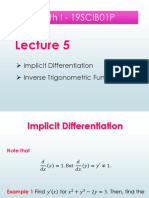
Module 5 - Derivatives of Inv Trig Functions
Uploaded by
Maria AndresModule 5 - Derivatives of Inv Trig Functions
Uploaded by
Maria AndresDIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
MODULE 5
DIFFERENTIATION OF
INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
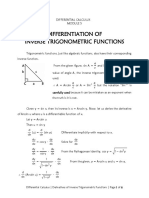
Trigonometric functions, just like algebraic functions, also have their corresponding
inverse function.
𝑎
From the given figure, sin A = and if we wish to find the
𝑐
value of angle A, the inverse trigonometric function will be
used.
𝑎 𝑎
∴ A = Arcsin or A = Sin-1 but the notation “Sin-1” is
𝑐 𝑐
carefully used because it can be mistaken as an exponent when
the truth is it is not.
Given y = sin x, then its inverse is x = Arcsin y. Now, let us derive the derivative
of Arcsin u where u is a differentiable function of x.
Let y = Arcsin u
Then u = sin y
d d
(u) = (sin y) Differentiate implicitly with respect to x.
dx dx
du dy dy
= cos y ∙ Solve for
dx dx dx
dy 1 du
= ∙ From the Pythagorean identity, cos y = √1 − sin2 y
dx cos y dx
dy 1 du
= ∙ From the given, y = Arcsin u and u = sin y,
dx 2 dx
√1−sin y
d 1 du
∴ (Arcsin u) = ∙
dx √1−u2 dx
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 1 of 6
Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Let u be a differentiable function of x
d 1 du
I. (Arcsin u) = ∙
dx √1 − u2 dx
Note:
d −1 du
II. (Arccos u) = ∙ The Arcsine and Arccosine,
dx √1 − u2 dx
Arctangent and Arccotangent,
d 1 du and Arcsecant and Arccosecant
III. (Arctan u) = ∙
dx 1+ u2 dx have equal derivatives but of the
d −1 du different sign.
IV. (Arccot u) = ∙
dx 1+ u2 dx
d 1 du
V. (Arcsec u) = ∙
dx u √u2 − 1 dx
d −1 du
VI. (Arccsc u) = ∙
dx u √u2 − 1 dx
EXAMPLE 1. Find the first derivative of y = Arcsin 2x.
Here u = 2x.
1 d
∴ y’ = ∙ ( 2x )
dx
√1 − (2x)2
2
= Ans.
√1 − 4x2
EXAMPLE 2. Find y’ if y = Arccos (x – 1)
-1 d
∴ y’ = ∙ (x–1)
dx
√1 − (x − 1)2
-1
= ∙1
√1 − (x2 −2x+1)
-1
= Ans.
√2x − x2
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 2 of 6
EXAMPLE 3. Find y” if y = Arctan 4x
1 d
∴ y’ = 2 ∙ ( 4x )
1 + (4x) dx
1
= ∙4
1 + 16x2
4
=
1 + 16x2
d 4 𝒄
∴ y” = ( 2 ) →
dx 1 + 16x 𝒗
-4 d
= ∙ ( 1 + 16x2 )
2 2 dx
(1 + 16x )
-4
= ∙ 32x
2 2
(1 + 16x )
-128x
= Ans. (no need to expand the denominator)
2 2
(1 + 16x )
EXAMPLE 4. Find y’ of the function y = Arccot tan x
-1 d
∴ y’ = 2 ∙ ( tan x )
1 + (tan x) dx
-1 d
= ∙ sec2x ∙ (x)
1+ tan2 x dx
-sec2 x
= since 1 + tan2x = sec2x
sec2 x
= -1 Ans.
