae*
0,7512
1,4340
[modul]
zvn'
22,648
138,866
Virtual spur gear toothing
7.1 Number of teeth of a virtual wheel with oblique teeth
7.2 Number of teeth of a virtual wheel with straight teeth
zv
29,239
179,280
dv'
295,928
1814,490
[mm]
7.4 Tip diameter
dva'
314,221
1848,462
[mm]
7.5 Base diameter
dvb'
278,082
1705,062
[mm]
7.6 Root diameter
dvf'
256,729
1790,970
[mm]
7.3 Reference diameter
7.7 Virtual center distance
av
1055,2089
7.8 Virtual Gear Ratio
iv
6,1315
8.0
Qualitative indexes of a gearing
8.1 Transverse contact ratio / overlap ratio
8.2 Total contact ratio
8.3 Resonance speed
e a | eb
eg
1,7933
1,1599
2,9531
nE1
4044,79
[ /min]
8.4 Resonance ratio
0,25
8.5 Approximate weight of the gearing
256,0848
8.6 Efficiency of the gearing
98,65%
8.7 Selected / Recomended lubricant viscosity
9.0
[mm]
v50
50
[kg]
50
[mm2/sec]
Coefficients for safety calculation
Common for the gearing
9.1 Stiffness of a tooth pair
c'
10,56
9.2 Meshing stiffness per unit face width
cg
16,85
9.4 Application factor
KA
1,000
9.5 Dynamic factor
KV
1,457
9.6 Number of cycles
NK
1,20E+09
4,85E+08
For pitting safety calculation
9.7 Face load factor (contact stress)
KHb
1,500
9.8 Transverse load factor (contact stress)
KHa
2,087
KH
4,562
9.10 Elasticity factor
ZE
189,81
9.11 Zone factor
ZH
2,402
Zbeta
0,958
9.9 Total factor of additional loads
9.12 Helix angle factor
9.13 Contact ratio factor
Zeps
0,747
9.14 Size factor
ZX
1,000
1,000
9.15 Lubricant factor
ZL
0,916
0,916
9.16 Peripheral speed factor
ZV
1,022
1,022
9.17 Roughness factor affecting surface durability
ZR
0,945
0,945
Automatic
n=; ZN=0.85
9.18 Bevel gear factor (flank)
ZK
9.19 Life factor for contact stress
ZN
0,850
0,850
ZB / ZD
1,000
1,000
9.20 Single pair tooth contact factor
Mineral oil
0,850
For bending safety calculation
9.21 Face load factor (root stress)
KFb
1,500
9.22 Transverse load factor (root stress)
KFa
2,087
9.23 Total factor of additional loads
9.24 Helix angle factor
9.25 Contact ratio factor
9.26 Notch sensitivity factor
KF
4,562
Ybeta
0,806
Yeps
0,625
Ydelta
0,994
1,016
9.27 Size factor
YX
0,958
0,958
9.28 Tooth-root surface factor
YR
1,003
1,003
9.29 Alternating load factor
YA
1,000
9.30 Production technology factor
YT
1,000
9.31 Life factor for bending stress
YN
0,850
0,850
YFS
4,212
3,502
SH
2,13
1,88
18,94
9.32 Tip factor, equal (YFa YSa)
10.0
Safety coefficients
10.1 Safety coefficient for surface durability
10.2 Safety coefficient for bending durability
SF
16,98
10.3 Safety in contact in one-time overloading
SHst
2,90
2,47
10.4 Safety in bending in one-time overloading
SFst
25,07
27,35
10.5 Nominal contact stress
SigmaH0
10.6 Contact stress
97,56
SigmaH
208,39
208,39
10.7 Pitting stress limit
SigmaHG
443,80
391,15
10.8 Permissible contact stress
SigmaHP
341,38
300,88
10.9 Nominal tooth-root stress
SigmaF0
4,73
3,93
10.10 Tooth-root stress
SigmaF
21,59
17,95
10.11 Tooth-root stress limit
SigmaFG
366,68
340,05
10.12 Permissible bending stress
SigmaFP
229,17
212,53
11.0
n=; YN=0.85
Force conditions (forces acting on the toothing)
11.1 Tangential force
Ft
3480,36
[N]
11.2 Normal force
Fn
3995,79
[N]
11.3 Axial force - (rotation acc. to the picture)
Fa
1864,84
613,04
11.4 Radial force (rotation acc. to the picture)
Fr
613,04
1864,84
11.5 Axial force (rotation opposite to the picture)
Fa
-916,14
1736,13
Fr
11.6 Radial force (rotation opposite to the picture)
[N]
[N]
1736,13
-916,14
11.7 Peripheral speed on the pitch diameter
v | vmax
14,37
< 12
[m/s]
11.8 Specific load / Unit load
wt | wt*
31,50
2,62
[N/mm | MPa]
Ro
7870
7870
[kg/m^3]
206
206
[GPa]
Rm
740
660
[MPa]
Rp0.2
440
380
[MPa]
0,3
0,3
12.0
Parameters of the chosen material
12.1 Density
12.2 Young's Modulus (Modulus of Elasticity)
