0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsCh-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Ch-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Uploaded by
Raadhiya GogiaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Ch-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Ch-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Uploaded by
Raadhiya Gogia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Ch-10 Light- Refraction - Notes Pt 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesCh-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Ch-10 Light - Refraction - Notes PT 1
Uploaded by
Raadhiya GogiaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
SUBJECT: SCIENCE
CLASS – X
Ch-10 LIGHT (Refraction)
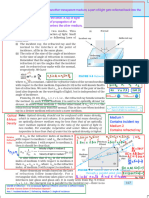
1. Define refraction of light.
Ans:
The phenomenon of the change in the path of the light as it
passes from one transparent medium to another is called
refraction of light.
The path along which the light travels in the first medium
is called incident ray and that in the second medium is
called refracted ray. The angles which the incident ray and
the refracted ray make with the normal at the surface of
separation are called angle of incidence (i) and angle of
refraction (r) respectively.
It is observed that:
(i) When a ray of light passes from an optically rarer
medium (air) to a denser medium (glass) it bends
towards the normal (∠ r < ∠ i) as shown in figure.
(ii) When a ray of light passes from an optically denser
(glass) to a rarer medium (air), it bends away from the
normal ( ∠ r > ∠ i )as shown in figure.
(iii) A ray of light travelling along the normal passes
undeflected, here ∠ r = ∠ i = 0o
State laws of refraction with diagram. Explain the term
absolute refractive index of a medium and write its
expression.
Ans:
Laws of Refraction: There are two laws of refraction-
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the
point of incidence lie in the same plane.
(ii) According to second law of refraction of light, the ratio of
sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is
constant for a given pair of media. (Snell’s law)
That is called refractive index and it is denoted by ‘µ’
Sini µ2
=
Sinr µ1
Refractive Index and Speed of Light-
Let the speed of light in medium 1 be v1 and that in medium
2 be v2. Now, the refractive index of medium 2 with respect
to medium 1 is equal to the ratio of speed of light in medium
1 to the speed of light in medium 2. This can be written as:
speed of light in medium2
Refractive index of Medium 1 to medium 2 =
speed of light in medium 1
2µ1 =v 2
V1
2 µ1 = µ 1
µ2
Refractive index of Medium 2 to medium 1 = speed of light in medium1
speed of light in medium 2
2 1 µ =v 1
V
µ
2
2µ 1 =
2
µ 1
Absolute RI= Speed of light in air (or vacuum)
Speed of light in other medium
µ= c
vm
Example 1: If the speed of light in vacuum is 3x10 8 m/s, find
the absolute refractive index of the medium in which light
travels with a speed of 1.4x10 8m/s.
Ans:
n= velocity of light in vacuum
velocity of light in medium
8
n= 3×10 = 2.14
1.4×108
Example2. The refractive index of water and glass are 4/3
and 3/2 respectively. Write the relation and
find the value of
refractive of water with respect to glass and glass with
respect to water.
Ans:
4 3
n = and n =
w 3 g 2
n 4×2=8
n = w=
g w ng 3×3 9
1 9
wng= n =
g w 8
3. What is meant by lateral displacement of light? Illustrate
with the help of diagram. List the factors on which lateral
displacement of a substance depend.
Ans: Lateral displacement is the perpendicular distance between
the incident ray produced and emergent ray.
It depends on
a. thickness of the slab
b. incident angle and
c. refractive index of
the material.
