Geo PP1 MS
Geo PP1 MS
Uploaded by
talaichebuCopyright:
Available Formats
Geo PP1 MS
Geo PP1 MS
Uploaded by
talaichebuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Geo PP1 MS
Geo PP1 MS
Uploaded by
talaichebuCopyright:
Available Formats
MANGU PREMOCK EXAMINATIONS
GEOGRAPHY
PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
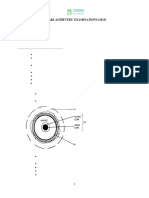
1. The diagram below shows some weather station instruments.
(a) Identify the instruments marked K, L and M. (3 marks)
K - Anemometer
L – Sunshine recorder
M – Rain gauge
(b) Give two modern methods of weather forecasting. (2 marks)
Use of artificial satellites.
Use of a radiosonde.
Use of computers.
Use of an aero sound.
Use of weather radars.
2. (a) Give the two main movements of the earth. (2 marks)
Rotation of the earth
Revolution of the earth
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***11*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
(b) State three reasons why the interior of the earth is very hot. (3 marks)
The original heat at formation is still being retained.
Due to the weight of overlying materials.
Due to the breakdown of radioactive elements.
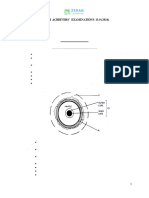
3. The diagram below show the occurrence of an earthquake
(a) Name the parts marked A, B and C (3marks)
A –Seismic focus
B – Epicentre
C – Shock waves
(b) List two scales used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake.(2 marks)
Richter scale
Moment magnitude scale
4. State five characteristics of coniferous forests. (5 marks)
Tree species are softwoods
Most tree species are evergreen.
The trees have a big portion of stem compared to the leaves.
Trees have a conical shape to allow snow to slide off easily.
Trees have needle like leaves.
Trees occur in big pure stands.
Trees have a thick bark which is waxy to protect them from winter cold.
The forest floor has very little or no undergrowth due to long winters.
Trees have wide shallow roots to utilize moisture from the top soil.
Trees are tall with flexible trunks to prevent breaking during strong winds.
5. (a) What is soil catena? (2 marks) Soil catena refers to the sequence variation of soil
derived from the same parent material down a slope from top to bottom.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***21*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
(b) State three factors that influence soil colour. (3 marks)
The chemical composition of the soil particles
The amount of organic matter present in the soil.
The type of parent material from which the soil has developed.
The drainage of the area in which the soil is found.
SECTION B
6. Study the map of Oyugis (1:50, 000, sheet 130/1) provided and use it to answer the
following questions.
(a) (i) Identify two relief features at grid square7342. (2 marks)
Hills
Steep slope
A river valley
A pass
(ii) Measure the distance of road E 212 from its junction with road C 18 to the
junction at grid square 7542. Give your answer in kilometres. (2 marks)
7.9 km (accept 7.8 km or 8.0 km)
(iii) Determine the six figure grid reference of Kitweru School. (2 marks)
748174
(b) (i) What is the vertical interval of the map? (1 mark)
50 feet
(ii) Determine the bearing of a jaggery factory at grid reference 788237 from a
church at grid reference 806188. (2 marks)
3400(accept 3390 or 3410)
(c) (i) Draw a square 10cm by 10cm to represent the region east of easting 85
from northing 30 to northing 40. On the square, mark and name.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***31*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
Kodera forest.
Oriang’ hill
A district boundary.
All weather road-bound surface.
A seasonal swamp (6 marks)
(ii) What is the scale of the sketch that you have drawn? (1 mark)
1:100,000
(d) (i) Citing evidence from the map, identify four crops grown in the area covered by the
map. (4 marks)
Crop - evidence
Coffee - presence of coffee factories
Sugarcane- presence of a jaggery factory and sugar research station
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***41*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
Cotton - presence of cotton stores
Maize - presence of flour mills
(ii) Describe the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map.
(5 marks)
There are more settlements on the eastern part of the map than in other parts.
There are clusters of settlements at shopping centres or markets
Kodera forest has no settlements
Areas with hills have no settlements
Regions with river valleys have very few or no settlements
There are no settlements within the seasonal swamp at mwakibagendi
Some settlements occur along main track motorable roads forming linear settlement
pattern.
