Unut Conversion 1
Unut Conversion 1
Uploaded by
Vincent SangCopyright:
Available Formats
Unut Conversion 1
Unut Conversion 1
Uploaded by
Vincent SangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Unut Conversion 1
Unut Conversion 1
Uploaded by
Vincent SangCopyright:
Available Formats
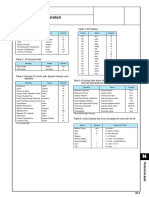
45.2.4 Derived units 42.2.
5 Decimal multiples and submultiples
All physical quantities have units derived from the base and Decimal multiples and submultiples of SI units are indicated by
supplementary SI units, and some of them have been given the prefix letters given in Table 45.2. Thus, MN is meganewton
names for convenience in use. Base, supplementary and some of and us is microsecond. Prefixes for the kilogram are expressed in
the derived units are listed in Table 45.1. terms of the gram, i.e. 1000kg= 1 Mg, not 1 kkg. There is a
preference to express stress as 1 N/mm2 instead of 1 MN/mm2.
Table 45.1 Systeme International base, supplementary and derived
units Table 45.2 Decimal prefixes
Quantity Unit name Derivation Unit Factor by which Prefix
symbol unit is multiplied Name Symbol
1018 exa E
Base
length Metre m 1015 peta P
mass Kilogram kg 1012 tera T
time Second s 109 giga G
electric current Ampere A 106 mega M
thermodynamic Kelvin K 103 kilo k
temperature 102 hecto h
luminous intensity Candela cd 10' deca da
amount of Mole mol 10 ' deci d
substance 10 2 centi c
10 3 milli m
Supplementary
plane angle Radian rad 10 6 micro u,
solid angle Steradian sr 10 9 nano n
Derived 10 l2 pico p
force Newton kgm/s 2 N 10 15 femto f
pressure, stress Pascal N/m 2 Pa 10 18 atto a
energy Joule N m, W s J
power Watt J/s W 45.2.6 Common variations and auxiliary units
electric charge, Coulomb As C
flux The main variations that are commonly applied to civil engi-
magnetic flux Weber Vs Wb neering are:
electric potential Volt J/C V Stress expressed as N/mm instead of pascals (Pa) (1 N/mm
magnetic flux Tesla Wb/m2 T = 1 MN/m= IMPa)
density Pressure, e.g. underwater, expressed as bar instead of pascals
resistance Ohm V/A Q (1 bar= 10OkPa, 1 mbar = 0.1 kPa)
inductance Henry Wb/A, Vs/A H Temperature expressed as 0C (Celsius or centigrade) instead
capacitance Farad C/V, A s/V F of K (kelvin) (O0C = 273.16K, 10O0C = 373.16 K)
conductance Siemens A/V S Mass expressed as tonne instead of kilograms (kg)
frequency Hertz s ' Hz ( I t =1000 kg)
luminous flux Lumen cd sr Im
illuminance Lux lm/m2 Ix Some of the common variations from the strict SI system are
radiation activity Becquerel s ' Bq listed in Table 45.3 and are here termed 'auxiliary' units.
