M.Sc. Chemistry
M.Sc. Chemistry
Uploaded by
Pragyan ChutiaCopyright:
Available Formats
M.Sc. Chemistry
M.Sc. Chemistry
Uploaded by
Pragyan ChutiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
M.Sc. Chemistry
M.Sc. Chemistry
Uploaded by
Pragyan ChutiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus of M.Sc.
in Chemistry
JIS UNIVERSITY,
81, Nilgunj Road, Agarpara,
Kolkata-700109
JIS University Page 1
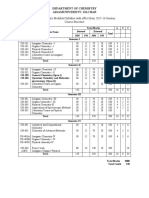
JIS UNIVERSITY, KOLKATA
M.Sc. in Chemistry
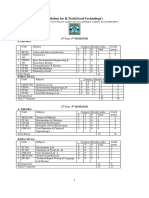
FIRST SEMESTER
Course PERIODS
CREDIT
Sl. Code SUBJECT
L T P
No.
THEORY
1 MCH-101 Analytical Chemistry I 3 1 0 4
2 MCH-102 Inorganic Chemistry I 3 1 0 4
3 MCH-103 Organic Chemistry I 3 1 0 4
4 MCH-104 Physical Chemistry I 3 1 0 4
Practical
5 MCH-191 Inorganic Chemistry Lab I 0 0 3 2
6 MCH-192 Organic Chemistry Lab I 0 0 3 2
7 MCH-193 Physical Chemistry Lab I 0 0 3 2
8 MSD-181 Project & Seminar 0 0 0 1
Total 12 4 9 23
JIS University Page 2
JIS UNIVERSITY, KOLKATA
M.Sc. in Chemistry
SECOND SEMESTER
Course PERIODS
CREDIT
Sl. Code SUBJECT
L T P
No.
THEORY
1 MCH-201 Analytical Chemistry II 3 1 0 4
2 MCH-202 Inorganic Chemistry II 3 1 0 4
3 MCH-203 Organic Chemistry II 3 1 0 4
4 MCH-204 Physical Chemistry II 3 1 0 4
5 MCS-201 Computer Applications in Physics and Chemistry 2 0 2 3
PRACTICAL
6 MCH-291 Inorganic Chemistry Lab II 0 0 3 2
7 MCH-292 Organic Chemistry Lab II 0 0 3 2
8 MCH-293 Physical Chemistry Lab II 0 0 3 2
9 MSD-281 Project & Seminar 0 0 0 1
10 MSD-282 Skill Development 0 0 0 1
Total 14 4 11 27
JIS University Page 3
JIS UNIVERSITY, KOLKATA
M.Sc. in Chemistry
THIRD SEMESTER
Course PERIODS
CREDIT
Sl. Code SUBJECT
L T P
No.
THEORY
1 Principles and Applications of Molecular 3 1 0 4
MCH-301
Spectroscopy
2 MCH-302 Biological Chemistry 3 1 0 4
3 MCH- Special Paper I (Inorganic/Organic/Physical) 3 1 0 4
303/304/305
4 MCH- Special Paper II (Inorganic/Organic/Physical) 3 1 0 4
306/307/308
5 MCH- Elective I 3 0 0 3
309/310
PRACTICAL
6 MCH- Inorganic/Organic/Physical Chemistry Lab III 0 0 9 6
391/392/393
7 MSD-381 Project & Seminar 0 0 0 1
Total 15 4 9 26
JIS University Page 4
JIS UNIVERSITY, KOLKATA
M.Sc. in Chemistry
FOURTH SEMESTER
Course PERIODS
CREDIT
Sl. Code SUBJECT
L T P
No.
THEORY
1 MCH-401 Spectroscopy for Structure Elucidation 3 1 0 4
2 MCH-402 Polymer and Materials Chemistry 3 1 0 4
3 MCH- Special Paper III (Inorganic/Organic/Physical) 3 0 0 3
403/404/405
4 MCH- Special Paper IV (Inorganic/Organic/Physical) 3 0 0 3
406/407/408
5 MCH- Elective II 3 0 0 3
409/410
PRACTICAL
6 MCHD-491 PROJECT 0 0 12 8
7 MSD-481 Project & Seminar 0 0 0 1
8 MSD-482 Skill Development 0 0 0 1
Total 15 2 12 27
JIS University Page 5
Semester III
Specialization Paper I
MCH-303: Advanced Bioinorganic and Organometallics
MCH-304: Advanced Organic Synthesis I
MCH-305: Advanced Quantum Mechanics
Specialization Paper II
MCH-306: Advanced Topics in Inorganic Chemistry I
MCH-307: Pericyclic and Photochemistry
MCH-308: Solid State Chemistry
Elective paper I
MCH-309: Supramolecular Chemistry & Drug Design
MCH-310: Nuclear Chemistry
Semester IV
Specialization Paper III
MCH-403: Inorganic Reaction Mechanism & Photochemistry
MCH-404: Advanced Organic Synthesis II
MCH-405: Electrochemistry
Specialization Paper IV
MCH-406: Advanced Topics in Inorganic Chemistry II
MCH-407: Heterocyclic Chemistry
MCH-408: Statistical Mechanics
Elective paper II
MCH-409: Chemical Applications of Group Theory
MCH-410: Advanced Spectroscopy
JIS University Page 6
Detailed Syllabus of First semester
MCH-101: Analytical Chemistry I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Introduction
Scope and objectives, classification of analytical methods, method selection, sample
processing, s teps in a quantitative analysis, quantitative range, data organisation, analytical
validations, limit of detection and quantification, tools of analytical chemistry and good lab
practices.
Unit-2: Separation techniques
Solvent extraction: principle, distribution ratio and partition coefficient, successive extraction
and separation, different methods of extraction systems, Craig extraction and counter current
distribution, problems.
Chromatography: general principle, classification, mathematical relations of capacity, selectivity
factor, distribution constant and retention time, chromatogram, elution in column
chromatography: band broadening and column efficiency, van Deemter equation, column
resolution, numerical problems, gas chromatography, high performance chromatography and
supercritical fluid chromatography: principles, methods, comparison and applications, thin-layer
chromatography, size-exclusion chromatography, ion chromatography and capillary
electrophoresis: principles, methods and applications.
Unit-3: Environmental chemistry
Introduction: environmental segments, atmospheric structure chemistry of lower and upper
atmosphere, radiation balance of earth.
Air pollution: major air pollutant, air quality standards and norms, determination of air
pollutants, Greenhouse effect, mechanistic pathways of smog formation and ozone hole, acid
rain, global warming, technology of air pollution abatement.
Water pollution: classification of water pollutants, characteristics of waste water, water quality
parameters and their measurements, biochemical effects of As, Pb, Cd, Hg and their chemical
speciation, eutrophication, waste water treatment: preliminary, primary, secondary, tertiary
treatment.
Solid waste disposal and management: classification and origin, methods of solid waste disposal,
microbiology involved in solid waste disposal.
Soil pollution: chemical composition of the soil, the exploitation of the mineral resources and
abuse of the earth, soil pollution due to natural and artificial agencies and its effects, remedial
measures to check the pollution.
Energy and Environment: energy sources, renewable and non-renewable, primary and secondary
fossil fuels, their occurrence and estimation.
JIS University Page 7
Recommended Books
1. R. L. Pecsok, L. D. Shields, T. Cairns and L.C. Mc William, Modern Methods of Chemical Analysis,
2nd Edition (1976), John Wiley, New York.
2. G. D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, 5th Edition (1994), John Wiley & Sons, New York.
3. D. A. Skoog, D.M. West, F.J. Holler, S.R. Crouch, Analytical Chemistry - An Introduction, 7th Edition
(2000), Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, London.
4. J. H. Kennedy, Analytical Chemistry: Principles, 2nd Edition (1990), Saunders Holt, London.
5. Mani Vasakam, Physico Chemical Examination of Water, Sewage and Industrial effluents, Pragati
Prakashan, 1991
6. F. W. Fifield and W. P. J. Hairens, Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2nd Edition (2000), Black
Well Science Ltd.
7. Colin Baird, Environmental Chemistry, W. H. Freeman and Company, New York (1995).
8. A. K. De, Environmental Chemistry, 4th Edition (2000), New Age International Private Ltd., New
Delhi.
9. Peter O. Warner, Analysis of Air Pollutants, 1st Edition (1996), John Wiley, New York.
10. S. M. Khopkar, Environmental Pollution Analysis, 1st Edition (1993), Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi.
11. S. K. Banerji, Environmental Chemistry, 1st Edition (1993), Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi.
JIS University Page 8
MCH-102: Inorganic Chemistry I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Lanthanides and Actinides
Lanthanides and Actinides, extraction, properties, redox chemistry, general characteristics,
spectral and magnetic properties.
Unit-2: Quantum mechanical approach to Chemical bonding
LCAO-MO and Huckel approximation to H2+, H2, homo and hetero diatomic, triatomic and
polyatomic molecules/ions, application of V.B. and M.O. theories to diatomic and polyatomic
molecules.
Unit-3: Coordination chemistry and Electronic spectra
Crystal field theory, crystal field diagram, concept of CFSE and OSPE and their applications,
Jahn-Teller distortions, Spectrochemical and Nephelauxetic series, thermodynamic, structural,
and kinetic aspects of CFT, ligand field theory, molecular orbital theory and angular overlap
model.
Electronic spectral properties of transition metal complexes: microstates, determination of
spectroscopic ground state/term symbols, Orgel and Tanabe-Sugano diagrams, selection rules for
spectral transition, d-d spectra, charge transfer spectra and calculation of crystal field parameters.
Recommended Books
1. F.A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th Edn. (1999), John Wiley & Sons,
New York.
2. J. E. Huheey, E. A. Keiter and R. L. Keiter, Inorganic Chemistry, Principles of structure and reactivity,
Harper Collins 1993.
3. R. S. Drago, Physical Methods in Inorganic Chemistry, International Edn. (1971), Affiliated East-West
Press, New Delhi.
4. Keith F. Purcell and John C. Kotz, Inorganic Chemistry, W. B. Sauders Com. (1987), Hong Kong.
5. K. Veera Reddy, Symmetry and Spectroscopy of Molecules, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., New
Delhi (1999).
6. B.N. Figgis, Introduction to Ligand Fields, Wiley Eastern Ltd. New Delhi (1976).
7. D. J. Newman, Betty, Crystal Field, Science, 2000
8. M. Chanda, Structure and Chemical bond, Tata McGraw Hill Atomic Edition, 2000.
9. D. F. Shriver, P. W. Atkins and C. H. Langford, Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 1990.
JIS University Page 9
MCH-103: Organic Chemistry I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit 1: Reaction mechanism I
Concise review on nucleophilic, electrophilic substitution reactions, and elimination reactions,
neighbouring group participation: the phenonium ion, participation by π and σ bonds,
Anchimeric assistance, classical versus non-classical carbonium ions- the present status.
Unit 2: Aromaticity
Huckel’s rule, concept of aromaticity in benzenoid and nonbenzenoid systems, alternate and non-
alternante hydrocarbons, annulenes, heteroannulenes, fullerenes, anti-aromaticity, pseudo-
aromaticity, homo-aromaticity.
