Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Uploaded by
kingstonCopyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Uploaded by
kingstonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-5
Uploaded by
kingstonCopyright:
Available Formats
1
ULTRASONIC TESTING
UT Q BANK A-5
1. The test system which relies on reflected energy to find discontinuities
is called
a. Through-transmission
b. Pulse-echo
c. Longitudinal wave
d. Continuous wave
2. The test system that uses either pulsed or continuous sound and
indicates discontinuities as a reduction in received energy magnitude
is called
a. Contact testing
b. Longitudinal wave testing
c. Pulse-echo testing
d. Through – transmission testing
3. The test method where the transducer is coupled to the test specimen
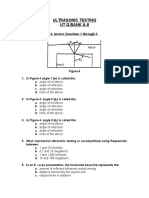
though a thin layer of couplant is called
a. Immersion testing
b. Contact testing
c. Coupled wave testing
d. Through – transmission testing
4. The test method where both the transducer and the test specimen are
placed in a tank filled with a liquid (water) is called
a. Contact testing
b. Submerged testing
c. Immersion testing
d. Through-transmission testing
5. The ability of an ultrasonic test instrument to detect discontinuities is
not affected by the surface condition, shape, or metallurgical
characteristics of a specimen to be tested
a. True
b. False
6. Pulse-echo testing provides specific data on the relative size of the
discontinuity and its distance from the surface of the test specimen
a. True
b. False
2
7. The requirement that the transmitting and receiving transducers have
to be precisely aligned on the test specimen is a disadvantage of:
a. Contact testing
b. Longitudinal wave testing
c. Pulse-echo testing
d. Through –transmission testing
8. Which of the following factors is an advantage of contact testing over
immersion testing? (Choose two)
a. Greater beam penetration
b. Higher frequencies may be used
c. Better resolution
d. Portability
9. Which of the following factors is a disadvantage of contact testing?
a. decreased beam penetration power
b. Portability
c. Difficulty in maintaining a uniform acoustical coupling
d. Confined to high frequency testing only
10. Which of the following factors is an advantage of immersion testing
over the contact method?
a. Greater beam penetration power
b. Portability
c. Lower test frequencies may be used
d. Angulations for unfavorably oriented discontinuities
11. Which of the following is not an advantage of immersion testing?
a. Portability
b. Better resolution
c. Reduced transducer wear
d. Angulations ability
12. Equipment selection and operation are parameters of the ultrasonic
test system that are controlled by the operator
a. True
b. False
13. To improve the ultrasonic test of a given specimen, which of the
following may be modified ?(Choose two)
a. Specimen shape
b. Adjustment of instrument controls
c. Specimen surface condition
d. Specimen heat treat
3
14. The requirements on an ultrasonic test are:
a. Determined by operator judgment
b. Established by the reference standard block used.
c. Outlined in the acceptance standard
15. Standardization of ultrasonic test instruments is based on reflections
received from reference standards containing simulated discontinuities
of known size
a. True
b. False
16. Any precisely machined reference standard block may be used in
standardizing a test instrument for testing a given test specimen
a. True
b. False
17. In ultrasonic, pulse-echo testing is more widely used than through
transmission testing
a. True
b. False
18. A particular advantage of through – transmission testing is
a. No couplant is required
b. The depth of a discontinuity can be easily determined
c. Only one transducer is required
d. None of the above.
19. Proper test equipment selection is dependent on the :
a. Over all test situation
b. Metallurgical structure of the specimen
c. Test specimen geometry
d. Surface condition of the test specimen
20. Which of the following frequencies would probably result in the
greatest attenuation loss?
a. 1.0 MHz
b. 10.0 MHz
c. 25 kHz
d. 25 MHz
21. The characteristics of the internal grain structure of a test specimen do
not need to be considered when selecting the test frequency
a. True
b. False
4
22. To test large, flat specimens, the transducer should have:
a. A large surface area.
b. A small surface area
c. An acoustical lens
d. A curved surface
23. In order to find the smallest discontinuities during a test:
a. Use the lowest frequency possible
b. Use the highest frequency possible.