absorbed dose Gray J/kg Gy
mass density Kilogram per Table 45.3 Auxiliary units
cubic metre kg/m3
dynamic viscosity Pascal-second Pa s Quantity Symbol SI
concentration Mole per cubic
metre mol/m3 Angle
linear velocity Metre per second m/s degree (°) TC/180 rad
linear acceleration Metre per second- minute (') — —
squared m/s2 second (") - -
angular velocity Radian per second rad/s Area
angular Radian per second- acre a 100 m2
2
acceleration squared rad/s hectare ha 0.01 km2
torque Newton metre Nm barn barn 10 28 m2
current density Ampere per square
metre A/m 2 Energy
resistivity Ohm metre Qm erg erg 0.1 uJ
conductivity Siemens per metre S/m calorie cal 4.186 J
thermal capacity Joule per kelvin J/K electron-volt eV 0.160 aJ
specific heat Joule per kilogram gauss-oersted GaOe 7.96 uJ/m3
capacity kelvin J/(kg K)
thermal Watt per metre Force
conductivity kelvin W/(m K) dyne dyn 10 uN
luminance Candela per square
Length
metre cd/m2 Angstrom A 0.1 um
You might also like
- Electricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese SyllabusDocument307 pagesElectricians Licence 'A' (Domestic) - Maltese Syllabusdavidegrima100% (18)
- Radiologic Science For Technologists: Physics, Biology, and Protection. ISBN 0323081355, 978-0323081351Document23 pagesRadiologic Science For Technologists: Physics, Biology, and Protection. ISBN 0323081355, 978-0323081351gabrielhypsz100% (17)
- Young & Freedman University Physics 13thDocument2 pagesYoung & Freedman University Physics 13thFatih Yıldız0% (2)
- Conversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesConversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringElma CruzNo ratings yet
- UnitsDocument16 pagesUnitsVinayChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Unidades para Formato ApaDocument4 pagesUnidades para Formato ApaJaneNo ratings yet
- Power and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsDocument19 pagesPower and Energy Measurement Units and Techniques: 2.1 The SI System and Conversion FactorsSatyam SankhuaNo ratings yet
- The International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesThe International System of Units, Fundamental Constants, and Conversion FactorsSamir ZaghloolNo ratings yet
- SI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDocument6 pagesSI Base Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolHazem SobhiNo ratings yet
- PEAAPP1Document4 pagesPEAAPP1yvNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsDocument3 pagesAppendix A: SI Units: Rules About Writing UnitsLuis SanchezNo ratings yet
- Math FormulasDocument173 pagesMath Formulasrajkumar.manjuNo ratings yet
- Formulas 4Document1 pageFormulas 4Anavheoba Abraham100% (1)
- SI SystemDocument19 pagesSI SystemmyscribdzoneNo ratings yet
- Appendix---Conversion-Guide_1996_Handbook-of-Refractory-Carbides-and-NitrideDocument4 pagesAppendix---Conversion-Guide_1996_Handbook-of-Refractory-Carbides-and-NitrideWilson SCKUDLAREKNo ratings yet
- Lab Ex1Document7 pagesLab Ex1karluiscinensepogiNo ratings yet
- HT Rate Calculations - Helical CoilsDocument4 pagesHT Rate Calculations - Helical CoilssandeshNo ratings yet
- Reading 1Document11 pagesReading 1shafyvonommyNo ratings yet
- AppendixDocument9 pagesAppendixPhuc Truong DucNo ratings yet
- Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI) The Modernized Metric SystemDocument4 pagesSi Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI) The Modernized Metric Systemazizah salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument33 pagesUnit ConversionmukhleshNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument46 pagesEngineering PhysicsChe BlaiseNo ratings yet
- SI Unit Conversion TableDocument4 pagesSI Unit Conversion TableGhazali ZuberiNo ratings yet
- The Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Document5 pagesThe Modern Metric System : Si Quick Reference Guide: International System of Units (SI)Sama UmateNo ratings yet