The western parts have moderately distributed settlements
7. (a) (i) What is a mineral? (2 marks)
A mineral is a naturally occurring inorganic crystalline substance with a definite
chemical composition and physical properties.
OR
A mineral is an inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition occurring
naturally at or beneath the earth surface.
(ii) Give three ways used to classify rocks. (3 marks)
According to their mode of formation.
According to their chemical composition.
According to their age.
(b) (i) Describe how igneous rocks are formed. (5 marks)
High temperatures in the interior of the earth causes materials to be in molten
form.(magma)
High pressure underneath pushes the molten magma through lines of weakness such
as faults and vents.
If the pressure is low, magma fails to reach the earth’s surface. The magma cools and
solidifies below the surface forming intrusive igneous rocks.
If the pressure acting on magma is high, the magma reaches the surface as lava.
The lava cools on the earth’s surface forming extrusive igneous rocks.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***51*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
(ii) List three examples of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
Sand stone Grit Shale Mudstone Siltstone Claystone
Loess Breccia Conglomerate Boulder clay
(c) Explain three types of rock metamorphism. (6 marks)
During thermal/contact metamorphism, hot magma intrudes original crustal rocks
during vulcanicity. The hot magma may melt and recrystallize some sections of the
original rock thus altering them forming new minerals.
During dynamic metamorphism, intense compressional pressure acting within a
limited area thus alters the structure and texture of crustal rocks. Weight
materials overlying some sedimentary rocks may alter the structure of bottom
layers.
Regional metamorphism occurs during fold mountain formation. Intense
compressional force/pressure and heat act on sedimentary rocks over a wide area
altering both the structure and chemical composition of the rocks.
(c) Suppose you were to carry out a field study on rocks in the area surrounding your
school
(i) State three characteristics that you would look for while identifying
different rock types (3marks)
The hardness of the rocks
The density of the rocks
Texture of the rocks
Colour of different rocks
Lustre of the minerals farming the rock
Shape of the rock crystals
(ii) State three follow up activities for the field study (3marks)
Writing a report in essay form
Displaying photographs on rocks taken from the field
Displaying labelled samples
Laboratory testing of the mineral composition of some rocks collected
Discussing the findings in groups
Giving a lecture to the students who never went.
8. (a) (i) Differentiate between faulting and folding. (2 marks) Folding is the
process through which young sedimentary rocks bend upwards or downwards due to
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***61*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
compressional forces whereas faulting is the process through which crustal rocks
fracture due to tectonic forces such as tension, compression or shear.
(ii) Name five features formed as a result of faulting. (5 marks)
Rift valleys
Fault blocks (Block mountains and Horsts)
Tilt blocks
Escarpments/fault scarps
Fault steps
(b) The world map below shows the location of some fold mountains. Use it to answer
question (a)(i)
(i) Identify the fold mountains marked W, X, Y and Z (4 marks)
W – Rockies
X – Alps
Y – Andes Z – Ural
(ii) Citing relevant examples, explain how Fold Mountains were formed according to the
plate tectonics theory. (6 marks)
Fold Mountains are formed when two tectonic plates meet along compressional
tectonic plate boundaries
When an oceanic plate meets a continental plate the edges of the sediments and
materials at the margins into fold mountains e.g. Andes and Rockies
Fold Mountains are also formed when two continental plates meet squeezing the
materials in between into Fold Mountains e.g. Himalayas Atlas and Alps. (c)
Explain the effects of Fold Mountains on the following
(i) Transport. (2 marks)
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***71*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
Fold mountain scenery acts as a barrier to easy construction of roads, railways and
pipelines thus making it difficult to access some regions due to ruggedness.
(ii) Agriculture. (2 marks)
Leeward slopes of some fold mountain ranges receive dry winds leading to arid
conditions. This discourages crop farming but favours ranching and transhumance
Windward slopes of most fold mountains receive high orographic rainfall which supports
crop farming
(iii) Tourism. (2 marks)
Fold mountain scenery and snow-capped slopes are important tourist attractions with
some slopes favouring winter sports such as skiing and ice skating, e.g. Swiss Alps
(iv) Mining. (2 marks)
Along some slopes of some Fold Mountains, valuable minerals were exposed thus are
exploited for various economic uses e.g. copper and tin along the Andes slopes in Bolivia
and Chile.