c. Use through – transmission testing
d. Use a small transducer
24. Transducers incorporating a plastic wedge frontal member are
commonly used in straight- beam testing
a. True
b. False
25. The acoustical impedance of an ideal couplant should be between that
of the transducer and the test specimen.
a. True
b. False
26. The choice of a couplant is largely dependent on the surface condition
of the test specimen
a. True
b. False
27. Loss of back-surface reflection is evidence that sound is not being
returned to the:
a. Discontinuity
b. Transducer
c. Test specimen
d. Back surface
28. An ultrasonic instrument operator can control the number of cycles of
sound energy transmitted into a test specimen by adjusting pulse
length. A short pulse length results in (Choose two)
a. Less instrument sensitivity
b. Less penetration power
c. Better near-surface resolution
d. Increased penetration power
5
29. In contact testing, shear waves may be produced in a test specimen
by:
a. Placing an X-cut quartz crystal on the specimen and coupling with
oil.
b. Using two transducers, one on each side of the specimen
c. Using a shear-cut lens on the transducer
d. using an angle beam transducer
30. The first critical incident angle for longitudinal waves is the point at
which
a. The reflected angle is zero degrees
b. The refracted angle of the longitudinal wave mode is parallel to the
surface
c. The longitudinal wave mode is totally reflected
d. Both longitudinal and shear waves are transmitted in to the
specimen
31. What is the waveform developed when the shear wave mode is
refracted 90 degrees?
a. Longitudinal waves
b. Surface wave
c. Transverse wave
d. Transitional wave
32. Ultrasonic waves which travel around a gradual curve with little or no
reflection from the curve are called:
a. longitudinal waves
b. Surface waves
c. Shear waves
d. Transverse waves
33. Plate waves may be used to test;
a. Thin sheet.
b. Forgings
c. Bar stock
d. a, b and c.
34. With reference to single-transducer pulse –echo testing, two-
transducer pulse-echo testing has better:
a. Near surface resolution
b. Specimen penetration power
c. Resolution at all depths.
d. Sensitivity at all depths
6
35. Ultrasonic testing of castings is often not possible because of:
a. Rough surfaces
b. Small grain structure
c. Coarse grain structure
d. Irregular shape
36. Which of the following materials is most likely to produce the greatest
amount of sound attenuation over a given distance?
a. Hand forging
b. Coarse-grained casting
c. Extrusion
d. Fine-grained material
37. It is normal practice in testing bar stock to use both axial and radial
tests( test through both the length and width of specimen)
a. True
b. False
38. In straight beam contact testing, with the sound beam entering a flat
specimen such as a plate from one of the surfaces, the following type
of discontinuity will probably be detected:
a. Laminations with major dimensions parallel to surface
b. Tranverse –type discontinuities at an angle to the surface
c. Radial-type discontinuities with major dimension along length but
radially oriented to the surface
d. Porosity
39. A gross check of plate or sheet consists of marking off a grid pattern
on the material, either real or imaginary, and then testing each grid
square using:
a. A transducer wheel
b. A focused transducer
c. An angle-beam transducer
d. A straight –beam transducer
40. Before using an angle-beam transducer for testing plate, a reference
notch must be setup to determine the size of any discontinuities that
might be found
a. True
b. False
7
ULTRASONIC TESTING
UT Q BANK A-5
ANSWERS
QUESTIONS ANSWERS QUESTIONS ANSWERS
1 B 21 B
2 D 22 A
3 B 23 B
4 B 24 B
5 B 25 A
6 A 26 A
7 D 27 B
8 A AND D 28 B AND C
9 C 29 D
10 D 30 B
11 A 31 B
12 A 32 C
13 B AND C 33 A
14 C 34 A
15 A 35 C
16 B 36 B
17 A 37 A
18 D 38 A
19 A 39 D
20 D 40 A
You might also like
- Goa Schedule RatesDocument255 pagesGoa Schedule Rateskite technical3100% (7)
- UTT General Exam #2Document8 pagesUTT General Exam #2nathaniel ekaiko100% (4)
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-8Document9 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-8kingston100% (1)
