Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Uploaded by
Abby MontealegreCopyright:
Available Formats
Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Uploaded by
Abby MontealegreOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Therapeutic:: Brand Name: PLASIL Classifications
Uploaded by
Abby MontealegreCopyright:
Available Formats
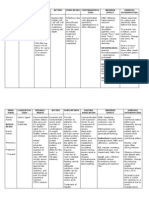
Brand Name: PLASIL CLASSIFICATIONS Therapeutic: Antiemetics ACTIONS Physiologic Mechanism Decreased nausea and vomiting.
. Decreased symptoms of gastric stasis. Pharmacologic Mechanism Blocks dopamine receptors in chemoreceptor trigger zone of the CNS. Stimulates motility of the upper GI tract and accelerates gastric emptying. INDICATION Management of esophageal reflux Treatment and prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting NURSING CONSIDERATIONS Assess patient for nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, and bowel sounds before and after administration. May cause drowsiness. Advise patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol and other CNS depressant while taking this medication. Advise patient to notify health care professional immediately if involuntary movement of eyes, face or limbs occurs.
Generic Name: Hyoscine ButylBromide Brand Name: Buscopan Classification: Belladona alkaloid, antimuscarinic Indication & Dosages: Spastic states
Adults: 0.4 to 0.8 mg P.O. Delirium, preanesthetic sedation and obstetric amnesia with analgesics
Adults: 0.3 to 0.65 mg I.V., I.M., or subcutaneously. Dilute solution with sterile water for injection before giving I.V.
Children: 0.006mg/kg I.V., I.M., or subcutaneously. Maximum dose, 0.3 mg. Dilute solution with sterile water for solution before giving I.V. To prevent nausea and vomiting from motion sickness
Adults: One Transderm-Scop, formulated to deliver 1mg scopolamine over 3 days, applied to the skin behing the ear at least 4 hours before antiemetic is needed. Or, 0.3 to 0.65 mg hydrobromide I.V., I.M. or subcutaneously. Or, 0.25 to 0.8 mg P.O. 1 hour before exposure to motion. Further doses of 0.25 to 0.8 mg may be given t.i.d., p.r.n. Children: 6 mcg/k or 200 mcg hydrobromide I.V., I.m., or subcutaneously Mode of Action: Inhibits muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on autonomic effectors innervated by postganglionic cholinergic neurons. May effect neural pathways originating in the inner ear to inhibit nausea and vomiting.
Contraindication: Contraindicated in patients with angleclosure glaucoma, obstructive uropathy, obstructive disease of the GI tract, asthma, chronic pulmonary disease, myasthenia gravis, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony, unstable CV status in acute hemorrhage, tachycardia from cardiac insufficiency, or toxic megacolon. Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitive to belladonna or barbiturates. Use cautiously in patients with autonomicneuropathy, hyperthyroidism, coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart failure, hypertension, hiatal hernia with ferlux esophagitis, hepatc or renal disease, known as suspected GI infection, or ulcerative colitis. Use cautiously in children. Use cautiously in patients in hot or humid environments; drug can cause heat stroke.
Side Effects: Frequent: Dry mouth (sometimes severe), decreased sweating, constipation. Occasional: Blurred vision; bloated feeling; urinary hesitancy; somnolence (with high dosage); headache; intolerance to light; loss of taste; nervousness; flushing; insomnia; impotence; mental confusion or excitement (particularly in the elderly and children); temporary light-headedness (parenteral form); local irritation(with parenteral form).
Adverse Reaction: Overdose may produce temporary paralysis of ciliary muscle; papillary dilation; tachycardia; palpitations; hot, dry, or flushed skin; absence of bowel sounds; hyperthermia; increased respiratory rate; EKG abnormalities; nausea; vomiting; rash over face or upper trunk; CNSstimulations; and psychosis (marked by agitation, restlessness, rambling speech, visual hallucinations, paranoid behavior, and delusions, followed by depression).
