BOW-Physics 1
BOW-Physics 1
Uploaded by
joshann251Copyright:
Available Formats
BOW-Physics 1
BOW-Physics 1
Uploaded by
joshann251Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
BOW-Physics 1
BOW-Physics 1
Uploaded by
joshann251Copyright:
Available Formats
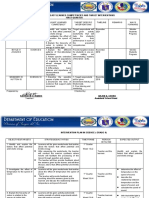
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
PHYSICS 1
Budget of Work
1st Semester, School Year 2023-2024
No. of No. of Written No. of Performance
Grading Content
Learning Competencies Teaching Works Tasks (Indicate
Period (Lesson/Topics)
Hours (Unit Tests) Particular Tasks)
First ORIENTATION & 1. Identify the grading system, requirements, and house rules 1. Reflection on the
Quarter INTRODUCTION for Physics 1 for a conducive learning environment. concept of Physics
2. Present the overview of concepts under Physics 1
3. Explain how Physics 1 will be beneficial to the students in
their everyday lives and to the strand they have chosen.
4. Present strategies which could be help them in learning 1
Physics 1
o Note taking strategies (Cornell & 5R’s)
o Weekly study schedule
o Critical thinking strategies “thinking how, instead of
why”
UNITS AND MEASUREMENT Week 1 STEM_GP12EU-Ia-1 Solve measurement problems 1 1. Measurement in 1. Guess the measure of
1. The effect of instruments involving conversion of units, expression of measurements in Physics a pen (measurement)
on measurements scientific notation 2. Uncertainty and 2. Dart Board game
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
2. Uncertainties and Week 1 STEM_GP12EU-Ia-2 Differentiate accuracy from Error Analysis (Precise and
deviations in measurement precision Accurate)
1
3. Sources and types of error Week 1 STEM_GP12EU-Ia-3 Differentiate random errors from 3. Worded Problem
systematic Errors solving thru oral
Week 1 STEM_GP12EU-Ia-5 Estimate errors from multiple recitation
1
measurements of a physical quantity using variance
VECTORS Week 1 STEM_GP12V-Ia-8 Differentiate vector and scalar 1. Vector 1. Locate my x in the
1
1. Vectors and vector quantities addition world of y (vector)
addition Week 1 STEM_GP12V-Ia-9 Perform addition of vectors 1 2. Worded Problem
Week 1 STEM_GP12V-Ia-10 Rewrite a vector in component solving thru oral
1 recitation
form
KINEMATICS Week 2 STEM_GP12Kin-Ib-12 Convert a verbal description of 1. Kinematics 1. Running from origin
1. Position, time, a physical situation involving uniform acceleration in one 1 Equation of forming a cross
distance, displacement, dimension into a mathematical description. Motion (speed vs velocity)
speed, average velocity, Week 2 STEM_GP12KINIb-14 Interpret displacement and 2. Graphical 2. Marble rolling in ramp
instantaneous velocity velocity, respectively, as areas under velocity vs. time and 1 Analysis of with a yarn from the
2. Average acceleration, and acceleration vs. time curves Motion top (displacement) vs
instantaneous acceleration Week 2 STEM_GP12KINIb-15 Interpret velocity and marble with a yarn
acceleration, respectively, as slopes of position vs. time and 1 from the bottom
velocity vs. time curves (velocity)
Week 2 STEM_GP12KINIb-16 Construct velocity vs. time and 3. Running in a curve vs
1 straight line (velocity
acceleration vs. time graphs, respectively, corresponding to a
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
given position vs. time-graph and velocity vs. time graph and vs. acceleration)
vice versa 4. Rolling marble in
Week 2 STEM_GP12KINIb-17 Solve for unknown quantities in different slope
equations involving one-dimensional uniformly accelerated 1 (velocity-acceleration
motion, including free fall motion vs time graph)
5. Worded Problem
solving thru oral
Week 2 STEM_GP12KINIb-19 Solve problems involving one-