Unit 3: Structural effects on reactivity
Linear free energy relationships (LFER), the Hammett equation, substitutent constants, theories
of substitutent effects, interpretation of σ-values, reaction constant ρ, deviations from Hammett
equation, dual - parameter correlations, inductive substituent constant, the Taft equation.
Unit 4: Stereochemistry
Molecular symmetry, chirality, point groups, stereoisomerism, configuration: relative and
absolute, determination of relative configuration: Prelog’s rule, Cram’s rule, and Sharpless rule,
conformation: conformational analysis of acyclic, cyclic, fused, spiro and bridged bicyclo-
systems with typical examples.
Recommended Books
1. Clayden, Greeves, Warren and Wothers, Organic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2001.
2. M.B. Smith & Jerry March, March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition (2001), John Wiley &
Sons, New York.
3. Peter Sykes, A Guide book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition (1997), Orient Longman
Ltd., New Delhi.
4. S. M. Mukherjee and S.P. Singh, Reaction Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Ist Edition (1990),
Macmillan India Ltd., New Delhi.
5. D. Nasipuri, Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, 2nd Edition (1994), Wiley Eastern Ltd., New
Delhi.
6. E.L. Eliel, S.H. Wilen and L.N. Mander, Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, Wiley Interscience,
New York (2004).
JIS University Page 10
MCH-104: Physical Chemistry I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Thermodynamics
Concise review of thermodynamics, concept of partial molar quantities and their significances,
Nernst heat theorem, consequences of Nernst heat theorem, entropy and third law of
thermodynamics: determination of absolute entropy, concept and significance of residual
entropy.
Thermodynamic probability and entropy, distribution laws: Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein
and Fermi-Dirac, concept of partition function: rotational, translational, vibrational and
electronic partition functions of diatomic molecules, concept of ensembles, relation between
partition functions with various thermodynamic functions, Gibb’s paradox.
Unit-2: Chemical kinetics
Concise review of chemical kinetics, fast reactions: luminescence and energy transfer processes,
kinetics study of fast reactions by stopped–flow and relaxation, and flash photolysis methods.
Rate equations of photochemical, chain and oscillatory reactions, thermodynamic treatment of
transition state theory, theories of unimolecular reactions: Lindemann-Christiansen hypothesis,
Hinshelwood, Rice-Ramsperger- Kassel (RRK), and Rice- Ramsperger-Kassel-Marcus (RRKM).
Unit-3: Surface chemistry
Adsorption: different types of adsorption, absorption vs adsorption, different adsorption
isotherms, unimolecular and bimolecular surface reaction, activation energy of such reactions,
volcano curve.
Transition state theory of surface reactions: rates of chemisorptions and desorption,
unimolecular and bimolecular surface reaction.
Micelles: Surface active agents and their classifications, micellization, factors affecting cmc of
surfactants. Thermodynamics of micellization: phase separation and mass action models.
Emulsions and reverse micelle.
Recommended Books
1. G.W. Castellan, Physical Chemistry, 3rd Edition, Narosa Publishing House
2. P.W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry, 8th Editions, Oxford University Press, New York
3. K.J. Lailder, Chemical Kinetics, 3rd Edition, Pearson
4. I.N. Levine, Physical Chemistry, 5th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publication Co, Ltd, New Delhi
5. B.K. Agarwal and M. Eisner, Statistical Mechanics, Wiley Eastern, New Delhi
6. D.A. Mcquarrie, Statistical Mechanics, California University Science Books
7. R. K. Patharia, Statistical Mechanics, Butterworth, Heinemann, Elsevier
8. Y. Moroi, Micelles: Theoretical and Applied Aspects, Plenum Press, New York (1992)
9. T. Engel, P. Reid, Thermodynamics, Statistical thermodynamics and Kinetics, Pearson
10. E. S. R. Gopal, Statistical Mechanics and Properties of Matter, Ellis Horwood, England,
1974.
JIS University Page 11
MCH-191: Inorganic Chemistry Lab I
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Quantitative analysis of metal ions in binary mixture by complexometric titrations
Synthesis and characterization of different coordination complexes
Separation and estimation of binary mixtures by ion-exchange method
Separation of cations or anions in a mixture by paper chromatography
MCH-192: Organic Chemistry Lab I
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Detection and identification of organic compounds through chemical test, UV and IR
Organic synthesis: Nitration, Bromination, Condensation, Reduction and Hydrolysis
involving at least two steps
MCH-193: Physical Chemistry Lab I
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Determination of specific rate constant of acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ester at two
different temperature and evaluate the corresponding thermodynamic parameters
Compare the strength of acids (HCl vs H2SO4) by studying the hydrolysis of ester
Evaluate the energy of activation for saponification of ester
Determination of rate constant of acid catalyzed hydrolysis of sucrose by a polarimeter
To construct the phase diagram of three component systems
Determination of heat of solution of oxalic acid from its solubility at different
temperature
Determination of isoelectric point
Verification of adsorption isotherm by adsorption of acetic acid on charcoal
Any other experiments related to thermodynamics, kinetics, adsorption and micelle
performed in the laboratory during the semester
Recommended Books
1. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, ELBS
2. Ghosal, Mahaparta and Nad, An Advanced Course in Practical chemistry
3. G. N. Mukherjee, Handbook of Practical Chemistry
4. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry
5. A. M. James, F. F. Prichard, Practical Physical Chemistry
6. Shoermaker, Garland, Experimental Physical Chemistry
JIS University Page 12
Detailed Syllabus of Second semester
MCH-201: Analytical Chemistry II
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Spectroscopic techniques
Theory, instrumentation and applications of X-rays (emission, absorption, diffraction and
fluorescence methods), atomic absorption spectroscopy, atomic fluorescence spectrometry,
atomic emission spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma-atomic absorption spectrometry.
Unit-2: Electroanalytical methods
Theory, instrumentation and applications of voltammetry, linear sweep voltammetry, anodic
stripping voltammetry, cyclic voltammetry, amperometry, coulometry, electrogravimetry and
polarography: electrochemical cell, reference and indicator electrodes, membrane electrodes,
electrode-solution interface layer, electrolytic process, DME, Cottrell equation, Ilkovic equation,
half wave potential and its significance, test of reversibility, current-voltage diagram.
Unit-3: Thermal methods
Theory, methodology and applications of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential thermal
analysis (DTA), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermal stability of covalent and
non-covalent bonds, thermal degradation, single crystal phase transformation,
thermochemiluminescence, thermometric titration, solid state reaction kinetics.
Recommended Books
1. R. L. Pecsok, L. D. Shields, T. Cairns and L.C. Mc William, Modern Methods of Chemical Analysis,
2 nd Edition (1976), John Wiley, New York.
2. G. D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, 5th Edition (1994), John Wiley & Sons, New York.
3. D.A. Skoog, Principles of Instrumental Analysis, 5th Edition (1998), Saunders College of Publishing,
Philadelphia, London.
4. D. A. Skoog, D.M. West, F.J. Holler, S.R. Crouch, Analytical Chemistry - An Introduction, 7th
Edition (2000), Saunders College Publishing, Philadelphia, London.
nd
5. J. H. Kennedy, Analytical Chemistry: Principles, 2 Edition (1990), Saunders Holt, London.
6. A. J. Bard, Electroanalytical Chemistry
7. J. W. Robinson, Atomic absorption Spectrometry
8. D. A. Skoog, D.M. West, F.J. Holler, Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry
9. H. H. Willard, L. L. Meritt, J. A. Dean and F. A. Settle, Instrumental Methods of Analysis
10. H.A. Strobel, Chemical Instrumentation: A Schematic Approach, 2nd Edition (1973)
JIS University Page 13
MCH-202: Inorganic Chemistry II
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Elements of group theory
Groups, subgroups, classes and characters, classes of symmetry operations, symmetry points
groups: representation of groups by matrices, representation of symmetry operator-tranformation
of basis vector, symmetry transformation of operators, the great orthogonality theorem and its
consequences, construction and application of character table.
Unit-2: Organometallic Chemistry I
Application of 18- electron and 16- electron rules to transition metal organometallics, structure,
bonding (pictorial mo-approach) and reactions of η2-ethylinic, η3-allylic and η5-cyclo-
pentadineyl compounds, structure and bonding of carbonyls, nitrosyls and related pi- acids, alkyl,
alkene, alkyne, π-allyl, polyene and cyclopolyene compounds; metal carbenes and carbynes,
isolobal analogy, Dewar-Chatt model, oxophilicity, Agostic interaction, organo-metallic
catalysts.
Unit-3: Bioinorganic Chemistry I
The roles of metal ions in biological process, Ion transport across biological membrane and its
significance, mechanism of Na+/K+-ion pump; Transport and storage of dioxygen: Active site
structures and bio functions of O2-uptake proteins: hemoglobin, myoglobin, hemocyanin and
hemerythrin, model synthetic dioxygen complexes.
Electron transfer in biology: Active site structures and functions of cytochromes, cytochrome
c; iron-sulfur proteins (ferredoxines). cytochrome c oxidase.
Recommended Books
1. F. A. Cotton, Chemical Applications of Group Theory
2. R. H. Crabtree, The Organometallic Chemistry of Transition Metals
3. B.D.Gupta and A.J. Elias, Basic Organometalltic Chemistry
4. I. Bertini, H. B. Grey, S. J. Lippard, J. S. Valentine, Bioinorganic Chemistry
5. Asim K. Das, Bioinorganic Chemistry
JIS University Page 14
MCH-203: Organic Chemistry II
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Reaction mechanism II
Addition to carbon-carbon multiple bonds: mechanistic and stereochemical aspects of addition
reactions involving electrophiles, nucleophiles and free radicals, regio- and chemo-selectivity,
orientation and reactivity, hydrogenation, hydroboration reaction.
Addition to carbon-hetero multiple bonds: mechanism of metal hydride reaction of substituted
and unsubstituted carbonyl compounds, acids, esters and nitriles. Addition of Grignard reagents,
organocopper, organozinc, organolithium and organosilane reagents to saturated and unsaturated
carbonyl compounds.
Unit-2: Organic Name reaction
Birch reduction, Aldol condensation, Wittig reaction, Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation, Nef
reaction, Favorskii reaction, Baeyer-Villiger oxidation, Claisen rearrangement, Beckmann
rearrangement, Shapiro reaction, Mitsunobu reaction, Hofmann-Loffler-Freytag reaction, Barton
reaction, Ene reaction, Mannich reaction, Stork enamine reaction, Michael addition, Robinson
annulation, Barton decarboxylation and deoxygenation reaction, Sharpless asymmetric
epoxidation, Norrish type-I & II reaction, di-pi methane rearrangement, paterno-Buchi reaction.
Unit-3: Reagents and Reactions
(i) Gilman’s reagent–Lithium dimethylcuprate, (ii) Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), (iii)
Dicyclohexyl carbodiimide (DDC), (iv) 1,3-Dithiane (Umpolung reagent), (v) Peterson’s
synthesis, (vi) Bakers yeast, (vii) DDQ, (viii) Palladium catalysed reactions, (ix) Woodward and
Prevost hydroxylation, (x) Iodotrimethyl silane.
