0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Humidification and Drying Problems
Uploaded by
Kuo SarongThis document contains information about humidification, drying, and dehumidification processes. It includes 12 problems providing data about air properties, cooling tower design, drier design, and heat and mass transfer calculations. The problems cover topics such as cooling and reheating air, determining tower size, calculating drying rates and times, and energy balances for humidification and drying equipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
Humidification and Drying Problems
Uploaded by
Kuo Sarong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
This document contains information about humidification, drying, and dehumidification processes. It includes 12 problems providing data about air properties, cooling tower design, drier design, and heat and mass transfer calculations. The problems cover topics such as cooling and reheating air, determining tower size, calculating drying rates and times, and energy balances for humidification and drying equipment.
Original Description:
Problems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document contains information about humidification, drying, and dehumidification processes. It includes 12 problems providing data about air properties, cooling tower design, drier design, and heat and mass transfer calculations. The problems cover topics such as cooling and reheating air, determining tower size, calculating drying rates and times, and energy balances for humidification and drying equipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Humidification and Drying Problems
Uploaded by
Kuo SarongThis document contains information about humidification, drying, and dehumidification processes. It includes 12 problems providing data about air properties, cooling tower design, drier design, and heat and mass transfer calculations. The problems cover topics such as cooling and reheating air, determining tower size, calculating drying rates and times, and energy balances for humidification and drying equipment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1/ 2
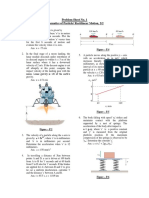
Ans. Dia = 2.71ft, Z = 5.
8ft, L = 15800 lb/h
Humidification and Drying
5. The air in a theatre 120x70x40 ft is to be
changed every 10 minutes and it is to be
A. Humidification supplied at 700F and 50% RH. The extreme
summer conditions of the air outside is 950F
1. Find the properties of moist air when the dry- and 70% RH. It is planned to cool and
bulb temperature is 80°F and the wet-bulb dehumidify this air to the desired humidity by
temperature is 67°F. the use of coke packed tower. The air will leave
Source: Perry 8th Ed. Pg. 12-8, Ex. 1. the tower sat’d and is to be reheated to the
desired temperature before being blown into
2. 1000cfm of air (A) at 950F dry bulb, 740F wet the theatre. Cooling water is available at 450F.
bulb is mixed with 2000cfm of air (B) at 650F dry
bulb, 540F wet bulb. Determine for the mixed UGa = 150, L/S = 1150, w/S =1200
stream:
(a) Dry bulb Temp. Ans. 74.70F a. What should be the height and diameter of
(b) Wet bulb temp. Ans 610F tower? Z = 7.85 ft, D = 12.58 ft
(c) Cfm of mixed stream. Ans 3014 cfm b. To what temp is the air cooled in the
tower? T = 50.50F
3. The ff data were obtained from a test on a
forced draft cooling tower
6. * Air in an amount of 1000cfm at 1500F, 20%RH
Water entering/min……..640 gal/min is passed over a refrigerated coil and thereby
Temp of entering water……….109.90F brought to 600F, 90% RH with the condensed
Temp of leaving water………….90.50F moisture withdrawn at 550F. The air is then
Humidity of entering air……….0.012 reheated by means of an electric heating coil at
Humidity of entering air……….0.031 1500F.
Temp of entering air………….830F a. Calculate the abs humidity, dew point (0F),
Temp of leaving air………….950F WB temp (oF) and enthalpy (BTU/lb) at each
Volume of tower…………2,200 ft3 3 streams.
a. Find the cu ft of air entering the tower per b. Compute the moisture removed in lb/min.
minute. Ans. 59500 cfm Ans. 1435 lb/min
b. Find the value of heat transfer coefficient. c. Compute the heat removed by the
Ans. 33.2 BTU/ft3/h/0F refrigerated coil, expressed as tons of
refrigeration (1 ton of refrigeration is 200
4. It is desired to design a coke-packed BTU/min removed.) Ans. 15.1 tons of ref.
dehumidifier to cool 2000 ft3 of saturated d. Calc the wattage of heating coil required.
air/min from 1300F to 650F. The operation is to Ans. 25kW
be conducted at normal barometric pressure.
