Syllabus Electrical Drives
Syllabus Electrical Drives
Uploaded by
pragatinareshCopyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus Electrical Drives
Syllabus Electrical Drives
Uploaded by
pragatinareshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Syllabus Electrical Drives
Syllabus Electrical Drives
Uploaded by
pragatinareshCopyright:
Available Formats
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
Syllabus Electrical Drives
SYLLABUS ELECTRICAL DRIVESMTH 504 ADVANCED MATHEMATICSSolution of Partial differential Equations :Application to Boundary Value Problems. Laplace and wave Equations and electrical engineering applications to boundary value problems. Solution of non-linear equations by Newtons, Kizners method, Jacobis and Gauss-SEIDEL iteration methods. Lagranges & Hermite interpolation, picewise interpolation, cubic splines, Two-point boundary value problems by numerical techniques for linear ODE. Cauchys residue theorem, evaluation of integrals by various contours, conformal mapping, Schwartz christofel transformation. Linear Programming : LPP formulation, simplex methods-phase I, phase II, Big M method, Cuality of LPP. Non Linear Programming : Unconstrained and constrained extremal problems, and their algorithms. Dynamic Programming : Bellmans Principle of Optimality, Dynamic Programming Approach optimal subdivision problem, Decomposition Applications to linear programming DPP algorithms. Reference Books :Higher Engineering Mathematics by B.S.GrewalOperations Research by Kanti Swaroop, P.K.Gupta and Man MohanOperations Research Algorithmic Approach Gillettee ED 501: POWER CONTROLLERINTRODUCTION : Various power semiconductor devices i.e. SCR, GTO, MOSFET, BJT, IGBT & MCTs & their protection, series-parallel operation, Heat sink calculations, Design of firing circuit for converters, choppers & inverters. PHASE CONTROLLED CONVERTERS :Analysis & design of 1-f bridge converter, 3-f bridge converter with and without freewheeling diode, effect of source impedence, power factor improvement techniques, pulse width modulated converters, Dual converters, converter for HVDC application & DC drives. CHOPPERS :Analysis & design of voltage commutated, current commutated and load commutated choppers, multiquadrant choppers, chopper for traction application. Resonant choppers, SMPS. INVERTERS :Detailed analysis of 1-f VSI, 3-f VSI (180 mode, 150 mode & 120 mode of conduction), various inverter commutation circuits, harmonic reduction techniques, PWM inverters, Inverters for HVDC application & AC drives. Advantages & limitation of current source inverters over VSI, 1- and 3- CSI. Resonant inverters. CYCLOCONVERTERS :1-f to 1-f, 3-f to 3-f cycloconverter circuits, circulating current scheme, non-circulating current operation, Mean output voltage, harmonics in supply current waveform & input-power factor. Concept of power quality Reference Books : 1. Thyristorised Power Controllers - G.K.Dubey, Doradla, Joshi, Sinha2. Power Electronics - C.W.Lander3. Power Electronics - Rashid4. Thyristorised power controlled converters & cycloconverters - B.R.Pelly5. Power Electronics N.Mohan6. Power Electronics Application - Vithyathil.7. Power Electronics Philip Kranes ED 502 : ELECTRICAL DRIVES I Electrical Drives Introduction, Choice of Electrical Drives, Dynamics of Electrical Drives, Concept of Multiquadrant operation, Components of load torques. Selection of motor power rating. D.C.Drive, speed torque, speed control. Starting, Breaking. Controlled rectified fed DC drive, chopper controlled dc drives. Close loop control of d.c. drive. Transient analysis. Induction Motor Drives : Three phase I.M., analysis and performance. Operation with unbalanced source voltages and single phasing, analysis of I.M. fed from Non-sinusoidal voltage supply. Starting, Braking, Transient analysis. Speed control methods of IM, v/f controlled induction motors, controlled current and controlled slip operation, PWM inverter drives, Multi-quadrant drives and field oriented control, slip power control, mathematical modeling of induction motor drives, transient response and stability analysis, single phase I.M. Close loop control of I.M. Drives. Synchronous Motor Drives, cylindrical rotor wound field motor, salient pole wound field motor, synchronous reluctance motor, Hysteresis synchronous motor, operation from fixed frequency supply, starting, braking, synchronous motor variable speed drives, starting large synchronous machines.
