Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis
Uploaded by
ShikhaKoulCopyright:
Available Formats
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis
Uploaded by
ShikhaKoulOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis
Uploaded by
ShikhaKoulCopyright:
Available Formats
Training done at C.R.
I (Kasauli)
Submitted by : Manisha Mittal (2306441) Shikha Koul (2306460)
Japanese encephalitis previously known as Japanese B encephalitis is a disease caused by the mosquito-borne Japanese encephalitis virus. Domestic pigs and wild birds are reservoirs of the virus, transmission to humans causes severe symptoms. This disease is most prevalent in Southeast Asia and the FarEast.
Group: Group IV ((+)ssRNA) Family: Flaviviridae
Genus: Flavivirus
Species: Japanese encephalitis virus Enveloped : Outer envelope is formed by envelope (E) protein and is the protective antigen.
1870s: Japan Summer encephalitis epidemics 1924: Great epidemic in Japan 6,125 human cases; 3,797 deaths 1935: First isolated From a fatal human encephalitis case 1938: Isolated from Culex tritaeniorhynchus
1940-1978 Disease spread with epidemics in China, Korea and India 1983: Immunization in South Korea Started as early as age 3 Endemic areas started earlier 1983-1987: Vaccine available in U.S. on investigational basis
Endemic in temperate and tropical regions of Asia
China, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand Vietnam, Cambodia, Myanmar, India, Nepal, Malaysia, Torres Strait Islands, Australia
Korea
Japan
China
India
Philipines
Indonesia
Reduced prevalence in Japan and U.S.A
Vector-borne disease Enzootic cycle Mosquitoes: Culex species Culex tritaeniorhynchus Reservoir: Ardeid (wading) birds Amplifying hosts Pigs, bats Possibly reptiles and amphibians Incidental hosts Horses, humans, others
35,000-50,000 cases annually. Incubation period: 6 to 8 days Most asymptomatic or mild signs Children and Elderly At highest risk for severe disease Elderly: High case fatality rate (30%) Mortality: 5-35%
Acute encephalitis Headache, high fever, stiff neck, stupor Severe encephalitis Paralysis, seizures, convulsions, coma and death
Neuropsychiatric sequelae 30-50% of survivors In utero infection possible Abortion of fetus
Laboratory Tests Tentative diagnosis Antibody titer: HI, IFA, ELISA JE-specific IgM in serum or CSF Definitive diagnosis Virus isolation: CSF sample, brain No specific treatment Supportive care
Vector control Eliminate mosquito breeding areas Adult and larval control Vaccination Equine and swine Humans Personal protective measures Avoid prime mosquito hours Use of repellants containing DEET
Live attenuated vaccine Used in equine and swine Successful for reducing incidence Inactivated vaccine (JE-VAX) Used for humans Japan, Korea, Taiwan, India, Thailand Used for endemic or epidemic areas Recommended for travelers Visiting endemic areas for > 30 days
JE-VAX, Vaccine
Japanese
Encephalitis
Virus
Inactivated, sterile, lyophilized vaccine
Prepared by inoculating mice intracerebrally with Japanese encephalitis virus, "Nakayama-NIH" strain.
Mice (3-4 weeks old) Intracerebral inoculation with JE virus NAKAYAMA- NIH strain Observation (4 days) Moribund mice
Bleed to death
Washing of mice
Cutting of brains Harvesting of brains
20% brain emulsion in PBS
Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 15 min at 4C Supernatant
Supernatant + protamine sulphate (0.09%) Kept at 4C for 2 hrs
Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 15 min at 4C Supernatant
Filter sterilization of the supernatant
VIRUS SUSPENSION
1) Test for sterility Bacterial Fungal Mycoplasma
2) Virus titre
INACTIVATION with Formalin (0.1%)
Keep at 4C for 45 days for inactivation Zonal centrifugation in K-II zonal centrifuge using sucrose (60%) density gradient Collection of fractions Pooling of fractions
BULK MATERIAL Test for staining Test for sterility Inactivation Preliminary potency FINAL BULK Thiomersal content Abnormal toxicity test Sterility tests
Distributed in vials & freeze dried Test : moisture pH Thiomersal content Formaldehyde Sterility Inactivation (in vivo) Abnormal Potency VACCINE
Final / Required conc. Total protein - 80g/ml Moisture content - 3% Thiomersal - 0.01% Formaline - 0.01% pH - 6.8-7.4 Dose - 1ml (adult) / 0.5ml (child) Shelf-life - 5yrs after freeze drying Optical density - 550-650nm
Sterility Test Virus Inactivation Test Abnormal Toxicity Test
Potency Test
World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) website
www.oie.int
USAHA Foreign Animal Diseases The Gray Book
www.vet.uga.edu/vpp/gray_book
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvbid/jencephalitis/ facts.htm
Queries ???
THANK YOU!!!
