0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
588 viewsITC Mud Fort
ITC Mud Fort
Uploaded by
rajat charayaThe ITC Mud Fort residential building in Bengaluru adopted various sustainable strategies to reduce its environmental impact and earn a 5-star GRIHA rating. These included passive solar design with adequate cross ventilation and daylighting, sustainable site planning with tree planting and permeable paving. Energy and water conservation measures like efficient fixtures, LED lighting, and a solar water heater reduced consumption. Waste was segregated on site and recycled, and materials with lower embodied energy were used in construction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
ITC Mud Fort
ITC Mud Fort
Uploaded by
rajat charaya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
588 views1 pageThe ITC Mud Fort residential building in Bengaluru adopted various sustainable strategies to reduce its environmental impact and earn a 5-star GRIHA rating. These included passive solar design with adequate cross ventilation and daylighting, sustainable site planning with tree planting and permeable paving. Energy and water conservation measures like efficient fixtures, LED lighting, and a solar water heater reduced consumption. Waste was segregated on site and recycled, and materials with lower embodied energy were used in construction.
Original Description:
housing
Original Title
ITC-mud-fort
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The ITC Mud Fort residential building in Bengaluru adopted various sustainable strategies to reduce its environmental impact and earn a 5-star GRIHA rating. These included passive solar design with adequate cross ventilation and daylighting, sustainable site planning with tree planting and permeable paving. Energy and water conservation measures like efficient fixtures, LED lighting, and a solar water heater reduced consumption. Waste was segregated on site and recycled, and materials with lower embodied energy were used in construction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
588 views1 pageITC Mud Fort
ITC Mud Fort
Uploaded by
rajat charayaThe ITC Mud Fort residential building in Bengaluru adopted various sustainable strategies to reduce its environmental impact and earn a 5-star GRIHA rating. These included passive solar design with adequate cross ventilation and daylighting, sustainable site planning with tree planting and permeable paving. Energy and water conservation measures like efficient fixtures, LED lighting, and a solar water heater reduced consumption. Waste was segregated on site and recycled, and materials with lower embodied energy were used in construction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
ITC Mud Fort
Location : 8, Jeevanahalli Main Road, Maruthiseva Nagar, Bengaluru
Site Area : 7673.15 m2
Built-up Area : 13875 m2
Air-Conditioned Area : 3889.2 m2
Non-Air-Conditioned Area : 1288.6 m2
Typology : Residential
Energy Consumption Reduction : 30.9% reduction in energy consumption compared to
GRIHA benchmark
Energy Performance Index (EPI) : 58.7 kWh/m2/year
Renewable Energy : Solar water heater of 6.5 kL capacity installed on site with a
potential of saving 47677 kWh per year
GRIHA Provisional Rating : 5 Stars
Year of Completion : 2017
The following strategies were adopted to reduce the building impact on the natural environment:
ÞÞ Solar Passive Design Strategies:
• Well-designed balconies have been provided along the façade to avoid solar radiation and heat ingress.
• Adequate window to wall ratio has been maintained in the project which allows cross ventilation and 75% day-lighting.
• Concrete wall offering a U-value of 0.39 W/m²K adds to the overall energy savings. Overall building envelope
is ECBC compliant.
• The architecture of the building with a central courtyard allows for a seamless flow of wind across the site.
• Apart from green spaces on the ground, the project has also provided green spaces at different levels with
terrace gardens adding to the thermal comfort.
ÞÞ Sustainable Site Planning:
• 3 meters high barricading was constructed all around the site to prevent air pollution.
• Out of the 49 existing trees, 7 trees were cut and 22 new trees were planted which are native to the region.
• More than 50% paved area uses high SRI pavers.
• Openings have been designed in the building to maximize cross ventilation.
ÞÞ Water management:
• Reduction of more than 59% from the GRIHA base case has been demonstrated in landscape water demand
through use of highly efficient drip irrigation system.
• Reduction of 60% from the GRIHA base case has been demonstrated in building water use by installing water
efficient flush and flow fixtures.