9. (a) Give three examples of West coast deserts. (3 marks)
Namib
Atacama
Californian
The Great Sandy Desert of Australia
(b) (i) Apart from rock pedestals, name four other features formed due to
wind erosion in arid regions. (4 marks)
Zeugen
Yardangs
Mushroom block
Deflation hollows and oases
Ventifacts
(ii) With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe how a rock pedestal is
formed. (7 marks)
Initially, there existed an outcrop rock mass with horizontal and alternating layers of
hard and soft rocks.
The heterogeneous rock lie on the path of prevailing wind on a desert.
The rock was weakened by both weathering and wind abrasion.
The soft layers are eroded faster thus forming hollows.
The hard/resistant layers are worn out slowly hence bulge.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***81*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
Abrasion is greater at the lower part of the outcrop rock thus greater undercutting.
With time, this resulted in an irregular rock pillar with a narrow base called a rock
pedestal.
[Diagrams 2 marks]
[Description 5 marks]
(c) Explain four factors that influence the rate of wind transport. (8 marks)
The strength and the speed of the wind. A strong wind transports heavier and more
materials than a weak wind.
Presence of obstacles such as outcrop rocks and vegetation reduce the wind speed
hence reducing its capacity to transport materials.
Nature of the materials transported. Light particles such as dust are transported to
great distances while heavier sand and pebbles over short distances.
Wind transport is effective during a hot and dry season. Weather changes such as
torrential rain washes air borne particles to the ground.
(d) State three negative influence of desert features. (3 marks)
Advancing sand dunes can be barriers across transport lines such as roads.
Spreading sand dunes encroach onto productive land hence desertification.
Flash floods from torrential rains in deserts deposit materials that block roads.
Excess surface run off flowing in wadis may sweep away and drown people
10. (a) (i) What is a lake? (2marks)
A lake is a mass of water which occupies a depression/basin/hollow on the surface
of the earth.
(ii) Give three processes that lead to formation of Lakes. (3marks)
Through earth movements.
Through vulcanicity.
Through erosion.
Through deposition.
Through mass movement.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***91*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
Through weathering by solution.
Through human activities.
(b) Describe how Lake Victoria was formed (6marks)
Internal land forming processes caused vertical earth movements which resulted in
down warping of a huge region.
Down warping led to the formation of a huge depression/basin.
Uplifting of landmasses around the depression during the formation of the Mau
Ranges and the Ruwenzori altered the drainage of the area.
Some rivers from Kenya which flowed westwards were cut off and diverted into the
depression.
Some rivers in Uganda such as Katonga, Kafu and Kagera were reversed to flow into
the depression.
Deposition of water into the depression caused further down warping.
The mass of water which accumulated formed Lake Victoria.
(c) Explain three factors why some Lakes in the Rift Valley in Kenya are saline.
(6marks)
Some rivers and surface runoff flowing over volcanic rocks empty salt solutions in some
lakes thus increasing salinity.
Some lakes lack surface outlets in form of rivers which lead to accumulation of salts.
Some lake beds are made of rocks rich in soluble salts where the lake water directly
dissolves some salts thus increasing salinity.
Some lakes are fed by springs rich in salty water which contributes to salinity.
Some lakes are located in high temperature regions with high evaporation rates thus
accumulation of salts.
(d) Explain four ways in which lakes influence the climate of the surrounding areas.
(8marks)
Large lakes contribute large quantities of moisture which aids in the formation of
convectional rainfall.
Lakes increase the absolute humidity of the surrounding area by adding extra moisture
through evaporation.
Lakes facilitate the development of land and lake breezes through creation of pressure
differences between water surface and the land surface.
Air currents from lakes lower the temperature of the surrounding regions during
the hot/summer season.
During winter, lake breezes may bring a warming effect to adjacent regions e.g. The
Great lakes of North America.
Land and lake breezes may strengthen or reverse the pattern of prevailing winds over
adjacent regions.