Unit-4: Natural Products I
Biosynthesis of (i) Non-nitrogenous secondary metabolites from Shikinic acid, flavonoids and
related polyphenolics, (ii) mono- and di-terpenoids from Mevalonic acid (iii) tri-terpenoids from
geranyl pyrophosphate.
Recommended Books
1. Clayden, Greeves, Warren, Organic Chemistry
2. F.A. Carey, R.J. Sundberg, Advanced Organic Chemistry
3. W. Carruthers, I. Coldham, Modern method of Organic Synthesis
4. Michael B. Smith, Jerry March, March's Advanced Organic Chemistry. Reactions, Mechanisms, and
Structure
5. Jie Jack Li , Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Reaction Mechanisms
6. Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frank G. Favaloro, Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic
Synthesis
7. I. L. Finar, Organic Chemistry (Volume 1 & 2)
JIS University Page 15
MCH-204: Physical Chemistry II
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Quantum Mechanics
Origin of quantum mechanics, Black-body radiation, photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Pair
production, de Broglie’s hypothesis: Davisson-Germer’s and Thomson’s experiment, Wave-
particle duality: Franck-Hertz experiment, Young’s double slit experiment, Heisenberg’s
uncertainty principle.
Operators, Eigen functions, Hermitian operator, Postulates of quantum mechanics, Angular
momentum, its commutative relations, Ladder operator, Pauli spin operator, Schrodinger wave
equation and its formulation as an eigen value problem.
Translational motion of a particle, particle in one, two and three dimensional boxes, harmonic-
oscillator, rotational motion of a particle: particle on a ring, particle on a sphere, rigid rotator,
step-potential, tunneling, hydrogen atom.
Introduction to approximation methods: Perturbation theory and Variational method.
Unit-2: Electrochemistry
Quantitative treatment of Debye-Hückel theory of ion-ion interaction, its applications and
limitations, modification of Debye-Hückel law for finite-sized ions, Debye-Hückel-Onsagar
equation, association of ions: Bjerrum and Fuoss model, electrode kinetics, current-overpotential
relationship, Tafel equation and its importance.
Recommended Books
1. I. N. Levine, Quantum Chemistry, 5th Edition (2000), Pearson Educ., Inc. New Delhi
2. Donald A McQuarrie, Quantum Chemistry, Viva Student Edition, Viva Books, NewDelhi
3. D. J. Grffiths, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
4. J. L. Powell, B. Crasemann, Quantum Mechanics
5. D. A. McQuarrie, J. D. Simon, Physical Chemistry, A Molecular Approach, (1998), Viva Books, New
Delhi
6. Richard L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics
7. R.K. Prasad, Quantum Mechanics
8. Samuel Glasstone, An Introduction To Electrochemistry, Affiliated East-West Press Pvt. Ltd.-New
Delhi (2000)
9. J. O’M. Bockris, A. K. N. Reddy, Modern Electrochemistry, Vol. 2 A & B, 2 nd Edition, Plenum Press,
New York (1998)
JIS University Page 16
MCH-291: Inorganic Chemistry Lab II
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Qualitative analysis of mixture of compounds containing six radicals of which two are rare
elements
Titrimetric estimation of mixtures of metal ions by EDTA
Spectroscopic estimation of inorganic complexes
Job’s method of continuous variation
MCH-292: Organic Chemistry Lab II
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Separation of binary mixtures of solid-solid/liquid-solid/liquid-liquid organic
compounds and identification of individual components
Small scale organic synthesis by exploiting common organic reactions and their
purification
MCH-293: Physical Chemistry Lab II
L-T-P: 0-0-3 Credit: 2
Determination of rate constant of alkaline hydrolysis of ester conductometrically
Conductometric titration of mixture of acids (HCl and CH3CO2H)
Determination of the individual strengths of (NH4)2SO4 and Na2SO4 in a mixture
conductometrically
Conductometric titration of Zn(II) vs K4[Fe(CN)6] and determination of composition of the
complex
Determination of CMC of SDS conductometrically
Potentiometric titration of mixture of acids (HCl and CH3CO2H)
Determination of the formal redox potential of Fe2+/Fe3+ system potentiometrically
Potentiometric titration of K4[Fe(CN)6] by ZnSO4 or Pb(NO3)2 and determination of
composition of the complex
Verification of Lambert and Beer’s law. Also determine the concentration of an unknown
solution from calibration curve
Determination of pKin of bromocresol green indicator
Recommended Books
1. A.I. Vogel, Qualitative Inorganic Analysis
2. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, ELBS
3. Ghosal, Mahaparta and Nad, An Advanced Course in Practical chemistry
4. G. N. Mukherjee, Handbook of Practical Chemistry
5. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry
6. A. M. James, F. F. Prichard, Practical Physical Chemistry
7. Shoermaker, Garland, Experimental Physical Chemistry
JIS University Page 17
Detailed Syllabus of Third semester
MCH-301: Principles and Applications of Molecular Spectroscopy
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Fundamentals
Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter, Einstein coefficient, transition probability,
transition dipole moments and selection rules, intensity of spectral lines, line-widths and line
shapes, Fourier transforms in spectroscopy.
Unit-2: Rotational and Vibrational spectroscopy
Classifications of molecules based on topicity, microwave and vibrational spectroscopy of
diatomic and polyatomic molecules, energy levels, selection rules, isotope effect, non-rigidity on
spectral features, vibration and group frequency, vibration-rotation spectra of diatomic
molecules, origin of P, Q, and R branch, hot bands, applications.
Unit-3: Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectra of diatomic molecules, rotational and rotation- vibrational Raman transitions,
effects of nuclear spin, polarization of Raman lines, applications.
Unit-4: Electronic spectroscopy
Origin, selection rules, spectral features, Franck-Condon principle, dissociation and pre-
dissociation, rotational fine structure, charge transfer spectra, fluorescence and phosphorescence
spectra, applications.
Unit-5: LASER spectroscopy
General features, principles, characteristics of laser, population inversion, basic elements in laser
pulsed, lasers, laser cavity modes, Q-switching, mode locking, harmonic
generation, different lasers: He-Ne, Nd-YAG, titanium-sapphire, dye lasers, semiconductor
lasers, and applications of lasers in spectroscopy.
Unit-6: Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Photoexcitation and photoionization, core level (XPS, ESCA) and valence level (UPS)
photoelectron spectroscopy, XPS and UPS of simple molecules, applications.
Unit-7: Nuclear Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Basic principles, relaxation times, intensity of NMR signals, electronic shielding, NMR in
liquids: chemical shifts, origin of spin-spin couplings, and qualitative idea about NMR spectra of
AX, AX2, A3X and AB systems.
FT-NMR: Rotating frame of reference, effect of radiofrequency pulses, FID, Multi pulse
operation, measurement of T1 by inversion recovery method, spin echo and measurement of T2.
JIS University Page 18
Recommended Books
1. J. M. Hollas, Modern Spectroscopy, 4th edition (2004) John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester.
2. C. N. Banwell and E.M. Mc Cash, Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy, 4th edition (1994),
Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
3. J. D. Graybeal, Molecular spectroscopy
4. I. N. Levine, Molecular spectroscopy
5. G. Herzburg, Infrared and Raman Spectra (1945), Spectra of Diatomic Molecules (1950), Van
Nostrand, New York.
6. J. R. Lakowicz, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
7. W. Demtroder, Laser Spectroscopy
8. G. M. Barrow, Introduction to Molecular Spectroscopy, McGraw-Hill International Book
Company, Tokyo, 1982.
9. R. K. Harris, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, (1986) Addison Wesley, Longman
Ltd, London.
10. A Carrington and A. D. Mc Lachlan, Introduction to Magnetic Resonance, (1979) Chapman and
Hall, London.
JIS University Page 19
MCH-302: Biological Chemistry
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Proteins and Nucleic Acids
Natural and synthetic amino acids, different synthetic strategy of peptides, structure and function
of protein and nucleic acids, Ramachandran plot, denaturation of proteins, factors affecting
denaturation, structural aspect of protein with respect to haemglobulin and myoglobulin, protein
folding, doble helical structure of DNA, RNA, various forms of DNA (a, b, c, z) and RNA (m&
t), transcription and translation, gene expression, DNA binding protein-zinc-finger protein, and
oxygen uptake proteins: Hemerythrin and Hemocyanin.
Unit-2: Enzymes, Carbohydrates, Lipids, Hormones and Steroids
Classification, function and regulation of enzymes, active sites, Vitamins as coenzymes and co-
factors, enzyme kinetics, TON and TOF, enzyme inhibitors, structure and function of Carbonic
anhydrase, Superoxide dismutase, Urease, Hydrogenase, and Carboxy-peptidase etc. Structure,
function and reactions of carbohydrates, lipids, hormones and steroids; Epinephrine,
Norepinephrine, Cholesterol, Prostaglandins, and cell membranes.
Unit-3: Bioenergetics
Glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation, membrane
transport mechanism.
Recommended Books
1. L. Stryer, Biochemistry, 5th edition (2002), Freeman & Co., New York.
2. D. L. Nelson and M. M. Cox, Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry, 3rd edition (2002) McMillan
North Publication.
3. M. N. Hughes, Inorganic Chemistry of Biological Processes, (1981) John Wiley.
4. M. B. Smith, Organic Synthesis, (1995) McGraw Hill Inc., New York.
5. D. Voet, J. G. Voet, Biochemistry 3rd Edition (2004), Wiley International Publication.
JIS University Page 20
MCH-303: Advanced Bioinorganic and Organometallics
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Bioinorganic Chemistry II
Role of alkaline earth metal ions in biological systems: (i) Catalysis of phosphate transfer by
Mg2+ ion, (ii) Ubiquitous regulatory role of Ca2+ in muscle contraction
Metalloenzymes: catalase, peroxidise, SOD, cytochrome-450, NOS, Urease, Hydrogenase.
Biological and abiological nitrogen fixing systems. Molybdo enzymes: nitrate reductases, sulfite
oxidase.
Photosynthesis and chlorophylls, photosystem-I and photosystem-II and their roles in cleavage of
water, model systems.
Bioinorganic chemistry of human iron metabolism: ferritin and transferin.
Vitamins and coenzymes: Vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 coenzymes, model systems.
Toxicity and drugs: Toxic effects of metal ions, detoxification by chelation therapy, metal
dependent diseases and metal complexes as drugs, Pt, Ru, Rh and Au drugs.
Unit-2: Organometallic Chemistry II
Complexes of π and σ-donor ligands: Complexes of dioxygen and dinitrogen, nitrosyl, tertiary
phosphines and arsines as ligands, transition metal alkenyls, alkynyls, carbenes and carbines.
π-complexes of unsaturated molecules: Preparation, bonding and structure of alkene, alkyne,
allyl, dienyl and trienyl complexes; reactions with special reference to organic synthesis.