You might also like
- 1.acute PharyngitisDocument88 pages1.acute PharyngitisIhsan Hanif0% (1)
- Rheumatic Fever and RHDDocument49 pagesRheumatic Fever and RHDbereket gashuNo ratings yet
- Japanese EncephalitisDocument9 pagesJapanese EncephalitisAhmed Mawardi0% (1)
- Malaria PreventionDocument3 pagesMalaria PreventionRohit_Patkar_2942No ratings yet
- Skin Infestation PDFDocument30 pagesSkin Infestation PDFHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument44 pagesToxic Shock SyndromeIndicationNo ratings yet
- Polio PowerpointDocument10 pagesPolio PowerpointQzmp1No ratings yet
- Cns InfectionsDocument141 pagesCns InfectionsReda AlyNo ratings yet
- Meningocele & Spina BifidaDocument20 pagesMeningocele & Spina BifidaAstrid SabirinNo ratings yet
- StomatitisDocument74 pagesStomatitisZahoor Zaidi100% (1)
- Presented By: Gayramara Arben John ZDocument36 pagesPresented By: Gayramara Arben John ZgoykicoshenNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of AidsDocument30 pagesPrevention and Control of Aidsutsavshrestha05No ratings yet
- MalariaDocument23 pagesMalariaAryan RajNo ratings yet
- Preanesthetic Medication JasminaDocument44 pagesPreanesthetic Medication Jasminaanjali sNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentDocument18 pagesClinical Teaching On Neurological AssessmentFiyas BiNo ratings yet
- TaeniasisDocument23 pagesTaeniasisMardoni Efrijon33% (3)
- Prevention of Parent To Child Transmission of HIV : Dr. ShobhaDocument52 pagesPrevention of Parent To Child Transmission of HIV : Dr. ShobhajijaniNo ratings yet
- The Environment Prtection Act 1986Document17 pagesThe Environment Prtection Act 1986Bhuneshwari BisenNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument27 pagesTyphoid FeverApril Mergelle Lapuz100% (2)
- Poliomyelitis: By: Reema I. DabbasDocument35 pagesPoliomyelitis: By: Reema I. DabbasReema DabbasNo ratings yet
- Japanese Encephalitis by RobelDocument2 pagesJapanese Encephalitis by RobelRobel_Saoi_2309No ratings yet
- Enteric FeverDocument22 pagesEnteric FeverRuchika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Filaria PPT - ClassDocument59 pagesFilaria PPT - ClassGauravMeratwal100% (2)
- LaryngitisDocument40 pagesLaryngitisMikhail Guidicelli100% (1)
- Malaria Case StudyDocument6 pagesMalaria Case StudymichpaduaNo ratings yet
- CSOM TreatmentDocument21 pagesCSOM TreatmentSarwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Created By: Group 2 Alma Risa F Kinantih K Shofialfiyyah Siti Anzani SucinurindahsDocument15 pagesDiarrhea: Created By: Group 2 Alma Risa F Kinantih K Shofialfiyyah Siti Anzani SucinurindahsAlmaRisaFitrianaNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Diet Plan: Good ChoiceDocument3 pagesPost Operative Diet Plan: Good ChoiceDinesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Convulsive Disorders in ChildrenDocument44 pagesConvulsive Disorders in ChildrenMurugesanNo ratings yet
- Medication ChartDocument4 pagesMedication ChartShanon Belle100% (1)
- Antiepileptic Drugs.Document32 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs.pabitraNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument39 pagesMalariaAulia Ratu PritariNo ratings yet
- Chiken PoxDocument7 pagesChiken PoxShahzada KhurramNo ratings yet
- Japanese EncephalitisDocument2 pagesJapanese EncephalitisGomez Agustin LeslieNo ratings yet
- D.Y. Patil College of Nursing Kadamwadi, Kolhapur Subject: Child Health Nursing Case Presentation On Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDocument18 pagesD.Y. Patil College of Nursing Kadamwadi, Kolhapur Subject: Child Health Nursing Case Presentation On Type 1 Diabetes MellitusJuhi Johnson JadhavNo ratings yet
- Snake BiteDocument19 pagesSnake Bitepravat777No ratings yet
- TyphoidDocument10 pagesTyphoidpeterjongNo ratings yet
- Primary ComplexDocument12 pagesPrimary ComplexLevi PosadasNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma and Acute AsthmaDocument23 pagesBronchial Asthma and Acute Asthmavivien kate perixNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children: by DR L N Gachare Paediatrician/PulmonologistDocument35 pagesPneumonia in Children: by DR L N Gachare Paediatrician/PulmonologistAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- PoliomyelitisDocument50 pagesPoliomyelitisJohn John TorresNo ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument22 pagesWhooping CoughAqeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocument30 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysismed.student657No ratings yet
- Meniere'S Disease: Kiran Thokchom M. Sc. (N) Final Year RinpsDocument36 pagesMeniere'S Disease: Kiran Thokchom M. Sc. (N) Final Year RinpsRebizz BizzNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument29 pagesAnthraxstevensb055No ratings yet