• Total fresh water demand of the building is reduced by 89% because of circulation of recycled waste water for
various building activities.
ÞÞ Energy Optimization:
• High efficacy lamps are installed for exterior lighting which is operated by timer controller.
• Energy consumption is reduced to 31% as against the GRIHA benchmark. Building is equipped with efficient
LEDs and BEE 5-star rated air conditioners in the interiors.
• EPI reduction of 34.3% from GRIHA benchmark has been demonstrated.
• 68.5% of the habitable spaces are day lit and meet the daylight factors prescribed by the National Building Code
of India.
ÞÞ Renewable Energy Technology installed on site:
• Solar water heater of 6.5 kL capacity is installed in the building which has a saving potential of 47677 kWh per
year amounting to 73% savings as against conventional energy consumption.
ÞÞ Waste Management:
Bengaluru
• Multi-colored bins are used in the building for segregation of dry and wet waste.
• Demarcated segregated space has been allocated for collecting waste from the entire building before transferring
it to the recycling/disposal stations.
ÞÞ Sustainable Building Materials:
• Pozzolana Portland Cement (PPC) and Gyproc plaster indicating use of 30% fly-ash content by weight has been
used in plaster and masonry mortar.
• Low embodied energy materials are used for building construction.
Integrated Design Team:
Client : ITC Limited
Project Coordinator : Central Projects Organisation, ITC Limited
Principal Architect : M/s CnT Architects
Landscape Architect : M/s OIKOS Studios
Project Management Consultant : Central Projects Organisation, ITC Limited
Structural Consultant : M/s isa –Structural Studio
Electrical Consultant : M/s AECOM
Green Building Design and Certification : M/s Environment Design Consultant Pvt. Ltd.
You might also like
- CFR o & M Manual - Pearson NoidaDocument30 pagesCFR o & M Manual - Pearson Noidaverma.ankita91No ratings yet
- Group Literature StudyDocument63 pagesGroup Literature StudyPrachi SomaniNo ratings yet
- TeriDocument15 pagesTeriAr Shahbaz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Latest Griha Version (Griha-V2019-Abridged-Manual)Document170 pagesLatest Griha Version (Griha-V2019-Abridged-Manual)rajat charaya100% (3)
- Case Study (1) - CompressedDocument6 pagesCase Study (1) - CompressedRaghavendra RaoNo ratings yet
- Video 3.7: Kalpana Housing Complex, AurovilleDocument2 pagesVideo 3.7: Kalpana Housing Complex, AurovilleAissatou Inna YayaNo ratings yet
- Romi KhoslaDocument32 pagesRomi KhoslaSugandha GuptaNo ratings yet
- ECO Friendly Architecture: Assignment - 4Document7 pagesECO Friendly Architecture: Assignment - 4Shalaka DhandeNo ratings yet
- Lit StudyDocument25 pagesLit StudyMerlin JoelNo ratings yet
- Green Building Case Study: India'S First Net-Zero Energy Building-Indira Paryavaran Bhavan, New DelhiDocument9 pagesGreen Building Case Study: India'S First Net-Zero Energy Building-Indira Paryavaran Bhavan, New Delhirupali lateNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document8 pagesPresentation 1Nirbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study2-Sanskar KalakendraDocument8 pagesCase Study2-Sanskar KalakendraVed BhandwalkarNo ratings yet
- Unitech Horizon: Housing Case StudyDocument1 pageUnitech Horizon: Housing Case StudyTanya SirohiNo ratings yet
- Ashol Lall: Beacon of Sustainable Architecture: IRRAD Gurgaon by Ashok B Lall ArchitectsDocument2 pagesAshol Lall: Beacon of Sustainable Architecture: IRRAD Gurgaon by Ashok B Lall ArchitectsMonisha100% (1)