Metal-metal single and multiple bonding (pictorial MO–approach), bond orders, bonding in
direhnium compounds, Isolobal and Isoelectronic relationships.
Transition metal complexes in catalysis: Hydrogenation, hydroformylation, polymerization, and
Waker process.
Recommended Books
1. M. N. Hughes, Inorganic Chemistry of Biological Processes, 2nd Ed.(1981), John-Wiley & Sons, New
York.
2. W. Kaim and B. Schwederski, Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life,
An Introduction and Guide, Wiley, New York (1995).
3. S. J. Lippard and J. M. Berg, Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry, University Science Books, (1994).
4. I. Bertini, H. B. Grey, S. J. Lippard and J. S. Valentine, Bioinorganic Chemistry, Viva Books Pvt. Ltd.,
New Delhi (1998)
5. F. A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th Ed. (1999) John Wiley & Sons.
6. J. E. Huheey, Keiter and Keiter, Inorganic Chemistry.
7. R. H. Crabtree, The Organometallic Chemistry of Transition Metals, John Wiley.
8. Ch. Elschenbroich and A. Salzer, Organometallics, VCH.
9. J. P. Collman, L. S. Hegedus, J. R. Norton and R.G. Finke, Principles and Applications of
Organotransition metal Chemistry, Univ. Sci. Books, Mill Valley. California.
JIS University Page 21
MCH-304: Advanced Organic Synthesis I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Radical reaction in Organic Chemistry
Definition, generation of free radicals, detection, shapes and stability, stable free radicals.
Example of addition, substitution, oxidation, cyclization and rearrangement involving radical
reaction mechanism.
Unit-2: Protection and Deprotection
The role of protective groups in organic synthesis, principle of protection and deprotection,
Different procedure for protection and deprotection of hydroxyl (including 1,2- and 1,3-
dihydroxy ), phenols, amines, carbonyls and carboxylic groups.
Unit-3: Redox reactions in Organic synthesis
Fundamentals, Oxidation of alcohols: By Chromium and Manganese reagents, Silver carbonate,
oxidation via alkoxysulphonium salts and other methods. Oxidation of Carbon-Carbon double
bonds: dihydroxylation, diastereoselective epoxidation of homoallylic alcohols, photosensitized
oxidation of alkenes, Pd-catalyzed oxidation of alkenes, use of Ruthenium tetroxide and
Thallium (III) nitrate as oxidizing agents for organic substrate, other oxidizing agents. Reduction
by dissolving Metals: reduction with metal and acid (reduction of carbonyl compounds),
desulphurisation of thio-acetals, reduction of organic compounds by di-imide, lowvalent
Titanium reagents, trialkyltin hydrides, trialkylsilanes and other reagents.
Unit-4: Natural Products II
Structure and stereochemistry of alkaloids (Atropine/ Quinine); Terpenoids (Abietic acid/ β-
Carotene); Steroids (Cholesterol). Biosynthesis of Atropine, Quinine, Abietic acid, β-Carotene,
Cholesterol.
Recommended Books
1. Clayden, Greeves, Warren and Wothers, Organic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2001.
2. M.B. Smith & Jerry March, March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition (2001), John Wiley &
Sons, New York.
3. Peter Sykes, A Guide book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition (1997), Orient Longman
Ltd., New Delhi.
4. S. M. Mukherjee and S.P. Singh, Reaction Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Ist Edition (1990),
Macmillan India Ltd., New Delhi.
5. F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg,, Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-A
6. F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg, Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-B
JIS University Page 22
MCH-305: Advanced Quantum Mechanics
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Fundamental principles
Postulates of quantum mechanics, Schmidt orthonormalisation, Fourier transformation, delta
function with examples, tunneling, bound states, the Virial theorem.
Unit-2: Approximation methods in quantum mechanics
Stationary perturbation theory for non-degenerate and degenerate systems and its applications to
rotator, Stark effect, the Helium atom, Variation method, principles of linear and non-linear
variation methods and its applications, JWKB approximation, time-dependent perturbation
theory, radiative transitions, transition probability and rates, Einstein coefficients, selection rules.
Unit-3: Quantum mechanics of many electron atoms
Pauli’s antisymmetry principle, antisymmetry of many electron wave function, spin and spatial
orbitals, Slater determinant, closed-shell and open-shell electron configurations, multi-electron
pure-spin state wave functions, formulation of a multi-electron closed-shell electron
configuration energy, introduction of core, Coulomb and exchange integrals with their
properties, independent particle model, multi-electron atomic Hartree Hamiltonian and related
SCF equations solution, vertical ionization potential and Koopman’s theorem, Hatree-Fock-
Roothaan method for closed cell systems, Roothaan equation, discussion of electron correlation,
Condon Slater rule.
Unit-4: Quantum mechanics of molecules
Born-Oppenheimer approximation, Valence bond theory, Molecular orbital treatment for
homonuclear molecule, Hückel MO treatment of simple polyenes, separation of electronic and
nuclear motion, basis sets for the molecular orbital calculations of polyatomic molecules,
configuration interaction calculations of polyatomic molecules, illustrative examples of Ab initio
HF and post HF calculations, atomic charge and bonding indices in polyatomic molecules.
Recommended Books
1. P. W. Atkins and R. S. Friedman, Molecular Quantum Mechanics, 3rd edition (1997), Oxford
University Press. Oxford.
2. I. N. Levine, Quantum Chemistry, 5th edition (2000), Pearson Educ., Inc., New Delhi.
3. D. A. McQuarrie and J. D. Simon, Physical Chemistry: A Molecular Approach, (1998), Viva Books,
New Delhi.
4. A. K. Chandra, Introductory Quantum Chemistry, 4th edition (1994), Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
5. L. Pauling and E. B. Wilson, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics with Applications to Chemistry,
(1935), McGraw Hill, New York.
6. G. C. Schatz and M. A. Ratner, Quantum Mechanics in Chemistry, Dover Publication, Inc, New
York, 2002.
7. Richard L. Liboff, Introductory Quantum Mechanics
8. D. J. Grffiths, Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
9. J. L. Powell, B. Crasemann, Quantum Mechanics
10. R. K. Prasad, Quantum Mechanics
JIS University Page 23
MCH-306: Advanced Topics in Inorganic Chemistry I
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Redox Reaction
General remark, complementary and non-complementary redox reactions, outer-sphere reaction,
inner-sphere reaction, effect of bridging ligand in inner-sphere reaction, kinetics and mechanism,
electron tunneling hypothesis, heteronuclear redox reaction and simplified Marcus theory,
Marcus cross relationship and its application, remote attack, doubly-bridged process, ligand
exchange, intervalence electron transfer, induced reaction, electron transport in biological
systems and their simulations
Unit-2: Crystalline solid
Single crystal and poly crystal (twinning problem) lattice, unit cell-primitive and non-primitive
unit cells, unit cell parameters and crystal systems. Space group-Hermann–Mauguin notations,
space group in triclinic and monoclinic system. Indexing of lattice planes, Miller indices.
Bragg’s equation, reciprocal lattice and its relation to direct lattice; Bragg’s reflection in terms of
reciprocal lattice-sphere of reflection and limiting sphere; relation between dhkl and lattice
parameters.
Unit-3: Main-group clusters
Geometric and electronic structure, three-, four- and higher connect clusters, the closo, nido,
arachno-borane structural paradigm, Styx No. of neutral and boron hydrides, Wade Mingos and
Jemmis electron counting rules, clusters with nuclearity 4-12 and beyond 12. Structure, synthesis
and reactivity of the clusters compounds.
Recommended Books
1. F. A. Cotton and G.Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th Edn. (1999), John-Wiley &
Sons,New York.
2. James E. Huheey, Inorganic Chemistry, 4th Edn. (1993), Addison Wesley Pub. Co., New York
3. N. N. Greenwood and A. Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd Edn. (1997), Butterworth
Heinemann, London.
JIS University Page 24
MCH-307: Pericyclic and Photochemistry
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Concept on M.O. and V.B. theory
Introduction to H ̈ ckel molecular orbital (MO) method as a mean to explain modern theoretical
methods. Advanced techniques in PMO and FMO theory.Molecular mechanics, semi empirical
methods and Ab Initio methods. Pictorial Representation of MOs for molecules, Qualitative
Application of MO Theory to reactivity, Valence bond configuration mixing diagrams.
Relationship between VB configuration mixing and resonance theory. Reaction profiles.
Potential energy diagrams.
Unit-2: Pericyclic reaction
Introduction, phase and symmetry of orbitals, types of pericyclic reactions; Cycloaddition
reactions: definition, FMO-approach, co-relation diagram, Dewar’s PMO-approach for
cycloaddition (2+2 and 4+2) reactions, Woodward-Hoffmann selection rules, regioselectivity,
secondary orbital interaction, Lewis acid catalysis, site selectivity, periselectivity.
Regioselectivity in 1,3-Dipolar cycloadditions, Electrocyclic reactions: definition, FMO-
approach, Dewar’s PMO-approach for electrocyclic reactions, electroreversion, stereochemical
effects, Woodward-Hoffmann rules, Chelotropic reactions: definition, FMO-approach for
cholatropic reactions, Woodward-Hoffmann rules, stereochemical outcome, Sigmatropic
rearrangement: definition, types of sigmatropic reactions, Hydrogen shifts and carbon shifts ([1,
j] and [i, j]), FMO-approach, Dewar’s aromatic transition state approach, selection rules, Claisen
and Cope rearrangements, Ene reaction: definition, FMO-approach for ene reactions, effects of
Lewis acids.
Unit-3: Organic Photochemistry
Basic Principles, Jablonski diagram, excited state (S1 and T1) of some organic molecules, Cis-
trans mechanism, photo chemical reactions of carbonyl compounds, olefins and conjugated
carboyl compounds, photo induced functionalisation of organic molecules involving Norrish
type I, Norrish type II, Paterno Buchi Reaction, di-π- methane rearrangement, photo reduction of
ketones, substitution in aromatic system.
Recommended Books
1. S.M. Mukherjee and S.P. Singh, Pericyclic Reactions &Photochemistry, MacMillan India, New Delhi.
2. I. Fleming, Pericyclic Reactions, Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999).
3.Clayden, Greeves, Warren and Wothers, Organic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2001.
4. M.B. Smith & Jerry March, March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition (2001), John Wiley &
Sons, New York.
5. S. M. Mukherjee and S.P. Singh, Reaction Mechanism in Organic Chemistry, Ist Edition (1990),
Macmillan India Ltd., New Delhi.
6. D. Nasipuri, Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds, 2nd Edition (1994), Wiley Eastern Ltd., New
Delhi.
JIS University Page 25
MCH-308: Solid State Chemistry
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Crystal structure and X-ray diffraction
Definitions related to crystal structure, reciprocal lattice, Brillouin Zones, structure factor, Laue
equations and Bragg’s law, X-ray diffraction experiments: powder method and single crystal
method.
Unit-2: Solid State reactions & Phase transitions
General principles and experimental procedure of solid state reactions, growth of single crystals:
Czochralski method, Bridgman and Stockbarger methods. Thermodynamic and Burger’s
classification of phase transition, kinetics of phase transition, nucleation and growth.
