100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K viewsClassification of Steels
Classification of Steels
Uploaded by
Weber HahnThis document classifies steels based on their microstructural cleanliness and composition. It divides steels into two main categories: non-alloy steels and alloy steels. Non-alloy steels are further broken down into base steels, quality steels, and special steels based on their mechanical properties and impurity levels. Alloy steels are classified as quality steels or special steels based on their carbon levels and alloying elemental composition. The document also discusses elements that may be present in steels, including alloying elements, by-elements, and impurity elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Classification of Steels
Classification of Steels
Uploaded by
Weber Hahn100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views13 pagesThis document classifies steels based on their microstructural cleanliness and composition. It divides steels into two main categories: non-alloy steels and alloy steels. Non-alloy steels are further broken down into base steels, quality steels, and special steels based on their mechanical properties and impurity levels. Alloy steels are classified as quality steels or special steels based on their carbon levels and alloying elemental composition. The document also discusses elements that may be present in steels, including alloying elements, by-elements, and impurity elements.
Original Description:
f
Original Title
Classification+of+Steels
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document classifies steels based on their microstructural cleanliness and composition. It divides steels into two main categories: non-alloy steels and alloy steels. Non-alloy steels are further broken down into base steels, quality steels, and special steels based on their mechanical properties and impurity levels. Alloy steels are classified as quality steels or special steels based on their carbon levels and alloying elemental composition. The document also discusses elements that may be present in steels, including alloying elements, by-elements, and impurity elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views13 pagesClassification of Steels
Classification of Steels
Uploaded by
Weber HahnThis document classifies steels based on their microstructural cleanliness and composition. It divides steels into two main categories: non-alloy steels and alloy steels. Non-alloy steels are further broken down into base steels, quality steels, and special steels based on their mechanical properties and impurity levels. Alloy steels are classified as quality steels or special steels based on their carbon levels and alloying elemental composition. The document also discusses elements that may be present in steels, including alloying elements, by-elements, and impurity elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Classification of Steels
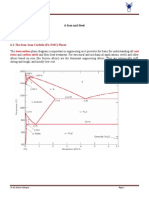
according to EN 10020, this classification is based on microstructural cleanless
Steels
Non Alloy Steels Alloy Steels
Base Steels Quality Steels Special Steels Quality Steels Special Steels
Definition is based on: Definition is based on:
Mechanical Properties: Chemical Compositon:
• Tensile Strength (old standard) • Carbon Level
• Yield Strength (new standard) • Alloying Elements
• Elongation
• Impact Energy (new standard)
Base Steels
• no special expectation
• No any request of heat treatment
• Limits:
– Rm<670 N/mm2
– Re <360 N/mm2
– C > 0.1%
Elements in an Alloy I
1.Alloying elements: Elements which are
deliberately added to
alloy.(carbon is an essential element for
steel, therefore carbon is not considered as
alloying element in steel)
The Minimum Limits of Alloying Element in Steel. (Lower values can be
ignored «see By element»)
Al 0,10 Ta 0,05 Pb 0,40
Cu 0,40 Mn 1,60 Ti 0,05
Bi 0,10 Mo 0,08 Ni 0,30
B 0,0008 Nb 0,05 W 0,10
Co 0,10 Ce 0,10 Zr 0,05
Cr 0,30 Si 0,50 V 0,10
others (C, P, S, O, N) Te 0,10
Elements in an Alloy II
2.By Elements: Elements which are left
in the alloy or come
from liquid processing.
They don’t have
negative effect on
properties.
The most important represantatives of this group are Si and Mn in plain
carbon steels (non alloyed steel). Si and Mn are added to a plain carbon steel
not for alloying but for liquid processing purposes during steel making, as
deoxidant.
Elements in an Alloy III
3.Impurity elements: Elements which are
not desired in the
alloy.
They are left in an alloy
because of
technological and/or
economical reasons.
