Unit 3.3 PDF
Uploaded by
Rahul KumarUnit 3.3 PDF
Uploaded by
Rahul KumarMEASUREMENT OF THREE PHASE POWER
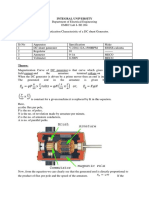
Power measurement in an AC circuit is measured with the help of a Wattmeter. A
Wattmeter is an instrument which consists of two coils called Current
coil and Potential coil. The current coil having low resistance is connected in series
with the load so that it carries the load current. The potential coil having the resistance
is connected across the load and carries the current proportional to the potential
difference.
For measuring the power in a 3 phase or Poly Phase system, more than one wattmeter
is required, or more than one readings are made by one wattmeter. If more than one
wattmeter is connected for the measurement, the process becomes convenient and
easy to work with instead of taking various readings with one wattmeter.
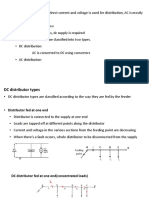
THREE-WATTMETER METHOD
Three Wattmeter method is employed to measure power in a 3 phase, 4 wire system.
However, this method can also be employed in a 3 phase, 3 wire delta connected load,
where power consumed by each load is required to be determined separately.
The connections for star connected loads for measuring power by three wattmeter
method is shown below.
The pressure coil of all the three wattmeter’s namely W1, W2 and W3 are connected to
a common terminal known as the neutral point. The product of the phase current and
line voltage represents as phase power and is recorded by individual wattmeter.
The total power in a three wattmeter method of power measurement is given by the
algebraic sum of the readings of three wattmeter’s i.e.
Where,
W1 = V1I1 W2 = V2I2 W3 = V3I3
Except for 3 phase, 4 wire unbalanced load, 3 phase power can be measured by using
only Two Wattmeter Method.
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
TWO WATTMETER METHOD
Two Wattmeter Method can be employed to measure the power in a 3 phase, three
wire star or delta connected the balanced or unbalanced load. In Two wattmeter
method the current coils of the wattmeter are connected with any two lines, say R and
Y and the potential coil of each wattmeter is joined on the same line, the third line i.e.
B as shown below in figure (A).
The total instantaneous power absorbed by the three loads Z1, Z2 and Z3, are equal to
the sum of the powers measured by the Two wattmeters, W1 and W2.
Measurement of Power by Two Wattmeter Method in Star Connection
Considering the above figure (A) in which Two Wattmeter W1 and W2 are connected,
the instantaneous current through the current coil of Wattmeter, W1 is given by the
equation shown below.
Instantaneous potential difference across the potential coil of Wattmeter, W1 is given
as
Instantaneous power measured by the Wattmeter, W1 is
The instantaneous current through the current coil of Wattmeter, W2 is given by the
equation
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
Instantaneous potential difference across the potential coil of Wattmeter, W2 is given
as
Instantaneous power measured by the Wattmeter, W2 is
Therefore, the Total Power Measured by the Two Wattmeter’s W1 and W2 will be
obtained by adding the equation (1) and (2).
Where P – the total power absorbed in the three loads at any instant.
Measurement of Power by Two Wattmeter Method in Delta Connection
Considering the delta connected circuit shown in the figure below.
The instantaneous current through the coil of the Wattmeter, W1 is given by the
equation
Instantaneous Power measured by the Wattmeter, W1 will be
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
Therefore, the instantaneous power measured by the Wattmeter, W1 will be given as
The instantaneous current through the current coil of the Wattmeter, W2 is given as
The instantaneous potential difference across the potential coil of Wattmeter, W2 is
Therefore, the instantaneous power measured by Wattmeter, W2 will be
Hence, to obtain the total power measured by the Two Wattmeter the two equations,
i.e. equation (3) and (4) has to be added.
Where P is the total power absorbed in the three loads at any instant.
The power measured by the Two Wattmeter at any instant is the instantaneous power
absorbed by the three loads connected in three phases. In fact, this power is the
average power drawn by the load since the Wattmeter reads the average power
because of the inertia of their moving system.
