0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 viewsHeat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Heat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Uploaded by
Claire RallosThis document defines key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) The three laws of thermodynamics, various gas laws like Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's law, and thermodynamic properties including temperature, pressure, volume, enthalpy, and entropy.
2) The relationships between these properties, such as how enthalpy depends on internal energy and pressure-volume work, and how different processes affect entropy.
3) Equations of state that describe the thermodynamic behavior of gases including the ideal gas law, van der Waals, and Virial equations of state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Heat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Heat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Uploaded by
Claire Rallos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesThis document defines key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) The three laws of thermodynamics, various gas laws like Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's law, and thermodynamic properties including temperature, pressure, volume, enthalpy, and entropy.
2) The relationships between these properties, such as how enthalpy depends on internal energy and pressure-volume work, and how different processes affect entropy.
3) Equations of state that describe the thermodynamic behavior of gases including the ideal gas law, van der Waals, and Virial equations of state.
Original Description:
Formula
Original Title
Phy Chem Formulas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document defines key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) The three laws of thermodynamics, various gas laws like Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's law, and thermodynamic properties including temperature, pressure, volume, enthalpy, and entropy.
2) The relationships between these properties, such as how enthalpy depends on internal energy and pressure-volume work, and how different processes affect entropy.
3) Equations of state that describe the thermodynamic behavior of gases including the ideal gas law, van der Waals, and Virial equations of state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesHeat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Heat Released (Exo) Heat Absorbed (Endo)
Uploaded by
Claire RallosThis document defines key concepts in thermodynamics including:
1) The three laws of thermodynamics, various gas laws like Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's law, and thermodynamic properties including temperature, pressure, volume, enthalpy, and entropy.