Visit: www.mwalimuresources.co.ke ***101*** Call/WhatsApp: 0735649658
You might also like
- Geography - Geography Form 1 - Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesGeography - Geography Form 1 - Marking SchemeJoy Tech100% (1)
- Geography Form 2 - Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesGeography Form 2 - Marking Schemewillynjoroge345No ratings yet
- Answer All The Questions in Section A. in Section B Answer Question 6 and Any Other Two. Section. ADocument9 pagesAnswer All The Questions in Section A. in Section B Answer Question 6 and Any Other Two. Section. Aandy gideonNo ratings yet
- GEOG-P1-M.SDocument13 pagesGEOG-P1-M.SAmos sifunaNo ratings yet
- Geography F4 PP1 MSDocument10 pagesGeography F4 PP1 MSDennis KemoiNo ratings yet
- Geo F4 MSDocument8 pagesGeo F4 MSkiruimeshack04No ratings yet
- HsGeography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2023-7538Document11 pagesHsGeography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 2 Exams 2023-7538sernetogutuNo ratings yet
- Champ PP1 SchemeDocument11 pagesChamp PP1 Schemevincentnjuki7No ratings yet
- KLM S1 Geo PP1 MSDocument10 pagesKLM S1 Geo PP1 MS25850338naomiNo ratings yet
- Geography PP1 MsDocument9 pagesGeography PP1 MsnamelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- GEO PP1 MS (1)Document12 pagesGEO PP1 MS (1)ex VideozNo ratings yet
- Geo AnswersDocument6 pagesGeo Answersnicodemusbett5No ratings yet
- Ageo f2 M Scheme Ui2252021002Document8 pagesAgeo f2 M Scheme Ui2252021002s3rmakotaNo ratings yet
- 312 1 QsDocument8 pages312 1 Qswerep72No ratings yet
- Sigea PP1-MS - 112521Document12 pagesSigea PP1-MS - 112521qotingiNo ratings yet
- Geog PP1 MSDocument11 pagesGeog PP1 MSMAN254 MANASNo ratings yet
- SCHEME Physical GeographyDocument12 pagesSCHEME Physical Geographyunderdawg992No ratings yet
- Geography f1t2 MsDocument10 pagesGeography f1t2 Msjohnsly931No ratings yet
- CG 2024Document14 pagesCG 2024oderodomnick7No ratings yet
- Geo PP1 MSDocument11 pagesGeo PP1 MStomkyondaNo ratings yet
- Sigea pp1QDocument5 pagesSigea pp1QqotingiNo ratings yet
- Crescendo 2 2024 PP1 MSDocument11 pagesCrescendo 2 2024 PP1 MSvincentnjuki7No ratings yet
- KCSE 2016 Geography Paper 1 Questions With Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesKCSE 2016 Geography Paper 1 Questions With Marking SchemechichiNo ratings yet
- Geo f3t1 2672021 003Document4 pagesGeo f3t1 2672021 0033HP5 Cheung On KiNo ratings yet
- Geography F3 QSDocument5 pagesGeography F3 QSkalandemary7No ratings yet
- Geography Marking Scheme Topical AnalysedDocument51 pagesGeography Marking Scheme Topical AnalysednamelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- Geography App Marking Scheme RevisionkeDocument30 pagesGeography App Marking Scheme RevisionkeokonjirasNo ratings yet
- Geo p1Document4 pagesGeo p1VernonNo ratings yet
- Sibugeo 1 2024 Paper1 MSDocument9 pagesSibugeo 1 2024 Paper1 MSyator563No ratings yet
- Kcse Geo Latest Predictions 2024Document66 pagesKcse Geo Latest Predictions 2024Charles OmondiNo ratings yet
- Geo Top National Schools 2024Document65 pagesGeo Top National Schools 2024Derrick Kipyegon0% (1)
- Sem 2-2013-2014 AnswerDocument26 pagesSem 2-2013-2014 AnswerBryan LeeNo ratings yet
- Geography Marking ChemeDocument8 pagesGeography Marking Chemebillymwangaza7No ratings yet
- Geography PP1 QuizDocument4 pagesGeography PP1 QuizarettecirqueNo ratings yet
- Geography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) (2011) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedDocument11 pagesGeography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) (2011) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedViraat GautamNo ratings yet