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 3 of 6
EXAMPLE 5. Find the first derivative of y = Arcsec 6ax
1 d
∴ y’ = ∙ ( 6ax )
dx
6ax √(6ax)2 − 1
6a
=
6ax √36a2 x2 −1
1
= Ans.
x √36a2 x2 −1
EXAMPLE 6. Find the first derivative of y = Arccsc6x
Here y = Arccsc6x = ( Arccsc x )6 → un
d
∴ y’ = 6 ( Arccsc x )5 ∙ ( Arccsc x )
dx
−1 d
= 6 Arccsc5x ∙ ∙ (x)
x √x2 − 1 dx
−6arccsc5 x
= Ans.
x √x2 − 1
EXAMPLE 7. Find y’ of xy = Arctan xy
d d
( xy ) = ( Arctan xy )
dx dx
1 d
xy' + y = 2 ∙ ( xy )
1 + (xy) dx
1
xy' + y = ∙ ( xy’ + y ) Multiply 1 + x2y2 on both sides
1 + x2 y2
( xy’ + y ) ( 1 + x2y2 ) = xy’ + y
xy' ( 1 + x2y2 ) + y ( 1 + x2y2 ) = xy’ + y
xy' ( 1 + x2y2 ) – xy’ = y – y ( 1 + x2y2 )
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 4 of 6
y’ [ x ( 1 + x2y2 ) – x ] = y [ 1 – ( 1 + x2y2 ) ]
y ( −x2 y2 )
y’ =
x3 y2
y
=− x Ans.
EXAMPLE 8. Find y’ of Arccos y + Arcsin x = 2
d d
( Arccos y ) + ( Arcsin x ) = 0
dx dx
-1 d 1 d
∙ (y)+ ∙ (x) = 0
√1 − y2 dx √1 − x2 dx
-y' 1
+ =0
√1 − y2 √1 − x2
-y' -1
=
√1 − y2 √1 − x2
√1 − y2
y’ = Ans.
√1 − x2
EXAMPLE 9. Find y’ if x = Arctan t and y = ( 1 + t2 )9
dx d dy d
∴ = ( Arctan t ) ∴ = ( 1 + t2 )9
dt dt dt dt
1 d
= = 9 ( 1 + t2 )8 ∙ ( 1 + t2 )
1 + t2 dt
= 18t ( 1 + t2 )8
dy dy dt
∴ = ∙
dx dt dx
= 18t ( 1 + t2 )8 ∙ ( 1 + t2 ) Grouping symbols!
= 18t ( 1 + t2 )9 Ans.
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 5 of 6
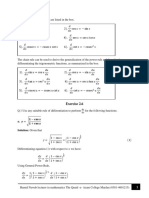
Exercise 5.1
Name: _________________________________________ Date: _______________________
Course, Year and Section: _________________________
Find the first derivative of the following functions with respect to x.
1. y = Arctan ( 1 – 2x )
2. y = Arcsin √x
3. x Arcsin a + y Arccos b = 1
Differential Calculus | Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions | Page 6 of 6
You might also like
- Module 1 - Tests of Hypothesis For A Single Sample100% (1)Module 1 - Tests of Hypothesis For A Single Sample27 pages
- Inverse Trig Derivatives (Derivatives of Inverse…No ratings yetInverse Trig Derivatives (Derivatives of Inverse…1 page
- Complete_Inverse_Trigonometric_DifferentiationNo ratings yetComplete_Inverse_Trigonometric_Differentiation3 pages
- Module in Math 11 Lesson 7 Derivatives of Transcendental Functions Part 1No ratings yetModule in Math 11 Lesson 7 Derivatives of Transcendental Functions Part 17 pages
- Inverse Trigonometric - Inverse DerivativesNo ratings yetInverse Trigonometric - Inverse Derivatives34 pages
- Module 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsNo ratings yetModule 6. Differentiation of Transcendental Funtions23 pages
- 3_5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Part OneNo ratings yet3_5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Part One16 pages
- L11 - Derivatives of Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetL11 - Derivatives of Trigonometric Functions17 pages
- Module No. 5: TCC21 - Differential and Integral CalculusNo ratings yetModule No. 5: TCC21 - Differential and Integral Calculus3 pages
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions4 pages
- Basic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 11: Implicit Differentiation100% (1)Basic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 11: Implicit Differentiation16 pages
- Derivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order DerivativesNo ratings yetDerivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order Derivatives12 pages
- Sin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetSin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions3 pages
- MAT060 13 Implicit Differentiation Bent UsmanNo ratings yetMAT060 13 Implicit Differentiation Bent Usman11 pages
- Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetDerivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions17 pages