12.3 Tensile Strength, Ultimate
12.4 Tensile Strength, Yield
12.5 Poison's Ratio
12.6 Contact Fatigue Limit
SHlim
590
520
[MPa]
12.7 Bending Fatigue Limit
SFlim
452
410
[MPa]
12.8 Tooth Hardness - Side
VHV
235
200
[HV]
235
200
[HV]
5,00E+07
5,00E+07
12.9 Tooth Hardness - Core
JHV
12.10 Base Number of Load Cycles in Contact
NHlim
12.11 Wohler Curve Exponent for Contact
qH
12.12 Base Number of Load Cycles in Bend
NFlim
12.13 Wohler Curve Exponent for Bend
qF
Additions section
10
10
3,00E+06
3,00E+06
13.0
Power, warming-up, gearbox surface
13.1 Ambient air temperature
20,00
[C]
13.2 Maximum oil temperature
60,00
[C]
13.3 Coefficient of heat dissipation
10,00
[W/m2/K]
13.4 Power losses
0,68
[kW]
13.5 Gearbox surface (min.)
1,69
[m2]
14.0
Preliminary design of shaft diameters (steel)
Recommended shaft diameter for:
14.1
- Main power-transmitting shafts
DA
95,57
128,68
[mm]
14.2
- Small, short shafts
DB
74,27
99,99
[mm]
15.0
Auxiliary calculations
15.1 Transmission ratio calculation using the number of teeth
z1,z2 = i
21
52
= 2,4762
15.2 Transmission ratio calculation using the speed
n1,n2 = i
2000,0
750,0
= 2,6667
Mk1,n1=Pw1
270,0
1600,0
= 45,2356
15.3 Power calculation using the pinion speed and torque moment
16.0
Graphical output, CAD systems
16.1 2D drawing output to:
DXF File
16.2 2D Drawing scale
Automatic
16.3 Detail:
Gear
You might also like
- Flame Test & Spectroscopy Virtual LabDocument4 pagesFlame Test & Spectroscopy Virtual LabFilip Salek50% (2)
- Final Pot Ptfe Design Sheet - 02.01.13Document47 pagesFinal Pot Ptfe Design Sheet - 02.01.13Sandeep Kumar75% (4)
- This Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The CalculationDocument7 pagesThis Kisssoft Demoversion May Not Be Used For Professional Application ! Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The Calculationpablo_stzNo ratings yet
- Gear4 02Document101 pagesGear4 02pratapslairNo ratings yet
- CX1Document7 pagesCX1acceleron8No ratings yet
- Gear Pair 1 GearDocument2 pagesGear Pair 1 GearYunji GuNo ratings yet
- Spur Gearing, Helical Gearing (mm/ISO)Document6 pagesSpur Gearing, Helical Gearing (mm/ISO)oman1148No ratings yet
- KissoftDocument7 pagesKissoftGopi Krishnan VNo ratings yet
- Bevel-Gear-Calculation (Bevel-Gear-Pair) : 1. Tooth Geometry and MaterialDocument1 pageBevel-Gear-Calculation (Bevel-Gear-Pair) : 1. Tooth Geometry and MaterialPIRATASANTANANo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation ShaftDocument115 pagesDesign and Calculation ShaftDavid Lambert100% (3)
- Teague's ShaftDocument145 pagesTeague's ShaftBUDAPESNo ratings yet
- Corner Cast in Place AnchorDocument7 pagesCorner Cast in Place Anchorwaweng22No ratings yet
- Thong So Banh RangDocument7 pagesThong So Banh RangVũ Trường LamNo ratings yet
- Sugar Beet Conveyor Belt Gear Box-Pinion-11kwDocument4 pagesSugar Beet Conveyor Belt Gear Box-Pinion-11kwShabanali OmraniNo ratings yet
- Calculation of A Cylindrical Spur Gear Pair: Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The CalculationDocument10 pagesCalculation of A Cylindrical Spur Gear Pair: Important Hint: at Least One Warning Has Occurred During The CalculationM036No ratings yet
- Calculation of A Helical-Toothed Cylindrical Gear Pair: Changed On 12.11.2024, 14:24:02 Changed by UserDocument14 pagesCalculation of A Helical-Toothed Cylindrical Gear Pair: Changed On 12.11.2024, 14:24:02 Changed by UserdharmeshNo ratings yet
- Program PT AngrenajeDocument7 pagesProgram PT AngrenajeBalla AttilaNo ratings yet
- Ussymetrical Gear Terminology Used in AircraftDocument12 pagesUssymetrical Gear Terminology Used in AircraftilhamNo ratings yet
- Peikko Designer, Printing-20140828Document6 pagesPeikko Designer, Printing-20140828Filipe FeioNo ratings yet
