0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 viewsQMS (Final)
QMS (Final)
Uploaded by
sherrybanoThis document provides an overview of quality management systems and standards. It discusses key concepts such as defining quality, the elements of an effective quality management system, quality techniques and standards like ISO 9001, the benefits of documenting quality processes, and the structure and requirements of ISO 9001. The presentation emphasizes that ISO 9001 specifies requirements for an organization's quality management system to ensure customer satisfaction and compliance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
QMS (Final)
QMS (Final)
Uploaded by
sherrybano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views54 pagesThis document provides an overview of quality management systems and standards. It discusses key concepts such as defining quality, the elements of an effective quality management system, quality techniques and standards like ISO 9001, the benefits of documenting quality processes, and the structure and requirements of ISO 9001. The presentation emphasizes that ISO 9001 specifies requirements for an organization's quality management system to ensure customer satisfaction and compliance.
Original Title
QMS (final)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document provides an overview of quality management systems and standards. It discusses key concepts such as defining quality, the elements of an effective quality management system, quality techniques and standards like ISO 9001, the benefits of documenting quality processes, and the structure and requirements of ISO 9001. The presentation emphasizes that ISO 9001 specifies requirements for an organization's quality management system to ensure customer satisfaction and compliance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views54 pagesQMS (Final)
QMS (Final)
Uploaded by
sherrybanoThis document provides an overview of quality management systems and standards. It discusses key concepts such as defining quality, the elements of an effective quality management system, quality techniques and standards like ISO 9001, the benefits of documenting quality processes, and the structure and requirements of ISO 9001. The presentation emphasizes that ISO 9001 specifies requirements for an organization's quality management system to ensure customer satisfaction and compliance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 54
1
PRESENTED TO: SIR ALI ZUQARNAIN
PRESENTED BY:
SHEHR BANO YAWAR ALI (10585)
MUHAMMAD SAAD AWAN (10302)
QAMROSH ZAHEER (10443)
SYED MUHAMMAD FAHAD (8165)
What Is Quality?
Degree to which a set of inherent characteristics
fulfils requirements
2
Identify, understand and agree customer requirements
Plan to achieve them
Measure, monitor & control processes/activities
Requires A System
3
Meeting Our Customers Requirements
Doing Things Right the First Time; Freedom from Failure
(Defects)
Consistency (Reduction in Variation)
Continuous Improvement
Quality in Everything We Do
4
A belief in the employees ability
to solve problems
A belief that people doing the
work are best able to improve it
A belief that everyone is
responsible for quality
5
MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
6
7
Management Support
Mission Statement
Proper Planning
Customer and Bottom Line Focus
Measurement
Empowerment
Teamwork/Effective Meetings
Continuous Process Improvement
Dedicated Resources
ELEMENTS FOR
What Is A Quality Management System?
People
Processes
Materials
Equipment
Resources
Planned
Individually
System
Best Practice
Implemented
Collectively
Documented
System
Describes how
this happens
8
Quality Techniques & QMS Standards
Quality
Control
Quality
Assurance
Quality
Management
(Detection) (Prevention) (Direction)
BS 5750
1979-1987
ISO
9001/2/3
1987-2000
ISO 9001
2000
9
Why Document in
Quality Management
Communication Tool
Manage Change
Aids consistency
Record of Best Practice
Enables Effective Audit
ISO 9001 Pre-requisite
10
Documented Q.M.S.
POLICY
QUALITY
MANUAL
PROCEDURES
LOCAL/WORK INSTRUCTIONS
RECORDS / FORMS
INTENT
WHAT?
PROOF
HOW?
WHY?