http://manit.ac.in Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
Reference Books :1. Power semi conductor controlled drives by G.K.Dubey 2. Fundamentals of Electrical Drives by G.K.Dubey3. Electrical Machine & Power Electronics by P.C.Sen4. Electrical Drives by S.A. Nasar ED 503 : MODELLING AND ANALYSIS OF ELECTRICAL MACHINESReview : Primitive machine, voltage and torque equation.Concept of transformation change of variables & m/c variables and transform variables. Application to D.C. machine for steady state and transient analysis, and equation of cross field commutator machine. Induction Machine : Voltage, torque equation for steady state operation, Equivalent circuit, Dynamic performance during sudden changes in load torque and three phase fault at the machine terminals. Voltage & torque equation for steady state operation of 1- induction motor & scharge motor. Synchronous Machine : Transformation equations for rotating three phase windings, Voltage and power equation for salient and non salient alternator, their phasor diagrams, Simplified equations of a synchronous machine with two damper coils. Operational Impedances and Time Constants of Synchronous Machines : Park's equations in operational form, operational impedances and G(P) for a synchronous machine with four Rotor Windings, Standard synchronous machine Reactances, time constants, Derived synchronous machine time constants, parameters from short circuit characteristics. Approximate Methods for Generator & System Analysis : The problem of power system analysis, Equivalent circuit & vector diagrams for approximate calculations, Analysis of line to line short circuit, Application of approximate method to power system analysis. Reference Books:1. Analysis of Electric Machinery - P.C.Krause2. The General theory of Electrical Machines B.Adkins3. The General theory of AC Machines - B.Adkins & R.G.Harley4. Generalised theory of Electrical m/c P.S.Bhimbra5. Electro Mechanical Energy Conversion - White & Woodson ED-511 ELECTIVE I MICROCOMPUTER AND ITS APPLICATIONS Programmable Peripheral Devices PPT 8255, various operating modes, fixing diagram, PIT 8253, programming and modes of operation, PIC 8259, operating modes. Interfacing - Interfacing of peripherals, A/D & D/A converters, 8255, 8253, 8259 with 8/16 bit microprocessor/Data Acquisition system. Microcontroller - 8051 Architecture, Counter/Timers, Instructions, Programming, Interfacing, Applications, Comparison of 8085, 8086, 8057 etc. Programmable logic controller PLC Architecture, programming, Counter/Timers and its applications. References :1. Microprocessor Architecture programming & applications Gaonkar2. Microprocessors & interfacing D.V.Hall3. The 8051 Microcontroller K.J.Ayala4. Introduction to programmable logic controller Gary DunningED-512 ELECTIVE I DSP & ITS APPLICATIONS Introduction to DSP - Classification of signals, Multichannel and multi dimensional continuous v/s discrete time signals, continuous v/s discrete valued signals, continuous time sinusoidal signal, discrete time sinusoidal signals, sampling of analog signal, sampling theorem, quantification and coding of D/A conversion. Discrete Time Signal and Systems - Discrete time signal, systems, Z-transform & Inverse Z-transform, analysis of discrete time, linear time invariant systems, co-relation of discrete time systems. Frequency Analysis Of Signals - Frequency analysis of analog signals, frequency analysis of discrete time signals. Properties of Fourier Transform, Frequency Domain Characteristics, Time Frequency Dualities, Sampling of signals in time and frequency domain, DFT & FFT. Design Of Digital Filter - Design of linear phase FIR filter using window & frequency sampling method. Design of equiripple linear phase filters. Comparision of design methods for linear phase FIR filters. Design of IIR filters from analog filters. Direct Design Technique for digital IIR filters. DSP Application - Introduction to digital signal processors chips, case study of different DSP applications. Application of filters to analog & digital signal processor, FET spectrum analyzer. Reference Books :1. Digital Signal Processing Digital Signal Processing S. Mitra
http://manit.ac.in
W.D.Stanley2. Analog & Digital Signal Processing Ashok Ambardar3.
Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
ED-551 MICROCOMPUTER CONTROLLED DRIVESDC Drives - Converter fed DC Drives, Microcontroller hardware circuit, flow charts waveforms, Performance characteristics of dc drives fed through single phase converters, 3-phase converters, dual converters, 1-phase fully controlled converter and 3-phase fully controlled converter fed dc drive, Chopper fed DC Drives, hardware, circuits and waveforms., various modes of operation Performance Characteristic Of AC Drives - Description and Performance behaviour of 3-phase induction motor drive Microcomputer controlled inverter fed ac drive - Detailed power circuit, generation of firing pulses and firing circuit, flow charts and waveforms for 1-phase, 3-phase non pwm and 3-phase pwm inverter fed induction drives. Sampling techniques for pwm inverter. Mathematical modeling of frequency controlled drive - Development of mathematical model for various components of frequency controlled induction drive, mathematical model of the system for steady state and dynamic behaviour, Study of stability based on the dynamic model of the system. Close loop control of microcomputer based drives - Ref. speed, actual speed digital speed measurement (various methods). Types of controllers, position and velocity algorithm, close loop control of microcomputer based Drives.