Impurities can be found in the microstructure in
two forms. 1- As Dissolved in solid solution or
2- As Inclussion (the worst form!!!)
Elements in an Alloy III
Depending on Impurity levels:
Steels can be divided in to 3 sub groups
1. Base Steels (P, S>0,045%)
2. Quality Steels (0,035%<P, S <0,045%)
3. Special Steels (P, S<0,035%)
• Alloyed steels are always Quality or Special Steel
• Steels to be quenched (heat treatment) should
be Quality or preferentially Special steel!..
Standards about Inclusions
• EN 10247
• ASTM E45
• ISO 4967
You might also like
- Worksheet - Integrating 21st Century Skills in Classroom-Based AssessmentDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Integrating 21st Century Skills in Classroom-Based AssessmentDianne Bajet75% (8)
- MetallurgyDocument17 pagesMetallurgyirajfarji2481No ratings yet
- Inclusions in Steel by Calcium TreatmentDocument89 pagesInclusions in Steel by Calcium TreatmentSuleyman HaliciogluNo ratings yet
- AluminiumDocument48 pagesAluminiumGhiffariAwliyaMuhammadAshfania100% (1)
- Alloys and Types of SteelDocument16 pagesAlloys and Types of SteelRajatNo ratings yet
- Industry Analysis - Coursera - 100%Document1 pageIndustry Analysis - Coursera - 100%MASHI MAR.100% (1)
- CASE 580L: Replacement Parts CatalogDocument156 pagesCASE 580L: Replacement Parts Catalogsumi adams100% (4)
- Classification of SteelsDocument3 pagesClassification of SteelsHaider EjazNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 06 - Nickel and Its AlloysDocument16 pagesLECTURE 06 - Nickel and Its AlloysMarisa RobertsNo ratings yet
- Composition of Steels PDFDocument5 pagesComposition of Steels PDFNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- High Speed SteelDocument14 pagesHigh Speed SteelKushan Gajjar100% (1)
- Iron Carbon DiagramDocument8 pagesIron Carbon Diagramashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- 05 - Phase Transformation in Welding PDFDocument36 pages05 - Phase Transformation in Welding PDFIrfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Steel SheetDocument38 pagesHot Rolled Steel Sheetkhwanta-bta100% (4)
- Induction Furnace Belgaum ReportDocument29 pagesInduction Furnace Belgaum ReportQuynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- British Columbia On Defects in BilletsDocument119 pagesBritish Columbia On Defects in BilletsStutee Nanda100% (1)
- Steel Dynamics Bar Book Rev 2 New CoverDocument194 pagesSteel Dynamics Bar Book Rev 2 New CoverNina LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument21 pagesHeat TreatmentChernet MerknehNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and Mettlurgy QBDocument12 pagesEngineering Materials and Mettlurgy QBSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Wire Tube DrawingDocument48 pagesWire Tube DrawingSarthak JadhavNo ratings yet
- 09 Wire DrawingDocument21 pages09 Wire DrawingsdhgwdNo ratings yet
- Free Cutting SteelsDocument6 pagesFree Cutting SteelsRidvan GecuNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Casting (8-20)Document20 pagesCentrifugal Casting (8-20)Rabindra DashNo ratings yet
- Steel MakingDocument35 pagesSteel MakingBharichalo007No ratings yet
- Tramp Elements and Billet CarckingDocument7 pagesTramp Elements and Billet CarckingOmar TahaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Welding - Anb Refresher Course - Module 01Document65 pagesIndian Institute of Welding - Anb Refresher Course - Module 01aravindanNo ratings yet
- Alloying ElementsDocument4 pagesAlloying ElementsLakshmi NarayananNo ratings yet
- Steel Making FundamentalsDocument42 pagesSteel Making FundamentalsHimadhar Sadu100% (1)