- Gatundu 2015 GEO PP1 QnsDocument3 pagesGatundu 2015 GEO PP1 Qnsedward mokayaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 - Geography - Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesForm 2 - Geography - Marking SchemeMejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Geography PP 1Document5 pagesGeography PP 1Badmind JnrNo ratings yet
- Bujiset Marking Scheme Geog PP1 CorrectedDocument13 pagesBujiset Marking Scheme Geog PP1 Correctedvincentnjuki7No ratings yet
- KCSE 2019 Geography Paper 1 Questions With Marking SchemeDocument9 pagesKCSE 2019 Geography Paper 1 Questions With Marking SchemechichiNo ratings yet
- Geo F2 MS 1Document4 pagesGeo F2 MS 1Selifa AbutiNo ratings yet
- Ultra Public School Final Geography Class Ix PreboardDocument7 pagesUltra Public School Final Geography Class Ix PreboardPiyali BhowmikNo ratings yet
- Geography JOINT PP1 QPDocument5 pagesGeography JOINT PP1 QPnamelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- Bujiset Geo PP1 Questions CorrectedDocument6 pagesBujiset Geo PP1 Questions Correctedvincentnjuki7No ratings yet
- Geography MocksDocument440 pagesGeography MocksCollins KC SuperiorNo ratings yet
- The City School Geography-6-MSDocument7 pagesThe City School Geography-6-MSamnaaziz4w31683No ratings yet
- Geography 2023 Top School's MocksDocument100 pagesGeography 2023 Top School's Mocksmicah isaboke100% (1)
- Geography 240805 085842Document4 pagesGeography 240805 085842emlyanne135No ratings yet
- Faulting KcseDocument10 pagesFaulting Kcsevictorkapere1No ratings yet
- Geography - Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesGeography - Marking Schemefarouksaid739No ratings yet
- Geography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) (2013) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedDocument10 pagesGeography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) (2013) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedViraat GautamNo ratings yet
- Geography Form 2 Marking Scheme Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023Document9 pagesGeography Form 2 Marking Scheme Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023shadykym2008No ratings yet
- Geography Paper 1Document6 pagesGeography Paper 1namelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- Geography Paper 1 Answers Model20012023004Document9 pagesGeography Paper 1 Answers Model20012023004olimugeorgeogolaNo ratings yet
- Geography 2024 PAPERDocument4 pagesGeography 2024 PAPERunderdawg992100% (2)
- Geography Paper 1 Form 4 Term 1 Exam 2018Document7 pagesGeography Paper 1 Form 4 Term 1 Exam 2018namelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- Geo Form Two Holiday Assignment 2024 December GeographyDocument14 pagesGeo Form Two Holiday Assignment 2024 December Geographywacdavid3No ratings yet
- Geography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedDocument10 pagesGeography H.C.G. - Paper-2 (Two Hours) : Part I Is Compulsory. All Questions From Part I Are To Be AttemptedViraat GautamNo ratings yet
- F2 Geog TQDocument27 pagesF2 Geog TQkmuliliNo ratings yet
- Reconstructing Archaeological Sites: Understanding the Geoarchaeological MatrixFrom EverandReconstructing Archaeological Sites: Understanding the Geoarchaeological MatrixNo ratings yet
- Phys PP2 MSDocument6 pagesPhys PP2 MStalaichebuNo ratings yet
- Geography Form 4 Paper 1 - Question PaperDocument14 pagesGeography Form 4 Paper 1 - Question PapertalaichebuNo ratings yet
- Phy Pp2 Kcse 2024 Prediction Trials - PDF - Capacitor - WavesDocument83 pagesPhy Pp2 Kcse 2024 Prediction Trials - PDF - Capacitor - WavestalaichebuNo ratings yet
- BST PP1 MSDocument5 pagesBST PP1 MStalaichebuNo ratings yet
- Hist PP2 MSDocument5 pagesHist PP2 MStalaichebuNo ratings yet
- Geo PP2 MSDocument10 pagesGeo PP2 MStalaichebuNo ratings yet
- Cre PP1 MSDocument6 pagesCre PP1 MStalaichebuNo ratings yet