- UT Level IDocument27 pagesUT Level Ifysal_845134100% (1)
- PT Specific 1Document4 pagesPT Specific 1vsnaiduqc100% (3)
- Questions Nde Level 1-2-UTDocument57 pagesQuestions Nde Level 1-2-UTMOhammed PatelNo ratings yet
- TWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2Document4 pagesTWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2HassanSobohNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer For UT2Document51 pagesQuestion and Answer For UT2Moh Lebkia0% (1)
- Ut General ExamDocument7 pagesUt General ExamMalik Zghoul75% (4)
- UT Level II QuestionsDocument28 pagesUT Level II QuestionsMahade Hasan Dipu100% (8)
- Viscosity by Ford Viscosity Cup: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesViscosity by Ford Viscosity Cup: Standard Test Method ForDr. Ahmed Abdel-HakimNo ratings yet
- Rusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4Document9 pagesRusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-6Document8 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-6kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-4Document10 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-12: 5° From The Test SurfaceDocument11 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-12: 5° From The Test Surfacekingston100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing 8Document5 pagesUltrasonic Testing 8Duy Le AnhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-8: 5. WhenDocument8 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-8: 5. Whenkingston100% (1)
- Rusayl Institute: Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 5Document16 pagesRusayl Institute: Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 5kingston100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-7Document9 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-7kingston100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing 2Document5 pagesUltrasonic Testing 2Duy Le AnhNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-13Document9 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-13kingston100% (1)
- Ut Lev-I Gen (Kavi 10-10-06)Document10 pagesUt Lev-I Gen (Kavi 10-10-06)kingston50% (2)
- Utq Bank 6Document27 pagesUtq Bank 6kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-11: and Reflected at An InterfaceDocument11 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-11: and Reflected at An Interfacekingston100% (2)
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-14Document11 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-14kingston0% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing: Answer All QuestionsDocument11 pagesUltrasonic Testing: Answer All QuestionsaspoiaspoiNo ratings yet
- Ut Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBDocument25 pagesUt Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBkingston100% (2)
- UT L1 General Thickness Testing ExaminationDocument3 pagesUT L1 General Thickness Testing ExaminationdaddadNo ratings yet
- UT Level I QuestionsDocument23 pagesUT Level I QuestionsMahade Hasan Dipu100% (1)
- UTT General Exam #3Document9 pagesUTT General Exam #3nathaniel ekaiko100% (1)
- UT Level 2Document51 pagesUT Level 2VLADIMIR Krav0% (1)
- Asnt Ut L2Document18 pagesAsnt Ut L2QAMAR ALI KHANNo ratings yet
- Important Ut Q Nov'12 - 1Document4 pagesImportant Ut Q Nov'12 - 1Dibyendu Bera100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Quiz 1: First Name Last NameDocument7 pagesUltrasound Quiz 1: First Name Last NameahmedNo ratings yet
- UT GeneralDocument6 pagesUT GeneralAmr El Refay50% (2)
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1kingstonNo ratings yet
- QZ EqDocument6 pagesQZ Eqgalati12345100% (1)
- PT Quiz & Ans 3Document6 pagesPT Quiz & Ans 3Goutam Kumar DebNo ratings yet
- LatihanDocument18 pagesLatihanAhmad Dulfi100% (1)
- UT QuizDocument6 pagesUT QuizGoutam Kumar Deb100% (1)
- TWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 4Document4 pagesTWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 4HassanSoboh0% (1)