- International UnitsDocument10 pagesInternational Unitspilas_nikolaNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversion Factors: Shuhong WangDocument5 pagesUnits and Conversion Factors: Shuhong Wangoblex99No ratings yet
- Base Si UnitsDocument10 pagesBase Si UnitsJehana NaolNo ratings yet
- Physics Science (Lecture ExportDocument55 pagesPhysics Science (Lecture ExportSATYAM RATHOURNo ratings yet
- SI Units RulesDocument13 pagesSI Units RulesKarthikeyan GNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes BGCSEDocument118 pagesPhysics Notes BGCSEdintshangthemoNo ratings yet
- SI Base UnitsDocument11 pagesSI Base UnitsHasan BashoriNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)Document167 pagesGravimetric Analysis (PDFDrive)ChilaNo ratings yet
- Basic Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDocument2 pagesBasic Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDhruv AsodariaNo ratings yet
- Si Bi̇ri̇mleri̇ PDFDocument1 pageSi Bi̇ri̇mleri̇ PDFMurat C.No ratings yet
- SMathLib 095Document10 pagesSMathLib 095Wesly CenterwallNo ratings yet
- Basic and Derived Si UnitsDocument2 pagesBasic and Derived Si UnitsJey KNo ratings yet
- Introductory Physics - Mashuri L. Warren - San Francisco, 1979 - W. H. Freeman - 9780716710080 - Anna's ArchiveDocument716 pagesIntroductory Physics - Mashuri L. Warren - San Francisco, 1979 - W. H. Freeman - 9780716710080 - Anna's ArchiveNIpun KumarNo ratings yet
- Astm 02Document623 pagesAstm 02Bilel RebaiNo ratings yet
- Si Units PDFDocument4 pagesSi Units PDFசெல்வ குமார்No ratings yet
- Physics Muster PDFDocument36 pagesPhysics Muster PDFMarlon FariaNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations, Constants, and Conversion Factors: Section 11Document15 pagesAbbreviations, Constants, and Conversion Factors: Section 11princeowusuafriyie20No ratings yet
- Named Units Derived FromDocument5 pagesNamed Units Derived FromYuunari LingNo ratings yet
- Basic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Document2 pagesBasic & Derived Quantity (SI Units)Muhammad Noman Mughal75% (4)
- Analy Tisch e Chemie EnglischDocument168 pagesAnaly Tisch e Chemie EnglischHas GomNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1Document8 pagesLesson 1: Units, Physical Quantities, and Vectors: Physics 1GM ShioriNo ratings yet
- ASME Secc II D Si UnitsDocument3 pagesASME Secc II D Si UnitsCARLOS MARIONo ratings yet
- Units+Dimensions Sshandout2024Document14 pagesUnits+Dimensions Sshandout2024kariukiesther913No ratings yet
- Graphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)Document18 pagesGraphic Relationships of SI Units With Names (U.S. National Bureau of Standards, LC 1078, December 1976.)annisa putriNo ratings yet
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDocument6 pagesQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsRajkumar ANo ratings yet
- 2 Units and MeasurementDocument19 pages2 Units and Measurementgakphysics9No ratings yet
- 4-D020-R0-Conductor Sizing-20111121Document8 pages4-D020-R0-Conductor Sizing-20111121vigneshwarannnNo ratings yet
- TD 302 Cemp EEx-d Technische Catalogus ATEX 63-315Document87 pagesTD 302 Cemp EEx-d Technische Catalogus ATEX 63-315TrePcaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Reckoner 1.10.2014Document28 pagesElectrical Reckoner 1.10.2014RamkiNo ratings yet
- Source:: S.I. Units of MeasurementDocument2 pagesSource:: S.I. Units of Measurementnripen kalitaNo ratings yet
- Easurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: IDocument28 pagesEasurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: Ipankaj baviskarNo ratings yet
- (NBS Special Publication, 330) International Bureau of Weights and Measures - The International System of Units (SI) PDFDocument2 pages(NBS Special Publication, 330) International Bureau of Weights and Measures - The International System of Units (SI) PDFMihay BerlinschiNo ratings yet
- Derived QuantityDocument3 pagesDerived Quantityclara veronicaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors PDFDocument3 pagesConversion Factors PDFArbenson CNo ratings yet