11
ISO 9001 - Q.M.S. Requirements
ISO 9004 - Q.M.S. Guidelines on Performance Improvement
ISO 9000 - Q.M.S. Fundamentals & Vocabulary
12
The Structure of Quality Standards
1. Customer Focus
2. Leadership
3. Involvement of People
4. Process Approach
5. System Approach to Management
6. Continual Improvement
7. Factual Approach to Decision Making
8. Mutually Beneficial Supplier Relationships
ISO 9001:2000
Based on the 8 Quality Management Principles:
13
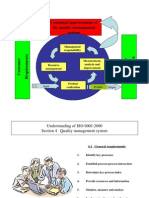
14
Continual improvement of
the quality management system
Requirements
Satisfaction
Customers
Customers
Resource
management
Measurement,
analysis and
improvement
Product
Realisation
Management
Responsibility
Input Output
Product
15
ISO9001 defines what the organization does to
ensure that its products or services satisfy the
customer's quality requirements and comply
with any regulations applicable to those
products or services.
ISO 14000 is primarily concerned with
"environmental management". In plain
language, this means what the organization
does to minimize harmful effects on the
environment caused by its activities.
16
ISO 14001 is an internationally recognised standard for environmental
management system which can be applied by any organisation.
It has much in common with ISO 9001, in particular the PLAN - DO -
CHECK- ACT concept.
As a minimum, ISO 14001 requires a commitment to legal compliance,
continual improvement and pollution prevention.
It involves the identification and assessment of all environmental aspects
and impacts in order to determine which are significant.
These must then be managed so as to minimise harm to the environment.
ISO14001 - Environmental management system model
for the international standard
Environmental Policy
Planning
Environmental aspects
Legal and other requirements
Objectives and targets
Environmental management
programmes
Implementation and Operation
Structure and responsibility
Training, awareness and competence
Communication
EMS documentation
Document control
Operational control
Emergency preparedness and response
Checking and Corrective Action
Monitoring and measurement
Non-conformance and corrective
and preventative action
Records
EMS audits
Continual
improvement
Management Review
17
ISO 14001
Fundamental requirements
18
19
From
Motivation through fear and loyalty
To
Motivation through shared vision
Attitude: Its their problem Ownership of every problem affecting
the customer
Attitude: the way weve always done it
Continuous improvement
Decisions based on assumptions/ judgment
calls
Decisions based on data and facts
Everything begins and ends with
management
Everything begins and ends with
customers
Crisis management and recovery Doing it right the first time
Choosing participative OR scientific
management
Choosing scientific AND participative
management
20
21
Control
&
Improvement
22
23
Process set-up?
Risks?
Objectives of the process?
Which contributes to the goals of the
organization?
Resources and
conditions?
Results of the process?
Measurement and steering?
?
1
2 3
4
24
The ISO 9000:2000 series consists of 3 Primary
standards
ISO 9000: QMS concepts and vocabulary
ISO 9001: QMS requirements
ISO 9004: QMS guidelines
This is supported by an additional standard
ISO 10011: QMS auditing guidelines
25
ISO 9001 specifies the requirements for a
quality management system that may be
used for internal application by
organizations, certification, or contractual
purposes.
26
27
ISO 9004 gives guidance on a wider
range of objectives of a quality
management system to improve the
organisations overall performance.
It is not a guideline for implementing
ISO 9001 and is not intended for
certification or contractual use.
28
ISO 9001:2008 is divided into 8 sections:
the first 3 are introductory
The requirements begin at section 4 and have the
following headings:
Quality management system
Management responsibility
Resource management
Product realisation
Measurement, analysis and improvement
29
30
QUALITY MANAGEMENT
PRINCIPLES
Quality Management System
The organisational structure, responsibilities,
procedures, processes and resources
for implementing quality management.
ISO 9001:2000 Process model
Customer
satisfaction
Customer
Customer
?
Delivery of
Services
Management
Resources Measurement
31
32
1. SCOPE
Includes the design and construction of clean room, ventilation
and air conditioning system, metal finishing system,
environmental control system for automotive and other
industrial or commercial applications. Exclusion Design and
development validation.