References:1. Power semiconductor controlled drives, Dubey G.K., Prentiee-HALL 19892. Power electronics and variable frequency drives, Bose B.K., IEEE Press 19973. Control of electric drives, Leonard W, Springer Verlag, NY,1985 4. Microcomputer control of power electronics and drive, Bose B.K.5. Adjustable a.c. drive, Bose B.K.6. Thyristor contro of Electronic drive, V.Subramanyam ED-552 ADVANCED CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN AND COMPENSATION TECHNIQUES :The Design Problem, Preliminary design considerations. Basic comparators, cascade compensation in time domain and frequency domain, feedback compensation, Different types of controllers. STATE VARIABLE ANALYSIS :State variables, state space representation, Transfer matrix, state model for linear continuous time systems. Eigen values, eigen vectors, Diagonalization, Solution of state equation, concept of controllability and observability. Pole placement by state feedback. DISCRETE TIME SYSTEMS :Introduction to discrete time systems , Time domain, representation & transformation analysis of discrete time systems, time domain approach and z domain approach. Pulse transfer function, Controllability and observability of discrete time systems stability analysis in z plane. NON LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS :Introduction, characteristics limit cycles, singular points, Basic non linear components phase plane methods, Describing functions, Definition, D.F. for basic non linearities, Absolute stability, circle and popov criterion, Liapunov functions. LINEAR OPTIONAL AND ADAPTIVE CONTROL :Linear optimal regulator problem, finite time horizon, Principle of optimality, Hamilton Jacobi equation, Riceati differential equation, steady state solutions (LQR), Algebraic Riceati equation, properties, gain and phase margin, sensitivity, non linearities, optimal state estimation, Kalman filter, Output feedback control (LQG). Reference Books : 1. Digital Control Engineering - M.Gopal2. Adaptive and Optimal Control - A.P.Sage & Landue3. Optimal Control A.P.Sage4. Discrete Time Control System - Katsuniko Ogata5. Modern Control Engineering Nagarth Gopal ED-553 INSTRUMENTATION IN ELECTRICAL DRIVES
Review of Transducers - Introduction, measurement of translational and rotational displacement. Resistive potentiometers, strain gauges; differential transformer, synchros, induction potentiometers, piezoelectric transducer; Electro-optical devices, Digital displacement transducers (Translational and rotary encoders).Magnetic and photoelectric pulse counting for speed. Transducers for Torque voltage; current; power; frequency; power factor; and phase angle measurement. Signal Conditioning - Necessity, Instrumentation amplifiers, chopper stabilized amplifiers, Impedance converters, Noise problems, shielding and grounding.Concept of filters; Low pass filters; high pass filters; band pass filters ;band rejection filters; digital filters. Integration and differentiation of signals, Dynamic compensation, Linearisation, Concept of A/D and D/A Converters (voltage to frequency and frequency to voltage converter) sample/hold amplifiers, Microprocessor applications in signal conditioning.
http://manit.ac.in Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
Data Transmission And Recording- Cable transmission of analog voltage and current signals, cable transmission of digital data, Fiber optic data transmission, FM/FM radio telemetry, synchroposition repeater systems. Microprocessor Based Measurement Of Electrical Quantities - Microprocessor based measurement of frequency, phase angle; power factor; voltage; current; reactance; resistance; KVA; KW; KWh and KVAR Computerised Data Acquisition System - Elements of data acquisition systems, data loggers, instrument interconnection systems; Block diagram and details of computerized data acquisition systems Instrumentation schemes for close loop control of Dc drives and AC drives. Reference Books: 1. Measurement systems, Application and Design by Ernest O.Docbelin.2. measurement by A.K.Shawney.3. Fundamental of microprocessor and microcomputers by B.Ram. ED-554 TRACTION DRIVES
Electrical and
Electric Traction Systems, Mechanics of Train movement, speed time curves, preliminary investigations of energy consumption, and ideal speed torque characteristics of Traction motors. Constructional and Design aspects of DC single phase and 3-phase I.Ms for Electric traction ,constraints and comparison w.r.t. commercial machines, problem associated with voltage rises. Temporary Interruption of supply, commutation of current rush, Ability of motors to withstand current rushes. Solid-state device controllers for DC Traction motors used for starting, speed control and electric braking in Electric traction for main line and suburban services. Controllers for 1-phase Traction motors, trends in main line railways using polyphase I.Ms and their controllers. Electric braking requirements and thyristorised controllers. Battery operated vehicles for city service, Light weight batteries, Diesel-Electric Traction systems for main line service and controllers.Soft starting of Traction motors, Conservation of Electrical energy. Reference Books :
1. Electric Traction by A.T.Dover2. Thyristorised Power Controllers by G.K.Dubey, Dorodla, Joshi& Sinha.3 Electronics by M.S.Berde.4. Modern Electric Traction by Prakash. ED-561 ELECTIVE II ADVANCE POWER ELECTRONICS DC-DC Switch Mode converter- Control of DC - DC Converter. BUCK, BOOST, BUCK-BOOST Converters etc. P.W.M. Converter- PWM Techniques, Current controlled techniques, High Power Factor Converters. Resonant Converters - Classification, Concepts, Load-Resonant Converters, Resonance-Switch Converters, Zero voltage Switching. Power Supplies - Linear Power Supplies, Overview of Switching DC Power Supply, Control and Protection of SMPS. Switching Mode Inverters - Basic concept, 1-F, 3-F Inverters Switching, Schemes and applications. Reference Books : Power Electronics Ned Mohan Power Electronics M. H. Rashid Power Electronics M. D. Singh Power Electronics Joseph Vithythal Power Electronics Philip KranesPower Electronics G. K. Dubey