- Utq Bank 3Document10 pagesUtq Bank 3kingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 5Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 5kingstonNo ratings yet
- Twi Training and Certification: Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2Document6 pagesTwi Training and Certification: Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2Zouhair BenmabroukNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)Document6 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing (PT)kingston100% (1)
- UT Level II GeneralDocument10 pagesUT Level II GeneralkingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 3Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 3kingstonNo ratings yet
- First Name Last Name : LPF Stands ForDocument35 pagesFirst Name Last Name : LPF Stands ForVicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial IIIDocument21 pagesTutorial IIIravindra_jivani0% (1)
- UT Level II Questions EGYPTAPR12 PDFDocument16 pagesUT Level II Questions EGYPTAPR12 PDFrupam100% (1)
- Level 1 UT Test Part 2Document12 pagesLevel 1 UT Test Part 2JoshnewfoundNo ratings yet
- MPIGENQUESTDocument5 pagesMPIGENQUESTsaenal rapiNo ratings yet
- Ut Level 1Document39 pagesUt Level 1Harendra LatiyanNo ratings yet
- Helier PT QBDocument22 pagesHelier PT QBkingston100% (2)
- Model Test Magnetic Particle TestingDocument24 pagesModel Test Magnetic Particle TestingAnu AnoopNo ratings yet
- PTIIGENERALDocument5 pagesPTIIGENERALsaenal rapiNo ratings yet
- TWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 8Document5 pagesTWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 8HassanSoboh100% (1)
- QB On Testing Methods 5Document7 pagesQB On Testing Methods 5shailesh jhaNo ratings yet
- Astm A194Document3 pagesAstm A194kingstonNo ratings yet
- The Effect of CarbonDocument4 pagesThe Effect of CarbonkingstonNo ratings yet
- To Understand The Term Bending Moment We Have To First Understand What IsDocument3 pagesTo Understand The Term Bending Moment We Have To First Understand What IskingstonNo ratings yet
- Elastic Stress Analysis For Heat Exchanger Channel Head For Protection Against Plastic Collapse and Protection Against Local Failure (FEA)Document8 pagesElastic Stress Analysis For Heat Exchanger Channel Head For Protection Against Plastic Collapse and Protection Against Local Failure (FEA)kingstonNo ratings yet
- ASNT RECER RT QB (Aligned) MAIN FOILDERDocument26 pagesASNT RECER RT QB (Aligned) MAIN FOILDERkingston100% (2)
- Solid Mechanics Plane Stress and Plane StrainsDocument8 pagesSolid Mechanics Plane Stress and Plane StrainskingstonNo ratings yet
- Geometric Unsharpness: RadiographyDocument3 pagesGeometric Unsharpness: RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- Girth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniquesDocument12 pagesGirth Flange Load Calculation Using by FEA TechniqueskingstonNo ratings yet
- VT QB S4 Pro Wiyh KeyDocument12 pagesVT QB S4 Pro Wiyh Keykingston100% (1)
- Filters in RadiographyDocument1 pageFilters in RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- Asnt Recer RT QB Level IDocument9 pagesAsnt Recer RT QB Level Ikingston100% (1)
- MT Level - I QB 5Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 5kingstonNo ratings yet
- Nig VT Spec QB S2 - Level IiDocument12 pagesNig VT Spec QB S2 - Level Iikingston100% (1)
- RT 19Document3 pagesRT 19kingstonNo ratings yet
- Activity (Of Radionuclides) : Home Education Resources NDT Course Material RadiographyDocument1 pageActivity (Of Radionuclides) : Home Education Resources NDT Course Material RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- Secondary (Scatter) Radiation and Undercut ControlDocument2 pagesSecondary (Scatter) Radiation and Undercut ControlkingstonNo ratings yet
- Exposure Vaults & Cabinets: RadiographyDocument1 pageExposure Vaults & Cabinets: RadiographykingstonNo ratings yet
- RT 11Document4 pagesRT 11kingstonNo ratings yet
- More Information On Radiation SafetyDocument2 pagesMore Information On Radiation SafetykingstonNo ratings yet