2. Normative References :
- ISO 9000:2005
- ISO 9001: 2008 QMS
- ISO 9001:2000 QMS
- ISO 9002:1994
33
3. Terms and Definition
Definitions Terms used by an organization; Processes, interaction,
improvement The focus is on looking at: What we do. Who we are
doing it for. Improving how we provide service.
4. General requirements
Documentation requirements Control of document Documents must
show a control number, adoption and revision dates, in order to
ensure use of the most recent information. Control of records Each
record must be controlled in order to ensure uniform quality.
34
4. General requirements
- General Documents
- Quality Manual
- Control of Documents
- Control of Records
35
5. Management Responsibility
- Commitment
- Focus
- Policy
- Objectives
- Planning
These correspond to the following
principles: Customer focus
Leadership
6. Resource Management
- Provide quality resources
- Provide quality personnel
- Provide quality infrastructure
- Provide quality environment
This corresponds to the following principle: Involvement of People
7. Product Realization
Control of the following process realization, planning, customer, communication,
product development, purchasing, function, operation, monitoring
These correspond to: Get the facts before you decide Focus on customers Use a
process approach Work with your suppliers
36
8. Measurement, Analysis and Improvement
- Perform remedial processes Monitor and measure quality Control
- nonconforming products
- Analyze quality information
- Make quality improvements
This corresponds to: Get the facts before you decide Encourage continual
improvement
37
38
International, expert consensus on state-of-the-art
practices for quality and environnemental management.
Common language for dealing with customers and
suppliers worldwide in B2B.
Increase efficiency and effectiveness.
Model for continual improvement.
Model for satisfying customers and other stakeholders.
39
Build quality into products and services from design
onwards.
Address environmental concerns of customers and
public, and comply with government regulations.
Integrate with global economy.
Sustainable business
Unifying base for industry sectors
Qualify suppliers for global
supply chains
Technical support for regulations
40
Documented procedures required by this standard and
those needed by the organisation to control its
processes.
41
Establish & maintain a manual including:
scope of QMS with details/justification for any exclusions
procedures or reference to them
description of sequence and interaction of processes
included in QMS
The quality manual shall be controlled
42
Quality Manual
ISO 9001 IS SIMPLY
A SYSTEM FOR
CREATING
PAPERWORK!!!
43
The extent of the QMS documentation depends on the
following:
a) size and type of the organisation
b) complexity and interaction of the processes
c) competence of personnel
Note: The documented procedures may be in any
form or type of medium.
44
45
QMS documents shall be controlled.
A documented procedure shall be
established:
to approve documents prior to use
to review/update & re-approve as
necessary
to identify changes and current revision
status
to ensure relevant versions are available
to ensure legibility and identification
to control documents of external origin
to control obsolete documents
46
QMS records shall be maintained to provide evidence of
conformance to requirements and effective QMS
operation.
A documented procedure shall be established for :
Identification,
storage
retrieval
protection
retention time and
disposition of records.