- CCM Mechanical-Design PresentationDocument63 pagesCCM Mechanical-Design PresentationRavi Kant kumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Metal Flow in WeldingDocument40 pagesChemical Reactions and Metal Flow in WeldingJim GrayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Engineering Alloys (Ferrous and Non-Ferrous) : StructureDocument63 pagesUnit 2 Engineering Alloys (Ferrous and Non-Ferrous) : StructureKelvin TyhNo ratings yet
- Effect of Elements in SteelDocument3 pagesEffect of Elements in SteelJayakrishnan Radhakrishnan100% (1)
- Iron - Carbon Phase DiagramDocument33 pagesIron - Carbon Phase Diagramvishnu anand100% (3)
- Flame HardeningDocument29 pagesFlame Hardeningzaid sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electro-Slag Remelting (ESR)Document22 pagesIntroduction To Electro-Slag Remelting (ESR)Jahanzeb BhattiNo ratings yet
- WeldabilityDocument26 pagesWeldabilityvivek bhangaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Casting InSteelCon 2007Document8 pagesLecture Casting InSteelCon 2007radynasrNo ratings yet
- Melting Stainless Steel Using An Induction FurnaceDocument5 pagesMelting Stainless Steel Using An Induction FurnaceErman DurmazNo ratings yet
- The Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) PhaseDocument8 pagesThe Iron-Iron Carbide (Fe-Fe3C) PhaseRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- 6 Type Induction FurnaceDocument6 pages6 Type Induction Furnacehodeegits9526No ratings yet
- Defination of Dead Mild SteelDocument1 pageDefination of Dead Mild SteelV. A. TripathiNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Language of SteelDocument7 pagesA Guide To The Language of SteelIwona AnkaNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Alloying Elements On Steels 1Document36 pagesThe Effects of Alloying Elements On Steels 1Common ManNo ratings yet
- Alloys: I) IntroductionDocument12 pagesAlloys: I) IntroductionNikhil ShelarNo ratings yet
- Steckel Mill 1 PDFDocument178 pagesSteckel Mill 1 PDFSomnathNaskarNo ratings yet
- 07 - Zinc and Its AlloysDocument22 pages07 - Zinc and Its Alloysessnelson100% (1)
- Arc Welding EquipmentDocument6 pagesArc Welding Equipmentm_er100No ratings yet
- Billet Defects - Pinhole and Blowhole Formation, Prevention and Evolution PDFDocument10 pagesBillet Defects - Pinhole and Blowhole Formation, Prevention and Evolution PDFSebastian KrdnasNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument73 pagesMetalswadkknpp.admnacctsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials IDocument143 pagesEngineering Materials InumanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Steel Classification and Standard: Suwarno, PHDDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Steel Classification and Standard: Suwarno, PHDmirfanwibisono100% (1)
- Screenshot 2022-12-31 at 7.45.47 PM PDFDocument73 pagesScreenshot 2022-12-31 at 7.45.47 PM PDFHardi HedayatNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Alloy Steel PDFDocument52 pagesCarbon and Alloy Steel PDFmaz234100% (3)
- 3 Steel PDFDocument16 pages3 Steel PDFSohanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lect 9. Steel Classification and PropertiesDocument28 pagesLect 9. Steel Classification and PropertiesRio BuiNo ratings yet
- SteelsDocument28 pagesSteelssaba AnasNo ratings yet
- Steels: Professor R.Manivannan Department of Mechanical Engineerin GDocument28 pagesSteels: Professor R.Manivannan Department of Mechanical Engineerin GManivannan JeevaNo ratings yet
- SteelsDocument28 pagesSteelsPAUL PRAVEEN A 15PHD0053No ratings yet
- SteelsDocument28 pagesSteelsMalik Ansar HayatNo ratings yet