recitation page 79-80
dimensional motion with constant acceleration in contexts such
1 (solving for unknown
as, but not limited to, the “tail-gating phenomenon”, pursuit,
quantities)
rocket launch, and freefall problems
6. Free fall (problem
solving)
KINETICS Week 3 STEM_GP12KIN-Ic-20 Describe motion using the 1. Motion in 1D and 1. Catching the bouncing
1
1. Relative Motion concept of relative velocities in 1D and 2D 2D ball (Projectile Motion)
a. Position, distance, Week 3 STEM_GP12KIN-Ic-22 Deduce the consequences of 1. Projectile motion 2. Longest distance of a
displacement, speed, the independence of vertical and horizontal components of 1 2. Circular motion paper plane
average velocity, projectile motion (Projectile Motion)
instantaneous velocity, Week 3 STEM_GP12KIN-Ic-23 Calculate range, time of flight, 3. Yank me (Circular
1
average acceleration, and maximum heights of projectiles motion)
and instantaneous Week 3 STEM_GP12KIN-Ic-25 Infer quantities associated with 1 4. Worded Problem
acceleration in 2- and circular motion such as tangential velocity, centripetal solving thru oral
3- dimensions acceleration, tangential acceleration, radius of curvature recitation
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
2. Projectile Motion Week 3 STEM_GP12KIN-Ic-26Solve problems involving two-
3. Circular Motion dimensional motion in contexts such as, but not limited to ledge
1
jumping, movie stunts, basketball, safe locations during firework
displays, and Ferris wheels
NEWTON’S LAW Week 4 STEM_GP12N-Id-28 Define inertial frames of 1. Newton’s Law of 1. Egg drop activity (1st
1
1. Newton’s Law’s of Motion reference. Motion Law)
2. Inertial Reference Frames Week 4 STEM_GP12N-Id-31 Identify action-reaction pairs. 1 2. Types of contact 2. Ball Ramp (2nd Law)
3. Action at a distance force Week 4 STEM_GP12N-Id-32 Draw free-body diagrams. 1 forces 3. Balloon Rocket in a
4. Types of contact forces: Week 4 STEM_GP12N-Ie-33 Apply Newton’s 1st law to obtain 3. Free-body rope with straw (3rd
tension, normal force, quantitative and qualitative conclusions about the contact and 1 Diagrams Law)
kinetic and static friction, noncontact forces acting on a body in equilibrium 4. Worded Problem
fluid resistance Week 4 STEM_GP12N-Ie-34Differentiate the properties of static solving thru oral
5. Action-Reaction Pairs 1 recitation
friction and kinetic friction
6. Free-Body Diagrams Week 5 STEM_GP12N-Ie-36 Apply Newton’s 2nd law and
7. Applications of Newton’s kinematics to obtain quantitative and qualitative conclusions
8. Laws to single-body and 1
about the velocity and acceleration of one or more bodies, and
multibody dynamics the contact and noncontact forces acting on one or more bodies
9. Problem solving using
Week 5 STEM_GP12N-Ie-38 Solve problems using Newton’s 1
Newton’s Laws
Laws of motion in contexts such as, but not limited to, ropes and
pulleys, the design of mobile sculptures, transport of loads on
conveyor belts, force needed to move stalled vehicles,
determination of safe driving speeds on banked curved roads
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
WORK AND ENERGY Week 5 STEM_GP12WE-If-40 Calculate the dot or scalar 1. Work 1. Pulling chair using a
1
1. Dot or Scalar Product product of vectors 2. Kinetic & rope in different angle
2. Work done by a force Week 5 STEM_GP12WE-If-41 Determine the work done by a Potential energy (Work & Power)
1
3. Work-energy relation force acting on a system 3. Conservation of 2. Falling vs moving
4. Kinetic energy Week 6 STEM_GP12WE-If-42 Define work as a scalar or dot Energy book (Potential &
1
5. Power product of force and displacement Kinetic)
6. Conservative and Week 6 STEM_GP12WE-If-43 Interpret the work done by a 3. Pendulum