Nursing Responsibilities: Advise patient to apply patch the night before a planned trip. Transdermal method releases a controlled therapeutic amount of drug. Transderm-Scop is effective if applied 2 or 3 hours before experiencing motion but is more effective if applied 12 hours before. Instruct patient to remove one patch before applying another
Instruct patient to wash and dry hands thoroughly before and after applying the transdermal patch (on dry skin behind the ear) and before touching the eye because pupil may dilate. Tell patient to discard patch after removing it and to wash application site thoroughly. Tell patient that if patch becomes displaced, he should remove it and apply another patch on a fresh skin site behind the ear. Alert patient to possible withdrawal signs or symptoms (nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness) when transdermal system is used for longer than 72 hours. Advice patient that eyes may be ore sensitive to light while wearing patch. Advice patient to wear sunglasses for comfort Urge patient to report urinary hesitancy or urine retention.
Indications for Furosemide Treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, chronic renal failure, hepatic cirrhosis, and acute pulmonary edema. It is also used for treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other hypertensives. Can also be used for treatment of hypercalcemia. Routes and Dosage of Furosemide Edema and Hypertension PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially, 20-80 mg/dose; may increase by 20-40 mg/dose at 6-8 hour intervals. May titrate up to 600 mg/day in severe edematous state, CHILDREN: 1-6 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6-12 hours. IM/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 20-40 mg/dose; may repeat in 1-2 hours and increase by 20 mg/dose. CHILDREN: 1-2 mg/kg/dose q6-12 hours. NEONATES: 1-2 mg/kg/dose q12-24 hours. IV infusion: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Bolus of 0.1 mg/kg, then 0.1 mg/kg/hour; may double q2hours. Maximum: 0.4 mg/kg/hour. CHILDREN: 0.05 mg/kg/hour, titrate to desired effect. Action of Furosemide Enhances excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium by direct action at ascending limb of loop of Henle and produces a diuretic effect. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Furosemide Side Effects of Furosemide Increase in urinary frequency or volume Nausea Gastric upset with cramping Diarrhea or constipation Electrolyte disturbances Dizziness or light headedness Headache Blurred Vision Paresthesia Photosensitivity Rash
Weakness Bladder spasm Restlessness Diaphoresis Flank or loin pain
Adverse Reactions of Furosemide Excessive diuresis may lead to increased water loss and electrolyte depletion resulting to hypokalemia, hyponatremia, and dehydration. Sudden volume depletion may result in increased risk f thrombosis, circulatory collapse, or sudden death. Acute hypotensive episodes may occur, sometimes several days after beginning of therapy. Ototoxicity manifested as deafness, vertigo, and tinnitus may occur especially in patients with severe renal impairment. It can exacerbate diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erthematosus, gout, and pancreatitis. Blood dyscrasias have been reported.
Nursing Consideration for Clients Taking Furosemide Give with food to avoid gastroinestinal upset, preferably with breakfast (to prevent nocturia). If given IM, temporary pain at injection site may be noted. Check vital signs especially blood pressure for hypotension prior to administration. Assess baseline electrolyte, particularly check for low potassium. Assess edema, skin turgor, and mucous membranes for hydration status. Assess muscle strength and mental status. Obtain baseline weight. Initiate Input and Output monitoring. Note extent of diuresis.