Determination of Power Factor from Wattmeter Readings
The Two Wattmeter Method is explained, taking an example of a balanced load. In
this, we have to prove that the power measured by the Two Wattmeter i.e. the sum of
the two wattmeter readings is equal to root 3 times of the phase voltage and line
voltage (√3VLIL Cosϕ) which is the actual power consumed in a 3 phase balanced
load.
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
The connection diagram of a 3 phase balanced load connected as Star Connection is
shown below.
The load is considered as an inductive load, and thus, the phasor diagram of the
inductive load is drawn below.
The three voltages VRN, VYN and VBN, are displaced by an angle of 120 degrees
electrical as shown in the phasor diagram. The phase currents lag behind their
respective phase voltages by an angle ϕ.
Now, the current flowing through the current coil of the Wattmeter, W1 will be given
as
Potential difference across the pressure or potential coil of the Wattmeter, W1will be
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
To obtain the value of VRB, reverse the VBN and add it to the VRN as shown in the
phasor diagram above. The phase difference between VRB and IR is (30⁰ - ϕ).
Therefore, the power measured by the Wattmeter, W1 is
Current through the current coil of the Wattmeter, W2 is given as
Potential difference across the Wattmeter, W2 is
The phase difference VYB and IY is (30⁰ + ϕ).
Therefore, the power measured by the Wattmeter, W2 is given by the equation shown
below.
Since, the load is in balanced condition, hence,
Therefore, the wattmeter readings will be
Now, the sum of two Wattmeter readings will be given as
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
The above equation (1) gives the total power absorbed by a 3 phase balanced load.
Thus, the sum of the readings of the two wattmeters is equal to the power absorbed in
a 3 phase balanced load.
Now,
Dividing equation (3) by equation (2) we get,
Power factor of the load is given as
Measuring Instruments by Shivam Gupta
You might also like
- Experiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper ApparatusNo ratings yetExperiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper Apparatus3 pages
- Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsNo ratings yetAnalog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Conversions20 pages
- Sns College of Technology Department of Eee: SVC-SVC InteractionNo ratings yetSns College of Technology Department of Eee: SVC-SVC Interaction7 pages
- LAB 1: Per Unit System in Transmission and DistributionNo ratings yetLAB 1: Per Unit System in Transmission and Distribution13 pages
- Instant download Nonlinear Phenomena in Power Electronics attractors bifurcations chaos and nonlinear control 1st Edition Soumitro Banerjee pdf all chapter100% (8)Instant download Nonlinear Phenomena in Power Electronics attractors bifurcations chaos and nonlinear control 1st Edition Soumitro Banerjee pdf all chapter60 pages
- Study of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar ApplicationsNo ratings yetStudy of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar Applications25 pages
- Slides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 2No ratings yetSlides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 259 pages
- 05-Nonpilot OC Protection of Transmission LinesNo ratings yet05-Nonpilot OC Protection of Transmission Lines23 pages
- Electronics Laboratory Simulation of BJT AmplifierNo ratings yetElectronics Laboratory Simulation of BJT Amplifier14 pages
- Exercise Problems Electrical Machines 291010No ratings yetExercise Problems Electrical Machines 2910109 pages
- Scott Connection (T T) : Teaser Transformer, With 0.866 Tapped Windings (Vertical Member of T)No ratings yetScott Connection (T T) : Teaser Transformer, With 0.866 Tapped Windings (Vertical Member of T)8 pages
- SKEE 2742 Basic Electronics Lab: Experiment 2 BJT Small-Signal AmplifierNo ratings yetSKEE 2742 Basic Electronics Lab: Experiment 2 BJT Small-Signal Amplifier8 pages
- three phase power measurement using wattmetersNo ratings yetthree phase power measurement using wattmeters90 pages
- Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method - 5No ratings yetMeasurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method - 54 pages
- Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method 5No ratings yetMeasurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method 54 pages
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Rasd 20 3: Dynamic Analysis For Ball Mill FoundationNo ratings yetRasd 20 3: Dynamic Analysis For Ball Mill Foundation13 pages
- Download Complete Self Esteem for Teens Six Principles for Creating the Life You Want 1st Edition Lisa M. Schab PDF for All Chapters100% (1)Download Complete Self Esteem for Teens Six Principles for Creating the Life You Want 1st Edition Lisa M. Schab PDF for All Chapters67 pages
- Fracture Strength of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars Supported by A Horizontal Glass Fiber Post: An in Vitro StudyNo ratings yetFracture Strength of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars Supported by A Horizontal Glass Fiber Post: An in Vitro Study6 pages
- Pengaruh Marketing Mix Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian Pada Orange MartNo ratings yetPengaruh Marketing Mix Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian Pada Orange Mart100 pages
- Physics 219 Summary of Linear Response TheoryNo ratings yetPhysics 219 Summary of Linear Response Theory5 pages
- PPDM Well Status Classification Houston 2013No ratings yetPPDM Well Status Classification Houston 201345 pages
- "My Starbucks Idea": The Company Is Not Sufficiently Market-Focused and Customer-Driven"No ratings yet"My Starbucks Idea": The Company Is Not Sufficiently Market-Focused and Customer-Driven"2 pages
- Experiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper ApparatusExperiment No. 13: Objective: To Investigate The Use of JFET As A Constant Current Source & As Chopper Apparatus
- Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsAnalog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Conversions
- Sns College of Technology Department of Eee: SVC-SVC InteractionSns College of Technology Department of Eee: SVC-SVC Interaction
- LAB 1: Per Unit System in Transmission and DistributionLAB 1: Per Unit System in Transmission and Distribution
- Instant download Nonlinear Phenomena in Power Electronics attractors bifurcations chaos and nonlinear control 1st Edition Soumitro Banerjee pdf all chapterInstant download Nonlinear Phenomena in Power Electronics attractors bifurcations chaos and nonlinear control 1st Edition Soumitro Banerjee pdf all chapter
- Study of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar ApplicationsStudy of Boost Converter With Inverter For Stand Alone Solar Applications
- Slides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 2Slides - 17 - CH 18 - Network Theorems (Ac) - Updated - 2
- Electronics Laboratory Simulation of BJT AmplifierElectronics Laboratory Simulation of BJT Amplifier
- Scott Connection (T T) : Teaser Transformer, With 0.866 Tapped Windings (Vertical Member of T)Scott Connection (T T) : Teaser Transformer, With 0.866 Tapped Windings (Vertical Member of T)
- SKEE 2742 Basic Electronics Lab: Experiment 2 BJT Small-Signal AmplifierSKEE 2742 Basic Electronics Lab: Experiment 2 BJT Small-Signal Amplifier
- Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method - 5Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method - 5
- Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method 5Measurement of Resistance and Inductance of A Choke Coil Using Three Voltmeter Method 5
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem Blockset
- Rasd 20 3: Dynamic Analysis For Ball Mill FoundationRasd 20 3: Dynamic Analysis For Ball Mill Foundation
- Download Complete Self Esteem for Teens Six Principles for Creating the Life You Want 1st Edition Lisa M. Schab PDF for All ChaptersDownload Complete Self Esteem for Teens Six Principles for Creating the Life You Want 1st Edition Lisa M. Schab PDF for All Chapters
- Fracture Strength of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars Supported by A Horizontal Glass Fiber Post: An in Vitro StudyFracture Strength of Endodontically Treated Maxillary Premolars Supported by A Horizontal Glass Fiber Post: An in Vitro Study
- Pengaruh Marketing Mix Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian Pada Orange MartPengaruh Marketing Mix Terhadap Keputusan Pembelian Pada Orange Mart
- "My Starbucks Idea": The Company Is Not Sufficiently Market-Focused and Customer-Driven""My Starbucks Idea": The Company Is Not Sufficiently Market-Focused and Customer-Driven"