nonconservative forces force in one dimension as an area under a Force vs. Position 1 (Conservative energy)
7. Gravitational potential curve 4. Book dragging on the
energy Week 6 STEM_GP12WE-Ig-48 Relate the gravitational potential floor (non-
8. Elastic potential energy 1 conservative energy)
energy of a system or object to the configuration of the system
9. Equilibria and potential Week 6 STEM_GP12WE-Ig-49 Relate the elastic potential 5. Worded Problem
energy diagrams 1 solving thru oral
energy of a system or object to the configuration of the system
10. Energy Conservation, Week 6 STEM_GP12WE-Ig-50 Explain the properties and the recitation
Work, and Power 1
effects of conservative forces
Problems Week 7 STEM_GP12WE-Ig-53 Use potential energy diagrams
to infer force; stable, unstable, and neutral equilibria; and 1
turning points
Week 7 STEM_GP12WE-Ihi-55 Solve problems involving work, 1
energy, and power in contexts such as, but not limited to,
bungee jumping, design of roller-coasters, number of people
required to build structures such as the Great Pyramids and the
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
rice terraces; power and energy requirements of human
activities such as sleeping vs. sitting vs. standing, running vs.
walking.
CENTER OF MASS, Week 7 STEM_GP12WE-Ihi-56Differentiate center of mass and 1. Center of Mass 1. Circular disc styro
1
MOMENTUM, IMPULSE AND geometric center 2. Impulse and foam rolling upward
COLLISIONS Week 7 STEM_GP12MMICIh-57 Relate the motion of center of Momentum (center of mass)
1. Center of mass mass of a system to the momentum and net external force 1 3. Collisions 2. Rolling Marble in a
2. Momentum acting on the system ramp (Momentum,
3. Impulse Week 8 STEM_GP12MMICIh-58Relate the momentum, Impulse and Collision)
1
4. Impulse-momentum impulse, force, and time of contact in a system 3. Worded Problem
5. relation Week 8 STEM_GP12MMICIi-60Compare and contrast elastic solving thru oral
1
6. Law of conservation of and inelastic collisions recitation
7. momentum Week 8 STEM_GP12MMICIi-61Apply the concept of restitution
8. Collisions 1
coefficient in collisions
9. Center of Mass, Impulse, Week 8 STEM_GP12MMICIi-63Solve problems involving center 1
10. Momentum, and Collision of mass, impulse, and momentum in contexts such as, but not
Problems limited to, rocket motion, vehicle collisions, and ping-pong.
TOTAL 40 hours
ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-1 Calculate the moment of inertia 1. Rotation 1. Ring vs disc rolling
1
Second AND ROTATIONAL about a given axis of single-object and multiple-object systems 2. Equilibrium (rotation)
Quarter DYNAMICS Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-3 Calculate magnitude and 2. Skyhook Center of
1 Gravity (Equilibrium)
direction of torque using the definition of torque as a cross
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
1. Moment of inertia product 3. Worded Problem
2. Angular position, angular Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-4 Describe rotational quantities solving thru oral
1
velocity, angular using vectors recitation
acceleration Torque Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-5 Determine whether a system is
1
3. Static equilibrium in static equilibrium or not
4. Rotational kinematics Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-6 Apply the rotational kinematic
1
5. Work done by a torque relations for systems with constant angular accelerations
Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-9 Determine angular momentum
1
of different systems
Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-10 Apply the torque-angular
1
momentum relation
Week 1 STEM_GP12REDIIa-8 Solve static equilibrium