- Rail Niram Nilayam, HyderabadDocument8 pagesRail Niram Nilayam, HyderabadmanonmaniNo ratings yet
- Sidhartha Estella - Sector 103, GurgaonDocument24 pagesSidhartha Estella - Sector 103, GurgaonSunil SheoranNo ratings yet
- Center, Noida: Patni (i-GATE) KnowledgeDocument1 pageCenter, Noida: Patni (i-GATE) KnowledgeMuskaan RampalNo ratings yet
- Passive Cooling Technique in Composite ClimateDocument34 pagesPassive Cooling Technique in Composite ClimateUmang VashisthaaNo ratings yet
- Literature StudyDocument27 pagesLiterature StudyHaktasticDemonNo ratings yet
- Ar. Raj Rewal: Working LifeDocument15 pagesAr. Raj Rewal: Working Lifepranita chavan0% (1)
- Desktop Study - International (Architectural College) - 1Document38 pagesDesktop Study - International (Architectural College) - 1lakshmi akshaya maddiNo ratings yet
- Himalayan Institute of AlternativesDocument2 pagesHimalayan Institute of AlternativesMathewsNo ratings yet
- AR Anupama KundooDocument7 pagesAR Anupama KundooShreya MagoNo ratings yet
- Linked Hybrid by Steven HollDocument16 pagesLinked Hybrid by Steven HollbarathiNo ratings yet
- Case Study: 04-Teri University, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi: VISIT TIME: (3:00pm-5pm)Document9 pagesCase Study: 04-Teri University, Vasant Kunj, New Delhi: VISIT TIME: (3:00pm-5pm)Pragati SinghalNo ratings yet
- Ar. B S Bhooshan: Philosophy and WorksDocument30 pagesAr. B S Bhooshan: Philosophy and WorksLeelaprasad ChigurupalliNo ratings yet
- Infosys Campus: ProjectDocument19 pagesInfosys Campus: ProjectSharvani MedaNo ratings yet
- Buildings 239 12 Olympia Tech Park Chennai 0Document19 pagesBuildings 239 12 Olympia Tech Park Chennai 0Hastala vistaNo ratings yet
- Ar. Hafeez ContractorDocument32 pagesAr. Hafeez ContractorHardutt Purohit100% (1)
- Anil LaulDocument58 pagesAnil LaulKavi PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Curtain Wall Casestudy: 1.Kmc Corporate Office HyderabadDocument5 pagesCurtain Wall Casestudy: 1.Kmc Corporate Office HyderabadNimse ManavNo ratings yet
- Study Report-Element One, GurgaonDocument63 pagesStudy Report-Element One, GurgaonLakshay LakshayNo ratings yet
- Laurie Baker (Document2 pagesLaurie Baker (Chitrarth GargNo ratings yet
- Case Study KalpanaDocument14 pagesCase Study KalpanaSamy100% (1)
- Apartment: The Construction and Assigned Usage of House or Building Collectively, For The Purpose of Sheltering PeopleDocument1 pageApartment: The Construction and Assigned Usage of House or Building Collectively, For The Purpose of Sheltering PeopleAbhinav BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Edifice Atal Akshay Urja BhavanDocument4 pagesEdifice Atal Akshay Urja BhavanAarti PalNo ratings yet
- Gandhi Ghat Barrack Pore, 1949Document5 pagesGandhi Ghat Barrack Pore, 1949Apurva mahadikNo ratings yet
- Sangath: Hot and Dry AhemdabadDocument16 pagesSangath: Hot and Dry AhemdabadAditi ZawarNo ratings yet
- Erikarai Cob Home: Special FeaturesDocument3 pagesErikarai Cob Home: Special Featuresdharshini deivasigamaniNo ratings yet
- 1.final Concept Sheet PDFDocument1 page1.final Concept Sheet PDFShruti JhaNo ratings yet
- Kohinoor Square Tower, Kohinoor Group, MumbaiDocument23 pagesKohinoor Square Tower, Kohinoor Group, MumbaiPushpak GaikarNo ratings yet
- Humanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat AurovilleDocument11 pagesHumanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat Auroville Humanscape S Habitat AurovilleKaran NayakNo ratings yet
- Ladakh Ecological Development Group (Ledeg) Hostel, LehDocument27 pagesLadakh Ecological Development Group (Ledeg) Hostel, LehAstha SinghNo ratings yet