ndication for Digoxin Digoxin is used as a prophylactic management and treatment of CHF, control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation. It is also used in the treatment and prevention of recurrent paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. Routes and Dosage of Digoxin Dosage should be adjusted in elderly patients with renal dysfunction. Larger doses often required for adequate control of ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter. Administer loading dosage in several doses at 4 to 8 hour intervals. Usual Dosage for Adults (Rapid Loading Dosage) IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.6-1 mg PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: Initially 0.5-0.75 mg, additional doses of 0.125-0.375 mg at 6 to 8 hour intervals. RANGE: 0.75-1.25 mg Usual Dosage for Adults (Maintenance Dosage) PO/IV: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 0.125-0.375 mg/day Usual Dosage for Children (Rapid Loading Dosage)
IV: Children >10 years: 8-12 mcg/kg; 5-10 years: 15-30 mcg/kg; 2-5 years: 25-35 mcg/kg; 1-24 mos: 30-50 mcg/kg; FULL-Term: 20-30 mcg/kg; PREMATURE: 15-25 mcg/kg PO: Children >10 years: 10-15 mcg/kg; 5-10 years: 20-35 mcg/kg; 2-5 years: 30-40 mcg/kg; 1-24 mos: 30-50 mcg/kg; FULL-TERM: 25-35 mcg/kg; PREMATURE: 20-30 mcg/kg Usual Dosage for Children (Maintenance Dosage) PO/IV: CHILDREN: 25%-35% loading dose (20%-30% for premature). Dosage in Renal Impairment Total digitalizing dose should decrease by 50% in end-stage renal disease. If creatinine clearance is 10-50 mg/min, dosage should be 25%-75% normal. If creatinine clearance is <10ml/min, dosage should be 10%-25% normal. Action of Digoxin Digoxin increases the influx of calcium from extracellular to intracellular cytoplasm. It potentiates the activity of the contractile heart muscle fibers and increases the force of myocardial contraction. Decreases conduction through the SA and AV nodes. Side Effects and Adverse Reactions of Digoxin Side Effects of Digoxin None known; however, there is a very narrow margin of safety between a therapeutic and toxic result.
Adverse Reactions of Digoxin GI disturbances (anorexia, nausea, vomiting) Neurologic abnormalities (fatigue, headache, depression, weakness, drowsiness, confusion, nightmares) Facial pain Personality changes Ocular disturbances (photo phobia, light flashes, halos around bright objects, yellow or green color perception) may be noted
Nursing Considerations for Clients Taking Digoxin Assess apical pulse for 60 secs (30 secs if on maintenance therapy). If pulse is <60/min (<70min for children), withhold drug, contact physician. Blood samples are best taken 6-8 hours after dose or just before next dose. May be given without regard to meals. Tablets may be crushed. Monitor pulse for bradycardia, EKG for arrhythmias for 1-2 hours after administration (excessive slowing of pulse may be a first clinical sign of toxicity). Assess for GI disturbances, neurologic abnormalities (signs of toxicity) every 2-4 hours during digitalization (daily during maintenance). Monitor serum potassium, magnesium levels.
You might also like
- KAPS Exam Paper For Australian Pharmaceutical Council ExamDocument40 pagesKAPS Exam Paper For Australian Pharmaceutical Council ExampiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidejenwiley318096% (75)
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart FailureTrisha Vergara100% (1)
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 pagesGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Drug CardsDocument19 pagesDrug Cardslani83% (6)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- NANDA-I, NOC, and NIC Linkages in Nursing Care Plans For HospitalDocument190 pagesNANDA-I, NOC, and NIC Linkages in Nursing Care Plans For HospitalAngel Riley Hampton100% (2)
- Tetralogy of Fallot Case PresentationDocument32 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Case PresentationUday Kumar50% (2)
- LVAD in An Hbo2 ChamberDocument5 pagesLVAD in An Hbo2 ChamberTony LeeNo ratings yet
- Organo-Therapy Handbook 2Document5 pagesOrgano-Therapy Handbook 2kaswalder100% (1)
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide DiclofenacDocument7 pagesMetoclopramide DiclofenacRasco, Allen jayNo ratings yet
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- V. Phenothiazines (ALIPHATIC)Document3 pagesV. Phenothiazines (ALIPHATIC)Christine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument5 pagesAcetazolamideIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (DR)Document19 pagesDrug Study (DR)09159054476No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument4 pagesAcetazolamideAnkit RuhilNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- 33-36 Medications PDFDocument15 pages33-36 Medications PDFJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument8 pagesDrugsShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 pagesComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNo ratings yet