- Modified Ferrous 3Document29 pagesModified Ferrous 3jacksparrow4583No ratings yet
- Metals OverviewDocument60 pagesMetals OverviewkaelcorbettNo ratings yet
- BME (Steel)Document8 pagesBME (Steel)Mohil JainNo ratings yet
- 1926 - 2009 More Then 80 Years in The Transmission Field: Head Quarters/ Registered OfficeDocument35 pages1926 - 2009 More Then 80 Years in The Transmission Field: Head Quarters/ Registered OfficeWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Draka Medium CablesDocument9 pagesDraka Medium CablesWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- ACSRDocument3 pagesACSRWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Useful Word Shortcuts For Working On IEC Documents : General Key(s) General Key(s) Styles From The IEC Template Key(s)Document1 pageUseful Word Shortcuts For Working On IEC Documents : General Key(s) General Key(s) Styles From The IEC Template Key(s)Weber HahnNo ratings yet
- Hydropower: Make Your Project A SuccessDocument9 pagesHydropower: Make Your Project A SuccessWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- MT-010-004 CMSA Louth - Rathrussan 110 KV Proposed ModificationsDocument1 pageMT-010-004 CMSA Louth - Rathrussan 110 KV Proposed ModificationsWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Bare Overhead Conductors-2015Document63 pagesBare Overhead Conductors-2015Weber HahnNo ratings yet
- Substations: Editors: T. Krieg, J. FinnDocument2 pagesSubstations: Editors: T. Krieg, J. FinnWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- 17 Depliant E-I Stripping Tools - LowDocument32 pages17 Depliant E-I Stripping Tools - LowWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- CH 16 PLS CADD PDFDocument9 pagesCH 16 PLS CADD PDFgvsbabu63No ratings yet
- Insulators Catalogue 2015Document31 pagesInsulators Catalogue 2015Weber HahnNo ratings yet
- 35-110 KV SC - SL - TowerDocument2 pages35-110 KV SC - SL - TowerWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- A1X3H9 - Plan and ProfileDocument5 pagesA1X3H9 - Plan and ProfileWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Annual-Report 2016 EnglishDocument49 pagesAnnual-Report 2016 EnglishWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- 35-110 KV SC - A 120-TOWER PDFDocument2 pages35-110 KV SC - A 120-TOWER PDFWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- MT-009-004 Temporary Construction Material Storage Yard Palisade Gate DetailDocument1 pageMT-009-004 Temporary Construction Material Storage Yard Palisade Gate DetailWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Annual-Report 2016 EnglishDocument49 pagesAnnual-Report 2016 EnglishWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- MT-010-006 MSA Arva - Navan 110 KV Proposed ModificationsDocument1 pageMT-010-006 MSA Arva - Navan 110 KV Proposed ModificationsWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- MT-010-005 MSA Arva - Navan 110 KV Existing StructuresDocument1 pageMT-010-005 MSA Arva - Navan 110 KV Existing StructuresWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Material For Fibre Optic Lines PDFDocument21 pagesMaterial For Fibre Optic Lines PDFWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Earth Wire FittingsDocument11 pagesEarth Wire FittingsWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- North-South 400 KV Interconnection Development Volume 1B - Planning Drawings MAY 2015 Drawing No. Description Scale Drawing No. Description ScaleDocument1 pageNorth-South 400 KV Interconnection Development Volume 1B - Planning Drawings MAY 2015 Drawing No. Description Scale Drawing No. Description ScaleWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- Vibration Dampers: Subject To Change Without NoticeDocument8 pagesVibration Dampers: Subject To Change Without NoticeWeber HahnNo ratings yet