Unit-3: Free electron & Band theory of solids
Free electron gas model of metals, free electron gas in a one-dimensional and three dimensional
box, Bloch theorem, Kronig-Penny model, tight binding approximation, Band theory of
insulators and semiconductors, intrinsic semiconductors, extrinsic semiconductors, doped
semiconductors, rectifiers, transistors, p-n junctions and their applications, Schottky and Frenkel
defects, stoichimetric imbalance, origin of colours.
Unit-4: Thermal & Magnetic properties of solids
Electronic specific heat, lattice heat capacity, Hall effect, Einstein theory, Debye theory, Born's
modification of the Debye theory. Origin and classifications of magnetic substance, magnetic
moment, ferromagnetic, antiferromagentic and ferromagnetic ordering, magnetic susceptibility,
Curie and Cuire-Weiss law, super exchange, magnetic domains, and hysteresis.
Recommended Books
1. C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, Chichester.
2. O. Madelung, Introduction to Solid State Theory
3. A. R. West, Solid State Chemistry and its Applications, (1984) John Wiley and Sons, Singapore.
4. L.V. Azaroff, Introduction to Solids, (1977) Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi.
5. A. J. Dekker, Solid State Physics, Prentice Hall
JIS University Page 26
MCH-309: Supramolecular Chemistry & Drug Design
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Supramolecular Chemistry
Fundamentals: definitions of supramolecular chemistry, host-guest chemistry, chelate and
macrocyclic effects, preorganisation, thermodynamic and kinetic selectivity, supramolecular
interactions (i..e. cation –π, π-π etc.), cation, anion and neutral molecule binding: crown ethers,
podands/ lariat ethers, spherands, cryptands, complexation of organic cations, calixarenes, cation
host to anion host, shape selectivity, guanidinium receptors, coordination interactions, cavitands:
cyclodextrins and molecular tweezers. molecular switches.
Catenanes, rotaxanes and molecular knots: Self assembly and templates, strict self assembly and
self assembly with covalent modification, electrostatic and H-bonding effects in templating,
catenanes/ catenands/ catenates, rotaxanes/ pseudo-rotaxanes, metal templates for catenanes
(Sauvage), π stacking in catenane and rotaxane formation (Stoddart), helicates and molecular
knots. Molecular devices: history and future of nanoscale machines, relation to host-guest
chemistry (definition of supramolecular device), supramolecular photochemistry, photo- and
electro-chemical sensors, dendrimers, molecular device components, machines based on
catenanes/ rotaxanes, chemically assembled electronic nanocomputing.
Unit-2: Drug design and Antineoplastic agent
Concept of pharmacodynamics, drug targets: enzymes, receptors, nucleic acids; concept on
pharmacokinetics: drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion, concept on lead
compound and lead modification, pharmacophore, concept of prodrug and soft drug, structure
activity relationship (SAR), factors affecting bioactivity; Antineoplastic agents: synthesis and
mode of action of mechlorethamine, cyclophosphamide, melphalan, and 6-mercaptopurine.
Cardiovascular drugs: introduction to cardiovascular diseases, synthesis and mode of action of
amyl nitrate, sorbitrate, diltiazem, quinidine, verapamil, methyl dopa; local antiinfective drugs
and antibiotics: synthesis and mode of action of sulphonamides, nalidixic acid, norfloxacin,
aminosalicyclic acid, ethinamide, fluconazole, chloroquin and premaquin; Antibiotics: cell wall
biosynthesis, inhibit-lactam rings, synthesis of penicillin.
Recommended Books
1. J. M. Lehn, Supramolecular Chemistry- Concepts and Perspectives
2. Schneider, H. J., Yatsimirski, Principles and Methods in Supramolecular Chemistry
3. Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-A, F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg
4. Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-B, F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg
JIS University Page 27
MCH-310: Nuclear Chemistry
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Theory of radioactive decay
Quantum mechanical aspects of radioactive disintegration, alpha decay paradox and its
explanation in terms of tunnel effect, Geiger-Muller relationship, time-dependant perturbation
theory, Golden rule and its application in explaining beta and gamma transition, selection rules.
Unit-2: Nuclear force and structures
Two body problem - properties of deuteron and derivation of depth-range relationship, its
applications in explaining nature of nuclear force, elementary particles; nuclear models - strong
and weak interaction, nuclear magnetic dipole moment and electric quadruple moment in terms
of shell model, collective model, Fermi gas model.
Unit-3: Nuclear reactions general features
Types of nuclear reaction, conservation laws, nuclear reaction dynamics, mechanism of nuclear
reaction, use of uncertainty principle, resonance and non-resonance reaction, optical model and
calculation of mean free path, nuclear fission and fusion reaction, calculation of fission
probability from Bohr-Wheeler’s theory Centre of mass system and laboratory co-ordinate.
Unit-4: Nuclear detectors
Classification of nuclear detectors, G. M. detector-operational principle, dead time, proportional
detectors: proportional counter performance, flow-type proportional counter, gas multiplication
factor, scintillation detectors: different types with examples, pulse shape analysis, resolution and
detection efficiency, liquid scintillation detectors, detection of neutrons, semiconductor detector:
general characterization, depletion depth, reverse bias, requirement of cryogenic condition,
resolution and efficiency, pulse rise time, with a brief account of n-type and p-type
semiconductor, Si lattice, Ge-Li, Si-Li - a comparison intrinsic and doped-semiconductor-
fabrication surface barrier detector; some basic ideas of pulse processing and shaping, single-
and multi-channel analysers, digital and analogue systems, applications in space research,
development of detector assembly with requirement of newer space and defence technology viz.,
nuclear missile, Coincidence counting Determination of absolute disintegration rates, decay
scheme studies.
Recommended Books
1. B. Harvey, Introduction to Nuclear Physics and Chemistry, Prentice Hall, New York, 1965.
2. H. J. Arnikar, Essentials of Nuclear Chemistry, 4th Edn Reprint, New Age International (P) Ltd
Publications, New Delhi, 2001.
3. G. R. Choppin and J. Rydberg, Nuclear Chemistry: Theory and Applications, Pergamon, Oxford, 1980.
4. D. D. Sood, A.V. R Reddy and N. Ramamoorty, Fundumentals of Radiochemistry, Yancas, Mumbai,
2004.
JIS University Page 28
MCH-391: Inorganic Chemistry Lab III
L-T-P: 0-0-9 Credit: 6
To study the kinetics of different inorganic reactions by conductometric, colorimetric,
and spectrophotometric method
Estimation of selected ores, minerals, and alloys
Synthesis and characterization of different coordination complexes
MCH-392: Organic Chemistry Lab III
L-T-P: 0-0-9 Credit: 6
Qualitative analysis of liquid sample (color, odour, solubility etc.); Thin Layer
Chromatography (TLC, preparation of TLC plates, analysis), boiling point
determination; functional groups tests, UV-VIS spectral characterizations: (measure max,
and explain), Assign 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR spectra, Identify the liquid substance.
Extraction of Renewable chemicals: Take a particular part of a plant such as fruit, leaf,
bark, heavy wood, etc. Weight it. Extract with a particular solvent. Remove the volatiles.
Purify. Weigh the product. Calculate % yield, Analyze the product by Thin Layer
Chromatography, calculate Rf value. UV-VIS spectral characterizations: measure
max,and explain. Submit the product with proper label.
Quantitative Estimation of: (a) Sugars (Glucose, Cane sugar), (b) Phenol, (c) Aniline, (d)
Nitrogen by Kjldahl method, (e) Saponification and Iodine value.
MCH-393: Physical Chemistry Lab III
L-T-P: 0-0-9 Credit: 6
Synthesis, characterization and applications of nanomaterials
Synthesis and characterization of polymers utilizing different polymerization techniques
Recommended Books
1. A.I. Vogel, Qualitative Inorganic Analysis
2. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, ELBS
3. Ghosal, Mahaparta and Nad, An Advanced Course in Practical chemistry
4. G. N. Mukherjee, Handbook of Practical Chemistry
5. A.I. Vogel, A Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry
6. A. M. James, F. F. Prichard, Practical Physical Chemistry
7. Shoermaker, Garland, Experimental Physical Chemistry
JIS University Page 29
Detailed Syllabus of Fourth semester
MCH-401: Spectroscopy for Structure Elucidation
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Ultra-Violet & Infrared spectroscopy
Absorption of dienes, polyenes, carbonyl compounds and α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds,
Woodward rule and its applications. Different vibration modes, bond stretching, absorption
region of functional groups, electrical and steric effects, effects of hydrogen bonding, Fingerprint
region and interpretation of IR spectra.
Unit-2: NMR spectroscopy
Principles, relaxation phenomenon, chemical shifts, coupling constants, spin-spin interactions,
simplification of complex spectrum, spin decoupling, nuclear Overhauser effect, detailed
interpretation of 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT, two dimensional NMR: COSY, NOESY.
NMR spectra of paramagnetic coordination compounds, dipolar and contact shifts, 11B, 19F, 27Al,
and 31P – NMR spectroscopy with typical examples.
Unit-3: Mass spectroscopy
Principles, different techniques, fragmentation modes, factors influencing ion abundance,
rearrangements, cleavage associated with common functional groups, molecular and metastable
ion peak, Nitrogen rule and interpretation of mass spectra.
Combined applications of different spectroscopic techniques (UV, IR, NMR, Mass) in
elucidation of structure.
Unit-4: EPR & Mössbauer
Origin, principle, hyperfine splitting, factors affecting the magnitude of g-value, anisotropy in
hyperfine coupling constants, zero-field splitting, Kramers’ degeneracy, nuclear quadrupole
interactions, Mössbauer effect, isomer shift, quadrupole splitting, typical spectra of iron and tin
compounds, NQR.
Unit-5: Optical rotatory dispersion & Circular dichroism
Principles of ORD and CD, different techniques, Cotton effect, Faraday and Kerr effects,
applications in determining absolute configuration of metal complexes, amino acids and proteins.
Recommended Books
1. R. M. Silverstein and F.X. Webster, Spectroscopic Identification of Organic Compounds, 6th Edition
(2003) John Wiley, New York.
2. D. H. Williams and I.F. Fleming, Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry, 4th Edition (1988),
Tata-McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
3. P. Y Bruice, Organic Chemistry, 2nd Edition (1998) Prentice-Hall, New Delhi.
4. E. A. V. Ebsworth, D. W. H. Rankin and S. Cradock, Structural Methods in Inorganic Chemistry, 1st
Edition (1987), Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, London.
5. R. S. Drago, Physical Methods in Chemistry, International Edition (1992), Affiliated East-West
Press, New Delhi.
6. R. S. Drago, Physical Methods in Inorganic Chemistry, 1st Edition (1971), Affiliated East-West
Press, New Delhi.