2) The relationships between these properties, such as how enthalpy depends on internal energy and pressure-volume work, and how different processes affect entropy.
3) Equations of state that describe the thermodynamic behavior of gases including the ideal gas law, van der Waals, and Virial equations of state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
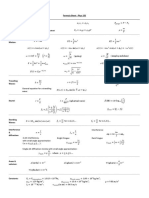
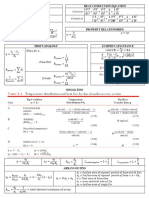
Thermal Equilibrium Zero Slope and Inflection Point
𝑇𝐴 = 𝑇𝐶 = 𝑇𝐵 𝜕𝑃 𝜕2 𝑃
(𝜕𝑉) = 0 (𝜕2 𝑉) = 0
𝑇 𝑇
Ideal Gas Law
𝑃𝑉 = 𝑛𝑅𝑇 Most probable speed
Boyle’s Law (constant n, T) 2𝑅𝑇
𝑢𝑚𝑝 = √
𝑃1 𝑉1 = 𝑃2 𝑉2 𝑀
Charles’ Law (constant n, P) Average speed
𝑉1 𝑉2 8𝑅𝑇
= 𝑢 = √ 𝜋𝑀 𝑢𝑚𝑝 < 𝑢 < 𝑢𝑟𝑚𝑠
𝑇1 𝑇2
Avogadro’s Law (constant T, P) Root-mean-square speed
𝑉1 𝑉2
= 3𝑅𝑇
𝑛1 𝑛2 𝑢𝑟𝑚𝑠 = √
𝑀
Gay-Lussac’s Law (constant n, V)
𝑃1 𝑃2 Interpreting Temperature
= 𝑇 ∝ ̅̅̅̅
𝐾𝐸 =
1
𝑚𝑉 2 ̅̅̅̅
𝐾𝐸 =
3
𝑅𝑇
𝑇1 𝑇2 2 2
Molar Mass Origin of Pressure
𝑀=
𝑚
𝑀=
𝑚𝑅𝑇
=
𝜌𝑅𝑇 𝐹
𝑛 𝑃𝑉 𝑃 𝑃=
𝐴
Density Graham’s Law of Effusion
𝑃𝑀
𝜌= 𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒1 𝑀2
𝑅𝑇
=√
𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑒2 𝑀1
Dalton’s Law (constant V, T)
𝑛1 𝑅𝑇 𝑛2 𝑅𝑇 Work
𝑃𝑇 = ∑ 𝑃𝑖 = + +⋯
𝑉 𝑉 𝑤 = 𝐹 × 𝛥𝑥 = 𝑃 × 𝛥𝑉
Partial Pressure
𝑛1 𝑃1 Potential Energy
𝑃𝑖 = 𝑥𝑖 𝑃𝑡 𝑥𝑖 = = 𝑃𝐸 = 𝑚𝑔ℎ
𝑛𝑇 𝑃𝑇
Molar Volume Kinetic Energy
𝑉 1
𝑉̅ = 𝐾𝐸 = 𝑚𝑣 2
𝑛 2
Compressibility factor Ideal gas: Z=1 Specific Heat/ Sensible Heat
𝑃𝑉̅ 𝑞 = 𝑚𝑐𝑝 𝛥𝑇
𝑍= Latent Heat
𝑅𝑇 𝑞 = 𝑚𝛥𝐻𝑡𝑟
Van der Waals EOS
𝑛𝑅𝑇 𝑛2 𝑎 𝑅𝑇 𝑎 Equation for P-V Work
𝑃= − 𝑃= ̅−𝑏
− ̅2
𝑉− 𝑛𝑏 V2 𝑉 𝑉 𝑤 = − ∫ 𝑃𝑒𝑥𝑡 𝑑𝑉
Redlich-Kwong EOS: 1st Law of Thermodynamics
𝑅𝑇 𝐴 𝛥𝑈 = 𝑞 + 𝑤
𝑃= −
𝑉̅ − 𝐵 √𝑇(𝑉̅)(𝑉̅ + 𝐵) Sign Conventions
𝛥𝑈 < 0 𝑞 < 0, Heat 𝑤 < 0, by the sys.
Virial EOS released(exo) on surr
𝐵 𝐶 𝐷 ′𝑃2
𝑍 =1+ + + +. . . = 1+𝐵𝑃+𝐶 ′
+ 𝛥𝑈 > 0 𝑞 > 0, Heat 𝑤 > 0, on the sys.
̅
𝑉 ̅2
𝑉 ̅3
𝑉 absorbed(endo) by surr
𝐷′𝑃3 +. ..
Work for reversible process
Partial Derivative
𝜕𝑧 𝑤𝑟𝑒𝑣 = − ∫ 𝑃 𝑑𝑉
( )
𝜕𝑥 𝑦 Enthalpy
Boyle Temperature
𝑎 𝐻 ≡ 𝑈 + 𝑃𝑉
𝑇𝐵 = Heat Transfer
𝑏𝑅
𝑞𝑣 = 𝛥𝑈 (𝑉 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡) 𝑞𝑃 = 𝛥𝐻 (𝑃 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡)
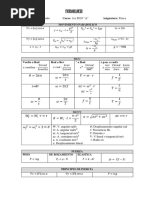
Relationship of 𝜟𝑼 and 𝜟𝑯 Isenthalpic Process (𝛥𝐻 = 0)
(assuming ideal gas) 𝛥𝑇 = 0 or 𝑇2 = 𝑇1
𝛥𝐻 = 𝛥𝑈 + 𝛥(𝑃𝑉) = 𝛥𝑈 + 𝛥𝑛𝑔𝑎𝑠 𝑅𝑇
Joule-Thomson Coefficient
(gases not involved) 𝜕𝑇
𝛥𝐻 = 𝛥𝑈 𝜇𝐽𝑇 = ( ) (for real gases, 𝑇2 ≠ 𝑇1 )
𝜕𝑃 𝐻
Calorimeter/Calorimetry (constant Pressure) 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
𝑞𝑐𝑎𝑙 + 𝑞𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 +. . . = −𝑞𝑟𝑥𝑛 ∆𝑆𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑣 ≥ 0
𝛥𝐻𝑟𝑥𝑛 = −𝑞𝑐𝑎𝑙 = −𝐶𝑐𝑎𝑙 𝛥𝑇 𝛥𝑆𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑣 = 𝛥𝑆𝑠𝑦𝑠 + 𝛥𝑆𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑟 ≥ 0
𝛥𝑆𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑣 > 0(𝑖𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒)