- English Paper 2 2024 PredictionDocument4 pagesEnglish Paper 2 2024 PredictiontalaichebuNo ratings yet
- EM Paper 1Document1,156 pagesEM Paper 1sCience 123No ratings yet
- Introduction To HydrologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To HydrologyMark Anthony TajonNo ratings yet
- Write A Story Beginning WithDocument2 pagesWrite A Story Beginning WithQiao XinNo ratings yet
- A Tale of Two BirdsDocument9 pagesA Tale of Two BirdsBhatRashidNo ratings yet
- Internship Report RMCDocument13 pagesInternship Report RMCRushikesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Nixon Caroline Tomlinson Michael Power Up 6 Home BookletDocument40 pagesNixon Caroline Tomlinson Michael Power Up 6 Home BookletEssential English CentreNo ratings yet
- 2 二年级英文听写生词表Document6 pages2 二年级英文听写生词表Tiang Wan Hiong50% (2)
- Kami Export - Y9-12 Reading-Passage 19-Literature 7-For PrintDocument3 pagesKami Export - Y9-12 Reading-Passage 19-Literature 7-For PrintNick WanNo ratings yet
- Giáo Trình LPTD 4Document40 pagesGiáo Trình LPTD 4Hưng Trịnh TrọngNo ratings yet
- Tomorrow's Weather - Google SearchDocument1 pageTomorrow's Weather - Google Searchpromisebrevard10No ratings yet
- Study Guide, UnitDocument5 pagesStudy Guide, UnitBrenda GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 3 - Q4 - W2Document3 pagesDLL - Science 3 - Q4 - W2shyfly21No ratings yet
- DP Operations Guidelines - SEACORDocument7 pagesDP Operations Guidelines - SEACORRoyNo ratings yet
- The City Planners - Margaret AtwoodDocument52 pagesThe City Planners - Margaret AtwoodDevoto EnglishNo ratings yet
- Research About NATURAL and MANMADE DisasterDocument10 pagesResearch About NATURAL and MANMADE DisasterCynan Quintana TarenoNo ratings yet
- EF3e Elem Quicktest 05Document3 pagesEF3e Elem Quicktest 05Ignacio OrmaecheaNo ratings yet
- HS-EDC146E HS-EDS142THPE Mini Station With Shutter - Introduction - 2020Document2 pagesHS-EDC146E HS-EDS142THPE Mini Station With Shutter - Introduction - 2020Yung SangNo ratings yet
- I Became Close To VillainDocument1,008 pagesI Became Close To VillainEvey ReisNo ratings yet
- Umbrella HouseDocument6 pagesUmbrella HouseGonzalo Agulló FernándezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Ice Hotel Unit 3: Hurricane Who?Document8 pagesUnit 1: The Ice Hotel Unit 3: Hurricane Who?Анастасия МузаNo ratings yet
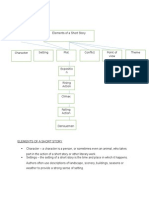
- Character Point of View Conflict Plot Setting ThemeDocument6 pagesCharacter Point of View Conflict Plot Setting ThemeLuis RascoNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Steel Structure S2123Document23 pagesPresentation of Steel Structure S2123Wanna PhyoNo ratings yet
- Pecos Bill Worksheet PDFDocument1 pagePecos Bill Worksheet PDFAruni Nelum BatepolaNo ratings yet
- Maritime Fax Transmissions - HFUndergroundDocument9 pagesMaritime Fax Transmissions - HFUndergroundhectormaster933No ratings yet
- Subunit 1.4 - Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesSubunit 1.4 - Climate Changemoreabhimanyu4No ratings yet
- Urban Resilience To Floods in Coastal Cities: Challenges and Opportunities For Ho Chi Minh City and Other Emerging Cities in Southeast AsiaDocument10 pagesUrban Resilience To Floods in Coastal Cities: Challenges and Opportunities For Ho Chi Minh City and Other Emerging Cities in Southeast AsiaHandikaNo ratings yet
- India Poltical MapDocument1 pageIndia Poltical MapvjNo ratings yet
- 11 Geography 2023-24Document2 pages11 Geography 2023-24adonlineclassmhssNo ratings yet
- VJC 314/16 NOV/SGN-HUI: - Not For Real World NavigationDocument17 pagesVJC 314/16 NOV/SGN-HUI: - Not For Real World NavigationVan TinNo ratings yet
- N-HWY Up-Int. Voc-Quizzes - U1Document3 pagesN-HWY Up-Int. Voc-Quizzes - U1Elwely AbdellahiNo ratings yet