- Differentiation of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetDifferentiation of Inverse Trigonometric Functions3 pages
- Lesson 11 Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetLesson 11 Inverse Trigonometric Functions14 pages
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions3 pages
- Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetDerivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions4 pages
- Math I - 19SCIB01P: Implicit Differentiation Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetMath I - 19SCIB01P: Implicit Differentiation Inverse Trigonometric Functions15 pages
- Chapter 5 Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetChapter 5 Inverse Trigonometric Functions12 pages
- Lesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetLesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions12 pages
- Implicit Differentiation For Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsNo ratings yetImplicit Differentiation For Inverse Trigonometric Functions16 pages
- The differentiation of all inverse of trigonometricNo ratings yetThe differentiation of all inverse of trigonometric3 pages
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Engg Econ GRP 3&4 Quiz (Economics, Study, Method)No ratings yetEngg Econ GRP 3&4 Quiz (Economics, Study, Method)5 pages
- Module 7 - Derivatives of Expo FunctionsNo ratings yetModule 7 - Derivatives of Expo Functions7 pages
- Module 5 - Derivatives of Inv Trig Functions100% (1)Module 5 - Derivatives of Inv Trig Functions6 pages
- Differentiation of Logarithmic FunctionNo ratings yetDifferentiation of Logarithmic Function11 pages
- Trigonometric Tables: Degrees Radians Sin (X) Cos (X) Tan (X) Sec (X) CSC (X) Cot (X)No ratings yetTrigonometric Tables: Degrees Radians Sin (X) Cos (X) Tan (X) Sec (X) CSC (X) Cot (X)16 pages
- Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 TrigonometryNo ratings yetJsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 Trigonometry6 pages
- C1 Lesson 2 - Constructing Probability Distribution100% (1)C1 Lesson 2 - Constructing Probability Distribution19 pages
- Mystical Rose School of Caloocan Inc.: # 15 Ilang-Ilang ST., Almar Subdivision Camarin Caloocan CityNo ratings yetMystical Rose School of Caloocan Inc.: # 15 Ilang-Ilang ST., Almar Subdivision Camarin Caloocan City2 pages
- CT - Differentiation - Differentiation Sheet - 22072020 - Differentiation SheetsNo ratings yetCT - Differentiation - Differentiation Sheet - 22072020 - Differentiation Sheets12 pages
- Pre-AP Calculus Spring Final Cheatsheet - For Part I ONLY: Exponential Growth & Decay FunctionsNo ratings yetPre-AP Calculus Spring Final Cheatsheet - For Part I ONLY: Exponential Growth & Decay Functions2 pages
- Newton Raphson Method:: Find Roots of The EquationNo ratings yetNewton Raphson Method:: Find Roots of The Equation15 pages
- E10 (2015) 9 Expressing Results According To ASTM E10: 220 HBW Brinell Hardness of 220No ratings yetE10 (2015) 9 Expressing Results According To ASTM E10: 220 HBW Brinell Hardness of 2203 pages
- List of Formulas For Mathematics CFS IIUMNo ratings yetList of Formulas For Mathematics CFS IIUM2 pages
- Class 12 Accountancy CBSE Chapter 4 Admission of A PartnerNo ratings yetClass 12 Accountancy CBSE Chapter 4 Admission of A Partner5 pages
- Ni n 1671385116 Converting Fractions Decimals and Percentages Ver 3No ratings yetNi n 1671385116 Converting Fractions Decimals and Percentages Ver 32 pages
- Sequence Geometric or Not Common Ratio (R)No ratings yetSequence Geometric or Not Common Ratio (R)17 pages
- fractions-worksheets-4th-grade-worksheet-1No ratings yetfractions-worksheets-4th-grade-worksheet-17 pages
- 2.1 Implicit Differentiation, Second Derivatives PDFNo ratings yet2.1 Implicit Differentiation, Second Derivatives PDF11 pages
