Bonding
Bonding
Uploaded by
Jhanelle S. Dixon-LairdCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonding
Bonding
Uploaded by
Jhanelle S. Dixon-LairdOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Bonding
Bonding
Uploaded by
Jhanelle S. Dixon-LairdCopyright:
Available Formats
Bonding, Structure and Properties
When atoms join together, either with the same atom or a different atom, the way it joins, has
considerable effect on its structure and then consequently on its properties. The joining of an
atom to another atom is called Bonding. Bonding involves each atom either donating or
accepting electron from another atom. It is also done through sharing electrons. There are three
types of bonding that will be discussed here.
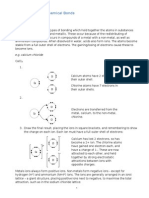
Ionic Bonding
The bonding involves ions as the name suggests. When an atom becomes a positive ion by losing
an electron, this positive ion will look for a negative ion to attract. A negative ion will be the
atom that has gained an electron. When these positive and negative ions meet, through attraction
of opposites a bonding will be formed, which is known as ionic bonding.
The substances that would have this type of bondings are compounds of metals with non-metals.
For example Sodium Chloride, which involves metal such as Sodium and non-metal such as
Chlorine, both become ions. Sodium has one electron in its outer shell, which it will lose to
become a positive ion. Chlorine has seven electrons in its outer shell therefore will gain one
electron to form a stable outer shell and become a negative ion. The structure, which is present in
ionic bonded compounds, is Giant Lattice. Ionic bonding shows properties of high melting and
boiling point. They are very hard but brittle and conduct electricity when dissolved in water, or
molten. They are often soluble in water and generally insoluble in non-polar solvents.
Covalent Bonding
This type of bonding involves sharing of electrons between the two atoms. It is present in non-
metals such as Carbon, Chlorine, and Oxygen. For example, in Oxygen, there are 6 electrons in
the outer shell. It would bond with another Oxygen by sharing its two electron with other
Oxygen’s two electron therefore sharing a total of four electrons.
This is a double bond. In a single bond only one pair of electrons are shared such as between
Chlorine and Chlorine.
Covalent bonds are strong and have a very high melting and boiling point. It does not conduct
electricity and is insoluble in water and non-polar solvents.
Metallic Bonding
This bonding joins metal atoms together for example Magnesium atoms. Many MgAtoms bond
together to form a solid metal.
Magnesium atoms are positive ions surrounded by delocalised electrons. Due to these
delocalised electrons, they conduct electricity. The melting and boiling points are generally high
in Metallic bonding. Metals typically have a shiny, metallic lustre.
Read more: http://www.articlesbase.com/science-articles/bondingstructure-and-properties-
1416654.html#ixzz16jYVfdf6
Under Creative Commons License: Attribution
You might also like
- DB58 Engine Manual (En)Document210 pagesDB58 Engine Manual (En)carlosalazarsanchez_86% (7)
- Wongani Msiska Comp 1640 CourseworkDocument9 pagesWongani Msiska Comp 1640 Courseworkwongani msiskaNo ratings yet
- Telemecanique PDFDocument16 pagesTelemecanique PDFRM HaroonNo ratings yet
- Techno Commecrial Offer - HTMC, LBS PanelDocument5 pagesTechno Commecrial Offer - HTMC, LBS PanelkapilNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument19 pagesIonic BondingbillahsaadatNo ratings yet
- JhbjhbiiuhiDocument4 pagesJhbjhbiiuhiAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument37 pagesStructure and Bondingalexia.farrellNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDocument18 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- Privacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcseDocument8 pagesPrivacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcsetashaNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument39 pagesIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Document5 pagesAtomic Bonding (Metallic, Ionic, Covalent, and Van Der Waals Bonds)Aris YusepNo ratings yet
- Bonding Basics: Shells Atom ElectronsDocument7 pagesBonding Basics: Shells Atom ElectronsClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesfezthebombNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Vs Metallic BondingsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument4 pagesBondingPuvaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesChemical Bonds Reading ComprehensionsgibbsNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument5 pagesBondinggkawsar22No ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding PPT 2023-2024Document52 pagesChemical Bonding PPT 2023-2024Naim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument5 pagesMetallic BondDinak ConsultingNo ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- Read and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!Document7 pagesRead and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!api-344880038No ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision Notes-LibreDocument17 pagesChemistry Revision Notes-LibreShridhar MathadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument41 pagesChemical BondingaswaniNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- Bonding Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesBonding Ionic Bondingapi-3723991No ratings yet
- Lewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithDocument4 pagesLewis Structure Shows A Representation of A Bond Between Atoms of A Molecule Also WithRen ManalotoNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument5 pagesChemical Bondscharshadali2004No ratings yet
- What Is A Mole?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Mole?Matthew CamilleriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document19 pagesChapter 2Melanie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument33 pagesBondingNathaniel WhyteNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliPro IdiotNo ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGDocument23 pagesStructure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGTrishana GreenNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument44 pagesChemical Bondingjas_ong_man_ling1996100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Notes Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesNotes Chemical BondingRammohan Balaji PrasadNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentalishbajaved159No ratings yet
- GCFGCGCFGFDGDocument15 pagesGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Storybook Group1 1Document6 pagesIonic Bonding Storybook Group1 1api-533864204No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.Document34 pagesIonic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.allenbrien077No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSalma IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Enlaces InteratómicosDocument40 pagesEnlaces InteratómicosNAYELI VIVEROS CRUZNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondsDocument4 pagesAtomic Bondsfatiman333333No ratings yet
- GEO 211 - Basic Mineralogy - Lesson 10 - Chemical BondsDocument51 pagesGEO 211 - Basic Mineralogy - Lesson 10 - Chemical Bondsbarekie86No ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Practical Research 1: Quarter 4 - Module 8: The Reference ListDocument24 pagesPractical Research 1: Quarter 4 - Module 8: The Reference ListSecret Lang100% (1)
- Tourism Management Perspectives: Mohamed Battour, Mohd Nazari IsmailDocument5 pagesTourism Management Perspectives: Mohamed Battour, Mohd Nazari IsmailNadhirah NanorNo ratings yet
- Lecture-14 Stall and Pitch ControlDocument6 pagesLecture-14 Stall and Pitch ControljameelahmadNo ratings yet
- User Manual Inspinia Mobile AppDocument14 pagesUser Manual Inspinia Mobile AppSmart House Soluții smart homeNo ratings yet
- Good Morning EveryoneDocument3 pagesGood Morning EveryoneAntoniette BactasaNo ratings yet
- Friday, February 24, 2023 Welcome To My ClassDocument30 pagesFriday, February 24, 2023 Welcome To My ClassNguyễn Thanh TùngNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipelaying Dynamic PDFDocument150 pagesOffshore Pipelaying Dynamic PDFdndudcNo ratings yet
- Time Management at WorkDocument6 pagesTime Management at WorkAgripa NyahumaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Statements AssignmentDocument6 pagesConditional Statements AssignmentMohammed Ashfaque JamalNo ratings yet
- Peggy Kamuf - A Derrida Reader - Between The Blinds-Columbia Univ PR (1991)Document667 pagesPeggy Kamuf - A Derrida Reader - Between The Blinds-Columbia Univ PR (1991)Seyda AtalanNo ratings yet
- Mba Payroll ManagementDocument43 pagesMba Payroll Managementpagariya20100% (1)
- Quiz 2 Fin377 Jan2021Document4 pagesQuiz 2 Fin377 Jan2021Farah Nurzahiah Binti SabriNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 PartBDocument61 pagesLecture3 PartBDiogo CecinNo ratings yet
- Om RT12 04 PDFDocument4 pagesOm RT12 04 PDFAlexAndreiNo ratings yet
- Violent Video Game Should Be ProhibitedDocument4 pagesViolent Video Game Should Be ProhibitedJatmiko Adi Nugroho AgribisnisNo ratings yet
- Eye Blink Sensor With Alarm Detection: Dr. V. R. PanditDocument21 pagesEye Blink Sensor With Alarm Detection: Dr. V. R. PanditAnushree IdekarNo ratings yet
- Wind Hydro 2Document6 pagesWind Hydro 2Vani TiwariNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Spring Block 3 Step 6 PPT Word ProblemsDocument20 pagesYear 6 Spring Block 3 Step 6 PPT Word ProblemsRay RabaraNo ratings yet
- Rolatoye@fudutsinma Edu NGDocument19 pagesRolatoye@fudutsinma Edu NGobeng kelvinNo ratings yet
- DLL 1stWEEK FABM1Document2 pagesDLL 1stWEEK FABM1Arris Sulit100% (2)
- AnaPhy SAS 1Document5 pagesAnaPhy SAS 1Zylith NanaseNo ratings yet
- Project Appraisal ManualDocument238 pagesProject Appraisal ManualBelayneh GetachewNo ratings yet
- What They Don't Teach You at Harward Business SchoolDocument1 pageWhat They Don't Teach You at Harward Business SchoolNarayana Sarma Marthi0% (3)
- IDirect Gokaldas Q2FY22Document6 pagesIDirect Gokaldas Q2FY22Bharti PuratanNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument11 pagesExecutive SummaryKushalNo ratings yet
- Dinamic PositioningDocument15 pagesDinamic PositioningdarijanNo ratings yet