problems in contexts but not limited to see-saws, cable-hinge-
1
strut system, leaning ladders, and weighing a heavy suitcase
using a small bathroom scale
GRAVITY Week 2 STEM_GP12G-IIb-16Use Newton’s law of gravitation to 1. Motion of 1. Spandex Gravity Well
1
infer gravitational force, weight, and acceleration due to gravity Heavenly Bodies (gravity)
1. Newton’s Law of Week 2 STEM_GP12Red-IIb- 18Discuss the physical 2. Ellipse Making
1
2. Universal Gravitation significance of gravitational field (Kepler’s law of
3. Gravitational field Week 2 STEM_GP12Red-IIb- 19Apply the concept of planetary)
1
4. Gravitational potential gravitational potential energy in physics problems. 3. Worded Problem
5. Energy Week 2 STEM_GP12Red-IIb- 20Calculate quantities related to 1 solving thru oral
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
6. Orbits planetary or satellite motion recitation
7. Kepler’s laws of planetary Week 3 STEM_GP12G-IIc-22For circular orbits, relate Kepler’s
motion third law of planetary motion to Newton’s law of gravitation and 1
centripetal acceleration
PERIODIC MOTION Week 3 STEM_GP12PMIIc-24 Relate the amplitude, frequency, 1. Periodic Motion 1. YouTube video /
1. Periodic Motion angular frequency, period, displacement, velocity, and 1 2. Production and rotating & pendulum
2. Simple harmonic motion: acceleration of oscillating systems Properties of (simple harmonic
3. spring-mass system, Week 3 STEM_GP12PMIIc-25 Recognize the necessary Waves motion)
simple conditions for an object to undergo simple harmonic motion 2. Worded Problem
4. pendulum Week 3 STEM_GP12PMIIc-27 Calculate the period and the 1 solving thru oral
5. Damped and Driven frequency of spring mass, simple pendulum, and physical recitation
Oscillation pendulum
6. Periodic Motion Week 4 STEM_GP12PMIId-28 Differentiate underdamped,
1
7. experiment overdamped, and critically damped motion
8. Mechanical waves Week 4 STEM_GP12PMIId-31 Define mechanical wave,
longitudinal wave, transverse wave, periodic wave, and 1
sinusoidal wave
Week 4 STEM_GP12PMIId-32 From a given sinusoidal wave
function infer the speed, wavelength, frequency, period, 1
direction, and wave number
MECHANICAL WAVES AND Week 4 STEM_GP12MWSIIe-34 Apply the inverse-square 1 1. Sounds Basics 1. Compression of
SOUNDS relation between the intensity of waves and the distance from waves in a bottle
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
1. Sound the source (sound)
2. Wave Intensity Week 5 STEM_GP12MWSIIe-35 Describe qualitatively and 2. Worded Problem
1
3. Interference and beats quantitatively the superposition of waves solving thru oral
4. Standing waves Week 5 STEM_GP12MWSIIe-36 Apply the condition for recitation
1
5. Doppler effect standing waves on a string
FLUID MECHANICS Week 5 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-40 Relate density, specific gravity, 1. Density 1. Layer of Density
1. Specific gravity mass, and volume to each other 2. Pressure (density)
1
2. Pressure Week 6 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-41 Relate pressure to area and 3. Archimedes’ 2. Step on the egg
3. Pressure vs. Depth force Principle and (pressure)
4. Relation Week 6 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-42 Relate pressure to fluid density Buoyancy 3. Coin vs ship
1
5. Pascal’s principle and depth. 4. Hydrodynamics (buoyancy)
6. Buoyancy and Week 6 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-43 Apply Pascal’s principle in 4. Ping pong ball
1
Archimedes’ Principle analyzing fluids in various systems levitation
7. Bernoulli’s principle Week 6 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-44 Apply the concept of buoyancy (Hydrodynamics)
1 5. Worded Problem