Cooling water is available at 550F and will be Ans for a.
permitted to rise to 1100F. It is agreed to use a
gas velocity of 12000 lb of DA/h/ft2 of total
cross section. Desired water velocity must be at 1 2 3
least 1150 lb/h/ ft2 of total cross section. H 0.0333 0.01 0.01
Calculate the height and diameter of tower
DP 92 57 57
required and the weight of cooling water per
WB tem 101.5 58 84
hour
Enthalpy 74 25 48
Use Uga = 250
B. DRYING b. Calculate the cross sectional area of the
drier in ft2. Ans. 11.9 ft2
7. A wet solid is dried from 25 to 10 per cent
11. A drier is to be designed to reduce the water
moisture under constant drying conditions in
content of a certain material from 180% to 10% dry
15 ks (4.17 h). If the critical and the equilibrium basis. The available air is at 700F and has an
moisture contents are 15 and 5 per cent absolute humidity of 0.010. In order to produce the
respectively, how long will it take to dry the desired drying condition, the air entering the drier is
solid from 30 to 8 per cent moisture under the to have a temperature of 120oF and a humidity of
same conditions?. Ans. 23.9 ks 0.010 and the exit air will leave at 1100F with 70%
RH. On the basis of 1000lb of product per hour and
8. Sheet material measuring 3 ft2 and 2 inches neglecting the heat capacity of the bone dry stock,
thick is dried from 50 to 2% moisture content calculate:
(WB) under constant drying conditions. The dry a. Air entering the preheater in ft3/min Ans. 11500
ft3/min
density of the material is 30lb/ft3 and its
b. Air entering the drier in ft3/min Ans. 12600
equilibrium moisture content is negligible.
ft3/min
Experiment showed that the rate of drying c. BTU per hour to be supplied by the preheater.
under constant conditions was constant at 1.0 Ans. 630,000 BTU/h
lb per sq ft per hr between moisture contents d. BTU per hour to be supplied by the heating
between 50% and 25%. Below 25% the rate surface within the drier. Ans. 1,529,000 BTU/h
decreased. Calculate the total time req. to dry e. Total BTU consumed per pound of evaporation.
the material from 50 to 2% water. Assume Ans. 1400BTU/lb.
drying to take place from the two sides only.
Ans. 3.97h 12. * The production of a certain drier is 1 ton/h and
the percentage moisture in the wet basis reduced
from 50% to 15%. The humidity of the air passing
9. * A slab of paper pulp 4x4x1/4 in is to be dried
through the drier rises from 0.01 to 0.02, while the
under a constant drying conditions from 66.7%
air temperature falls from 155 to 1000F. The stock
water to 35% wet basis. It is to be dried under enters and leaves at 830F. Calculate the heat lost to
such conditions that the drying rate at the the surroundings in BTU/h
critical point will be 0.307 lb/h/ft2. The dry Q = 393, 580 BTU/h
material in one slab weighs 5lb. How long will
the drying process take.
Data: xe = 0.5%, xc = 1.675 lb water/lb dry stock
Ans. 1.13h 2 Cor 5 : 17
10. Continuous, counter current adiabatic rotary Prepared by:
Engr. Mark Anthony Canson
drier is being designed for the production of
500 lb/h of product containing 2% moisture wet
basis from a feed containing 30% moisture. The
air entering the drier will have a dry bulb temp
of 2300F and a wet bulb temp of 1020F and the
air leaving the drier will be at 1150F. Because of
the small size of the crystals, the highest
allowable air velocity is 10lb/min of DA/ft2 of
cross section.
