0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsBasic Electronics Engineering
Basic Electronics Engineering
Uploaded by
sushilThe document is an exam paper for a Basic Electronics Engineering course. It contains 7 questions testing students' knowledge of topics like semiconductors, diodes, transistors, amplifiers, power supplies, digital signals, modulation, and oscilloscopes. Students are required to answer all questions in their own words within 3 hours. The questions have varying point values between 5-8 points each for a total of 100 points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Basic Electronics Engineering
Basic Electronics Engineering
Uploaded by
sushil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document is an exam paper for a Basic Electronics Engineering course. It contains 7 questions testing students' knowledge of topics like semiconductors, diodes, transistors, amplifiers, power supplies, digital signals, modulation, and oscilloscopes. Students are required to answer all questions in their own words within 3 hours. The questions have varying point values between 5-8 points each for a total of 100 points.
Original Description:
asss
Original Title
Basic Electronics Engineering (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document is an exam paper for a Basic Electronics Engineering course. It contains 7 questions testing students' knowledge of topics like semiconductors, diodes, transistors, amplifiers, power supplies, digital signals, modulation, and oscilloscopes. Students are required to answer all questions in their own words within 3 hours. The questions have varying point values between 5-8 points each for a total of 100 points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering
Basic Electronics Engineering
Uploaded by
sushilThe document is an exam paper for a Basic Electronics Engineering course. It contains 7 questions testing students' knowledge of topics like semiconductors, diodes, transistors, amplifiers, power supplies, digital signals, modulation, and oscilloscopes. Students are required to answer all questions in their own words within 3 hours. The questions have varying point values between 5-8 points each for a total of 100 points.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
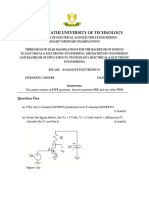
POKHARA UNIVERSITY
Level: Bachelor Semester – Spring Year : 2006
Programme: BE Full Marks: 100
Course: Basic Electronics Engineering Time : 3hrs.
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far
as practicable.
The figures in the margin indicate full marks.
Attempt all the questions.
1. a) Describe intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor in brief. 8
b) With the help of neat and clean curve explain V-I characteristics of p- 7
n junction diode and also discuss the important application of diode.
2. a) How does a semiconductor differ from conductor and insulator? 8
Explain with the help of energy band diagram.
b) Briefly explain the common emitter (CE) transistor input and output 7
characteristics showing the different regions of operation.
3. a) What do you understand by feedback? Explain the advantage of 7
negative feed back in an amplifier.
b) Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave center tap connection and 8
bridge connection. Explain with their working principle.
4. a) Derive the expression for rectification efficiency and ripple factor for 8
full wave rectifier.
b) What is the function of filter in power supply? Explain with help of 7
LC filter.
5. a) State and draw De-Morgans theorem by truth table and explain the 7
advantage of digital signal over analog.
b) Performs the following conversion: 8
i) (781.36)10 = ( ? )2
ii) (2ABD8)16 = ( ?)10
iii) (F5C.2B)16 = ( ?)8
iv) (10110110111)2 = ( ?)16
6. a) Define amplitude Modulation and draw the wave shapes of the 7
message signal, carrier and modulated wave.
b) Why is a CRT considered as a heart of Oscilloscope? Draw and
8
explain the general block diagram of CRO.
7. Write short notes on (Any Two): 5×2
a) OP-AMP
b) RC phase shift oscillator
c) Photo and diffusion current
You might also like
- Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics EngineeringsushilNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics EngineeringsushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics EngineeringAdhikari SushilNo ratings yet
- 2019 December EC100-I - Ktu QbankDocument2 pages2019 December EC100-I - Ktu Qbankvishnucharaanv.et24No ratings yet
- Model QP2 - Ec1001 1Document2 pagesModel QP2 - Ec1001 1vishesh091105No ratings yet
- r05310401 Linear Ic ApplicationsDocument8 pagesr05310401 Linear Ic ApplicationsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Circuits2Document1 pageElectronic Devices Circuits2Shaik BawajanNo ratings yet
- KTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedDocument16 pagesKTU EC205 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (AE, EC) - MAin - Jan - 2017 - Ktu Qbank-MergedsunNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper First/Second Semester B.E. Degree Examination Common To All Branches Basic Electronics Time: 3 Hrs. Max - Marks: 100Document4 pagesModel Question Paper First/Second Semester B.E. Degree Examination Common To All Branches Basic Electronics Time: 3 Hrs. Max - Marks: 100Pramodh RudeboxNo ratings yet
- r05221002 Linear Ic ApplicationsDocument7 pagesr05221002 Linear Ic ApplicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology End Sem 2Document2 pagesNational Institute of Technology End Sem 2Ankit -VNo ratings yet
- SEE QUESTION BANK FinalDocument4 pagesSEE QUESTION BANK Final1nh21ee035No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsRaj GhimireNo ratings yet
- Electronics - IDocument3 pagesElectronics - ISubhadeep RoyNo ratings yet
- 2023 Dec. ECT401-CDocument3 pages2023 Dec. ECT401-Cscoobyab2001No ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: December 2015 Semester End Main ExaminationsrameshNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Applied ElectronicsDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper Applied Electronicssachin barge100% (1)
- EST130 BASICS OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING, DECEMBER 2020Document3 pagesEST130 BASICS OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING, DECEMBER 2020fidropodruNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated Circuits EC S4 B.Tech KTU 2017Document1 pageAnalog Integrated Circuits EC S4 B.Tech KTU 2017ShemsNo ratings yet