and Archimedes’ principle
Week 7 STEM_GP12FM-IIf-46 Apply Bernoulli’s principle and solving thru oral
continuity equation, whenever appropriate, to infer relations 1 recitation
involving pressure, elevation, speed, and flux
TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Week 7 STEM_GP12TH-IIg-49 Explain the connection between 1. Heat and 1. Ball & ring experiment
1. Zeroth law of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics temperature, thermal 1 Temperature (Thermal Expansion)
thermodynamics and equilibrium, and temperature scales 2. Thermal 2. Balloon popping
Temperature Week 7 STEM_GP12TH-IIg-50 Convert temperatures and 1 Expansion (Conduction)
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
measurement temperature differences in the following scales: Fahrenheit, 3. Heat Transfer 3. Food Coloring in hot &
2. Thermal expansion Celsius, Kelvin cold water submerge
3. Heat and heat capacity Week 7 STEM_GP12TH-IIg-51 Define coefficient of thermal into its opposite
expansion and coefficient of volume expansion, sizes of stars, temperature
and surface temperatures of planets 1 (convection)
Week 7 STEM_GP12TH-IIg-52 Calculate volume or length 4. Radiometer (radiation)
changes of solids due to changes in temperature 5. Worded Problem
Week 7 STEM_GP12TH-IIg-53 Solve problems involving solving thru oral
temperature, thermal expansion, heat capacity, heat transfer, recitation
and thermal equilibrium in contexts such as, but not limited to, 1
the design of bridges and train rails using steel, relative severity
of steam burns and water burns, thermal insulation
IDEAL GASES AND LAWS Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-57 Enumerate the properties of an 1. 1st Law of 1. Mini hot air balloon
1
OF THERMODYNAMICS ideal gas Thermodynamics (1st law of
1. Ideal gas law Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-58 Solve problems involving ideal 2. 2nd Law of thermodynamics)
2. Internal energy of an ideal gas equations in contexts such as, but not limited to, the design 1 Thermodynamics 2. Upside down hot and
gas of metal containers for compressed gases cold water (2nd law of
3. Heat capacity of an ideal Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-60 Interpret PV diagrams of a thermodynamics)
1
gas thermodynamic process 3. Worded Problem
4. Thermodynamic systems Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-61 Compute the work done by a solving thru oral
1
5. Work done during volume gas using dW=PdV recitation
changes Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-62 State the relationship between 1
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
6. 1st law of thermodynamics changes internal energy, work done, and thermal energy
7. Thermodynamic supplied through the First Law of Thermodynamics
processes: adiabatic, Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIh-63 Differentiate the following
isothermal, isobaric, thermodynamic processes and show them on a PV diagram: 1
isochoric isochoric, isobaric, isothermal, adiabatic, and cyclic
8. Heat engines Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIi-67 Calculate the efficiency of a
1
9. Engine cycles heat engine
10. Entropy Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIi-68 Describe reversible and
11. 2nd law of irreversible processes
1
Thermodynamics Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIi-69 Explain how entropy is a
12. Reversible and irreversible measure of disorder
processes Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIi-70 State the 2nd Law of
1
Thermodynamics
Week 8 STEM_GP12GLTIIi-71 Calculate entropy changes for
various processes e.g., isothermal process, free expansion, 1
constant pressure process, etc.
