Lab 2 Report BJT Amplifier
Uploaded by
kuanzcLab 2 Report BJT Amplifier
Uploaded by
kuanzcTo investigate relationships between base to emitter voltage, base current, collector to emitter
voltage, and collector current for a mill watt style silicon transistor.
IB versus VBE graph
The graph above show the base current, IB against the base emitter voltage, VBE. The graph show the
input conductance of the transistor. This graph is usually used to determine the input resistance of
the transistor.
IC versus VCE graph (Step 4)
The graph above show the collector current, IC against the collector-emitter voltage, VCE. The graph
shows the output characteristic. We can obtain the value of output conductance (and also output
resistance) from the slope. As for the near horizontal part of the part show that there is almost no
changes in the collector current, IC when the collector-emitter voltage, VCE is varied. This is common
when the output of the transistor is connected to a large resistances.
Which has the greater effect of IC, changing the IB values or changing the VCE values?
But changing the IB values, the IC will change linearly only, while by changing the VCE, the IC changes
rapidly first before reaching saturation point. Therefore, changing the VCE has a greater effect before
it reaches saturation point.
Part B
Part C
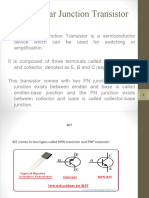
Type
Characteristic
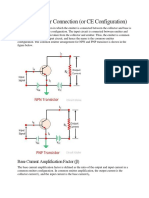
Common Base Common Emitter Common Collector
Input Terminal Emitter Base Base
Output Terminal Collector Collector Emitter
Input Impedance Low Medium High
Output Impedance High High Low
Phase Angle 0 180 0
Voltage Gain High Medium Low
Current Gain Low Medium High
Power Gain Low High Medium
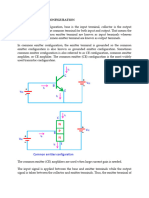
The power gain is the highest when the voltage gain and current gain is at middle level as shown in
the graph below.
Where when the load resistance is at the middle level produces the maximum power transfer. And
this configuration is for the common emitter.
What happens when a different resistance is used?
It depends on which resistance in the circuit is modified, and according to the table above, it will
change accordingly the circuit.
For example, a common base amplifier, the input terminal is Emitter, so with the resistance of the
input Emitter is changed, the Gain of the circuit will change too.
You might also like
- Configuration of Bipolar Junction TransistorNo ratings yetConfiguration of Bipolar Junction Transistor6 pages
- 4378I_3rd Semester_Electrical EngineeringNo ratings yet4378I_3rd Semester_Electrical Engineering96 pages
- Study of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of CC AmplifierNo ratings yetStudy of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of CC Amplifier4 pages
- The Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit: Bipolar TransistorNo ratings yetThe Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit: Bipolar Transistor10 pages
- Electronics-I.1 - Chapter 8 BJT Common Transistors Connection ConfigurationsNo ratings yetElectronics-I.1 - Chapter 8 BJT Common Transistors Connection Configurations46 pages
- Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit WorkingNo ratings yetCommon Emitter Amplifier Circuit Working11 pages
- Bipolar Junction Transistor PPT - RemovedNo ratings yetBipolar Junction Transistor PPT - Removed12 pages
- Input Impedance of An Amplifier and How To Calculate ItNo ratings yetInput Impedance of An Amplifier and How To Calculate It15 pages
- Department of Electronic Engineering University of Engineering and Technolgy Abbottabad CampusNo ratings yetDepartment of Electronic Engineering University of Engineering and Technolgy Abbottabad Campus4 pages
- Monday, September 15, 2014 2:45 PM: Electronics Page 1No ratings yetMonday, September 15, 2014 2:45 PM: Electronics Page 14 pages
- Course Code & Title - 19ecc03/ Analog ElectronicsNo ratings yetCourse Code & Title - 19ecc03/ Analog Electronics122 pages
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT PROBLEMS USING Common Emitter AmplifierNo ratings yetELECTRICAL CIRCUIT PROBLEMS USING Common Emitter Amplifier3 pages
- Common Emitter Transistor Amplifier BasicsNo ratings yetCommon Emitter Transistor Amplifier Basics9 pages
- EDC-TR-010_Electrical Tests for LV Underground Cable_Version 1.0No ratings yetEDC-TR-010_Electrical Tests for LV Underground Cable_Version 1.012 pages
- EDC-TR-009_UGC accessories Main Implementation Rules_Version 1.0No ratings yetEDC-TR-009_UGC accessories Main Implementation Rules_Version 1.09 pages
- Figure 1: Uncontrolled Rectifier With RL Load (R: 270 L: 0.3H)No ratings yetFigure 1: Uncontrolled Rectifier With RL Load (R: 270 L: 0.3H)5 pages
- For Information About Installing, Running and Configuring Firefox Including A List of Known Issues and Troubleshooting InformationNo ratings yetFor Information About Installing, Running and Configuring Firefox Including A List of Known Issues and Troubleshooting Information1 page