- Typical Hea No Shear LugDocument6 pagesTypical Hea No Shear Lugwaweng22No ratings yet
- M1 5xZ59xX-0 3225x25L-RA-1 5VSWK de enDocument2 pagesM1 5xZ59xX-0 3225x25L-RA-1 5VSWK de enYunji GuNo ratings yet
- Calculation of A Spur-Toothed Cylindrical Gear Pair: Changed On 23.10.2024, 14:06:38 Changed by UserDocument14 pagesCalculation of A Spur-Toothed Cylindrical Gear Pair: Changed On 23.10.2024, 14:06:38 Changed by UserdharmeshNo ratings yet
- Calcule WinchDocument125 pagesCalcule WinchMarian Manea67% (3)
- Calculation of A Helical Gear: 1. Tooth Geometry and MaterialDocument4 pagesCalculation of A Helical Gear: 1. Tooth Geometry and MaterialChetan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gears Component GeneratorDocument5 pagesBevel Gears Component Generatordinhtam13No ratings yet
- Calculo Flecha TerminadoDocument149 pagesCalculo Flecha TerminadoSebastián ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Toyo Rubber CouplingDocument14 pagesToyo Rubber CouplingGreg SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Spur Gears Component GeneratorDocument5 pagesSpur Gears Component Generatormisapera35No ratings yet
- Vertical Vessel Foundation Design Input Parameters: Geometrical DescriptionDocument8 pagesVertical Vessel Foundation Design Input Parameters: Geometrical DescriptionAnonymous xcFcOgMiNo ratings yet
- Página Inicial - MITCalc - CompletaDocument8 pagesPágina Inicial - MITCalc - CompletaDomingos AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Cap PlateDocument18 pagesCap PlateVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Report ShortDocument6 pagesReport Shortvikasanandg6264No ratings yet
- Type of Calculation Date Customer Name Ref: Roller Chain Drives 29/08/2012 07:50:08 ModelDocument6 pagesType of Calculation Date Customer Name Ref: Roller Chain Drives 29/08/2012 07:50:08 Modelgrupa2904No ratings yet
- APPLICATION: Parker 492620: Form Setup Date: 03/29/2000 Calculation Date: 10/2/2012Document8 pagesAPPLICATION: Parker 492620: Form Setup Date: 03/29/2000 Calculation Date: 10/2/2012nicoftaNo ratings yet
- Gear1 - 02Document74 pagesGear1 - 02adnantopalovicNo ratings yet
- Nachi Ballscrew BearingsDocument8 pagesNachi Ballscrew BearingsHakan AdaNo ratings yet
- Calcul Reductor WinchDocument41 pagesCalcul Reductor WinchAndrei TaseNo ratings yet
- Spur Gears Component GenDocument6 pagesSpur Gears Component GendexterisNo ratings yet
- Modulo 6, Angulo Helice 11.25Document4 pagesModulo 6, Angulo Helice 11.25Franklin LopezNo ratings yet
- Helical Gear Calculation Using SoftwareDocument10 pagesHelical Gear Calculation Using SoftwareM036No ratings yet
- Ai Hex HR4 SS - Rev001Document1 pageAi Hex HR4 SS - Rev001Sankalp BhatiyaNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairDocument23 pagesKisssoft Tut 008 E Cylindrical GearpairLuis TestaNo ratings yet
- KISSsoft Calculation Programs For Machine DesignDocument22 pagesKISSsoft Calculation Programs For Machine DesignAbhijeet DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Beam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataDocument33 pagesBeam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataazwanNo ratings yet
- Belleville Washer Example 1Document4 pagesBelleville Washer Example 1Vishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Medidas para Mecanizar Alojamiento Anillo Sello EspejoDocument11 pagesMedidas para Mecanizar Alojamiento Anillo Sello EspejoJhonatan Valencia MillanNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Los DatosDocument15 pagesAnalisis de Los DatosManuel A. Samaniego LaoNo ratings yet
- Assemblage Poteau-Semelle IsoléeDocument9 pagesAssemblage Poteau-Semelle IsoléeFrancklinMeunierM'ondoNo ratings yet