JIS University Page 30
MCH-402: Polymer and Materials Chemistry
L-T-P: 3-1-0 Credit: 4
Unit-1: Polymer Chemistry
Introduction, classification, different molecular weights and their determination, polymerization
techniques, detailed kinetics of condensation and addition polymerization, controlled
polymerizations, sequence and stereo-controlled polymer synthesis, properties of polymers in
solutions, Flory-Huggins model, glass transition temperature, crystallinity, mechanical
properties, polymer modification and manufacturing of commodity polymers: grafting, cross-
linking, blending, compounding.
Specialty polymers: Liquid crystalline polymers, conducting polymers, electroluminescent
polymers, inorganic polymer, biomedical polymers, and hybrid materials based on polymers.
Unit-2: Material Chemistry
Introduction, importance, classifications and theoretical aspect of nanomaterials, top down-
bottom up approach, different synthetic strategy of metal/metal oxide/semiconducting materials,
template based synthesis, size, shape and dimension controlled synthesis, growth kinetics,
composite nanostructures, properties and size effect of nanomaterials: optoelectronic,
mechanical, magnetic, and catalytic properties, applications of nanomaterials.
Different Instrumental Techniques for characterization: Basic principles and applications of X-
ray diffraction, electron microscopies (SEM, TEM), scanning probe microscopies (STM), atomic
force microscopy (AFM), optical microscopies [confocal microscopy, scanning near field optical
microscopy, particle size analysis (DLS)], thermal (DSC, DTA), optical (IR, FTIR, Raman) and
XPS.
Recommended Books
1. G. Odian, Principles of Polymerization, 3rd Edition (1991), John Wiley, Singapore
2. F. W. Billmayer, Jr., Text Book of Polymer Science, 3rd Edition (1984), Willey-Interscience, NY
3. C. Tanford, Physical Chemistry of Macromolecules
4. P. Bahadur, N.V. Sastry, Principle of Polymer Sciences, Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi
5. V.R. Gowarikar, N.V. Vishwanathan, J. Shreedhar, Polymer Sciences, Wiley Eastern, New Delhi
6. P. W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition, Oxford University Press, New York
7. P. J. Flory, Polymer Chemistry
8. C. N. R. Rao, A. Müller, A. K. Cheetham, The Chemistry of Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Properties and
Applications, Vols 1 and 2, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2004
9. C. Bréchignac, P. Houdy, M. Lahmani, Nanomaterials and Nanochemistry, Springer, London, 2006.
10. G. Cao, Nanostructures & Nanomaterials, Synthesis, Properties & Applications, Imperial College
Press, London, 2004. L. Cademartiri and G. A. Ozin, Concepts of Nanochemistry, Wiley-VCH,
Weinheim, 2009.
11. C. N. R. Rao, A. Muller and A. K. Cheetham, Nanomaterials Chemistry: Recent Developments and
New Directions, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany, 2007.
12. G.A. Ozin, A. C. Arsenault and L. Cadematiri, Nanochemistry: A Chemical approach to
Nanomaterials, Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2009.
JIS University Page 31
MCH-403: Inorganic Reaction Mechanism & Photochemistry
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Inorganic reaction mechanism
Substitution reactions in square planar, tetrahedral and octahedral geometries with special
reference to dn ion complexes: operational tests, aquation and anation, reactions without metal-
ligand bond breaking, kinetics of chelate formation, reaction mechanisms of organometallic
systems, studies on fast reactions, kinetic and activation parameters-tools to propose a plausible
mechanism; stereochemical changes: types of ligand rearrangements, isomerism in 4-, 5- and 6-
coordinated complexes; reactions of coordinated ligands: model choice of metal and ligand, acid-
base reaction, hydrolysis of esters, amides and peptides, aldol condensation, trans-amination,
template reactions, organic synthesis with special reference to macrocyclic ligand; reactions in
fluxional organometallic compounds.
Unit-2: Photochemistry of Transition metal complexes
Photoreactions of complexes of Cr(III) and Co(III), photo-aquation, photo-substitution and
photo-racemization, photochemistry of Ru(bpy)32+ and its application as photocatalyst for photo-
splitting of water, photooxidation of 2-propanol and photo-reduction of carbon dioxide, cyanide
bridged triruthenium(II) bipy complexes as antenna, photochemistry of diisocyanide bridged
diimers of Rh(I), applications of quenching and sensitization techniques in the identification of
reactive state in coordination complexes, photochemistry of transition metal carbonyls and
europium complexes.
Recommended Books
1. J. O. Edwards and W. A. Benjamin, Inorganic Reactions Mechanism, INC, New York, 1965.
2. C. H. Langford and H. B. Gray, Ligand Substitution Processes, W. A. Benjamin, New York, 1966.
3. F. Basolo and R. G. Pearson, Mechanism of Inorganic Reactions, 2nd Edn, Wiley, New York, 1967.
4. D. Katakis and G. Gordon, Mechanisms of Inorganic Reactions, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987.
5. R. G. Wilkinns, Kinetics and Mechanism of Reactions of Transition Metal Complexes, 2nd Edn, VCH,
Weinheim, 1991.
6. D. M. Roundhill, Photochemistry and Photophysics of Metal Complexes, Plenum Press, New York and
London (1994).
7. G. J. Ferraudi, Elements of Inorganic Photochemistry, John Wiley & Sons (1988).
8. V. Balzani and V. Carassiti, Photochemistry of Coordination Compounds, Academic Press, London
(1970).
9. O. Horvath and K.L. Stevenson, Charge Transfer Photochemistry of Coordination Complexes, VCH
Publishers Inc. (1993)
JIS University Page 32
MCH-404: Advanced Organic Synthesis II
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: The Disconnection approach
Basic principles, guidelines for disconnection with special emphasis on chemoselective,
regioselective, stereoselective and stereospecific reactions, functional group inter conversion,
synthon and reagent, synthetic equivalent, illogical electrophile and illogical nucleophile,
Umpolong synthesis. designing synthesis of some target molecules with proper retrosynthetic
analysis : Menthol, Taxol, Penicillin V, Reserpine, Progesterone, Estrone, Periplanone B, L-
Hexoses etc.
Unit-2: Special techniques in Organic synthesis
The background of organic synthesis, reactions with solid-supported reagents and catalyst, solid
phase synthesis, Phase transfer reactions, Sonochemistry, Microwave in organic synthesis, Ionic
liquid in organic synthesis, Electro organic synthesis, Concept of organocatalyst.
Unit-3: Asymmetric synthesis
Introduction, kinetic and thermodynamic principles to asymmetric synthesis, diastereoselective
& enantioselective synthesis; Methods of asymmetric synthesis: Resolution, use of chiral pool,
chiral auxiliaries, use of stoichiometric chiral reagents, asymmetric catalysis. Asymmetric
hydrogenation with special reference to Ru-BINAP catalysts, asymmetric reduction of prochiral
ketones with Baker’s Yeast & CBS-catalyst, asymmetric epoxidation with special reference to
Sharpless and Jacobsen epoxidation, asymmetric diethylzinc addition to carbonyl compounds,
asymmetric aldol reactions, asymmetric Michael reaction; industrial applications of asymmetric
synthesis.
Unit-4: Organometallic chemistry
Preparation, properties and reactions of Organomagnesium, Organolithium and Organozinc
reagents in synthesis. The role of Boron, Silicon, Sulphur and Phosphorus in organic synthesis.
Principle, preparation, properties and application of some transition metals in organic synthesis
with special reference to Copper, Palladium, Cobalt, Titanium and Nickel.
Unit-5: Green chemistry
The need of green chemistry, Principles of green chemistry, Concept of atom economy Tools of
green Chemistry – microwave, ultra sound, ionic liquids, supercritical H2O and CO2 as solvents,
etc. Green Chemistry in real world cases and planning green synthesis in chemical laboratory.
Recommended Books
1. Clayden, Greeves, Warren and Wothers, Organic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2001.
2. M.B. Smith & Jerry March, March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition (2001), John Wiley &
Sons, New York.
3. R. O. C. Norman and J. M. Coxon, Principle of organic synthesis
4. S. Warren, Organic synthesis: The disconnection approach
5. W. Carruthers, Modern methods of organic synthesis
6. Paul. T. Anantas and Tracy C. Williamson, Green Chemistry
7. Theory and Practice, Paul T. Anastas and John C. Warner, Green Chemistry
JIS University Page 33
MCH-405: Electrochemistry
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Ion-Solvent interaction
Born model and Born equation, enthalpy of ion-solvent interaction and its evaluation, Eley-Evan
model, solvation number and its determination
Unit-2: Electrical double Layer
OHP and IHP, potential profile across double layer region, potential difference across electrified
interface, structure of the double layer: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, and Stern models,
Butler-Volmer equation under near equilibrium and non-equilibrium conditions, exchange
current density, Tafel plot, thermodynamics of double layer, electrocapillary equation,
determination of surface excess and other electrical parameters.
Unit-3: Electrode Kinetics
Polarizable and non-polarizable interfaces, multistep reactions: a near equilibrium relation
between current density and over potential, concept of rate determining step, determination of
reaction order, stochiometric number, transfer coefficient.
Unit-4: Applications
Electrochemical cell, fuel cell, electrocatalysis, corrosion, and cyclic voltammetry etc.
Recommended Books
1. J. O’M. Bockris and A. K. N. Reddy, Modern Electrochemistry, Vol. 1 & 2A and 2B, (1998) Plenum
Press, New York.
2. A. J. Bard and L. R. Faulkner, Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd edition,
(2001) John Wiley &Sons, New York.
3. Samuel Glasstone, An Introduction to Electrochemistry: Edition 1st, East-West Press Pvt Ltd New
Delhi, India.
4. S. R. Morrison, Electrochemistry in Semiconductor and Oxidised Metal Electrodes, Plenum Press, New
York, 1980.
5. D. E. Kyriacou and D. A. Jannakoudis, Electrocatalysis for Organic Synthesis, Wiley, New York,
1986.
6. J. Goodisman, Electrochemistry: Theoretical Foundations, Wiley, New York, 1987.
7. J. O’M. Bockris and S. U. M. Khan, Surface Electrochemistry, Plenum Press, New York, 1993.
8. C. M. A. Brett and A. M. O. Brett, Electrochemistry: Principles, Methods and Applications, Oxford
University Press, Oxford, 1993.
9. P. W. Atkins, Physical Chemistry, 5th Edn, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1994.
10. K. V. Kordesch, Fuel Cells and Their Applications, VCH, Weinheim, 1994.
JIS University Page 34
MCH-406: Advanced Topics in Inorganic Chemistry II
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Magnetochemistry
Types of magnetic materials, magnetic susceptibility and its determination: Gouy, Faraday and
Evans methods, vibrating sample magnetometer, SQUID and NMR methods. Magnetic
anisotropy, diamagnetism in atoms and polyatomic systems, Pascal’s constants, Lande interval
rule, energies of J states, Curie equation, Curies law and Curie-Weiss law, First order and second
order Zeeman effects, temperature independent para magnetism, simplification and application
of Van Vleck susceptibility equation, quenching of magnetic moments of transition metal
compounds in cubic and axially symmetric crystal fields, low spin- high spin crosser, magnetic
behaviour of Lanthanides and Actinides, magnetic exchange interactions, magnetic materials.