- Indian Society For Non-Destructive Testing: Model Examination - PT Level IIIDocument8 pagesIndian Society For Non-Destructive Testing: Model Examination - PT Level IIIkingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 1Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 1kingstonNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Generators: WWW - Xraylamp.webd - PLDocument3 pagesX-Ray Generators: WWW - Xraylamp.webd - PLkingstonNo ratings yet
- LPT Kavi Cha QBDocument47 pagesLPT Kavi Cha QBkingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 4Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 2Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 2kingstonNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 3Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 3kingstonNo ratings yet
- PT QBDocument12 pagesPT QBkingstonNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)Document6 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing (PT)kingston100% (1)
- B1 1 김영한Document17 pagesB1 1 김영한bruceNo ratings yet
- Toys R UsDocument2 pagesToys R Usfairy_h2007No ratings yet
- Environmental Modeling and Lab: Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Modeling and Lab: Course DescriptionAllie MaeNo ratings yet
- 27 C 256Document13 pages27 C 256Jose M PeresNo ratings yet
- MSS SP-97 2012 Ntegrally Reinforced Forged Branch Outlet Fittings - Socket Welding, Threaded, and Buttwelding EndsDocument21 pagesMSS SP-97 2012 Ntegrally Reinforced Forged Branch Outlet Fittings - Socket Welding, Threaded, and Buttwelding Endsbesant varghees100% (2)
- Chapter 17: Managing MoneyDocument3 pagesChapter 17: Managing MoneyZwaliNo ratings yet
- Bangood CS85 AlarmeDocument19 pagesBangood CS85 Alarmecarvalhomeister0% (2)
- Nego Case Digest 1 PDFDocument70 pagesNego Case Digest 1 PDFJulie Ann PiliNo ratings yet
- Postgres PDFDocument6 pagesPostgres PDFRamon Anibal PegueroNo ratings yet
- Unsrat-Manado - Cracking ZoneDocument18 pagesUnsrat-Manado - Cracking ZoneChicopee HolyokeNo ratings yet
- Itecc StructureDocument2 pagesItecc StructureCu AgNo ratings yet
- Colgate PalmoliveDocument5 pagesColgate PalmoliveSourav LaikNo ratings yet
- Like Elon Musk An in Complete Guide Business Lessons From The Greatest Entrepreneur of All Time Michal Adam DominiczakDocument17 pagesLike Elon Musk An in Complete Guide Business Lessons From The Greatest Entrepreneur of All Time Michal Adam DominiczakVed KananiNo ratings yet
- Collection of Test English: - Prasuci RN - Achmad Wildan - Dimas WisnuDocument18 pagesCollection of Test English: - Prasuci RN - Achmad Wildan - Dimas WisnuSudrajat SHTMNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Modeling of Compliant Mechanisms Based On The Pseudo-Rigid-Body ModelDocument6 pagesDynamic Modeling of Compliant Mechanisms Based On The Pseudo-Rigid-Body Modelalio safarNo ratings yet
- DN 60548Document2 pagesDN 60548Victor Keiji MuraokaNo ratings yet
- OBIEE - Aggregate TablesDocument3 pagesOBIEE - Aggregate Tablesvenkatesh.gollaNo ratings yet
- Survey QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesSurvey QuestionnaireYour PlaylistNo ratings yet
- Financial Services Knowledge Series On Ifrs 17 General Measurement Model Volume IIDocument21 pagesFinancial Services Knowledge Series On Ifrs 17 General Measurement Model Volume IIMohammad IslamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Odd Sem 2023Document5 pagesSyllabus - Odd Sem 2023Maithra D.No ratings yet
- 03 Intro. Tension MemberDocument10 pages03 Intro. Tension MemberRi MarkuNo ratings yet
- Jonshon ScreenDocument25 pagesJonshon Screennazar750No ratings yet
- The Ball Piston EngineDocument13 pagesThe Ball Piston EnginedhairyashilNo ratings yet
- Ar 2019 Annual Report DojDocument66 pagesAr 2019 Annual Report DojNeanderthalNo ratings yet
- Brad Pitt As An ArchitectDocument18 pagesBrad Pitt As An ArchitectTatjana VorinskiNo ratings yet
- Tamil Keyboard Layout For Bamini FontDocument1 pageTamil Keyboard Layout For Bamini Fontrscm7522920% (1)
- Morales vs. Court of Appeals Morales vs. Court of AppealsDocument5 pagesMorales vs. Court of Appeals Morales vs. Court of AppealsKenmar NoganNo ratings yet
- ASTEK ŁańcuchyDocument610 pagesASTEK ŁańcuchyadasrafalskiNo ratings yet