- Ad 5 Case StudyDocument11 pagesAd 5 Case StudyPushkarani NNo ratings yet
- Library Study of Housing ApartmentsDocument28 pagesLibrary Study of Housing ApartmentsMandeep Kaur BainsNo ratings yet
- Case Study G. HousingDocument21 pagesCase Study G. HousingVaani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Office BuildingDocument4 pagesCorporate Office BuildingtanujaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingDocument4 pagesComparative Economic Analysis of Low Rise High Rise BuildingJaskiratNo ratings yet
- Building Economics: Infosys, HyderabadDocument8 pagesBuilding Economics: Infosys, HyderabadIshita Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Thesis Synopsis - 2021 PDFDocument23 pagesThesis Synopsis - 2021 PDFMadiha RehmathNo ratings yet
- Unitech Signature Tower-South City I - Gurugram: Report 3Document6 pagesUnitech Signature Tower-South City I - Gurugram: Report 3mandeepNo ratings yet
- Kohinoor Square - AltissimoDocument13 pagesKohinoor Square - Altissimovinaympe0% (1)
- Presentation ON Ar. Romi Khosla: Presented By: Harshita RanaDocument18 pagesPresentation ON Ar. Romi Khosla: Presented By: Harshita RanaHarshita RanaNo ratings yet
- Sarath City Mall Desktop FinalDocument14 pagesSarath City Mall Desktop Finalkeshi boddeda100% (1)
- KhargharDocument4 pagesKhargharMahima palNo ratings yet
- Laurie Baker Center of Habitat StudiesDocument9 pagesLaurie Baker Center of Habitat StudiesAksh RdNo ratings yet
- PMA Madhushala's Community Center Features Undulating and ArtisticDocument12 pagesPMA Madhushala's Community Center Features Undulating and Artisticflower lilyNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Site Planning:: Reducing Water ConsumptionDocument1 pageSustainable Site Planning:: Reducing Water Consumptionsaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- Engineers India LTD Campus: Integrated Design TeamDocument1 pageEngineers India LTD Campus: Integrated Design Teamm aNo ratings yet
- Construction of New Government Medical College, BalasoreDocument1 pageConstruction of New Government Medical College, BalasoreNaveen kishoreNo ratings yet
- BEL Academy For ExcellenceDocument1 pageBEL Academy For ExcellenceAarti PalNo ratings yet
- Infosys, ChennaiDocument2 pagesInfosys, ChennairajyamgarNo ratings yet
- FFF PDFDocument1 pageFFF PDFrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- AR Architecture and Planning: Part A: CommonDocument2 pagesAR Architecture and Planning: Part A: Commonrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- Rise of The Idea of ExpositionsDocument20 pagesRise of The Idea of Expositionsrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- Architecture - Residential Architecture of The 19th and 20th CenturiesDocument10 pagesArchitecture - Residential Architecture of The 19th and 20th Centuriesrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- HOA5 Lesson Plan Jan 2019Document3 pagesHOA5 Lesson Plan Jan 2019rajat charayaNo ratings yet
- History of Constructivism in The 20th Century: A.S.TroelstraDocument32 pagesHistory of Constructivism in The 20th Century: A.S.Troelstrarajat charayaNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 19th Century PDFDocument12 pagesArchitecture of 19th Century PDFrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- Saarrthi Sovereign Pune - 0Document1 pageSaarrthi Sovereign Pune - 0rajat charayaNo ratings yet
- HousingDocument6 pagesHousingrajat charayaNo ratings yet
- The Mines ActDocument33 pagesThe Mines ActSamuel RajNo ratings yet