ED-562 ELECTIVE II EVOLUTIONARY TECHNIQUES MODELSModel classification, Mathematical models, Physical Models, Analog Models, Estimation of Model parameters,
http://manit.ac.in Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
Design of experiments, System Identification. SIMULATION METHODOLOGY & COMPUTER SIMULATIONExperimental Nature of Simulation, Steps involved in simulation studies, Validation of Simulation Models, Computer Simulation of continuous & discrete systems; examples. NEURAL NETWORKSIntroduction, different network configurations (MLP, Hopfield, Kohonen etc.), Feedforward and recurrent networks, Training algorithms static error back propagation technique and dynamic training algorithms, Computer flow charts for training, NNW applications for control, identification, pattern recognition and system modeling & state estimation. FUZZY LOGICSConcept, Fuzzy relations, membership functions, if-then-rules, matrix representation, defuzzification, fuzzy controllers, applications. GENETIC ALGORITHMSIntroduction and concept, schemata, coding, reproduction, cross-over, and mutation, scaling, fitness, applications. Neuro-fuzzy networks, Genetic algorithm in fuzzy controllers, other hybrid applications. Reference Books :1. Geoffery Gordon, System Simulation, Prentice Hall India, 19982. Robert E.Shannon, Systems Simulation : Art and Science, Prentice Hall3. J.M.Zurada, Introduction to Artificial Neural System, Jaico Publ. House, Bombay, 19944. G.W.Irwin, K.Warwick & K.J.Hunt[Editors], Neural Network Application in Control, Instn of Elect. Engrs, U.K., 19955. D.T.Pham & L.Xing, Neural Networks for Identification, Prediction and Control, Springer-Verlag, London, 19956. V.Rao & H. Rao, C++ Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic, BPS, Delhi, 19967. D.E.Goldberg, Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and machine learning, Addision Wesley Publ. Co. INC, NY.
ED 601ELECTRIC DRIVES IIReview of power electronic converters for drive control, LCI fed IM Drive, Drive configuration, Commutation at different speed, control structure. FOC IM Drive, Drive configuration, Mathematical modeling, Direct and indirect FOC, Influence of parameter, VSI and CSI fed schemes, Adaptive drive control. Brushless dc drive, self control, CSI with load commutation, low speed commutation, inverter control strategies, performance. Permanent Magnet SM Drive, control fundamentals, converter configuration, synchronization, trapezoidal and sinusoidal drive control structure, performance. Switched Reluctance Motors, Principle of operation, converter circuits, sensors, speed control, performance characteristics. Advance Control Technique Application, Application of modern & evolutionary techniques in drives. Stepper motor and switch reluctance motor drives, solar and battery powered drives, Traction Drives, Energy conservation in Electrical Drives. Reference Books:1. Power semi conductor controlled drives by G.K.Dubey 2. Fundamentals of Electrical Drives by G.K.Dubey3. Electrical Machine & Power Electronics by P.C.SenElectrical Drives by S.A. NasarPower electronics and variable frequency drives by B. K. Bose ED-602POWER QUALITYUnderstanding Power quality, types of power quality disturbances, power quality indices, Causes and effects of power quality disturbances Causes and effects of harmonics, converter configuration and their contribution to supply harmonics, other sources of harmonics Radio interference, supply standards, elimination/suppression of harmonics, classical solutions & their drawbacks, passive input filters, high power factor pre-regulator, switching control circuit, transformer connections, Elimination/suppression of harmonics using active power filters topologies, and their control methods, PWM converter as a voltage source active filter, current source active filter, Electro-magnetic compatibility, constant frequency control, constant tolerance band control, variable tolerance band control, discontinuous current control. References Books :Power Quality by R.C. DugganPower system harmonics by A.J. ArrillgaPower electronic converter harmonics by Derek A. PaiceED-611 ELECTIVE III(i) REACTIVE POWER CONTROL AND FACTS
http://manit.ac.in Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
Introduction to FACTS- Basic Types of FACTS controllers, Static Var Compensator (SVC), Principle of operation, configuration and control of Thyristor Controlled Series compensator(TCSC), Applications, Static Compensator (STATCOM): Principle of operation, configuration and control, Unified Power Flow Controller(UPFC): Principle of operation, configuration and control. Oscillation Stability Analysis and Control: Introduction Linearised model of power systems installed with FACTS based Stabilizers Heffron-Phillips model of a SMIB system installed with SVC, TCSC and TCPS. Analysis and Design of FACTS based stabilizers: Analysis of damping torque contribution by FACTS based stabilizers installed in SMIB systems, Design of robust FACTS based stabilizers, Selection of installing locations. Transient Stability control with FACTS: Introduction Analysis of Power systems installed with FACTS devices: Power transmission control using Controllable Series Compensation(CSC), Power Transmission Control using SSSC, Power Transmission Control using UPFC, Power Transmission Control using Phase Shifting Transformer(PST), Power Transmission Control using UPFC, Control of FACTS devices for transient stability improvement General considerations of FACTS control strategy: CSC,SSSC, SVC, STATCOM and UPFC control strategy General Structure of the FACTS devices control.