𝛥𝑈𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏 = 𝑛𝐶 ̅ 𝑣 ∆𝑇 𝛥𝑆𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑣 = 0 (𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒)
𝛥𝐻𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏 = 𝛥𝑈𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏 + ∆𝑛𝑔 𝑅𝑇 = 𝑛𝐶 ̅ 𝑝 ∆𝑇 𝛥𝑆𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑣 < 0 (𝑛𝑜 𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑒𝑜𝑢𝑠 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑛 𝑜𝑐𝑐𝑢𝑟)
Hess’s Law of Heat Summation Statistical Definition of entropy
𝛥𝐻𝑟𝑥𝑛 = 𝛥𝐻1 + 𝛥𝐻2 + 𝛥𝐻3 +. .. 𝑆 = 𝑘 𝑙𝑛 𝑊
Boltzmann Constant: 𝑘 = 1.38 × 10−23 𝐽/𝐾
Standard enthalpies of Formation Entropy
𝑑𝑞
𝑜
𝛥𝐻𝑟𝑥𝑛 = ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝛥𝐻𝑓𝑜 (𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒕𝒔) − ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝛥𝐻𝑓𝑜 (𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒔) 𝛥𝑆 = ∫ 𝑇𝑟𝑒𝑣
𝛥𝐻
Bond enthalpies 𝛥𝑆𝑡𝑟 = 𝑇 𝑡𝑟 (latent heat)
𝑡𝑟
𝑜 𝑇2
𝛥𝐻𝑟𝑥𝑛 = ∑ 𝐵𝐸(𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒔) − ∑ 𝐵𝐸(𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒕𝒔) 𝛥𝑆 = 𝑚𝐶𝑝 𝑙𝑛 (sensible heat)
𝑇1
𝑇2 𝑉
Kirchoff’s Law 𝛥𝑆 = 𝑛𝐶𝑣 𝑙𝑛
𝑇1
+ 𝑛𝑅 𝑙𝑛 𝑉2 (ideal gas)
1
𝛥𝐻2 = 𝛥𝐻1 + 𝛥𝐶𝑝 (𝑇2 − 𝑇1 ) 𝑞𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑟
𝛥𝑆𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑟 = 𝑇
(constant temperature)
where: 𝛥𝐶𝑝 = ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝐶𝑝𝑖 (𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒕𝒔) − 𝑛𝑖 𝐶𝑝𝑖 (𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒔) 3rd Law of Thermodynamics
𝑆 (𝑎𝑡 0𝐾) = 0
Thermodynamic processes for ideal gases
Entropy of reaction at standard conditions
𝑞 = 𝑚𝑐𝛥𝑇 = 𝐶𝛥𝑇(solids and liquids)
𝑜
𝜕𝑈 𝛥𝑆𝑟𝑥𝑛 = ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝑆 ° (𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒅𝒖𝒄𝒕𝒔) − ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝑆 ° (𝒓𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒔)
𝛥𝑈 = 𝑞𝑉 → 𝐶𝑉 ≡ ( ) Gibbs Free Energy
𝜕𝑇 𝑉
𝐺 ≡ 𝐻 − 𝑇𝑆 ∆𝐺 = ∆𝐻 − 𝑇∆𝑆
𝜕𝐻 ∆𝐺 < 0(𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑒𝑜𝑢𝑠); ∆𝐺 = 0(𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑏𝑙𝑒); ∆𝐺 > 0(𝑛𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑝𝑜𝑛)
𝛥𝐻 = 𝑞𝑃 → 𝐶𝑃 ≡ ( )
𝜕𝑇 𝑃 (Temperature Dependence) (Using Gibbs free Energy Formation)
° ° °
𝐶𝑝 = 𝐶𝑉 + 𝑅 ∆𝐺𝑟𝑥𝑛 = ∆𝐻𝑟𝑥𝑛 − 𝑇∆𝑆𝑟𝑥𝑛
= ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝐺𝑓° (𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑠) − ∑ 𝑛𝑖 𝐺𝑓° (𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑑𝑢𝑐𝑡𝑠)
𝐶𝑉 𝐶𝑃 𝐶𝑉
𝛿=
𝐶𝑃 ∆𝐻 > 0 ∆𝐻 < 0
∆𝑆 > 0 ∆𝐺 < 0,at high temp. ∆𝐺 < 0 𝑎𝑡 𝑎𝑛𝑦 𝑡𝑒𝑚𝑝
Monatomic 3 5 5 ∆𝐺 > 0, at low temp.
𝑅 𝑅 ∆𝑆 < 0 ∆𝐺 > 0 𝑎𝑡 𝑎𝑛𝑦 𝑡𝑒𝑚𝑝 ∆𝐺 < 0,at low temp.