- Health & SafetyDocument21 pagesHealth & SafetyPoorna RathnayakaNo ratings yet
- 01 Nival Tech MEP Consultants Profile Jan 201Document22 pages01 Nival Tech MEP Consultants Profile Jan 201NagiahTNo ratings yet
- Massey University Low Decile School Research Paper PDFDocument58 pagesMassey University Low Decile School Research Paper PDFSaranyaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Calcium BufferDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Calcium BufferCarlos GanuzaNo ratings yet
- Baxi Climatizacion Slu - Sila RCV 300 - 1841vs03 - enDocument4 pagesBaxi Climatizacion Slu - Sila RCV 300 - 1841vs03 - encolomboiplNo ratings yet
- MSDS M.E.KDocument94 pagesMSDS M.E.KqNo ratings yet
- Air BalancingDocument23 pagesAir BalancingpNo ratings yet
- West of England Loss Prevention Bulletin The Carriage of Soya Beans in BulkDocument4 pagesWest of England Loss Prevention Bulletin The Carriage of Soya Beans in BulkCenk Çoban100% (1)
- Jandy Heaters LXI ManualDocument56 pagesJandy Heaters LXI ManuallunicyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Dynamic Modeling and Simulation of A Heating System For A Multi-Zone Office Building Equipped With Demand Controlled Ventilation Using MATLAB/SimulinkDocument6 pagesThermal Dynamic Modeling and Simulation of A Heating System For A Multi-Zone Office Building Equipped With Demand Controlled Ventilation Using MATLAB/SimulinkThành PhươngNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: Turbec T100Document154 pagesInstallation Manual: Turbec T100mritsoudisNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practice in PlumbingDocument294 pagesPrinciples and Practice in PlumbingKate Aponte100% (2)
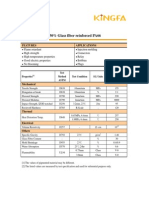
- PA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA66Document2 pagesPA66-RG301: Flame Retardant, 30% Glass Fiber Reinforced PA66watnaNo ratings yet
- Factories ActDocument47 pagesFactories ActarunNo ratings yet
- Field Monitoring Data On A Residential Exhaust Air Heat Pump System (Air-To-Air Heat Pump)Document7 pagesField Monitoring Data On A Residential Exhaust Air Heat Pump System (Air-To-Air Heat Pump)Tatiana GasparNo ratings yet
- Ashraef08pubsDocument40 pagesAshraef08pubsAbel Herrera Ordonez100% (1)
- Welding Safety Policy ProcedureDocument16 pagesWelding Safety Policy ProcedureIkyegh IshaNo ratings yet
- Nptel R and C Lecture Notes Lec 42Document38 pagesNptel R and C Lecture Notes Lec 42Kart01No ratings yet
- Disposable Formwork For Ventilated Under-Fl Oor CavitiesDocument24 pagesDisposable Formwork For Ventilated Under-Fl Oor CavitiesDaliform GroupNo ratings yet
- Window Facade Magazine Cover Stor WebDocument11 pagesWindow Facade Magazine Cover Stor WebTmt TarekNo ratings yet
- Direct-Heating Electric BoilersDocument2 pagesDirect-Heating Electric BoilersDorian MarcelNo ratings yet
- Smoke Control System CalcDocument14 pagesSmoke Control System Calckumar123raju100% (2)
- Effect of The Window Position in The Building Envelope On Energy ConsumptionDocument9 pagesEffect of The Window Position in The Building Envelope On Energy ConsumptionMemoonaNo ratings yet
- Annual Survey Checklist For Oil Chemical TankerDocument11 pagesAnnual Survey Checklist For Oil Chemical TankerrpNo ratings yet
- PHPP Workshop PresentationDocument121 pagesPHPP Workshop PresentationAna Gaina100% (1)
- Better Apartments Design Standards PDFDocument44 pagesBetter Apartments Design Standards PDFNivi100% (2)
- Sri Lanka Building CodeDocument58 pagesSri Lanka Building CodeIsuru Kasthurirathne33% (3)
- Car Park Jet FanDocument14 pagesCar Park Jet FanYan Aung50% (2)