47
48
Determine team, set budget
Internal auditor(s) training if using in-house resources
Hire consulting firm if applicable
Gap Assessment
Implement requirements of standard to meet your business
needs against the gap assessment
Go-Live
Hold Management Review Meeting
Conduct Internal Audit
Refine documentation
Employee involvement training
System adjustment
Registration audit Stage 1
System adjustment
Registration audit Stage 2
49
50
Submit application to registrar
Stage 1: Assessment of readiness
Stage 2: Assessment for registration audit
Registration/certification awarded for 3 years
Surveillance audits (at least annually)
Recertification audit at the end of 3
rd
year
51
52
53
54
You might also like
- 043 - Philippine Products Company V Primateria (1965) (Miguel, V)Document2 pages043 - Philippine Products Company V Primateria (1965) (Miguel, V)VM MIGNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Mutual Funds in IndiaDocument40 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Mutual Funds in IndiafathimathabasumNo ratings yet
- Business Project 304B Study GuideDocument49 pagesBusiness Project 304B Study GuideSakhumuzi Moya100% (1)
- Managing Workers Compensation (2001)Document311 pagesManaging Workers Compensation (2001)Richu PaliNo ratings yet
- Accenture Moving To The Cloud Strategy For Banks in North AmericaDocument16 pagesAccenture Moving To The Cloud Strategy For Banks in North AmericarishivacaNo ratings yet
- TS16949 Training OverviewDocument23 pagesTS16949 Training OverviewPraveen CoolNo ratings yet
- Form - COTO LogDocument45 pagesForm - COTO LogAmit KuarNo ratings yet
- L03-Project Quality ManagementDocument42 pagesL03-Project Quality ManagementMUHAMMAD AZEEM Khan100% (1)
- Auditor Training Module 2 - Audit ManagementDocument28 pagesAuditor Training Module 2 - Audit ManagementThant AungNo ratings yet
- Internal and External CommunicationDocument6 pagesInternal and External CommunicationIqah FauziNo ratings yet
- ISO 13485 - 2016-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesISO 13485 - 2016-WPS Officerajesh.bNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001 BrochureDocument2 pagesIso 9001 BrochuredcorpuzNo ratings yet
- 2 2018mac20 Risk Management and Assessment ProgrammeDocument36 pages2 2018mac20 Risk Management and Assessment ProgrammesulibyaNo ratings yet
- IMS Documentation Requirements: Presented By: Global Manager GroupDocument7 pagesIMS Documentation Requirements: Presented By: Global Manager Groupareib_hassanNo ratings yet
- Guidance On - Auditing Climate Change Issues in ISO 9001Document10 pagesGuidance On - Auditing Climate Change Issues in ISO 9001GMNo ratings yet
- LQMS 6Document76 pagesLQMS 6R C MathewNo ratings yet
- Iso 9001Document97 pagesIso 9001GalkandaNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 2000 Auditor TrainingDocument90 pagesISO 9001 2000 Auditor Trainingjoshua_sx1100% (12)
- Competence Vs QualificationDocument25 pagesCompetence Vs Qualificationjohnoo7No ratings yet
- Clauses IMSDocument14 pagesClauses IMSSameer BugdeNo ratings yet
- Common TS16949 Audit Findings - Perry JohnsonDocument48 pagesCommon TS16949 Audit Findings - Perry Johnsontehky63No ratings yet
- Iso 9001,2015 Master ListDocument5 pagesIso 9001,2015 Master Listhead.qcNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Operational Planning and ControlDocument33 pages8.1 Operational Planning and ControlMenodai MenodaiNo ratings yet
- SUPPLIER - Manual - Rev - H (Commercial String & Tool Company)Document18 pagesSUPPLIER - Manual - Rev - H (Commercial String & Tool Company)Jahmia CoralieNo ratings yet