- 17 Different Types of Houses in The PhilippinesDocument17 pages17 Different Types of Houses in The PhilippinesRuzel AmpoanNo ratings yet
- For Criminology Annual Revalida Exam: Prelim 1 SemesterDocument19 pagesFor Criminology Annual Revalida Exam: Prelim 1 SemesterArtemis Heist100% (1)
- Als1 Regulations Revised Aug 2016Document14 pagesAls1 Regulations Revised Aug 2016Sean WingNo ratings yet
- Beginner Series Episode 7 Guitar GuideDocument3 pagesBeginner Series Episode 7 Guitar Guidekittywan1901No ratings yet
- LocoNav Intro With Use CasesDocument27 pagesLocoNav Intro With Use CasesMaheshsinh RajputNo ratings yet
- McDaniel - Big-Brained People Are Smarter - A Meta-Analysis of The Relationship Between in Vivo Brain Volume and IntelligenceDocument10 pagesMcDaniel - Big-Brained People Are Smarter - A Meta-Analysis of The Relationship Between in Vivo Brain Volume and IntelligenceAlex MustateaNo ratings yet
- History of DevOps & Main ObjectivesDocument3 pagesHistory of DevOps & Main ObjectivesratixsbNo ratings yet
- Australia Awards Tuvalu Information For IntakeDocument8 pagesAustralia Awards Tuvalu Information For Intakequeen TinaNo ratings yet
- XI ENGLISH SAMPLE PAPER SET 1-5...Document30 pagesXI ENGLISH SAMPLE PAPER SET 1-5...Prajwal RoutrayNo ratings yet
- DME Synthesis Via Catalytic Distillation: Experiments and SimulationDocument6 pagesDME Synthesis Via Catalytic Distillation: Experiments and SimulationediabcNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING (CSE 113) B. Sc. (H), B. Tech.,B. Tech.+M. Tech.,B. Tech.+MBA (SEM. - TERM-01) 2018-19Document2 pagesPROGRAMMING FOR PROBLEM SOLVING (CSE 113) B. Sc. (H), B. Tech.,B. Tech.+M. Tech.,B. Tech.+MBA (SEM. - TERM-01) 2018-19Harshit AroraNo ratings yet
- XRRIA002EN-A Hotandcold03022011 FinalDocument3 pagesXRRIA002EN-A Hotandcold03022011 FinalDan MihailNo ratings yet
- Ocr Gcse Music Coursework Grade BoundariesDocument4 pagesOcr Gcse Music Coursework Grade Boundariesjxaeizhfg100% (2)
- TutorDocument3 pagesTutorJake Role GusiNo ratings yet
- FP3 AllDocument782 pagesFP3 AllAyse Kerim100% (1)
- Accordion BookDocument2 pagesAccordion BookdemonrageNo ratings yet
- A - LAPORAN PENDAHULUAN - KELOMPOK A (New)Document12 pagesA - LAPORAN PENDAHULUAN - KELOMPOK A (New)Fahira SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Editorial Board - 2024 - Journal of Business ResearchDocument6 pagesEditorial Board - 2024 - Journal of Business ResearchsanidevixNo ratings yet
- CFD Final Project-SEM 7Document6 pagesCFD Final Project-SEM 7shanawarshoukat14No ratings yet
- ReflexologyDocument4 pagesReflexologyphong duongNo ratings yet
- Bucket 33 XS0231918060 56471 8333108Document4 pagesBucket 33 XS0231918060 56471 8333108Hyunjin ShinNo ratings yet
- Fruits & Vegetables - B.ingg 4Document33 pagesFruits & Vegetables - B.ingg 4Afif ManziNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Hospitality Management: Ingrid Y. Lin, Anna S. MattilaDocument21 pagesInternational Journal of Hospitality Management: Ingrid Y. Lin, Anna S. MattilaThean MendozaNo ratings yet
- Packaging_Industry_in_Vietnam.pdfDocument6 pagesPackaging_Industry_in_Vietnam.pdfsanthiya.weuphoriaNo ratings yet
- E-GP Strategy Plan Part2Document35 pagesE-GP Strategy Plan Part2JamalNo ratings yet
- Emsat Mock Exam: Section Questions MinutesDocument27 pagesEmsat Mock Exam: Section Questions MinutesAmor ChamekhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument80 pagesUntitledoutdash2No ratings yet