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument21 pagesAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyJhann0% (1)
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- Generic Name LasixDocument4 pagesGeneric Name LasixSabita PaudelNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument4 pagesAzithromycinBrittany ClontzNo ratings yet
- Medications: Medication Name Generic/Trade Classification Pregnancy CategoryDocument8 pagesMedications: Medication Name Generic/Trade Classification Pregnancy CategoryapalestiNo ratings yet
- METFORMINDocument4 pagesMETFORMINkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCaptopril Drug StudyKimzie Joy Basco100% (1)
- Medication FlashcardsDocument10 pagesMedication FlashcardsSilvio PerezNo ratings yet
- Medication ListDocument14 pagesMedication ListMarie LeyvaNo ratings yet
- Perindopril ErbumineDocument8 pagesPerindopril ErbumineYanna Habib-MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Weekly Drug CardsDocument43 pagesWeekly Drug CardsErica SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTDocument14 pagesPharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyRhanne Bolante100% (1)
- Atropine SulfateDocument5 pagesAtropine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Atorvastatin CalciumDocument2 pagesAtorvastatin Calciumshiraz.aNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Information: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument5 pagesPrescribing Information: 1. Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_20% (1)
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument39 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyJenny Rose GriñoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOB Drug StudyKismet Summons100% (8)
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ObDocument13 pagesDrug Study ObJash Michael BarbajoNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin 1Document31 pagesLevofloxacin 1Fallen AngelNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- Obat ObgynDocument8 pagesObat ObgynMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneAfidz Azuddin HaziqNo ratings yet
- Mini RinDocument5 pagesMini Rinlovely_dyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengNo ratings yet
- Docetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionDocument11 pagesDocetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionywNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Capstone Case Study Final - CHFDocument3 pagesCapstone Case Study Final - CHFapi-351999622No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Decreased Cardiac OutputCarmela Balderas Romantco80% (5)
- CCC Practice NBME Questions 1Document4 pagesCCC Practice NBME Questions 1NamarNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintDocument69 pagesCOVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintSkunk BOINo ratings yet
- Tromboembolismo Pulmonar Manejo PDFDocument7 pagesTromboembolismo Pulmonar Manejo PDFGeovannaHGNo ratings yet
- NutriDiet ReviewerDocument6 pagesNutriDiet ReviewerCherry BoticarioNo ratings yet
- Pink Puffer Blue BloaterDocument10 pagesPink Puffer Blue BloaterMelinda MarianniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PDFDocument71 pagesCardiovascular System PDFramadanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Artificial Intelligence Versus Real Time PhysicianDocument4 pagesComparison of Artificial Intelligence Versus Real Time PhysicianYony GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANANo ratings yet
- Cardio 2015 + AnswerDocument18 pagesCardio 2015 + Answerstella pangestikaNo ratings yet
- HF2019Document24 pagesHF2019Sima Noviantika100% (2)
- Weight-Bearing Exercise For Better Balance (WEBB)Document44 pagesWeight-Bearing Exercise For Better Balance (WEBB)Neha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Documento MeloDocument7 pagesDocumento MeloDanilsa CastroNo ratings yet
- Shock 2022 SeminarDocument17 pagesShock 2022 Seminarrosie100% (2)
- EMMaA - IMDocument100 pagesEMMaA - IMR IghtzedNo ratings yet
- ESC Guidelines On Cardio-Oncology - 2022Document133 pagesESC Guidelines On Cardio-Oncology - 2022nicolasNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Study Guide HandoutDocument86 pagesCardiology Study Guide Handoutalinida89100% (1)
- Cardio Nursing - Course Audit 2Document320 pagesCardio Nursing - Course Audit 2Ciella Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Document15 pagesChronic Heart Failure (Gagal Jantung Kronik)Grup 9B Viscera tahun 2No ratings yet
- Revalida QuestionsDocument6 pagesRevalida QuestionsCarolyn Calupitan100% (1)
- Refeeding Syndrome GuidelineDocument5 pagesRefeeding Syndrome GuidelinePejman AhmadiNo ratings yet
- CVS Short Cases: Yapa Wijeratne M/07/189Document2 pagesCVS Short Cases: Yapa Wijeratne M/07/189Li FaungNo ratings yet