- Communication Plan TemplateDocument1 pageCommunication Plan TemplateJorge Octavio Hurtado GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Best Practice Quality Policy StatementsDocument3 pagesBest Practice Quality Policy StatementsdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management FrameworkDocument21 pagesIntegrated Management FrameworkMuhammad ZafarNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit - 19!08!2022-GP ISO 17025 SlidesDocument33 pagesInternal Audit - 19!08!2022-GP ISO 17025 Slidesmuhammad imran aziz100% (1)
- ISO 9000-2008 AuditingDocument23 pagesISO 9000-2008 AuditingMohamed ShabirNo ratings yet
- QMS Deployment Kickoff CoveDocument16 pagesQMS Deployment Kickoff CoveAliNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management System (Ims) : Internal Auditor For Iso 9001, ISO 14000 AND OHSAS 18001 (COURSE CODE: IMS/1)Document6 pagesIntegrated Management System (Ims) : Internal Auditor For Iso 9001, ISO 14000 AND OHSAS 18001 (COURSE CODE: IMS/1)bawcockNo ratings yet
- Bsi Small Business Guide To Standards en GBDocument24 pagesBsi Small Business Guide To Standards en GBamlatas100% (1)
- IRCA and CQI Webinar SlidesDocument40 pagesIRCA and CQI Webinar SlidesabdelmutalabNo ratings yet
- Continual Improvement of The Quality Management SystemDocument27 pagesContinual Improvement of The Quality Management SystemLim Saw WahNo ratings yet
- SGS SSC ISO20121 Brochure A4 EN 12 V2Document8 pagesSGS SSC ISO20121 Brochure A4 EN 12 V2Troy Reynolds CMP EMDNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Conduct A Risk AssessmentDocument4 pagesExercise 2 Conduct A Risk AssessmentRoxana BaltatescuNo ratings yet
- QMS Training Guide Prep. Based On.... Clause 6 HAM. 19.15ECDocument17 pagesQMS Training Guide Prep. Based On.... Clause 6 HAM. 19.15ECKenate MergaNo ratings yet
- Pt. XXXXX: Internal Auditor Course On Quality Management SystemDocument39 pagesPt. XXXXX: Internal Auditor Course On Quality Management SystemImam MansyurNo ratings yet
- Win More Tenders With ISO Management SystemsDocument3 pagesWin More Tenders With ISO Management SystemsDavid100% (2)
- Introduction To Internal AuditingDocument59 pagesIntroduction To Internal AuditingPaviththira sivaNo ratings yet
- Implementing and Validating The Quality SystemDocument23 pagesImplementing and Validating The Quality SystemΑυτός είμαι εγώNo ratings yet
- Auditing (3Rd Party)Document7 pagesAuditing (3Rd Party)Neil Buyco VillamorNo ratings yet
- ISO IQA For DDFC by AJMAL29-04-14Document52 pagesISO IQA For DDFC by AJMAL29-04-14Waqas WaqasNo ratings yet
- APG InternalAudit2015 PDFDocument4 pagesAPG InternalAudit2015 PDFBulmaro SanchezNo ratings yet
- 9001 Audit Checklist-Monitoring Measurement and ImprovDocument7 pages9001 Audit Checklist-Monitoring Measurement and ImprovAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Quality Control DepartmentDocument5 pagesQuality Control DepartmentRonnel MatampaleNo ratings yet
- Summary: Context of The OrganizationDocument5 pagesSummary: Context of The OrganizationNC Rigor LuisNo ratings yet
- ISO 20121 Sustainable Event Management Systems EMS Presentation Peter Greenham IIGI FWR Group Independent Inspections CertificationDocument5 pagesISO 20121 Sustainable Event Management Systems EMS Presentation Peter Greenham IIGI FWR Group Independent Inspections CertificationfwrgroupNo ratings yet
- Management Review Meeting MinutesDocument10 pagesManagement Review Meeting MinutesSystamatic RaxaNo ratings yet
- 17vendor Pre-Qualification FormDocument10 pages17vendor Pre-Qualification FormHervian LanangNo ratings yet
- Accreditation BodiesDocument25 pagesAccreditation BodiesSadaf RaqeebNo ratings yet
- IMS Awarness 00Document14 pagesIMS Awarness 00RohitSoni100% (1)
- Pub100373 PDFDocument12 pagesPub100373 PDFedgelcer100% (1)
- Guide To Standards - Good Management Practice - CD31 PDFDocument31 pagesGuide To Standards - Good Management Practice - CD31 PDFthawatchai11222512No ratings yet