- Mil STD 271Document103 pagesMil STD 271Byungsuk ShimNo ratings yet
- Open Loop - 0125-0145Document21 pagesOpen Loop - 0125-0145control 4uonlyNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and MatterDocument4 pagesMagnetism and MatterPrabal MahatoNo ratings yet
- Mwe Unit Wise Preparation Plan: UNIT-1 MICROWAVE TUBES ..5 TopicsDocument3 pagesMwe Unit Wise Preparation Plan: UNIT-1 MICROWAVE TUBES ..5 TopicsSajjala Poojith reddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationDocument19 pagesChapter 12 Fundamentals of Thermal RadiationM5M5KHNo ratings yet
- BEE Record BookDocument57 pagesBEE Record BookIT039- Jeel KalariyaNo ratings yet
- Day 266 Solution: Ashmit DuttaDocument2 pagesDay 266 Solution: Ashmit DuttaObama binladenNo ratings yet
- Atomic-structure-Theory & Solved Examples Module-6Document17 pagesAtomic-structure-Theory & Solved Examples Module-6Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument66 pagesHeat ExchangersSaptarshi MandalNo ratings yet
- Introduction Emd Lab 1Document24 pagesIntroduction Emd Lab 1Izzianie Irdina Mohd RasidNo ratings yet
- A Level DerivationsDocument43 pagesA Level DerivationsCai MingleiNo ratings yet
- AS80 50 ManualDocument1 pageAS80 50 ManualwijiyatiNo ratings yet
- Topology and Preliminary Design Slotless Brushless Motor: of DCDocument3 pagesTopology and Preliminary Design Slotless Brushless Motor: of DCflorin91No ratings yet
- Neutral Currents in Three Phase Wye Systems: Power Systems Engineering DataDocument10 pagesNeutral Currents in Three Phase Wye Systems: Power Systems Engineering DataMehdi_Mashayekhi_172No ratings yet
- Alternating Current. Byju'sDocument222 pagesAlternating Current. Byju'sGaurav BhandariNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - MechanicsDocument2 pagesWeek 1 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 7: Electric Motors and GeneratorsDocument43 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 7: Electric Motors and Generatorserra100% (1)
- GPS - TG 15AE 38 02 - TongyuDocument1 pageGPS - TG 15AE 38 02 - TongyuAdie Phawank100% (1)
- Battery Inspection Checklist: Section A - Customer DataDocument4 pagesBattery Inspection Checklist: Section A - Customer DataRaed Al-Haj0% (1)
- Perc Comms 1Document9 pagesPerc Comms 1Miguel BulanteNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ChemistryDocument6 pagesReviewer in ChemistryStella SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Webassign: HWK 8 - Chapter 20 (Homework) Current Score: 54 / 59 Due: Wednesday, August 3 2016 11:59 PM PDTDocument10 pagesWebassign: HWK 8 - Chapter 20 (Homework) Current Score: 54 / 59 Due: Wednesday, August 3 2016 11:59 PM PDTJasdeep singhNo ratings yet
- HW#7 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHW#7 SolutionsChristopher ThaiNo ratings yet
- Rotation Debate Jun2022 SMALLDocument20 pagesRotation Debate Jun2022 SMALLP AntonyNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation Rayleigh JeansDocument4 pagesBlackbody Radiation Rayleigh JeansMyName One999No ratings yet
- Series Capacitor Compensated AC Filterless Flexible LCC HVDC With Enhanced Power Transfer Under Unbalanced FaultsDocument12 pagesSeries Capacitor Compensated AC Filterless Flexible LCC HVDC With Enhanced Power Transfer Under Unbalanced FaultsTRIAD TECHNO SERVICESNo ratings yet
- 12th - Physics - VOL 1 - EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.onlineDocument352 pages12th - Physics - VOL 1 - EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.onlineIntellekt Business Services100% (1)
- Focn Quiz-1 Section B 13-10-2023Document2 pagesFocn Quiz-1 Section B 13-10-2023vika43121No ratings yet
- Practice Test-02 - Arjuna NEET (2025) - 09.06.2024 - QuestionsDocument18 pagesPractice Test-02 - Arjuna NEET (2025) - 09.06.2024 - Questionskenyen.jarekNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Relay Operating TimeDocument30 pagesCalculation of Relay Operating TimeMortuzaNo ratings yet