You might also like
- Lab 6 Reflection Refraction OnlineDocument12 pagesLab 6 Reflection Refraction OnlineOmar El ErakiNo ratings yet
- Basic PhysicsDocument132 pagesBasic Physicsarun89000100% (7)
- Refractive IndexDocument3 pagesRefractive IndexVisakh VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Light: Refraction: It Is A Surface Phenomenon in Which A Ray of Light Bends From Its Path When It Travels FromDocument21 pagesLight: Refraction: It Is A Surface Phenomenon in Which A Ray of Light Bends From Its Path When It Travels From06. ANUSHKA ROYNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument15 pagesRefractionSudharsan Gupta Sudhir100% (1)
- Refraction 1Document8 pagesRefraction 1Sudharsan Gupta SudhirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - SECTION ADocument22 pagesChapter 4 - SECTION AAdith DeepakNo ratings yet
- 22 Refraction of LightDocument80 pages22 Refraction of LightoyamoopondoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22.1 4Document34 pagesChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Refraction of LightDocument23 pages3.2 Refraction of LightakhonyaphaniceNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Refraction of LightDocument21 pages3.2 Refraction of Lighthassanoruko21No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Light As Wave MotionDocument11 pagesChapter Three Light As Wave MotionSabrina NevilleLongbottom RitterNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light-NotesDocument3 pagesRefraction of Light-NotesdaansaiieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Analysis of FertilizersDocument12 pagesChemistry Project On Analysis of FertilizersAtharva Maheshwari0% (1)
- FertilizerDocument4 pagesFertilizerfafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Geometrical OpticsDocument12 pagesChapter 12 Geometrical OpticsTasha LuchembeNo ratings yet
- Analysis On FertilizersDocument22 pagesAnalysis On Fertilizersokesh27No ratings yet
- PHY 104 (Optics Part)Document18 pagesPHY 104 (Optics Part)abdulkareemyusuf438No ratings yet
- Refraction at Plane Surfaces Report To FinalDocument13 pagesRefraction at Plane Surfaces Report To FinalProy DC100% (1)
- 02 - Optics-Refraction (Final)Document36 pages02 - Optics-Refraction (Final)Armaan PruthiNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light: Minati Barman Associate Professor Head, Department of Physics J N College, BokoDocument10 pagesRefraction of Light: Minati Barman Associate Professor Head, Department of Physics J N College, Bokopmkhoa.l.2124No ratings yet
- REFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A LevelDocument47 pagesREFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A Levelssenyonjotrevor01No ratings yet
- LIGHT NOTES PART 5 (1)Document2 pagesLIGHT NOTES PART 5 (1)ARSHAD JAMILNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Document9 pagesLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument12 pagesRefraction of Lightsanch.kadam08No ratings yet
- Determination of Refraction IndexDocument3 pagesDetermination of Refraction IndexDrakalopNo ratings yet
- Jesc110 15Document1 pageJesc110 15Bharat SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Notes PART-4 LIGHTDocument4 pagesNotes PART-4 LIGHTKaushal Kishor KumarNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument19 pagesRefractionYugandhar Veeramachaneni50% (2)
- Class 10 - Physics - Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces SolutionsDocument68 pagesClass 10 - Physics - Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces SolutionsAndrik LalNo ratings yet
- 4 (A)Document19 pages4 (A)78kapiNo ratings yet
- Optics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimDocument16 pagesOptics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimjohnNo ratings yet
- Lesson13 Refractive IndexDocument12 pagesLesson13 Refractive IndexGemma WrigleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document58 pagesChapter 1DXN LUDHIANANo ratings yet
- 03 RefractionDocument18 pages03 RefractionHelenNo ratings yet
- 01 RefractionDocument6 pages01 RefractionSujit PradhanNo ratings yet
- Light EditedDocument41 pagesLight Editedmarc daniel ortizNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Ncertcuet Neet - 240827 - 224642Document3 pagesRay Optics Ncertcuet Neet - 240827 - 224642ShanitNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 14 Mar 2024Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 14 Mar 2024ampoluchandrakala5No ratings yet
- 09 Principles of OpticsDocument7 pages09 Principles of OpticsedNo ratings yet
- Light - PhysicsDocument41 pagesLight - PhysicsChristopher TigranesNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument14 pagesRefraction of Lightsalmansaid030No ratings yet
- Ray TheoryDocument13 pagesRay Theorygdmani008No ratings yet