2 2 3
∆𝐺 > 0, at high temp.
Diatomic 5 7 7 1 N = 1 kg-m/s2
𝑅 𝑅
2 2 5 1 J = 1 N-m
1 J = 9.87x10-3 L-atm
Polyatomic 3𝑅 4𝑅 4
1 cal = 4.184 J
3
1 Pa = 1 N/m2
1 bar = 1x105 Pa = 100 kPa
Isochoric (𝛥𝑉 = 0) (Gay-Lussac’s Law) 1 atm = 1.01325x105 Pa = 101.325 Pa
𝑞 = 𝛥𝑈 = 𝑛𝐶𝑉 𝛥𝑇 𝛥𝐻 = 𝑛𝐶𝑃 𝛥𝑇 𝑤 = 0 1 atm = 1.01325 bar
𝐶𝑣 1 atm = 760 torr
𝑄= 𝑉(𝑃𝑓 − 𝑃𝑖 )
𝑅 1 atm = 101.3 J
Isobaric (𝛥𝑃 = 0) (Charles’ Law) 1mmHg = 1 torr
𝑞 = 𝛥𝐻 = 𝑛𝐶𝑃 𝛥𝑇 𝛥𝑈 = 𝑛𝐶𝑉 𝛥𝑇 𝑤 = −𝑃𝛥𝑉 1mmHg = 13.5951 g/ cm3
1 L = 1x10-3 m3
Isothermal (𝛥𝑇 = 0) (Boyle’s Law) K = °C + 273.15
𝑉 R = 0.08205 L-atm/mol-K
𝑞 = −𝑤 𝛥𝐻 = 0 𝛥𝑈 = 0 𝑤 = −𝑛𝑅𝑇 𝑙𝑛 (𝑉2 ) = 0.08314 L-bar/mol-K
1
= 1.987 cal/mol-K
Reversible Adiabatic (𝑞 = 0) = 8.314 J/ mol-K
𝑤 = 𝛥𝑈 = 𝑛𝐶𝑉 𝛥𝑇 𝛥𝐻 = 𝑛𝐶𝑃 𝛥𝑇 𝑃1 𝑉1𝛿 = 𝑃2 𝑉2𝛿 = 62.36 L-torr/mol-K
Avogadro constant (NA) NA = 6.0221367x1023 mol-1
You might also like
- Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials: Standard Test Methods ForDocument28 pagesVickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials: Standard Test Methods ForHarry FalsafiNo ratings yet
- Manual InglesDocument34 pagesManual InglessergirojasNo ratings yet
- Symbols, Rules, and Guidelines Facts To Remember Facts To RememberDocument1 pageSymbols, Rules, and Guidelines Facts To Remember Facts To RememberAltaf NalbandhNo ratings yet
- Surfactant PDFDocument11 pagesSurfactant PDFqwertyNo ratings yet
- Laser DiodeDocument10 pagesLaser DiodeAnees Ahmad100% (1)
- Diesel CycleDocument1 pageDiesel CycleGladys Ruth PaypaNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument1 pageList of FormulasKevin ElevenNo ratings yet
- Resources For CH126P ExamsDocument4 pagesResources For CH126P ExamsSpry CylinderNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Free VibrationDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet For Free VibrationCesar MolinaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document8 pagesLec 4Sheikh SaifNo ratings yet
- Free Vibrations With DampingDocument2 pagesFree Vibrations With DampingMuhammad AnsNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument33 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesnethrasendilkumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMNo ratings yet
- Physic Calculation SheetDocument2 pagesPhysic Calculation Sheetsharon67% (3)
- ThermoDynamics ProcessDocument2 pagesThermoDynamics ProcessSTUDY BEASTNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Formulas 7.9.2022Document3 pagesHoja de Formulas 7.9.2022rozorrilla054No ratings yet
- Positive Sequence: ResistanceDocument8 pagesPositive Sequence: ResistanceirfanWPK100% (1)
- Fórmulas 3er Parcial - RemovedDocument1 pageFórmulas 3er Parcial - RemovedLossada D. BrunoNo ratings yet
- Phys340 Lec1-10 EqnsDocument8 pagesPhys340 Lec1-10 Eqnsapi-547379030No ratings yet
- PHY108 Spring22 EquationSheet4Document3 pagesPHY108 Spring22 EquationSheet4yasiv29532No ratings yet
- PDFsam MergeDocument4 pagesPDFsam Mergeyasiv29532No ratings yet
- CaseDocument3 pagesCaseZeeshan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula Sheet Rittik BahetiDocument20 pagesChemistry Formula Sheet Rittik BahetimanojadelNo ratings yet
- Movimiento Uniforme Acelerado: FR F WDocument2 pagesMovimiento Uniforme Acelerado: FR F Wtreb gostNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Phys 131: 0 1 1 2 2 Gauge 0Document1 pageFormula Sheet - Phys 131: 0 1 1 2 2 Gauge 0eNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet For ExamsDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet For ExamsRubicoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynimic Properties FormularyDocument5 pagesThermodynimic Properties FormularyTanssNo ratings yet