- Bisection Method (Metode Bagi Dua) : F (X) :X 3-5x 2-2x+10 Iterasi Ke-A C B G (A) (-2,0) Eps: 0.00001No ratings yetBisection Method (Metode Bagi Dua) : F (X) :X 3-5x 2-2x+10 Iterasi Ke-A C B G (A) (-2,0) Eps: 0.0000120 pages
- Module 1 - Tests of Hypothesis For A Single SampleModule 1 - Tests of Hypothesis For A Single Sample
- Module in Math 11 Lesson 7 Derivatives of Transcendental Functions Part 1Module in Math 11 Lesson 7 Derivatives of Transcendental Functions Part 1
- Module 6. Differentiation of Transcendental FuntionsModule 6. Differentiation of Transcendental Funtions
- Module No. 5: TCC21 - Differential and Integral CalculusModule No. 5: TCC21 - Differential and Integral Calculus
- Basic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 11: Implicit DifferentiationBasic Calculus: Quarter 3 - Module 11: Implicit Differentiation
- Derivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order DerivativesDerivatives of Algebraic Functions Theorems On Differentiation of Algebraic Functions and Higher-Order Derivatives
- Sin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsSin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Differentiation of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDifferentiation of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Math I - 19SCIB01P: Implicit Differentiation Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsMath I - 19SCIB01P: Implicit Differentiation Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Lesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsLesson 12 - Derivative of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Implicit Differentiation For Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsImplicit Differentiation For Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- The differentiation of all inverse of trigonometricThe differentiation of all inverse of trigonometric
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel Mathematics
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision Shortcuts
- Trigonometric Tables: Degrees Radians Sin (X) Cos (X) Tan (X) Sec (X) CSC (X) Cot (X)Trigonometric Tables: Degrees Radians Sin (X) Cos (X) Tan (X) Sec (X) CSC (X) Cot (X)
- Jsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 TrigonometryJsunil Tutorial Panjabi Colony Gali O1: UNIT-6 Trigonometry
- C1 Lesson 2 - Constructing Probability DistributionC1 Lesson 2 - Constructing Probability Distribution
- Mystical Rose School of Caloocan Inc.: # 15 Ilang-Ilang ST., Almar Subdivision Camarin Caloocan CityMystical Rose School of Caloocan Inc.: # 15 Ilang-Ilang ST., Almar Subdivision Camarin Caloocan City
- CT - Differentiation - Differentiation Sheet - 22072020 - Differentiation SheetsCT - Differentiation - Differentiation Sheet - 22072020 - Differentiation Sheets
- Pre-AP Calculus Spring Final Cheatsheet - For Part I ONLY: Exponential Growth & Decay FunctionsPre-AP Calculus Spring Final Cheatsheet - For Part I ONLY: Exponential Growth & Decay Functions
- Newton Raphson Method:: Find Roots of The EquationNewton Raphson Method:: Find Roots of The Equation
- E10 (2015) 9 Expressing Results According To ASTM E10: 220 HBW Brinell Hardness of 220E10 (2015) 9 Expressing Results According To ASTM E10: 220 HBW Brinell Hardness of 220
- Class 12 Accountancy CBSE Chapter 4 Admission of A PartnerClass 12 Accountancy CBSE Chapter 4 Admission of A Partner
- Ni n 1671385116 Converting Fractions Decimals and Percentages Ver 3Ni n 1671385116 Converting Fractions Decimals and Percentages Ver 3
- 2.1 Implicit Differentiation, Second Derivatives PDF2.1 Implicit Differentiation, Second Derivatives PDF
- Bisection Method (Metode Bagi Dua) : F (X) :X 3-5x 2-2x+10 Iterasi Ke-A C B G (A) (-2,0) Eps: 0.00001Bisection Method (Metode Bagi Dua) : F (X) :X 3-5x 2-2x+10 Iterasi Ke-A C B G (A) (-2,0) Eps: 0.00001