0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
421 viewsTutorial 8 AM1100
This is the eighth tutorial given in AM1100 (Basic Applied Mechanics) course in IIT Madras. This is without a solution, I will be uploading a solution to this soon...
Uploaded by
Sanchit GuptaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
421 viewsTutorial 8 AM1100
This is the eighth tutorial given in AM1100 (Basic Applied Mechanics) course in IIT Madras. This is without a solution, I will be uploading a solution to this soon...
Uploaded by
Sanchit GuptaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
You are on page 1/ 2
DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MECHANICS
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MADRAS
AM1100 Engineering Mechanics
Tutorial VIII- Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
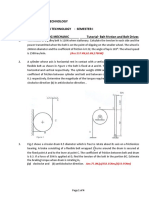
1. The homogeneous rectangular plate has a mass of 20 kg and is supported in the vertical plane by
the light parallel links shown. If a couple M = 100 N.m is applied to the end link AB with the
system initially at rest, calculate the force supported by the pin at C as the plate lifts off its
support with = 300.
2. Gear A has a mass of 24 kg and a centroidal radius of
gyration of 150 mm. Gear B has a mass of 6 kg and a
centroidal radius of gyration of 75 mm. Calculate the
acceleration of gear B when a torque M of 8 N.m is
applied to the shaft of gear A (Gear teeth not shown).
3. The uniform 12 kg square panel is suspended from point C
by the two wires at A and B. If the wire at B suddenly breaks,
calculate the tension T in the wire at A an instant after the
break occurs.
4.
The unbalanced wheel has a mass of 10 kg and
rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface.
When the mass centre G passes the horizontal line
through O as shown, the angular velocity of the
wheel is 2 rad/s. For this instant compute the
normal force N and friction force F acting on the
wheel at its point of contact with the horizontal
surface. The wheel has a radius of gyration about
its mass centre of 64 mm.
5. A 15-kg roll of wrapping paper in the form of a
solid cylinder with a diameter of 300 mm is
resting on a horizontal surface. If a force of 40 N
is applied to the paper at the angle = 300 ,
determine the initial acceleration a of the centre
of the roll and the corresponding angular
acceleration . The coefficient of kinetic friction
between the paper and the horizontal surface is
0.2.
6. The two wheels shown here represent two extreme
conditions of distribution of mass. For case A all of the
mass m is assumed to be concentrated in the centre of the
hoop in the axial bar of negligible diameter. For case B all
of the mass m is assumed to be concentrated in the rim.
Determine the angular acceleration of each of the two
wheels as they roll without slipping down the incline. Also
specify the minimum coefficient of static friction s
required to prevent each wheel from slipping.
You might also like
- Assignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023No ratings yetAssignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/20239 pages
- Assignment 2 Mekanik Mesin S1 - 20132014No ratings yetAssignment 2 Mekanik Mesin S1 - 201320142 pages
- Tutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum MethodsNo ratings yetTutorial Eight - Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies - Impulse Momentum Methods9 pages
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersNo ratings yetPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question Papers4 pages
- Anna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsNo ratings yetAnna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important Questions12 pages
- F at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg CarNo ratings yetF at Each Wheel. Assume A Constant Deceleration For The 1500-kg Car12 pages
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13No ratings yetNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 1319 pages
- Design of Machinery Jntua Previous PapersNo ratings yetDesign of Machinery Jntua Previous Papers20 pages
- Am1100 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial 3: P Required To Cause The Cylinder To SlipNo ratings yetAm1100 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial 3: P Required To Cause The Cylinder To Slip4 pages
- EE2001 Digital Systems Quiz 1: (A+B+C) (A'+B'+D') (A'+B'+C') (A+B+DNo ratings yetEE2001 Digital Systems Quiz 1: (A+B+C) (A'+B'+D') (A'+B'+C') (A+B+D1 page