- 19 09 VariationalFormulationDocument12 pages19 09 VariationalFormulationatharva.betawadkarNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMid Term Cheat Sheethalide90No ratings yet
- IFD SediDocument2 pagesIFD SediZed Brier OdilaoNo ratings yet
- Hezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 8Document44 pagesHezam Alasqah CHE 354 HW 8TimelessNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Fórmulas Física 2018Document2 pagesHoja de Fórmulas Física 2018David AvilésNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCheat Sheet PDFesenalieva03No ratings yet
- Digital Assignment I: Reg No: - Name: - Course: - Course Code: - FacultyDocument9 pagesDigital Assignment I: Reg No: - Name: - Course: - Course Code: - FacultyThennarasu RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Formulario TermodinamicaDocument2 pagesFormulario TermodinamicaDiego Díaz MartínezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 03 - Diffusion Equation, SS, SSSDocument21 pagesLecture 03 - Diffusion Equation, SS, SSSagabalaagabala10No ratings yet
- MIE100H1 - 20195 - 631572298320MIE 100 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesMIE100H1 - 20195 - 631572298320MIE 100 CheatsheetSCR PpelusaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Material Cheat Sheet AutosavedDocument5 pagesMechanics of Material Cheat Sheet AutosavedJuhaina Alwardi100% (1)
- Momentum and Heat Transfer AnalogyDocument6 pagesMomentum and Heat Transfer AnalogyAman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Part 4: Force, Pressure and Torque Measurement: Strain GaugesDocument3 pagesPart 4: Force, Pressure and Torque Measurement: Strain Gauges123andybNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Equation SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Equation SheetFabiola RamirezNo ratings yet
- EEE2044S 2021 Exam Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEEE2044S 2021 Exam Formula SheetChristine PiusNo ratings yet
- Formulario CircuitoDocument1 pageFormulario Circuitoyessica.reyes2915No ratings yet
- + + So Integrating Factor Will Be So × × + / +Document4 pages+ + So Integrating Factor Will Be So × × + / +Jaya ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- EMT Short Questions For MSCDocument38 pagesEMT Short Questions For MSCJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet 22Document3 pagesFormula Sheet 22Rana Muhammad Aliyan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Any Rise in Temperature: Isothermal CompressionDocument6 pagesAny Rise in Temperature: Isothermal CompressionSANLU HTUTNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Formulas of Physics ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesFundamental Formulas of Physics Thermodynamicsimajedu3kNo ratings yet
- Formulario PruebaDocument1 pageFormulario PruebaKarla Berenice Neira ParraNo ratings yet
- Formulario FisicaDocument1 pageFormulario Fisicanayely merchanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulasDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics FormulaskennethNo ratings yet
- 2 Slide Deck DST Heat Transfer Fundamentals 2023 PAO IIDocument22 pages2 Slide Deck DST Heat Transfer Fundamentals 2023 PAO IIAngel BlacioNo ratings yet
- Physics 4 Formula Sheet 2017Document1 pagePhysics 4 Formula Sheet 2017john100% (1)
- Procesos Con Gas IdealDocument2 pagesProcesos Con Gas IdealAlejandra VergaraNo ratings yet
- AERO213 MockExam2022Document9 pagesAERO213 MockExam2022JordanNo ratings yet
- Transient Heat ConductionDocument13 pagesTransient Heat ConductionAbubakar Siddique YousafNo ratings yet
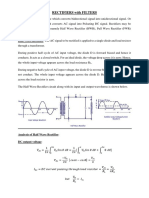
- EDC Unit-I RectifiersDocument12 pagesEDC Unit-I Rectifiersneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
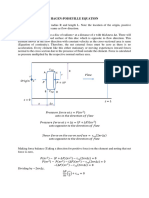