References:1. Reactive Power Control in Power Systems T J E Miller John Wiley, 19822. Computer modeling of Electrical Power Systems J Arriliga and N R Watson Wiley, 20013. Understanding FACTS N G Hingorani and IEEE Press, 20004. Flexible ac Transmission Systems(FACTS) Y.H. Song and A.T. JohnsIEE Press, 1999
ED-612 ELECTIVE III (ii) SPECIAL MACHINES Introduction : Review of adjustable speed drives, permanent magnet materials and circuits. Square-wave, Sine-wave P.M. brushless motor drives - Principle, construction, operation and drive application.P.M. & synchronous-reluctance based motors - Principle, construction, operation and drive application.Switched reluctance motors, Linear induction motors, Stepper motors - Principle, construction, operation and drive application. Energy efficient motors Reference Books : 1. Power electronics control of AC machine by J.M.P. Murphy.2. Brushless Permanent-magnet and reluctance motor Drives by T.J.E. Miller3. Power electronics and variable frequency drives edited by B.K.Bose4. Linear induction machine by S.A.Nasar5. Energy efficient electric motors by J.C. Andreas. ED-613 ELECTIVE III (iii) EHV AC & DC TRANSMISSION 1. Long line theory, long distance transmission problems, corona power loss and audible noise. Radio Interference RIV and excitation functions, Reactive Power compensation of EHV AC lines, FACTs devices. 2. Sequential impedances of AC systems EHVAC transmission overvoltages, insulation design of lightning and switching over voltages. High voltage testing of AC equipments.3. Comparision of EHV AC & DC transmission HVDC system configuration and components conversion and inversion, Analysis of three phase bridge converter and Performance equations abnormal operations of converter. 4. Control of HVDC system, Principle of DC link control, current and Extinction angle control power and reactive power control, alternative inverter control modes. 5. Harmonics and AC/DC filters, Influence of AC system strength on AC/DC system interaction responses to DC and AC system faults. Modelling of HVDC system.
Reference Books :1. Begemudre R.D., EHVAC Transmission Engineering Willy Eastern Ltd.2. P.Kundur Stability and Control - Mc Graw Hill Publication.3. Arrillaga J., HVDC Transmission - Peter Peregrinus Pub.4. EHV AC & HVDC Transmission Systems - Khanna Pub. 5. Padiyar K.R., HVDC Power Transmission Systems W Eastern Ltd.ED 541 LAB - IMACHINES & DRIVES LAB List of Experiments:Study of Generalized Converter.(a) Record the waveforms at various points of the firing circuit for 1phase HW & bridge, 3-phase half wave & fully controlled bridge converters.(b) Record the output voltage, output current,
http://manit.ac.in Powered by Joomla! Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal (MP)
voltage across one thyristors, input current, with R & R-L load(c) Study the effect of load/source inductance and free wheeling diode.(d) Study the harmonic spectrum of input current. Study the speed control of single-phase converter fed DC motor.(a) Record the output voltage and input/output current waveforms in open loop speed control in continuous and discontinuous mode of operation.(b) Study the harmonics spectrum of input current.(c) Perform the load test. Study of single-phase AC regulator (a) Record the waveform at various points of the firing circuit.(b) Record the output voltage, input/output current, voltage across thyristors with (i) Resistive load, and (ii) Inductive load (iii) Fan load.(c) Study the harmonics spectrum of input current. Study the v/f speed control method of the three-phase Induction Motor.(a) Record the output voltage and line current waveforms.(b) Measure the speed, terminal voltage and line current at various frequencies.(c) Study the harmonics spectrum of input current. Study of speed control of separately excited chopper fed DC drive.(a) Record the waveforms at various points of firing circuit.(b) Study voltage and current commutation circuit.(c) Record the output voltage, input/output current waveforms with (i) R-Load (ii) R-L load, and (iii) Motor load. (a) Perform dynamic braking and plugging on DC shunt motor and record time taken by the motor to come to rest at different external resistance settings.(b) Perform dynamic braking on three-phase I.M. and record the time taken by the motor to come to rest at different DC current. (a) Study the speed control of 3-phase I.M. using the concept of Kramer control.(b) Plot the speed of the motor v/s field current of DC motor.(c) Record the various waveforms.
http://manit.ac.in
Powered by Joomla!