- Proiect Om2Document20 pagesProiect Om2Gabriel CimpeanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Metric Gear Technology - QTC Q410-416, 417Document1 pageElements of Metric Gear Technology - QTC Q410-416, 417Zo StevanovicNo ratings yet
- Gear PresentationDocument35 pagesGear PresentationGaurav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Gearbox Project ReportDocument11 pagesGearbox Project Reportalexpatow50% (2)
- OMDocument16 pagesOMLiviu AndreiNo ratings yet
- PlateDocument3 pagesPlateAdnan RanaNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument29 pagesReportvikasanandg6264No ratings yet
- Beam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataDocument32 pagesBeam Design Detail Report: Material and Design DataazwanNo ratings yet
- O.GB - gp1.gp1: Calculation of A Helical Gear PairDocument102 pagesO.GB - gp1.gp1: Calculation of A Helical Gear PairS.DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandEngineering Vibroacoustic Analysis: Methods and ApplicationsStephen A. HambricNo ratings yet
- Combustion Engines: An Introduction to Their Design, Performance, and SelectionFrom EverandCombustion Engines: An Introduction to Their Design, Performance, and SelectionNo ratings yet
- Mccallum 1989Document8 pagesMccallum 1989Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Fluent Lecture 3 Turbulence ModelingDocument50 pagesFluent Lecture 3 Turbulence ModelingΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Fluent Lecture 2 Boundary ConditionsDocument54 pagesFluent Lecture 2 Boundary ConditionsΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 4Document65 pagesCFD Lecture 4Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 3Document79 pagesCFD Lecture 3Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- CFD Prelab1Document34 pagesCFD Prelab1Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- SpitfireDocument30 pagesSpitfireΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Libble EuDocument240 pagesLibble EuΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- CFD Prelab1 QuestionsDocument1 pageCFD Prelab1 QuestionsΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Three-Dimensional Small-Disturbance Solutions Disturbance SolutionsDocument19 pagesThree-Dimensional Small-Disturbance Solutions Disturbance SolutionsΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Trailing Vortex Wake Encounters at Altitude - A Potential: Flight Safety Issue?Document17 pagesTrailing Vortex Wake Encounters at Altitude - A Potential: Flight Safety Issue?Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- ETC11 2015 Madrid Conf in A NutshellDocument32 pagesETC11 2015 Madrid Conf in A NutshellΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- Part II - The Inviscid Problem - Rev1.1Document31 pagesPart II - The Inviscid Problem - Rev1.1Κυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- 2 MW Product BrochurepdfDocument16 pages2 MW Product BrochurepdfDragan VuckovicNo ratings yet
- Pressure Transducers ComparisonDocument5 pagesPressure Transducers ComparisonΚυριάκος ΒαφειάδηςNo ratings yet
- QBlade GuidelinesDocument48 pagesQBlade GuidelinesΚυριάκος Βαφειάδης100% (1)
- Ns26 1 Connection Design Handout 4perDocument25 pagesNs26 1 Connection Design Handout 4perHectorNo ratings yet
- Dissertation RJM Pijpers September 2011Document294 pagesDissertation RJM Pijpers September 2011MarkoNo ratings yet
- EC9-1,3 - Design of Aluminium Structures - Structures Susceptible To Fatigue PDFDocument100 pagesEC9-1,3 - Design of Aluminium Structures - Structures Susceptible To Fatigue PDFnebojsadj6411No ratings yet
- TOFD For Weld Root Corrosion and ErosionDocument7 pagesTOFD For Weld Root Corrosion and Erosionmarouane abdelmoumen100% (1)