TOTAL 40 hours
Prepared: Checked: Noted:
JOSH ANN BAUTISTA AUREA P. DUNGCA ATTY. LARRY JUN R. LOBO
SHS Teacher I Master Teacher I Secondary School Principal II
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region III – Central Luzon
Schools Division Office of Angeles City
Angeles City National High School
Senior High School
STEM, Subject Group Head
Address: Mabuhay Street, Purok 3, Brgy. Pampang, Angeles City 2009
Contact Information: 0951-915-6625; 0923-617-4812
E-mail Address: acnhs.seniorhs@depedangelescity.com
You might also like
- General Physics I DLLDocument52 pagesGeneral Physics I DLLLaarni Chan75% (12)
- Mass-Spring System: Applications of Linear Differential EquationsDocument28 pagesMass-Spring System: Applications of Linear Differential EquationsABIR'S GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Tarlac State University: College of Teacher Education Bachelor of Elementary Education DepartmentDocument8 pagesTarlac State University: College of Teacher Education Bachelor of Elementary Education DepartmentMichelle Facun MorenoNo ratings yet
- BOW-Physics 1 RevisedDocument11 pagesBOW-Physics 1 Revisedjoshann251No ratings yet
- BOW-Physics 1 FinalDocument11 pagesBOW-Physics 1 Finaljoshann251No ratings yet
- DLL Gen Physics 1 Q1 Week 1 - 2024-2025Document5 pagesDLL Gen Physics 1 Q1 Week 1 - 2024-2025marilou garciaNo ratings yet
- DLL W1Document2 pagesDLL W1Harold MoralesNo ratings yet
- 3.september 5-9Document3 pages3.september 5-9Lyka BugarinNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 DLL1Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 DLL1Ed John OcampoNo ratings yet
- DLL - General PhysicsDocument4 pagesDLL - General PhysicsMariel Grace JameroNo ratings yet
- Gen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 1Document4 pagesGen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 1Heidi YutucNo ratings yet
- General Physics Lesson ExemplarDocument9 pagesGeneral Physics Lesson ExemplaranthonydongonNo ratings yet
- Q2 Math9 November-22-25Document7 pagesQ2 Math9 November-22-25Mohan William SharmaNo ratings yet
- G7 Q4 Week 01Document6 pagesG7 Q4 Week 01jell estabilloNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJay MellizaNo ratings yet
- DLL-1st Quarter - wk1Document5 pagesDLL-1st Quarter - wk1MELANIE ZARATENo ratings yet
- Week 1 TGDocument2 pagesWeek 1 TGJohn Paul ZagadoNo ratings yet
- DLL - W1 - 1ST SemDocument6 pagesDLL - W1 - 1ST SemMarvin DamascoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Lesson Plan - Vi VI: I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesMathematics Lesson Plan - Vi VI: I. ObjectivesDelilah ManzanNo ratings yet
- DLL SY24 1st W1Document4 pagesDLL SY24 1st W1Jeraldine CuetoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide Quarter Number: Quarter 1 Subject MatterDocument2 pagesTeaching Guide Quarter Number: Quarter 1 Subject Mattermina doteNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat 6th Week For COT FinalDocument5 pagesDLL Stat 6th Week For COT FinalJessa May MarcosNo ratings yet
- NimslpDocument7 pagesNimslpMikael Zohan UngkayNo ratings yet
- Sample DLL AlexisDocument4 pagesSample DLL AlexisAlexis Castillo IINo ratings yet
- wlpq1wk 1 2Document4 pageswlpq1wk 1 2Bing Sepe CulajaoNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 DLL2Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 DLL2Ed John OcampoNo ratings yet
- Gen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 1Document4 pagesGen Phy 1 Quarter 1 Week 1Bernardo GaborniNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document2 pagesWeek 1Marvin Darius LagascaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction (Vector Addition)Document2 pages01 Introduction (Vector Addition)sangcapluisjamakiNo ratings yet
- Mid General Module 1Document23 pagesMid General Module 1Julliefe DuranteNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 8-2Document2 pagesDLL Math 8-2Ai RenNo ratings yet