Generated: 10 August, 2009, 12:07
You might also like
- PED Syllabus FinalDocument24 pagesPED Syllabus Finalsaravanan_KLUNo ratings yet
- JFTTRHGHMJBDocument21 pagesJFTTRHGHMJBBikash Ranjan DashNo ratings yet
- Advanced Torque Control of Robot Manipulators Driven by Ac InductionDocument15 pagesAdvanced Torque Control of Robot Manipulators Driven by Ac InductionCaroline MeloNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For M.Tech Sponsored ElectricalDocument3 pagesSyllabus For M.Tech Sponsored ElectricalArsalaan NazeerNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineeringrjrahul25No ratings yet
- Upsc Electrical Engineering Syllabus PDF 7ec21c12Document5 pagesUpsc Electrical Engineering Syllabus PDF 7ec21c12mojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- Scheme: Paper-1 General Studies & Mental AbilityDocument2 pagesScheme: Paper-1 General Studies & Mental AbilityRajashekar ReddyNo ratings yet
- CC C CCC C C C C - C - !" #$%!&' !! - : Paper-2 (Concerned Subject) Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesCC C CCC C C C C - C - !" #$%!&' !! - : Paper-2 (Concerned Subject) Electrical EngineeringRamadugula Rama Subrahmanya VenkateswararaoNo ratings yet
- EED-321 Electrical Control Engineering L T P 3 1 3Document6 pagesEED-321 Electrical Control Engineering L T P 3 1 3minjutNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines and Power TransformersDocument2 pagesElectrical Machines and Power TransformersMichael DavisNo ratings yet
- VIT Power Electronics and Drives Syllabus 2012Document18 pagesVIT Power Electronics and Drives Syllabus 2012LinuNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EEE 2019Document5 pagesSyllabus EEE 2019jaberyemeniNo ratings yet
- 6th Semester SyllabusDocument6 pages6th Semester SyllabusaniketNo ratings yet
- EEC-501 Electrical Machine-II: Basics of Synchronous MachineDocument15 pagesEEC-501 Electrical Machine-II: Basics of Synchronous Machineyour friendNo ratings yet
- MDU B.tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem SyllabusDocument8 pagesMDU B.tech Electrical Engineering 5th Sem SyllabusDhruv AhujaNo ratings yet
- EX-701 Utilization of Electrical EnergyDocument10 pagesEX-701 Utilization of Electrical EnergyVikesh gondNo ratings yet
- Genco Syllabus For EEE BranchDocument2 pagesGenco Syllabus For EEE BranchMansa ManuNo ratings yet
- Ies SyllabusBooks For IesDocument2 pagesIes SyllabusBooks For IesAlind DubeyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Electrical Engg CseDocument7 pagesSyllabus Electrical Engg CseKrishna Mohan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusashwinivema1980No ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Electrical EngineeringbasabNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Industrial DrivesDocument3 pagesPower Electronics and Industrial Drivesvatsalshah24No ratings yet
- Paper-1: IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument3 pagesPaper-1: IES Electrical Engineering SyllabusJampana ShivaramakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Electrical Pune MetroDocument2 pagesSyllabus - Electrical Pune MetroPrasad WalsingeNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ElectricalDocument2 pagesSyllabus ElectricalRameshwar Kasbe PatilNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Syllabus For IESDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Syllabus For IESSanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Electrical Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesUPSC CSE Electrical Engineering Syllabusbpsharmab1p1No ratings yet
- 03 Electrical PDFDocument3 pages03 Electrical PDFSultan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Annexure - I SYLLABUS For Test (POST - Assistant Engineer/ Electrical), Now Re-Designated As Assistant Executive Engineer/ ElectricalDocument2 pagesAnnexure - I SYLLABUS For Test (POST - Assistant Engineer/ Electrical), Now Re-Designated As Assistant Executive Engineer/ ElectricalSowmyaNo ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusdeepak jangidNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Syllabus For UPSC Main ExaminationDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Syllabus For UPSC Main ExaminationsujaraghupsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and DrivesDocument2 pagesPower Electronics and DrivesAlfredo VMNo ratings yet
- BE-EEE Courses DescriptionDocument7 pagesBE-EEE Courses DescriptionShrayan BarmanNo ratings yet
- Indicative SyllabusDocument2 pagesIndicative Syllabusstudyking408No ratings yet
- Upsc CSE Ele SyllabusDocument2 pagesUpsc CSE Ele SyllabusgppNo ratings yet
- RGPV Syllabus Btech Ee 5 Sem All SubjectsDocument17 pagesRGPV Syllabus Btech Ee 5 Sem All SubjectsSandeep TaleNo ratings yet
- IES Books& SyllabusDocument4 pagesIES Books& SyllabusRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Paper - I 1. Circuit Theory:: Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesPaper - I 1. Circuit Theory:: Electrical EngineeringEr Paramjit SinghNo ratings yet