- Relative Equilibrium of LiquidsDocument16 pagesRelative Equilibrium of LiquidsYsabelle TagarumaNo ratings yet
- 31-MBD-127 Inlet Separator-Rev.0 (On Pile)Document53 pages31-MBD-127 Inlet Separator-Rev.0 (On Pile)Didi Hadi RiantoNo ratings yet
- Digital Vacuum Gauge: Owner 'S ManualDocument16 pagesDigital Vacuum Gauge: Owner 'S Manualcarmen hernandezNo ratings yet
- PDF Material Modeling in Finite Element Analysis 1st Edition Z. Yang (Author) downloadDocument81 pagesPDF Material Modeling in Finite Element Analysis 1st Edition Z. Yang (Author) downloadalagebthame28100% (1)
- Effects of On-Line Melt Blending of Polypropylene With Polyamide 6 On The Bulk and Strength of The Resulting BCF YarnDocument10 pagesEffects of On-Line Melt Blending of Polypropylene With Polyamide 6 On The Bulk and Strength of The Resulting BCF YarnianNo ratings yet
- ST Notes16 M-Diagram by Parts 1Document8 pagesST Notes16 M-Diagram by Parts 1John Feil JimenezNo ratings yet
- Reagent Consumption in Cus XDocument4 pagesReagent Consumption in Cus XJeromeNo ratings yet
- Study On Performance Characteristic of Medium Consistency Pump - AMEDocument13 pagesStudy On Performance Characteristic of Medium Consistency Pump - AMELeonardo TerraNo ratings yet
- Floor Deck Profile TS 47/180: Product Data SheetDocument3 pagesFloor Deck Profile TS 47/180: Product Data SheetMohamed Kareem100% (1)
- Fielding Notching and Drilling of Glued Laminated Timber BeamsDocument1 pageFielding Notching and Drilling of Glued Laminated Timber BeamsTimothy CruseNo ratings yet
- WpsDocument2 pagesWpsnaseema1100% (1)
- 1.3532 16NiCrMo16-5Document3 pages1.3532 16NiCrMo16-5RedNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Cbse Science Sample Paper Term 2 2012-13 Model 2Document14 pagesClass 10 Cbse Science Sample Paper Term 2 2012-13 Model 2Sunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- 02 - Machine Dynamics - Lec2 - DC Motor2Document25 pages02 - Machine Dynamics - Lec2 - DC Motor2Ahmed ArfaNo ratings yet
- Stirling EngineDocument18 pagesStirling EngineIntan Vara DibaNo ratings yet
- Selection of NDE MethodsDocument6 pagesSelection of NDE MethodsNABIL HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Tufnol WhaleDocument3 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Tufnol WhaleRay FaiersNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Rate, Both Civil and Mechanical/Electrical With All Corrigendum and Addendum As On 03-Nov-2021Document159 pagesSchedule of Rate, Both Civil and Mechanical/Electrical With All Corrigendum and Addendum As On 03-Nov-2021SK FARIDULNo ratings yet
- Design of RiprapDocument15 pagesDesign of RiprapMalav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Work and Mechanical EnergyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 Work and Mechanical Energyehab maysaraNo ratings yet
- 0.56" Seven-Segment Numeric LED Display: LTS-5x01A/5x03A LTD-5x21A/5x23A Series LTC-5653x-01/5753x-01Document5 pages0.56" Seven-Segment Numeric LED Display: LTS-5x01A/5x03A LTD-5x21A/5x23A Series LTC-5653x-01/5753x-01subairiNo ratings yet
- L13 Acceptance Standards 2018Document4 pagesL13 Acceptance Standards 2018Debendra Dev KhanalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment: (Single Correct Choice Type) Q.1Document3 pagesChemistry Assignment: (Single Correct Choice Type) Q.1Samridh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Poisson's RatioDocument2 pagesPoisson's RatioS.Mohana sundaramNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Background of ESAComp Analyses - PART V - Adhesive Bonded Joints - Bolted JointsDocument57 pagesTheoretical Background of ESAComp Analyses - PART V - Adhesive Bonded Joints - Bolted JointsOliver RailaNo ratings yet