- 03 Refraction of LightDocument22 pages03 Refraction of LightDonna100% (6)
- Geometrical OpticsDocument30 pagesGeometrical Opticsdildar123No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 LightDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Lightshereen fahmyNo ratings yet
- WaveOptics paper 05Document9 pagesWaveOptics paper 05Jityaa N. NNo ratings yet
- Mll Content Physics xDocument26 pagesMll Content Physics xginsane05No ratings yet
- 342 CCDocument2 pages342 CCAyushmaan GoelNo ratings yet
- Waves & Optics Revision 3Document15 pagesWaves & Optics Revision 3Isaiah ThomasNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit-1 Notes 2022-23Document15 pagesAp Unit-1 Notes 2022-23Smd nazeebNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexDocument7 pagesRay Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexranjithNo ratings yet
- Laws of Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesLaws of Refraction of Lightpadmja4purohitNo ratings yet
- Optics 2023-11-26 13 - 54 - 58Document16 pagesOptics 2023-11-26 13 - 54 - 58tawhidnabin.sylhetNo ratings yet
- Optics BookletDocument31 pagesOptics BookletZachNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - 2Document70 pagesRay Optics - 2Raj Kumar PerliNo ratings yet
- Physics-2 Practical HandoutDocument82 pagesPhysics-2 Practical Handoutملهم الخصيبيNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-2-FINALSDocument11 pagesPHYSICS-2-FINALSrazdaulayan7No ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument15 pagesRefraction of LightJohn Johnson0% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 Optics GMFDocument39 pagesUNIT 6 Optics GMFVarun SahuNo ratings yet
- Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) For Pavement: Feasibility TestDocument6 pagesMultichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) For Pavement: Feasibility TestFlávia SantosNo ratings yet
- Phy161 Lab Report 12Document9 pagesPhy161 Lab Report 12Javier Luis SantosNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesReflection and Refraction of Lightajithrailway100% (1)
- Light 2022Document31 pagesLight 2022daley dailyNo ratings yet
- B583bba8 - 1 16667078626527 3265Document19 pagesB583bba8 - 1 16667078626527 3265jain.radha.aggrNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Document13 pagesReflection of Light Printed Notes Class 8Typist VBCNo ratings yet
- Q4 Physical Sci Module 2Document6 pagesQ4 Physical Sci Module 2Cakelee CortiñasNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument11 pagesLight Worksheetkobayashirei602No ratings yet
- ADLC Science 8 - Light & Optical Systems PDFDocument33 pagesADLC Science 8 - Light & Optical Systems PDFLizaNo ratings yet
- InterferometersDocument18 pagesInterferometersrohit singhNo ratings yet
- NSO Class 11 PCM Solved Sample PaperDocument10 pagesNSO Class 11 PCM Solved Sample PaperMurtaza LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh International School: English Section, Riyadh KSADocument15 pagesBangladesh International School: English Section, Riyadh KSANahian SaburNo ratings yet
- Physics For The TechnicianDocument644 pagesPhysics For The TechniciankaaehtlaNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics PDFDocument65 pagesWave Optics PDFSubham roushan100% (3)
- Electromagnetic Engineering Maptele 2008-2009: ProgramDocument68 pagesElectromagnetic Engineering Maptele 2008-2009: ProgramBrent Quispe PalacinNo ratings yet
- Advanced Optical Wireless Communication Systems PDFDocument404 pagesAdvanced Optical Wireless Communication Systems PDFPrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 6Document29 pagesPhysical Science Module 6aziekiellaxamanafuellasNo ratings yet
- C 10 Refraction of Light NotesDocument13 pagesC 10 Refraction of Light NotesHarsh GulatiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing - NDTDocument25 pagesUltrasonic Testing - NDTsekarsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument37 pagesScience 10 - Reflection and Refraction of Lightjohn charles garaldeNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Notes PDFDocument16 pagesPhysics Form 4 Notes PDFIbrahim hasanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Packet # 2Document3 pagesForm 2 Science Packet # 2Kenneth FrancisNo ratings yet
- Signed-Off Science8 q1 Mod5 ColorsOfLight v2Document31 pagesSigned-Off Science8 q1 Mod5 ColorsOfLight v2Teacher Mel83% (6)
- PHY11-2 /A1 Casticimo, Milicah M. AR-2 DECEMBER 17, 2013 HW#6Document10 pagesPHY11-2 /A1 Casticimo, Milicah M. AR-2 DECEMBER 17, 2013 HW#6Higashi RyujiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B Review PowerpointDocument148 pagesAP Physics B Review Powerpointparthz92No ratings yet
- Neets Module 10 SummaryDocument11 pagesNeets Module 10 SummarySigmund VesaNo ratings yet