- r059210404 Electronic Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pagesr059210404 Electronic Circuit AnalysisSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- 1 Ec205 Electronic Circuits (Ae, Ec)Document2 pages1 Ec205 Electronic Circuits (Ae, Ec)ABHILESH G KNo ratings yet
- Illustrate The Concept of Capacitor Charging and DischargingDocument4 pagesIllustrate The Concept of Capacitor Charging and DischargingVignesh naga trinadh KalepuNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument8 pagesSemiconductorchhabrarudra5No ratings yet
- Model QP1 - Ec1001 1Document2 pagesModel QP1 - Ec1001 1vishesh091105No ratings yet
- EEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - ExamDocument5 pagesEEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - Exameric wahomeNo ratings yet
- AC 2011 PaperDocument8 pagesAC 2011 PaperAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- Rr311402 Digital ElectronicsDocument8 pagesRr311402 Digital ElectronicsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- WWW Manaresults Co inDocument2 pagesWWW Manaresults Co inRehaman ShaikNo ratings yet
- 2023-CMSA-CC-4-TH-Basic-ElectronicsDocument2 pages2023-CMSA-CC-4-TH-Basic-Electronicsb8a9cq4jNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesAnswer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 Marks.: Page 1 of 2sheena mNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Paper-2 (PCC-EE-302) : Analog Electronic Total Marks - 70 Duration: 3HrsDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering Paper-2 (PCC-EE-302) : Analog Electronic Total Marks - 70 Duration: 3HrsAmlan SarkarNo ratings yet
- RT 31026042019Document1 pageRT 31026042019Syed AshmadNo ratings yet
- 3460 (1)Document2 pages3460 (1)sayantandutta449No ratings yet
- Electronics-1 - 09-12-24Document1 pageElectronics-1 - 09-12-24arpitpatil8229No ratings yet
- Ee 3 Sem Electronic Devices and Circuits 2016Document3 pagesEe 3 Sem Electronic Devices and Circuits 2016Priyanshu AgaseNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument9 pagesAnalog ElectronicsAadarshNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Rec201 1Document4 pagesBasic Electronics Rec201 1ranveeryadav3710No ratings yet
- Ec8252ed Set2 PDFDocument2 pagesEc8252ed Set2 PDFRajkumar PerumalNo ratings yet
- Ect301 Linear Integrated Circuits, December 2022Document2 pagesEct301 Linear Integrated Circuits, December 2022Dinil DhananjayanNo ratings yet
- Ee3402-Lic Model Exam QuestionDocument7 pagesEe3402-Lic Model Exam QuestionSurya NatarajanNo ratings yet
- C1EC01 C1405 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Set1Document2 pagesC1EC01 C1405 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Set1Sudhakar_08No ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements and InstrumentationsDocument4 pagesElectronic Measurements and InstrumentationsSatish BunnyyNo ratings yet
- Linear Digital Ic Applications Nr210502 November AmDocument2 pagesLinear Digital Ic Applications Nr210502 November AmNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Ic ApplicatonsDocument4 pagesLinear and Digital Ic ApplicatonsViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedDocument2 pagesTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not Providedpcjoshi02No ratings yet
- Answer Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswer Answer All Questions, Each Carries 3 MarksAjayShankarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Eee, Ece, Cse, Eie, It, MCT)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Eee, Ece, Cse, Eie, It, MCT)pramodNo ratings yet
- EDC Model PapersDocument12 pagesEDC Model PapersanithaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics CseDocument2 pagesBasic Electronics CseUmashankar VermaNo ratings yet
- Jntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesJntuworld: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringRajeev BujjiNo ratings yet
- r05210404 Electronic Circuit Analysis November 2008Document8 pagesr05210404 Electronic Circuit Analysis November 2008Tamire santhosh mohanNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument6 pagesKings: Question BankRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- BESCK204CDocument2 pagesBESCK204Cdarshangowda0525No ratings yet
- I A) B) 2 A) B) If 3 A) B) C) : Unitvnnsifv''.. Examination (R&S)Document2 pagesI A) B) 2 A) B) If 3 A) B) C) : Unitvnnsifv''.. Examination (R&S)Adithyan JNo ratings yet
- Computational Liquid Crystal Photonics: Fundamentals, Modelling and ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational Liquid Crystal Photonics: Fundamentals, Modelling and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyFrom EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionFrom EverandHeterojunction Bipolar Transistors for Circuit Design: Microwave Modeling and Parameter ExtractionNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Steel Moment-Resisting Frame 1994 Northridge Earthquake Federal Emergency Management AgencyDocument1 pageSteel Moment-Resisting Frame 1994 Northridge Earthquake Federal Emergency Management AgencysushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Engineering IIDocument2 pagesWater Resource Engineering IIsushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Water Resource Engineering IDocument3 pagesWater Resource Engineering IsushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Water Supply EngineeringDocument2 pagesWater Supply EngineeringsushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- System Software 2009 (Back)Document1 pageSystem Software 2009 (Back)sushilNo ratings yet
- Cliquez Ici Pour Regarder Le Cours en FrançaisDocument5 pagesCliquez Ici Pour Regarder Le Cours en FrançaissushilNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarkssushilNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Engineering Set IIDocument2 pagesWater Supply Engineering Set IIsushilNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of LubricationDocument1 pageMechanism of LubricationsushilNo ratings yet
- Fly Level Booking Sheet Project:-Location:-: S.no BS IS FS Rise Fall HI Reduced LevelDocument2 pagesFly Level Booking Sheet Project:-Location:-: S.no BS IS FS Rise Fall HI Reduced LevelsushilNo ratings yet