Unit-2: Cluster, Cage, Ring of main group transition-metal clusters
Capping rules, metal-ligand complexes vs heteronuclear cluster, isolobal analogs of p-block and
d-block clusters, limitations and exceptions, clusters having interstitial main group elements,
cubane clusters and naked or Zintl clusters, metal-carbonyl clusters, structures, capping and
electron counting, molecular clusters in catalysis, clusters to materials, boron-carbides and
metalborides, illustrative examples from recent literature.
Unit-3: Inorganic Polymers
Classification, types of inorganic polymerization, comparison with organic polymers, Boron-
oxygen and boron-nitrogen polymers, silicones, coordination polymers, sulphur-nitrogen,
sulphur-nitrogen-fluorine compounds, binary and multi-component systems, hemolytic inorganic
systems.
Recommended Books
1. F. A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th Edn. (1999), John-Wiley & Sons,
New York.
2. N. N. Greenwood and A. Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd Edn. (1997), Butterworth
Heinemann, London.
3. F. E. Mabbs and D. J. Machin, Magnetism and Transition Metal Complexes, Dover Publications, New
York, 2008.
4.O. Kahn, Molecular Magnetism, VCH, New York, 1993.
5. P. Day and A. E. Underhill (Eds), Metal-organic and Organic Molecular Magnets, RSC, London, 2000.
6. J. S. Miller and M. Drillon (Eds), Magnetism: Molecules to Materials, V; Molecule-based Magnets,
Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005.
7. B. D. Cullity and C. D. Graham, Introduction to Magnetic Materials, 2nd Ed, John Wiley & Sons, New
York, 2011.
8. F. Vogtle, Supramolecular Chemistry: An Introduction, Wiley, Chichester, 1991.20 20
9. V. Balzani and F. Scandola, Supramolecular Photochemistry, Ellis Horwood, Chichester, 1991.
10. J. -M. Lehn, Supramolecular Chemistry: Concepts and Perspectives, VCH, Weinheim, 1995.
11. J. W. Steed and J. L. Atwood, Supramolecular Chemistry, 2nd Ed, John Wiley & Sons.
JIS University Page 35
MCH-407: Heterocyclic Chemistry
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Fundamentals
Nomenclature of heterocycles: replacement and systematic nomenclature (Hantzsch-Widman
system) for monocyclic, fused and bridged heterocycles; aromatic heterocycles: tautomerism in
heterocyclic systems, reactivity of aromatic heterocycles; non-aromatic heterocycles:
conformation of six-membered heterocycles with reference to molecular geometry, barrier to
ring inversion, pyramidal inversion and 1,3-diaxial interaction, anomeric and related effects,
hydrogen bonding and intermolecular nucleophilic-electrophilic interactions; meso-ionic
systems: general classification, chemistry of some important meso-ionic heterocycles of type A
and B and their applications.
Unit-2: Heterocyclic synthesis
Principles of heterocyclic synthesis involving cyclization reactions and cycloaddition reactions;
synthesis and reactivity of 3-, 4-, 5- 6- & 7-membered heterocycles with one, two or more
heteroatoms (aziridines, oxiranes, thiiranes, azetidines, oxetanes, thietanes, diazines, triazines,
thiazines, azepines, oxepines); benzo-fused five and six-membered heterocycles: synthesis and
reactions including medicinal applications of benzopyrroles, benzofurans, benzothiophenes,
quinolizinium and benzopyrylium salts, coumarins and chromones; heterocycles in
pharmaceutical industry.
Recommended Books
1. J. A. Joule and K. Mills: Heterocyclic Chemistry (4 th Edition)
2. Clayden, Greeves, Warren and Wothers, Organic Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 2001.
3. M.B. Smith & Jerry March, March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry, 5th Edition (2001), John
Wiley & Sons, New York.
4. Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-A, F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg
5. Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part-B, F.A. Carey and R.J. Sundburg
JIS University Page 36
MCH-408: Statistical Mechanics
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Ensembles and Partition function
Probability, Equal a priori probability, concept of ensemble, Micro/Macro/Grand-canonical
ensemble, Ergodic hypothesis, phase space, quantization of phase space, Liouville theorem,
review of rotational, vibrational and translational partition functions, entropy of a two level
system, Gibbs paradox, equipartition of energy, applications of partition function to specific heat
of solids, chemical equilibrium ideal and real gases.
Unit-2: Quantum statistics
Bose-Einstein distribution law, Einstein condensation, thermodynamic properties of ideal BE
gas, Fermi-Dirac distribution law, degenerate Fermi gas, electron in metals, magnetic
susceptibility.
Unit-3: Fluctuations
Mean square deviation and fluctuation in ensembles, concentration fluctuation in quantum
statistics.
Unit-4: Non-equilibrium states, irreversible thermodynamics
Conservation of mass and energy in open systems, entropy production in chemical reactions,
entropy flow in open systems, forces and fluxes, linear phenomenological laws, Onsager’s
reciprocity or reciprocal relation, validity of Onsager equation and its verification, principle of
microscopic reversibility, stationary non-equilibrium states, Curie-Prigogine principle and its
applications.
Boltzmann transport equation, particle diffusion, and electrical conductivity.
Recommended Books
1. B. K. Agarwal and M. Eisner, Statistical Mechanics, (1988) Wiley Eastern, New Delhi
2. D. A. McQuarrie, Statistical mechanics, (1976) Harper and Row Publishers, New York
3. E. S. R. Gopal, Statistical Mechanics and Properties of Matter, Ellis Horwood, England, 1974
4. S. K. Ma, Statistical Mechanics, World Sci, Singapore, 1985
5. R. K. Pathria, Statistical Mechanics, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1996
6. B.B. Laud, Statistical Mechanics
JIS University Page 37
MCH-409: Chemical Applications of Group Theory
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: IR and Raman spectroscopy
Brief introduction to molecular vibrations, selection rules for fundamental transitions, symmetry
of normal modes of molecules, Infrared and Raman activity of some typical molecules
(molecules of C2v, C3v, C4v, D2h, D3h, D4h, Td and Oh point groups).
Unit-2: Molecular Orbital theory
Introduction, transformation properties of atomic orbitals, hybridization schemes for and
bonding, hybrid orbitals as LCAOs, construction of SALC’s and their use in calculation of π
MO’s under the H ̈ ckel approximations, calculation of MO’s of ABn type and sandwitch type
molecules, study of hybridization, selection rules, allowedness/forbiddenness of n-π* and π-π*
transitions, splitting of terms in octahedral and tetrahedral ligand fields, Orgel and Tanabe-
Sugano diagrams.
Recommended Books
1. F. A. Cotton, Chemical Applications of Group Theory, 3rd Edn. (1999), John Wiley & Sons,
New York.
2. G. L. Miessler and D. A. Tarr, Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Edn. (1999), Prentice Hall International Inc.,
London.
3. K. Veera Reddy, Symmetry and Spectroscopy of Molecules, New Age International Pvt. Ltd., New
Delhi (1999).
4. A. Vincent, Molecular Symmetry and Group Theory, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998.
5. D. M. Bishop, Group Theory and Chemistry, Oxford University Press, 1993.
6. V. Heine, Group Theory in Quantum Mechanics: An Introduction to Its Present Usage, Dover
Publication, New York, 1991.
7. R. McWeeny, Symmetry: An Introduction to Group Theory and Its Applications, Dover Publications,
New York.
JIS University Page 38
MCH-410: Advanced Spectroscopy
L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credit: 3
Unit-1: Fundamentals
Generation of singlet and triplet states, radiative and non-radiative transitions, fluorescence,
phosphorescence, quantum yield and life-time measurements, fluorescence quenching, resonance
energy transfer, solvation dynamics.
Unit-2: Laser Spectroscopy
Brief review of laser action, application of lasers as excitation source, time resolved fluorimetry,
transient absorption spectroscopy, surface plasmon spectroscopy, multiphoton spectroscopy,
single molecule spectroscopy, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, upconversion, microscopy
(optical, phase contrast, confocal, FLIM), SERS, and CARS.
Unit-3: Photophysical Processes
Unimolecular processes, delayed fluorescence, kinetics of bimolecular processes: collision
quenching, Stern-Volmer equation, concentration dependence of quenching and excimer
formation, excited state electron transfer processes: exciplex, twisted intramolecular charge
transfer processes, proton couple electron transfer processes, special photochemical reactions,
flash photolysis, laser flash photolysis.
Recommended Books
1. J. M. Hollas, Modern Spectroscopy, Wiley, New York, 1996.
2. D. N. Sathyanarayana, Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy and Related Techniques, University Press,
2001.
3. G. Aruldhas, Molecular Structure and Spectroscopy, 2nd Edn, Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007.
4. G. M. Barrow, Introduction to Molecular Spectroscopy, McGraw-Hill International Book Company,
Tokyo, 1982.
5. J. D. Graybeal, Molecular Spectroscopy, McGraw-Hill International Editions, Spectroscopy series,
1998.