a. Calculate the pounds of bone dry air
required per minute. Ans. 119 lb/min
You might also like
- Multiple Choice Chemical Technician Reviewer100% (22)Multiple Choice Chemical Technician Reviewer23 pages
- CHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 2014 For Students1No ratings yetCHE Thermodynamics Competency Exam 2013 2014 For Students13 pages
- Edinburgh EH14 4AS, United Kingdom Produced by Heriot-Watt University, 2018No ratings yetEdinburgh EH14 4AS, United Kingdom Produced by Heriot-Watt University, 2018119 pages
- Practice Problems in ADSORPTION and ION EXCHANGE - Solutions100% (2)Practice Problems in ADSORPTION and ION EXCHANGE - Solutions8 pages
- Faculty of Engineering and The Built Environment (Febe) Department of Chemical Engineering Unochb2: Unit Operations 2B TUTORIAL 4-EvaporationNo ratings yetFaculty of Engineering and The Built Environment (Febe) Department of Chemical Engineering Unochb2: Unit Operations 2B TUTORIAL 4-Evaporation2 pages
- Chapter 2 Single Vapor Compression SystemNo ratings yetChapter 2 Single Vapor Compression System32 pages
- Molecular Transport Equation and General Property Balance100% (1)Molecular Transport Equation and General Property Balance56 pages
- Designofcondenser 130801223803 Phpapp02No ratings yetDesignofcondenser 130801223803 Phpapp0217 pages
- Energy Balance Around The Conveyor WasherNo ratings yetEnergy Balance Around The Conveyor Washer5 pages
- Ps1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 1No ratings yetPs1-Che171 Chemical Reaction Engineering 12 pages
- Experiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction ConversionNo ratings yetExperiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction Conversion8 pages
- Exercise - Chemical Reaction EngineeringNo ratings yetExercise - Chemical Reaction Engineering4 pages
- Introductory Applications of Partial Differential Equations: With Emphasis on Wave Propagation and DiffusionFrom EverandIntroductory Applications of Partial Differential Equations: With Emphasis on Wave Propagation and DiffusionNo ratings yet
- ChE Board Exam Question (CO2 in Room Problem)No ratings yetChE Board Exam Question (CO2 in Room Problem)3 pages
- Review On Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry PDFNo ratings yetReview On Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry PDF13 pages
- Life Cycle Analysis of Rapeseed Oil Butyl Esters Produced From Waste and Pure Rapeseed OilNo ratings yetLife Cycle Analysis of Rapeseed Oil Butyl Esters Produced From Waste and Pure Rapeseed Oil2 pages
- History: Municipality Province Negros Oriental PhilippinesNo ratings yetHistory: Municipality Province Negros Oriental Philippines1 page
- General Chemistry (Atomic Model, Chemical Bonds, Solution and Nuclear Chemistry) PDFNo ratings yetGeneral Chemistry (Atomic Model, Chemical Bonds, Solution and Nuclear Chemistry) PDF5 pages
- Biochemistry of Bitterness in Bamboo ShootsNo ratings yetBiochemistry of Bitterness in Bamboo Shoots8 pages
- Ebbes Et Al 2024 Getting The Board On Board Marketing Department Power and Board InterlocksNo ratings yetEbbes Et Al 2024 Getting The Board On Board Marketing Department Power and Board Interlocks21 pages
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Unit 4 - Quartiles100% (2)A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Unit 4 - Quartiles6 pages
- Library Study: (Traditional Craft Center)No ratings yetLibrary Study: (Traditional Craft Center)37 pages
- IJMER - Volume5 Issue5 2 2016 214 225PDFNo ratings yetIJMER - Volume5 Issue5 2 2016 214 225PDF9 pages
- Netherlands Updated Syllabus - Jan. 2011No ratings yetNetherlands Updated Syllabus - Jan. 201111 pages
- Brief History of The Entertainment IndustryNo ratings yetBrief History of The Entertainment Industry6 pages