- CCCC C C C CCDocument3 pagesCCCC C C C CCManoj MeenaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Syllabus For Power Electronics - I (150903) Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument6 pagesMid Term Syllabus For Power Electronics - I (150903) Power Semiconductor Devicesiamketul6340No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: Objective: - 120 Que Stions Subjective: - 6 Que Stions Paper-I EM TheoryDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering: Objective: - 120 Que Stions Subjective: - 6 Que Stions Paper-I EM TheoryshonujamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Main Syll IasDocument3 pagesElectrical Main Syll IasRNikaNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Exam Syllabus: 1. Electrical Circuits and NetworksDocument1 pageApgenco Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Exam Syllabus: 1. Electrical Circuits and NetworksCh RajaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engg SyllabusDocument6 pagesElectrical Engg Syllabuschirag_cs7No ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFRishiNo ratings yet
- Rec SemiDocument20 pagesRec SeminadirNo ratings yet
- Gate 2021 EE SyllabusDocument2 pagesGate 2021 EE SyllabusAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesElectrical SyllabusSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Drives: Semiconductor Power Diodes, Transistors, Thyristors, TriacsDocument2 pagesPower Electronics and Drives: Semiconductor Power Diodes, Transistors, Thyristors, TriacsSunilkumarNo ratings yet
- B. E. Sem Vi (Electrical) E-601: Electrical Machines - IiiDocument10 pagesB. E. Sem Vi (Electrical) E-601: Electrical Machines - IiibaruaeeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Electronics Engineering: Sssutms SehoreDocument16 pagesElectrical Electronics Engineering: Sssutms SehoreolexNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ESEDocument3 pagesSyllabus ESESuvra PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Ap Eee SyllabusDocument3 pagesAp Eee SyllabusSujith kumarNo ratings yet
- JNTUH M.TECH PEDS 2013 SyllabusDocument24 pagesJNTUH M.TECH PEDS 2013 SyllabusSRINIVASA RAO GANTA100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument24 pagesPower ElectronicsSunilkumarNo ratings yet
- CBGS 8 Sem050318033746 PDFDocument9 pagesCBGS 8 Sem050318033746 PDFshashank barsainyaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsFrom EverandHandbook of Power Systems Engineering with Power Electronics ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseFrom EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNo ratings yet
- 2-11 Course FileDocument74 pages2-11 Course FilepragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Pragati Engineering College: 1-378, Adb Road, Surampalem, Near Peddapuram, E.G.Dt, A.PDocument2 pagesPragati Engineering College: 1-378, Adb Road, Surampalem, Near Peddapuram, E.G.Dt, A.PpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Internal Quality Assurance Cell: Welcomes NAAC Peer TeamDocument29 pagesInternal Quality Assurance Cell: Welcomes NAAC Peer TeampragatinareshNo ratings yet
- New Age International (P) LTD., Publishers: Subject and Semester Book Required EnrolmentDocument1 pageNew Age International (P) LTD., Publishers: Subject and Semester Book Required EnrolmentpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Ps 7Document3 pagesPs 7pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Presentation For: National Assessment and Accreditation CouncilDocument75 pagesPresentation For: National Assessment and Accreditation CouncilpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Piohr, We Compute The Derivative Piobr Piobe. Thus Pinbe Piobc PP-'iodqDocument34 pagesPiohr, We Compute The Derivative Piobr Piobe. Thus Pinbe Piobc PP-'iodqpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- SOUL Installation: Universities/Institutions and Colleges - State-Wise Sr. NoDocument2 pagesSOUL Installation: Universities/Institutions and Colleges - State-Wise Sr. NopragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Ps 9Document3 pagesPs 9pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- 9th PRC Commission - Go - Ms.no52 Dt.25!02!2010Document1,012 pages9th PRC Commission - Go - Ms.no52 Dt.25!02!2010emmreddyNo ratings yet
- Ps 10Document5 pagesPs 10pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Ppt2 (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesPpt2 (Compatibility Mode)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Ps 8Document3 pagesPs 8pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- TCSC For Protection PDFDocument9 pagesTCSC For Protection PDFpragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Final EceDocument156 pagesFinal EcepragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Jntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Em3)Document19 pagesJntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Em3)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Date: 17.05.2013 Notice: To The Managements of Private Un-Aided Professional Colleges / InstitutionsDocument1 pageDate: 17.05.2013 Notice: To The Managements of Private Un-Aided Professional Colleges / InstitutionspragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Final Ece-Sar (30.05.2013)Document200 pagesFinal Ece-Sar (30.05.2013)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- NAAC SSR of The VRSEC1 PDFDocument492 pagesNAAC SSR of The VRSEC1 PDFanil_049100% (1)