- Nazareth Institute of Alfonso Government Recognized CHED / TESDA / BID AccreditedDocument1 pageNazareth Institute of Alfonso Government Recognized CHED / TESDA / BID AccreditedMaria Gilane Releen100% (1)
- Week 1 2nd Q DLLDocument6 pagesWeek 1 2nd Q DLLLuisa GarcillanNo ratings yet
- DLL Pe 2Document4 pagesDLL Pe 2Jee En BeeNo ratings yet
- Tanauan City College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Batangas City of TanauanDocument23 pagesTanauan City College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Batangas City of TanauanQueenie Gonzales-AguloNo ratings yet
- DLL - Gen Math-Week 1Document5 pagesDLL - Gen Math-Week 1Jennelyn JacintoNo ratings yet
- COT1 2 Edited 3 1Document5 pagesCOT1 2 Edited 3 1Kristine Marie PamorNo ratings yet
- GM Quarter 1 Week 1Document5 pagesGM Quarter 1 Week 1Raul VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Q4 LE Mathematics 7 Lesson 7 Week 7Document11 pagesQ4 LE Mathematics 7 Lesson 7 Week 7Jessie YutucNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed 1Document4 pagesSemi Detailed 1REY N. VILLASTIQUENo ratings yet
- DLL 8Document11 pagesDLL 8Hazel MartinaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Weekly Home Learning Plan - Week 1Document12 pages1 - Weekly Home Learning Plan - Week 1do san namNo ratings yet
- Week 1 TGDocument4 pagesWeek 1 TGJohn Paul ZagadoNo ratings yet
- ENGPHYS SyllabusDocument5 pagesENGPHYS SyllabusKrissa C.No ratings yet
- G7-W1-Weekly Learning PlanDocument8 pagesG7-W1-Weekly Learning PlanMinda Balahya100% (1)
- Test AnalysisDocument2 pagesTest AnalysisMenchie PaynorNo ratings yet
- Grade Level Quarter / Domain DateDocument7 pagesGrade Level Quarter / Domain DateGen DeeNo ratings yet
- Gen p6 1 DLP MeasurementsDocument2 pagesGen p6 1 DLP MeasurementsSigfred Allen AlisboNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed-3 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSemi-Detailed-3 Lesson PlanREY N. VILLASTIQUENo ratings yet
- Junior-High DLPDocument10 pagesJunior-High DLPGrophel MesaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Council Weekly Home Learning Plan: 4 Quarter June 22 - July 6, 2021Document2 pagesGrade 7 - Council Weekly Home Learning Plan: 4 Quarter June 22 - July 6, 2021Fortune Myrrh BaronNo ratings yet
- S2 Physics Scheme 2024 3Document13 pagesS2 Physics Scheme 2024 3nanastase41No ratings yet
- Revised Q1 DLL Week 2Document6 pagesRevised Q1 DLL Week 2catherine narvaezNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q1 Wk5Document8 pagesScience8 Q1 Wk5Aizelle Taratara FaderoNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityDocument4 pagesSession 1 Session 2 Session 3 Session 4: Statistics AND ProbabilityEloiza Jane OrdenizaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To PhysicsA. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in General MathematicsReylaine Mitz BaldonNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen Math Week 6Document6 pagesDLL Gen Math Week 6Ram GazerNo ratings yet
- DLP 7 E's Particle Nature of Matter Group 3a Rtot 2018Document6 pagesDLP 7 E's Particle Nature of Matter Group 3a Rtot 2018KATHRYN CENTINALESNo ratings yet
- LLC With Intervention PlanDocument6 pagesLLC With Intervention PlanKATHLEEN DANDONo ratings yet
- Is the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionFrom EverandIs the Answer Reasonable?, Grade 4: The Test ConnectionNo ratings yet
- ADMModule - STEM - GP12N-Id-29Document23 pagesADMModule - STEM - GP12N-Id-29joshann251No ratings yet
- Soft Colors Ui Design For AgenciesDocument70 pagesSoft Colors Ui Design For Agenciesjoshann251No ratings yet
- KoreanDocument20 pagesKoreanjoshann251No ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated MotionDocument25 pagesUniformly Accelerated Motionjoshann251No ratings yet
- Simple Flashcards SlidesManiaDocument62 pagesSimple Flashcards SlidesManiajoshann251No ratings yet
- Coins PH Buy SellDocument10 pagesCoins PH Buy Selljoshann251No ratings yet