6. J. R. Lakowicz, Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy
7. R. Schinke, Photodissociation dynamics
8. W. Demtroder, Laser spectroscopy
9. R. D. Levine, Molecular Reaction Dynamics
10. J. I. Steinfeld, J. S. Francisco, W. L. Hase, Chemical Kinetics and Dynamics
JIS University Page 39
You might also like
- Kemp-Organic SpectrosDocument410 pagesKemp-Organic SpectrosAnonymous ezTZvNK90% (10)
- 02.05 Lab Electron Arrangement and EMR Line Spectra Virtual LabDocument5 pages02.05 Lab Electron Arrangement and EMR Line Spectra Virtual LabCaitlynNo ratings yet
- Biotech R2013Document82 pagesBiotech R2013Devi TNo ratings yet
- PetroChem Engg PDFDocument90 pagesPetroChem Engg PDFReginNo ratings yet
- Chemical EngineeringDocument99 pagesChemical EngineeringIplroy Jasaon0% (1)
- Course Curriculum: M.Sc. ChemistryDocument64 pagesCourse Curriculum: M.Sc. ChemistryJosephine TorresNo ratings yet
- MSC Orgchem Syllabus PVSL 2017 18 For Website PDFDocument41 pagesMSC Orgchem Syllabus PVSL 2017 18 For Website PDFLucky SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- MSC Orgchem Syllabus PVSL 2017 18 For Website PDFDocument41 pagesMSC Orgchem Syllabus PVSL 2017 18 For Website PDFLucky SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- 49crsbfile BSC (H) CHMCBCS2020-21 PDFDocument80 pages49crsbfile BSC (H) CHMCBCS2020-21 PDFJosephine TorresNo ratings yet
- Petroleum EnggDocument102 pagesPetroleum EnggHameed Bin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Petrochem Tech PDFDocument90 pagesPetrochem Tech PDFThirunavukarasuNo ratings yet
- B.E. MechDocument139 pagesB.E. MechmikyyeheyesNo ratings yet
- MSC Chemistry July2011Document65 pagesMSC Chemistry July2011Mohan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chem & ElectroChemDocument88 pagesChem & ElectroChemdrsomu ssnNo ratings yet
- M.SC (Chemistry)Document38 pagesM.SC (Chemistry)Khitish MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MSC Nit WarangalDocument30 pagesSyllabus MSC Nit WarangalAshish ChahalNo ratings yet
- Nims University: Master of Science (Chemistry) - MSCCHMDocument24 pagesNims University: Master of Science (Chemistry) - MSCCHMRAJESH KUMAR MishraNo ratings yet
- (Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019) : (Formerly West Bengal University of Technology)Document4 pages(Applicable From The Academic Session 2018-2019) : (Formerly West Bengal University of Technology)Classic GamingNo ratings yet
- B.tech. BBE R21 Padeepz AppDocument37 pagesB.tech. BBE R21 Padeepz AppSaidu HomeNo ratings yet
- Semester Syllabus For M. Sc. in Chemistry: School of Chemistry (AutonomousDocument22 pagesSemester Syllabus For M. Sc. in Chemistry: School of Chemistry (AutonomousDachou GeetuNo ratings yet
- MSC Organic ChemistryDocument69 pagesMSC Organic ChemistryRup panditNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFDocument70 pagesB.Tech. Chemical Engineering PDFJogi BogiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus 2019-22Document59 pagesChemistry Syllabus 2019-22Sakshi BhonsleNo ratings yet
- B Techr2015Document188 pagesB Techr2015End Semester Theory Exams SathyabamaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument87 pagesSyllabusParas PahalNo ratings yet
- MME B.tech MR22 Syllabus III To IV Semesters 1Document19 pagesMME B.tech MR22 Syllabus III To IV Semesters 1SUBRAT KUMAR SAHOONo ratings yet
- Autonoums - MECH UG CuriculumDocument5 pagesAutonoums - MECH UG Curiculum10rajNo ratings yet
- 4.122 MSC Chem Phy Sem III and IVDocument32 pages4.122 MSC Chem Phy Sem III and IVAsma MerchantNo ratings yet
- BTech Biotech FTDocument100 pagesBTech Biotech FThinderNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engg SyllabusDocument69 pagesChemical Engg SyllabusAnushka srivastavaNo ratings yet
- MME SyllabusDocument101 pagesMME SyllabusRaj MaloNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument26 pagesChemistryRimaNo ratings yet
- SchemeSyllabi MScChemistry 2021-23Document87 pagesSchemeSyllabi MScChemistry 2021-23S KNo ratings yet
- MSC Chemistry SyllabusDocument55 pagesMSC Chemistry Syllabusaniruddh pratapNo ratings yet
- Revised Scheme of Courses and Syllabi 4 Years (8-Semesters) B.Tech. Degree Programme in Chemical EngineeringDocument34 pagesRevised Scheme of Courses and Syllabi 4 Years (8-Semesters) B.Tech. Degree Programme in Chemical EngineeringGarima JainNo ratings yet
- B.tech Chemical Engineering, AmuDocument82 pagesB.tech Chemical Engineering, Amukeepingthefaith.izharNo ratings yet
- M.tech. Biotechnology (Effective From The Session - 2016-17)Document25 pagesM.tech. Biotechnology (Effective From The Session - 2016-17)Ravindra Mani TiwariNo ratings yet
- Civil Environmental Upto 4th Year Syllabus 2015Document62 pagesCivil Environmental Upto 4th Year Syllabus 2015dip pradhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Detailed SyllabusDocument26 pagesMechanical Engineering Detailed Syllabushikal987No ratings yet
- 10.b.e.ece - 29072022Document128 pages10.b.e.ece - 29072022Raghul PNo ratings yet
- MSC-PH-2015 NittDocument44 pagesMSC-PH-2015 Nittjohnsonchelsea123No ratings yet
- M.SC ChemistryDocument58 pagesM.SC Chemistryspsonline2029No ratings yet
- Centurion University of Technology & Management:: Paralakhemundi OdishaDocument15 pagesCenturion University of Technology & Management:: Paralakhemundi OdishaSadhan PadhiNo ratings yet
- R2016-UG-Curriculum & Syllabi-BT-ReaccreditationDocument26 pagesR2016-UG-Curriculum & Syllabi-BT-ReaccreditationSelva KapoorNo ratings yet
- MSC PH 2018 PDFDocument44 pagesMSC PH 2018 PDFKapil S Faujdar0% (1)
- B. Sc. IC (V) Semester III To VIDocument26 pagesB. Sc. IC (V) Semester III To VIManav PtelNo ratings yet
- B.SC ChemistryDocument20 pagesB.SC ChemistryGokulNo ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus TY Chemical W.E.F. AY 2020 21Document41 pagesRevised Syllabus TY Chemical W.E.F. AY 2020 21anil chavanNo ratings yet
- B. Sc. BiochemistryDocument36 pagesB. Sc. BiochemistryJackie Jagan ThalaNo ratings yet
- FT Syllabus Upto 4th Year 14.03.14 PDFDocument28 pagesFT Syllabus Upto 4th Year 14.03.14 PDFhmce kalyaniNo ratings yet
- M.E.ThermalDocument25 pagesM.E.ThermalMANI BNo ratings yet
- 2021 Batch MSC CurriculumDocument10 pages2021 Batch MSC CurriculumThiagarajan KamananNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Petro 2nd Yr Syllabus 26 June 2024Document17 pagesB.Tech Petro 2nd Yr Syllabus 26 June 2024Sakib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- R22B.Pharmacy I YearModifiedSyllabusDocument58 pagesR22B.Pharmacy I YearModifiedSyllabusvinaychintucNo ratings yet
- F.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry Syllabus (Approved by Academic Council On 11th July 2022)Document14 pagesF.Y.B.Sc. Chemistry Syllabus (Approved by Academic Council On 11th July 2022)Itz SinuNo ratings yet
- M.SC Chemistry Modified Syllabus With Effect From 2015-16 Session Course StructureDocument23 pagesM.SC Chemistry Modified Syllabus With Effect From 2015-16 Session Course StructureSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- R22B PharmacyCourseStructureandSyllabusDocument136 pagesR22B PharmacyCourseStructureandSyllabusnaaceeecjitsNo ratings yet
- BTech - R19 - I - IV YEAR Course Structure For PEDocument180 pagesBTech - R19 - I - IV YEAR Course Structure For PEsrinuNo ratings yet
- BSC Hs Chemistry Semester I To Vi CbcegsDocument76 pagesBSC Hs Chemistry Semester I To Vi CbcegsZhu RichNo ratings yet
- 6 Yr M.tech Curriculum PDFDocument95 pages6 Yr M.tech Curriculum PDFsobaraja2029No ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, Oligomerization and Polymerization Formation of Intercalation CompoundsFrom EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, Oligomerization and Polymerization Formation of Intercalation CompoundsA. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach to Quantitative Metal Analysis of Organic MatricesFrom EverandA Practical Approach to Quantitative Metal Analysis of Organic MatricesNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Organic Chemistry-2nd SemDocument4 pagesModel Question Paper Organic Chemistry-2nd SemPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound. Inorganic ChemistryDocument14 pagesCoordination Compound. Inorganic ChemistryPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Andrew's ExperimentDocument7 pagesAndrew's ExperimentPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism in Coordination CompoundDocument14 pagesIsomerism in Coordination CompoundPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- 13.14 C NMR SpectrosDocument17 pages13.14 C NMR SpectrosnanaNo ratings yet
- Nims University: Master of Science (Chemistry) - MSCCHMDocument24 pagesNims University: Master of Science (Chemistry) - MSCCHMRAJESH KUMAR MishraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022369720328286 MainDocument26 pages1 s2.0 S0022369720328286 MainYhomn AcerNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (Uv-Vis) - FinalDocument15 pagesUltraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy (Uv-Vis) - FinalSwati V NairNo ratings yet
- !!trends in Pharmaceutical Analysis and Quality Contro - 2022 - TrAC Trends in AnaDocument14 pages!!trends in Pharmaceutical Analysis and Quality Contro - 2022 - TrAC Trends in AnaMostafa AfifyNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence SpectrosDocument31 pagesFluorescence SpectrosApurba Sarker Apu100% (2)
- 2-Phenylethanol Mass Spectrum InterpretationDocument3 pages2-Phenylethanol Mass Spectrum InterpretationPAOLO GAMBACORTANo ratings yet
- IR InstrumentationDocument8 pagesIR InstrumentationVedika SeepersadNo ratings yet
- 2010 AusSpec Workshop SlidesDocument171 pages2010 AusSpec Workshop SlidesAnonymous 0sin2m0TKP100% (1)
- Various Tools and Techniques Used For Structural ElucidationDocument28 pagesVarious Tools and Techniques Used For Structural ElucidationAvinashNo ratings yet
- Note4 PDFDocument24 pagesNote4 PDFSimon SiuNo ratings yet
- 2022 04 08 487683 FullDocument22 pages2022 04 08 487683 FullEngr. Babar AliNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument543 pagesModern PhysicsFernando SoaresNo ratings yet
- DD Program SyllabusDocument14 pagesDD Program SyllabusDHANUSHTEJ VUNNAMNo ratings yet
- Uv SeminarDocument47 pagesUv SeminaralaisshamNo ratings yet
- Graphene Chlorophyll 01Document8 pagesGraphene Chlorophyll 01venugopallNo ratings yet
- Topic 11Document38 pagesTopic 11api-546066323No ratings yet
- Section 4Document29 pagesSection 4Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- BCS-CRM 181 - 3 Jun2013Document2 pagesBCS-CRM 181 - 3 Jun2013Ishmael WoolooNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Molecular Physics: Instructor Name: Professor Amal Kumar Das Institute: IIT KharagpurDocument1 pageAtomic and Molecular Physics: Instructor Name: Professor Amal Kumar Das Institute: IIT KharagpurmustafaphyNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis: Theory, Concepts, and ApplicationsDocument41 pagesUV-Vis: Theory, Concepts, and ApplicationsReese VespertineNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Marcelo Picolo, Uv-Vis SpectroDocument14 pagesJurnal Marcelo Picolo, Uv-Vis SpectroDinda Tryana SembiringNo ratings yet
- Biotechniques Theory and Practice Ebook PDFDocument329 pagesBiotechniques Theory and Practice Ebook PDFSherwann Vergara Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- DHW - Lecture 4 - Introduction To Spectrochemical Methods - 101016Document100 pagesDHW - Lecture 4 - Introduction To Spectrochemical Methods - 101016Sadiq AlmubarakNo ratings yet
- MSC Chemistry PG Day Ai PDFDocument24 pagesMSC Chemistry PG Day Ai PDFArangaNo ratings yet
- RPT 12 07Document118 pagesRPT 12 07CHRISTOS KALOUDISNo ratings yet
- PHY 004 Modern Physics Lecture Note 2Document7 pagesPHY 004 Modern Physics Lecture Note 2Michael DanielsNo ratings yet
- Theory of Color Physics 05 SlideDocument20 pagesTheory of Color Physics 05 SlideRikta IslamNo ratings yet