- Modern Control TheoryDocument137 pagesModern Control TheorypragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Expression of Interest For State Energy Conservation Awards 2013Document1 pageExpression of Interest For State Energy Conservation Awards 2013pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Application of PSO, Artificial Bee Colony and Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithms To Economic Load Dispatch: An AnalysisDocument4 pagesApplication of PSO, Artificial Bee Colony and Bacterial Foraging Optimization Algorithms To Economic Load Dispatch: An AnalysispragatinareshNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Survey For Optimal Location and Coordinated Control Techniques For FACTS Controllers in Power System Environments and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesA Comprehensive Survey For Optimal Location and Coordinated Control Techniques For FACTS Controllers in Power System Environments and ApplicationspragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Trainandoutput PatternsDocument2 pagesTrainandoutput PatternspragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document104 pagesLecture 5mezz3174444No ratings yet
- VAHAK Dual ChargerDocument1 pageVAHAK Dual ChargerElectrical DistributionNo ratings yet
- Schneider Transformers 800kva Wiring DiagramDocument8 pagesSchneider Transformers 800kva Wiring DiagramMukti AwanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Intro Electric DrivesDocument71 pagesModule 1 Intro Electric DrivesMohammad Amirul ShafiqNo ratings yet
- lecture 5 Diode applications-Full wave rectifiers(part-2)Document24 pageslecture 5 Diode applications-Full wave rectifiers(part-2)Ahmed AymanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ELK453EDocument6 pagesSyllabus ELK453Emdur67No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Power Electronics and Industrial Control Systems Devices and CharacteristicsDocument49 pages1 Introduction To Power Electronics and Industrial Control Systems Devices and CharacteristicsBassel HassanNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2022 (Only Ans.) - FinalDocument33 pagesGATE EE 2022 (Only Ans.) - FinalChilukuri JithendraNo ratings yet
- ABB Reapir Ans Service Center in BangaloreDocument8 pagesABB Reapir Ans Service Center in BangaloreAmsindiaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: Model: MZ-1246MG FCC Id: Bejx1241XgDocument2 pagesSchematic Diagram: Model: MZ-1246MG FCC Id: Bejx1241XgJacky Npl100% (1)
- POWER Prafulla 2015Document56 pagesPOWER Prafulla 2015Animesh NayakNo ratings yet
- Measurement Methodology For Accurate Modeling of Sic Mosfet Switching Behavior Over Wide Voltage and Current RangesDocument12 pagesMeasurement Methodology For Accurate Modeling of Sic Mosfet Switching Behavior Over Wide Voltage and Current RangesIsra JanNo ratings yet
- Various Types of Diodes With Their Characteristics & UsesDocument7 pagesVarious Types of Diodes With Their Characteristics & UsesRutvik100% (1)
- Voltage Multiplier Half and Full WaveDocument5 pagesVoltage Multiplier Half and Full WaveJohn Raymart CostalesNo ratings yet
- A High Performance GaN Power Module With Parallel Packaging For High Current and Low Voltage Traction Inverter Applications-1Document21 pagesA High Performance GaN Power Module With Parallel Packaging For High Current and Low Voltage Traction Inverter Applications-1李漢祥No ratings yet
- Lec 4 BDocument2 pagesLec 4 Bspeedaswin100% (1)
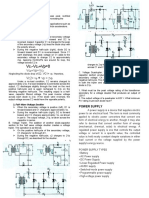
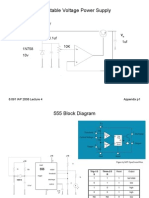
- High Performance Portable BenchSupply, DIYDocument9 pagesHigh Performance Portable BenchSupply, DIYBryan Fantasía FuryNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document26 pagesPresentation 1Siva ForeviewNo ratings yet
- Protection For Sub SSTI Conditions Using An Industrial Sub-Harmonic RelayDocument31 pagesProtection For Sub SSTI Conditions Using An Industrial Sub-Harmonic RelayAlex Aima ChacoNo ratings yet
- Large Wind Power Plants Modeling TechniquesDocument7 pagesLarge Wind Power Plants Modeling Techniquesmohamed berririNo ratings yet
- Electronic Experiment 4.Document9 pagesElectronic Experiment 4.forsan15432No ratings yet
- EC 307 Power Electronics and Instrumentation Lecture Notes, Module 6Document21 pagesEC 307 Power Electronics and Instrumentation Lecture Notes, Module 6vpzfaris100% (1)
- PcbtransDocument1 pagePcbtransConstantin StratulescuNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Probelems and SolutionsDocument11 pagesRectifier Probelems and SolutionsMichael Jerlit J EEENo ratings yet
- Flywheel Conceptual DesignDocument6 pagesFlywheel Conceptual DesignAhmed Al-lehyaniNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eletrico Alpha 510Document1 pageDiagrama Eletrico Alpha 510Justinofg14 LajNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument12 pagesCourse Syllabi Department of Electrical EngineeringPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- SMD Type IC: Low Dropout Linear Regulator AMS1117-X.XDocument3 pagesSMD Type IC: Low Dropout Linear Regulator AMS1117-X.XcarlosmarciosfreitasNo ratings yet
- Chapter I, II, III, IV PDFDocument84 pagesChapter I, II, III, IV PDFAsmaNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Exam Syllabus: 1. Electrical Circuits and NetworksDocument1 pageApgenco Assistant Engineer (Electrical) Exam Syllabus: 1. Electrical Circuits and NetworksCh RajaNo ratings yet