- Hagen Poisuille EquationDocument4 pagesHagen Poisuille EquationRochakNo ratings yet
- HT Equation SheetDocument8 pagesHT Equation SheetJohn GassonNo ratings yet
- Harmonics in EnglishDocument7 pagesHarmonics in EnglishSindel Parra GomoraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Formulas 2Document1 pageFluid Mechanics Formulas 2kennethNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument2 pagesThermoSalvador Monroy GalvánNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Forced Draft Tray DryerDocument1 pageForced Draft Tray DryerShoaib PathanNo ratings yet
- Wieland Coaxial Heat Exchangers WKC WKEDocument6 pagesWieland Coaxial Heat Exchangers WKC WKElabasom379No ratings yet
- Size Enlargement Study MaterialDocument21 pagesSize Enlargement Study MaterialSk jahidul Islam100% (2)
- Construction of Slabs On GroundDocument7 pagesConstruction of Slabs On GroundAshrafNo ratings yet
- Muons and Special RelativityDocument1 pageMuons and Special RelativityZephir AWTNo ratings yet
- Neet Xiip Aiats 0Document5 pagesNeet Xiip Aiats 0princesselesa685No ratings yet
- Manual Beam DesignDocument14 pagesManual Beam DesignRonald Kaaku67% (3)
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument17 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureMahesh k KNo ratings yet
- 5.smart Materials and Its ApplicationDocument23 pages5.smart Materials and Its ApplicationMukulNo ratings yet
- RM 505 Speedy Rain Turbine Parts ListDocument3 pagesRM 505 Speedy Rain Turbine Parts ListacanutrNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis R19 - UNIT-1Document50 pagesStructural Analysis R19 - UNIT-1sainadh upputhollaNo ratings yet
- Soiling Rates of PV Modules vs. Thermopile PyranometersDocument3 pagesSoiling Rates of PV Modules vs. Thermopile PyranometersAbdul Mohid SheikhNo ratings yet
- 0102-Physics Paper+With+Sol MorningDocument7 pages0102-Physics Paper+With+Sol MorningPushpanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- RC Design SUTDocument321 pagesRC Design SUTbseahorseNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument6 pagesSyllabusmohamed aamirNo ratings yet
- Slope Stability Analysis by Shear Strength Reduction Method: J C E UDocument3 pagesSlope Stability Analysis by Shear Strength Reduction Method: J C E ULutfiadji Agung HidayatNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Fixed Bed Adsorption Column: Effect of Velocity VariationDocument15 pagesModeling and Simulation of Fixed Bed Adsorption Column: Effect of Velocity VariationemebusamuelNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materialsgirish_deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Andrade Trouton 1997 On The Viscous Flow in Metals and Allied PhenomenaDocument12 pagesAndrade Trouton 1997 On The Viscous Flow in Metals and Allied Phenomenaxlbchatgpt1No ratings yet
- 2.5. PBM Serie Diverter EriksDocument20 pages2.5. PBM Serie Diverter EriksmguisseNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Test ItemDocument169 pagesGrade 9 Test ItemZhave RoncalesNo ratings yet
- 16.7 14.20 1978 54.79 ASTM A-283 Gr. C Ver Abaixo: Memorial de Cálculo de Espessura Mínima Do Costado (API 653)Document13 pages16.7 14.20 1978 54.79 ASTM A-283 Gr. C Ver Abaixo: Memorial de Cálculo de Espessura Mínima Do Costado (API 653)fabio50002No ratings yet
- Rheological Properties: University of Baghdad Collage of Engineering Department of PetroleumDocument9 pagesRheological Properties: University of Baghdad Collage of Engineering Department of Petroleumعلي خالد كاظم عبودNo ratings yet
- Flexible Solar CellsDocument2 pagesFlexible Solar CellsGautam GadgilNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test 1 Set2Document2 pagesCycle Test 1 Set2logeshboy007No ratings yet