- 21529-Business Process Powerpoint-Amazing Business Process Powerpoint-16-9Document1 page21529-Business Process Powerpoint-Amazing Business Process Powerpoint-16-9joshann251No ratings yet
- Problem Solution PowerPoint Presentation 4 3Document1 pageProblem Solution PowerPoint Presentation 4 3joshann251No ratings yet
- 21529-Business Process Powerpoint-Amazing Business Process Powerpoint-4-3Document1 page21529-Business Process Powerpoint-Amazing Business Process Powerpoint-4-3joshann251100% (1)
- 20MD006Document2 pages20MD006aae15904No ratings yet
- Resonance: Resonance Describes The Phenomenon of Increased Amplitude That Occurs WhenDocument10 pagesResonance: Resonance Describes The Phenomenon of Increased Amplitude That Occurs WhenLijukrishnanNo ratings yet
- Wang2021 Article Z-domainModelingOfPeakCurrentMDocument11 pagesWang2021 Article Z-domainModelingOfPeakCurrentMSinyxNo ratings yet
- Pid ControlDocument34 pagesPid Controlciocioi iancuNo ratings yet
- ECE Mathematical Methods OCT 2022 ECE Board ExamDocument4 pagesECE Mathematical Methods OCT 2022 ECE Board ExamMark angelo RegosoNo ratings yet
- Model (A)Document2 pagesModel (A)omar7arazNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Rain-Wind-Induced Vibration of Cables in Cable-Stayed Bridges and Its MitigationDocument17 pagesExperimental Investigation of Rain-Wind-Induced Vibration of Cables in Cable-Stayed Bridges and Its MitigationELIOT PEZO ZEGARRANo ratings yet
- Waves: PhysicsDocument53 pagesWaves: Physicsjannie nNo ratings yet
- PHYS2614 Module Information 2023Document2 pagesPHYS2614 Module Information 2023kamogelomotloung23202No ratings yet
- University of BasraDocument4 pagesUniversity of BasraAbood DosaryNo ratings yet
- RLC Circuit Lab Report - ENGN 1218 - PSPICE IncludeDocument12 pagesRLC Circuit Lab Report - ENGN 1218 - PSPICE IncludeS RahmanNo ratings yet
- SPH 300Document5 pagesSPH 300kyleNo ratings yet
- Astm E756 05 2017Document6 pagesAstm E756 05 2017배배No ratings yet
- ControlDocument84 pagesControlominopaul2No ratings yet
- Power Plant Protection and Control Strategies For Blackout AvoidanceDocument22 pagesPower Plant Protection and Control Strategies For Blackout Avoidance北科大-林立No ratings yet
- Escc3901iss3 - ESCC Generic Specification No 3901Document34 pagesEscc3901iss3 - ESCC Generic Specification No 3901gooogaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Handling Vessel Behavior in Horizontal Plane in A Uniform Current Field During OperationDocument19 pagesAnchor Handling Vessel Behavior in Horizontal Plane in A Uniform Current Field During OperationLuana MarchioriNo ratings yet
- Contoh REPORT Open Ended CONTROLDocument32 pagesContoh REPORT Open Ended CONTROLtiko lolipopNo ratings yet
- MoorDyn Users Guide 2017-08-16Document17 pagesMoorDyn Users Guide 2017-08-16Arvin MonsterNo ratings yet
- Core Pure Unit Test 6 Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesCore Pure Unit Test 6 Differential Equationsishiwork2019No ratings yet
- Notes-OscillationsDocument9 pagesNotes-OscillationsMordecai ChimedzaNo ratings yet
- Oscillations and Waves Simple Harmonic MotionDocument18 pagesOscillations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motionloda lassanNo ratings yet
- Ieee Standard For Power Systems-Insulation CoordinationDocument21 pagesIeee Standard For Power Systems-Insulation Coordinationcarlos_alfaro_herreraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 AE5022Document9 pagesAssignment 1 AE5022Geprek BentoNo ratings yet
- Met304 ADocument5 pagesMet304 AVenkitaraj K PNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Vibrations of A Cantilever BeamDocument11 pagesLab 2 - Vibrations of A Cantilever BeamNeel NadparaNo ratings yet
- Ship DynamicsDocument32 pagesShip DynamicsJofin LukoseNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Control For AircraftDocument48 pagesFuzzy Logic Control For AircraftLokesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Solar Tracker Laboratory - Instructor ManualDocument41 pagesSolar Tracker Laboratory - Instructor ManualSandro SouzaNo ratings yet