- Filariasis: Dr. Saida SharminDocument35 pagesFilariasis: Dr. Saida SharminBishwajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity UitmDocument25 pagesRadioactivity UitmMoody6861No ratings yet
- House FlyDocument45 pagesHouse FlysanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Seminar ON: Communicable DiseasesDocument159 pagesSeminar ON: Communicable DiseasesvishnuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Whooping CoughDocument37 pagesLecture 5 - Whooping CoughShaimaa AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Anti - Tubercular DrugsDocument88 pagesAnti - Tubercular DrugsEscitalopram 5mgNo ratings yet
- Survey of AmphibiansDocument35 pagesSurvey of AmphibiansAeriel Venice VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lourdes College Nursing Program NCM 105Document41 pagesLourdes College Nursing Program NCM 105Mayette Ludeña VillegasNo ratings yet
- Normal Newborn PP Final-1Document97 pagesNormal Newborn PP Final-1ettevyviNo ratings yet
- Visceral Leishmaniasis in IndiaDocument27 pagesVisceral Leishmaniasis in IndiaNishant SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis Alergi DR - NikenDocument21 pagesRhinitis Alergi DR - NikenDayita ApritutiNo ratings yet
- TB Case StudyDocument2 pagesTB Case StudyReisabelle LabianoNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem - Lecture - RabiesDocument25 pages5th Sem - Lecture - Rabiessouvikmaity2024No ratings yet
- Specific Neurological InfectionsDocument37 pagesSpecific Neurological InfectionsAli AlexNo ratings yet
- Group-2 - PMCH 3 UpdatedDocument29 pagesGroup-2 - PMCH 3 UpdatedKavya v KodathalNo ratings yet
- Pretest 02Document11 pagesPretest 02Muhammad Harist MurdaniNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives Explanation and ExercisesDocument2 pagesComparatives and Superlatives Explanation and ExercisesSteven Donaldson50% (2)
- Ad 0359774Document95 pagesAd 0359774Kit NottellingNo ratings yet
- The Five Antique (Transporting) Points: The Point at Which The Qi EmanatesDocument7 pagesThe Five Antique (Transporting) Points: The Point at Which The Qi EmanatesPRAKASSH RNo ratings yet
- CH 3 ClassificationDocument29 pagesCH 3 ClassificationRaKa aJJaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Objective QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Objective Questionsg c lallNo ratings yet
- Dog Approved People Food - Cesar MillanDocument5 pagesDog Approved People Food - Cesar MillanOrestis :. KonstantinidisNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Final Term Exam PaperDocument3 pagesClass 6 Final Term Exam Papertrilokbist04No ratings yet
- MCL BR-APE KN 1 2023 - Semester 2Document93 pagesMCL BR-APE KN 1 2023 - Semester 2rini setyaningsihNo ratings yet
- The Therian Bible PDFDocument24 pagesThe Therian Bible PDFerisari9467% (3)
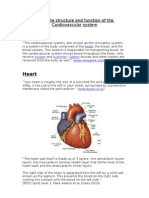
- Heart: Know The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesHeart: Know The Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular Systemnbeer93No ratings yet
- LitCharts-Cat and Mouse AnalysisDocument6 pagesLitCharts-Cat and Mouse AnalysisTim Tam100% (1)
- Lab 5. Primate Observation WorksheetDocument11 pagesLab 5. Primate Observation Worksheetwnhwv5byx6No ratings yet
- Crocodile PDFDocument289 pagesCrocodile PDFGalo Macias LopezNo ratings yet
- Pathology OF MALE Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesPathology OF MALE Reproductive SystemDio Reynaldi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Docsity 1 Faca o Comparativo Dos Adjetivos Ex Julie IsDocument13 pagesDocsity 1 Faca o Comparativo Dos Adjetivos Ex Julie IsRenan DantasNo ratings yet
- Terminology in Clinical SettingDocument13 pagesTerminology in Clinical SettingCiuss ThamrinNo ratings yet
- Common Freshwater Fishes of KeralaDocument18 pagesCommon Freshwater Fishes of KeralaVignesh Jayan100% (1)
- Yaws UphDocument44 pagesYaws UphJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- Ren 10Document1 pageRen 10ray72roNo ratings yet
- Dr. Moroni Final It ReportDocument42 pagesDr. Moroni Final It Reportogwal morrisNo ratings yet
- Footnote To YouthDocument3 pagesFootnote To YouthAbie PillasNo ratings yet
- National Parks in Odish: Wildlife SanctuariesDocument1 pageNational Parks in Odish: Wildlife SanctuariesSoumya SwainNo ratings yet
- CodexDocument199 pagesCodexGustavo PeñaNo ratings yet
- Q1 English-3 Summative Test #ADocument4 pagesQ1 English-3 Summative Test #AEstrella M. BellenNo ratings yet
- Intracellular AccumulationDocument38 pagesIntracellular AccumulationElena PoriazovaNo ratings yet
- A Bit of Fry and LaurieDocument8 pagesA Bit of Fry and LaurieAdrian IlinNo ratings yet
- SWOT-Analysis GaganDocument1 pageSWOT-Analysis GaganSATYAPRAKASH BEHERANo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument15 pagesAtelectasisAmit Kumar RanoNo ratings yet
- Beef Recipes For The HCG DietDocument17 pagesBeef Recipes For The HCG Dietlechiquita1No ratings yet