- Auditor Competence: © 2005 John E. (Jack) WestDocument22 pagesAuditor Competence: © 2005 John E. (Jack) WestFernandoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Supplier Audit: 1.1 Process Capability-Capabilitatea ProcesuluiDocument15 pagesGuidelines For Supplier Audit: 1.1 Process Capability-Capabilitatea ProcesuluiAdi Sava100% (1)
- NCMF Management Review Report 2017 1Document186 pagesNCMF Management Review Report 2017 1Thee BouyyNo ratings yet
- Cost of QualityDocument21 pagesCost of QualitymaherkamelNo ratings yet
- ISO27k Nonconformity Corrective Preventive Action FormDocument3 pagesISO27k Nonconformity Corrective Preventive Action FormJasim's Bhaigna100% (1)
- Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandQuality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document85 pagesChapter 10sherrybanoNo ratings yet
- Article GRP AssignDocument14 pagesArticle GRP AssignsherrybanoNo ratings yet
- Types of Debt Securities IssuedDocument8 pagesTypes of Debt Securities IssuedsherrybanoNo ratings yet
- President Lyndon B JohnsonDocument19 pagesPresident Lyndon B JohnsonsherrybanoNo ratings yet
- Highlights of The PlantDocument8 pagesHighlights of The PlantsherrybanoNo ratings yet
- Catch-Up Time For Dynamic NationsDocument12 pagesCatch-Up Time For Dynamic NationssherrybanoNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Powers DebenturesDocument9 pagesBorrowing Powers DebenturesNeha Shah100% (2)
- MPM Expenditure Audit Cheque Payment DraftDocument27 pagesMPM Expenditure Audit Cheque Payment DraftYolande Gyles LevyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityJigarNo ratings yet
- Bsi International Expo BrochureDocument12 pagesBsi International Expo Brochurenurul nufnoteNo ratings yet
- Long Test Entrepreneurship Name: - Gr&SecDocument2 pagesLong Test Entrepreneurship Name: - Gr&SecHSAM ScienceNo ratings yet
- Instructions For Form FillingDocument2 pagesInstructions For Form FillingPritesh MaparaNo ratings yet
- CISO Perspectives Data ClassificationDocument5 pagesCISO Perspectives Data ClassificationMSFTSIRNo ratings yet
- Leadership Pitch Deck FinalDocument14 pagesLeadership Pitch Deck Finalapi-260268510No ratings yet
- AP Econ Unit 3 PlansDocument4 pagesAP Econ Unit 3 Plansahraz93No ratings yet
- SMCMYEP0114099Document7 pagesSMCMYEP0114099VIkas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mystic Touch Perfume Sampler Promotion August 2024Document2 pagesMystic Touch Perfume Sampler Promotion August 2024aaronhNo ratings yet
- Magazines-Subscription Excel Sheet - Updated Till First Quarter 2011Document8 pagesMagazines-Subscription Excel Sheet - Updated Till First Quarter 2011amitbaggausNo ratings yet
- Manager ICT Governance Security and RiskDocument5 pagesManager ICT Governance Security and Riskkumusha123No ratings yet
- Overview of Enterprise Risk ManagementDocument64 pagesOverview of Enterprise Risk ManagementUsman HamidNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document17 pagesModule 4Bry An CañaresNo ratings yet
- David J. Shonk, Gonzalo A. Bravo, Luisa Velez-Colon & Cindy LeeDocument18 pagesDavid J. Shonk, Gonzalo A. Bravo, Luisa Velez-Colon & Cindy Leenaz_qd358No ratings yet
- Induction - PPT 2Document10 pagesInduction - PPT 2reelshivamNo ratings yet
- CapabilitiesDocument4 pagesCapabilitiesAnmol NadkarniNo ratings yet
- Sevket - Pamuk - Prices in The Ottoman Empire - 1469-1914Document18 pagesSevket - Pamuk - Prices in The Ottoman Empire - 1469-1914Hristiyan AtanasovNo ratings yet
- Rental SlipsDocument6 pagesRental SlipsShubhranshu JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Type of Industries in SipcotDocument227 pagesType of Industries in Sipcotponmanikandan1No ratings yet
- Project On PDCMDocument2 pagesProject On PDCMRohit MathurNo ratings yet
- Kanpur ConfectionariesDocument11 pagesKanpur Confectionariesarvind1289No ratings yet