VLSI Technology and Applications 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 4
Uploaded by
harshit420VLSI Technology and Applications 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 4
Uploaded by
harshit420VLSI Technology And Applications 10B11EC612
Tutorial Sheet 4
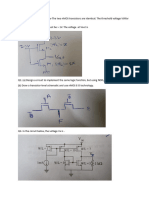
(1) Consider a CMOS inverter with the given parameters- kn=140 A/V2, kp=60 A/V2, Vto, n=0.7 V, Vto, p= - 0.7 V, VDD=3 V. (a) If the design is ideal and symmetrical, then find out the ratio of (W/L)p and (W/L)n. (b) Take the case when (W/L)p = (W/L)n, then find out the inverter threshold voltage. (2) A CMOS inverter is built in a process where kn=100 A/V2, kp=42 A/V2, Vto, n=0.7 V, Vto, p= - 0.8 V and a power supply of VDD=3.3 V is used. Calculate the inverter threshold voltage Vth if (W/L)n=10 and (W/L)p=14. (3) Find the ratio kn/kp needed to obtain a CMOS inverter threshold voltage of Vth=1.3 V with a power supply of 3 V. Assume that Vto, n=0.6 V and Vto, p= - 0.82 V. What would be the relative device sizes if the mobility values are related by n=2.2p? (4) Consider a resistive-load inverter circuit with VDD=5 V, k'n= 20 A/V2, Vt0= 0.8 V, RL= 200 K, and W/L = 2. Calculate the critical voltages-VOL, VOH, VIL, VIH on the VTC and find the noise margins of the circuit. (5) Design a resistive-load inverter with R=1 K, such that VOL = 0.6 V. The enhancement-type nMOS driver transistor has the following parameters: kn=22 A/V2, Vto, n=1 V, =0.2 V1/2, VDD=5 V. (a) Determine the required aspect ratio, W/L. (b) Determine VIL, VIH. (c) Determine noise margins NML and NMH.
You might also like
- STA Captain - S Log Solo RPG (TNG Cover) v1.41100% (21)STA Captain - S Log Solo RPG (TNG Cover) v1.41336 pages
- Dodge Ram 1500 2009 Workshop Service Repair Manual PDF Download0% (5)Dodge Ram 1500 2009 Workshop Service Repair Manual PDF Download2 pages
- Harbor Freight Cen-Tech CAN OBD II Code Reader EOBD Scanner 9861475% (8)Harbor Freight Cen-Tech CAN OBD II Code Reader EOBD Scanner 9861473 pages
- OceanofPDF - Com How To Draw Cool Stuff Shading Textures - Catherine V Holmes100% (5)OceanofPDF - Com How To Draw Cool Stuff Shading Textures - Catherine V Holmes294 pages
- Ase Study Guide - Parts Specialist (P2)No ratings yetAse Study Guide - Parts Specialist (P2)23 pages
- Manual Hyster 4000701-8000SRM1409 - (04-2012) - Us-En100% (5)Manual Hyster 4000701-8000SRM1409 - (04-2012) - Us-En84 pages
- Quality Control and Continuous ImprovementNo ratings yetQuality Control and Continuous Improvement14 pages
- Differential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 1100% (4)Differential Amplifiers Problems of MOS - 15 pages
- Problem Set 02_fbf2c20b-552e-4d65-8ec3-e715d0c53079No ratings yetProblem Set 02_fbf2c20b-552e-4d65-8ec3-e715d0c530794 pages
- EE619_Assignment2_1d23f2d4-fd35-469f-b861-3e570a0a10d5No ratings yetEE619_Assignment2_1d23f2d4-fd35-469f-b861-3e570a0a10d52 pages
- Analog Ic Design Assignment 2 With SolutionNo ratings yetAnalog Ic Design Assignment 2 With Solution38 pages
- V.R.Siddhartha Engineering College Department of ECE Assignment-I Questions (A, B, C, D)No ratings yetV.R.Siddhartha Engineering College Department of ECE Assignment-I Questions (A, B, C, D)2 pages
- Faculty of Engineering: Lab Sheet Ent 3036 Semiconductor DevicesNo ratings yetFaculty of Engineering: Lab Sheet Ent 3036 Semiconductor Devices20 pages
- Assignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierNo ratings yetAssignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational Amplifier5 pages
- Solutions in Red: Electronic Systems Course 2019 Autumn. January 17, 2020No ratings yetSolutions in Red: Electronic Systems Course 2019 Autumn. January 17, 20206 pages
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetNo ratings yetMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet2 pages
- EC3058D-VLSI Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-21No ratings yetEC3058D-VLSI Circuits and Systems Winter Semester-2020-212 pages
- 4 Calculation Examples 4.1 Switching Off Inductive LoadsNo ratings yet4 Calculation Examples 4.1 Switching Off Inductive Loads8 pages
- Extra Practice Problem Set For Exam I INEL 4207 - Digital Electronics - Fall 2012No ratings yetExtra Practice Problem Set For Exam I INEL 4207 - Digital Electronics - Fall 20122 pages
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 12.5/5 (3)
- Design of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsFrom EverandDesign of Electrical Circuits using Engineering Software ToolsNo ratings yet
- VLSI Technology and Applications - 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 1No ratings yetVLSI Technology and Applications - 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 11 page
- Vlsi T Technolo Ogy and D Applic Cations 10B11 1EC612: Tu Torial SH Heet - 6No ratings yetVlsi T Technolo Ogy and D Applic Cations 10B11 1EC612: Tu Torial SH Heet - 62 pages
- VLSI Technology and Applications - 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 3No ratings yetVLSI Technology and Applications - 10B11EC612: Tutorial Sheet - 31 page
- SEM MIT Top 10 Emerging Technology 04-30-12No ratings yetSEM MIT Top 10 Emerging Technology 04-30-122 pages
- Practical Projects For Self-Sufficiency - DIY Projects To Get Your Self-Reliant Lifestyle Started PDF88% (16)Practical Projects For Self-Sufficiency - DIY Projects To Get Your Self-Reliant Lifestyle Started PDF163 pages
- Owners Manual QSL9 CM2350 L102: Cummins Customer Assistance Center 1-800-DIESELS Applicable Only in U.S.A. and CanadaNo ratings yetOwners Manual QSL9 CM2350 L102: Cummins Customer Assistance Center 1-800-DIESELS Applicable Only in U.S.A. and Canada201 pages
- ASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 3No ratings yetASVAB Mechanical Comprehension Practice Test 38 pages
- Quantum Energy Generator (QEG) - REVISED Manual Edition (March 2015)100% (5)Quantum Energy Generator (QEG) - REVISED Manual Edition (March 2015)75 pages
- HemiSync - Gateway Experience - Wave V Exploring PDF100% (10)HemiSync - Gateway Experience - Wave V Exploring PDF16 pages
- Kartbuilding Blog: Archive For The 'Chassis Design' CategoryNo ratings yetKartbuilding Blog: Archive For The 'Chassis Design' Category9 pages