Aisc 34
Uploaded by
Stephanie ScottAisc 34
Uploaded by
Stephanie ScottPROJECT: STEEL BUILDING DESIGN CASE STUDY SUBJECT: Bracing connection, gusset plate design.
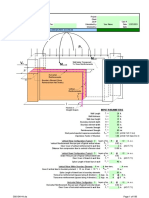
Brace line B1, second floor.
= resistance factor Fy = specified (ASTM) minimum yield stress Fu = specified (ASTM) minimum tensile strength Rn = strength t = thickness of connected part Pu = factored load to be resisted d = diameter of the bolt eb = one-half the depth of the beam, in. ec = one-half the depth of the column, in. db = depth of the beam, in. dc = depth of the column, in. w.p. = working point. N = horizontal distance of gusset plate, in. V = vertical distance of gusset plate, in. = distance from the face of the column flange to the centroid of the gusset-to-beam connection, in. = distance from the face of the beam flange to the centroid of the gusset-to-column connection, in. Aw =cross section area of the whitmore section
SHEET 122 of 131
Pu = B C D
127.0 k 96 k
Elevation View
13
A 30 Plan View Member A-E, Interior floor girder: W24x68 ASTM 992 db = 23.7 in Fy = 50 ksi Fu = 65 ksi Member A-B, Interior column: W10x49 ASTM 992 dc = 9.98 in Fy = 50 ksi Fu = 65 ksi Member A-C, Brace: 2L6x4x1/2LLBB A36 Fy = 36 ksi Fu = 58 ksi
W.P.
Column W10x49 Gusset Plate
Brace 2L6x4x1/2
13 15
Girder W24x68
Red font indicates user input
PROJECT: STEEL BUILDING DESIGN CASE STUDY SUBJECT: Bracing connection, gusset plate design. Use A325-N bolts in standard holes,3/4 in diameter. Design shear strength of one bolt, double shear (LRFD Table 7-10) Check bearing strength @ each bolt hole: Rn = (2.4 * d * t * Fu) = ( = 0.75) 45.7 kips > 31.8 kips
SHEET 123 of 131
Rn = 31.8 k
OK!
Check tension yielding on the Whitmore section:
Column Brace
13 15 Whitmore section
Gusset Plate
Girder
y = tan 30o * 6 = y
3.5
in
30
6
*Note: Assume simplified Whitmore section (double dashed area) for the purpose of this lab. This design will be more conservative. OK!
Rn = (Fu * Aw) = 248.0 kips > 127.0 kips ( = 0.9) Aw = (y + y + 2.5(Perp. distance between center of holes))*0.5
Red font indicates user input
PROJECT: STEEL BUILDING DESIGN CASE STUDY SUBJECT: Bracing connection, gusset plate design. Distribution of brace force to beam and column: (Uniform force method) From the member and frame geometry eb = db/2 = ec = dc/2 = tan = 11.85 4.99 1.154 in in 15
SHEET 124 of 131
13
in order to remain free of moments on the connection interfaces, the following expression must be satisfied:
tan * eb - ec = - * tan - * tan = 8.68 in
N
Column
0.5
allow 1/2 in. between gusset and column for the setback
Brace
13 15
Gusset Plate
ec
Girder
eb
W.P.
Try a gusset plate : 1/2 = = in. x 20 1/8 in. horizontally x in in 16.414 in OK! (If Less Than One) = 6.7 in 13 3/4 in. vertically
16.5 6.7
' = tan * eb - ec + * tan = ' = Use = N= V= 0.09 in
16.5 in and 20 1/8 in 13 3/4 in
Red font indicates user input
You might also like
- Shear Strength Controls 21.65 Kips/bolt: Section at ANo ratings yetShear Strength Controls 21.65 Kips/bolt: Section at A4 pages
- Notes: Proposed Ids Workshop Oilfields Supply Center LTDNo ratings yetNotes: Proposed Ids Workshop Oilfields Supply Center LTD1 page
- Design of Flush Extended End Plate ConnectionsNo ratings yetDesign of Flush Extended End Plate Connections3 pages
- Assume A Plate Girder of The Following Properties: Span of Beam (L)No ratings yetAssume A Plate Girder of The Following Properties: Span of Beam (L)10 pages
- 42-42 DETAIL-42 41-41 DETAIL-41 40-40 DETAIL-40: NotesNo ratings yet42-42 DETAIL-42 41-41 DETAIL-41 40-40 DETAIL-40: Notes1 page
- Atasehir Gardens Podium OF: Member: LocationNo ratings yetAtasehir Gardens Podium OF: Member: Location7 pages
- Design of Lacing: 2.5% of Axial Load Force in Each Lacing Bar (Flac)No ratings yetDesign of Lacing: 2.5% of Axial Load Force in Each Lacing Bar (Flac)4 pages
- Project Title: Revision: Sheet: Project No.: Designed By: Date: Subject: Checked By: DateNo ratings yetProject Title: Revision: Sheet: Project No.: Designed By: Date: Subject: Checked By: Date4 pages
- Staircase-3: A A Note: All Connection Design and Fabrication To Be Responsible by Contractor'S DesignerNo ratings yetStaircase-3: A A Note: All Connection Design and Fabrication To Be Responsible by Contractor'S Designer1 page
- Concrete Special Structural Wall ACI 318-08No ratings yetConcrete Special Structural Wall ACI 318-08188 pages
- Vertical Weld Design Bolt Design'!A1 Deflection!A1 Material Data'!a1 Index!a1 TrangNo ratings yetVertical Weld Design Bolt Design'!A1 Deflection!A1 Material Data'!a1 Index!a1 Trang7 pages
- Handrail For Staircase-3: DET - 145 E040 TYP DET - 145 E040 TYPNo ratings yetHandrail For Staircase-3: DET - 145 E040 TYP DET - 145 E040 TYP1 page
- Design of Non Composite Beams With Large OpeningsNo ratings yetDesign of Non Composite Beams With Large Openings73 pages
- Isolated Footing Schedule: Size of PedestalNo ratings yetIsolated Footing Schedule: Size of Pedestal1 page
- Rean'S Building 5/24/2002 Angle Plate Design: Framed Beam ConnectionNo ratings yetRean'S Building 5/24/2002 Angle Plate Design: Framed Beam Connection11 pages
- Column Interaction Diagram Units: KN, KN-M: English MetricNo ratings yetColumn Interaction Diagram Units: KN, KN-M: English Metric5 pages
- Built - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section PropertiesNo ratings yetBuilt - Up Column Design ("Effectiveness of Various Built-Up Columns") Section Properties2 pages
- Characterstic Strength:: Annexure-Vc Structural Design of Combined Footing For ColumnNo ratings yetCharacterstic Strength:: Annexure-Vc Structural Design of Combined Footing For Column2 pages
- Client Name: Prepared By: Date: A Project Name: Location: DescriptionNo ratings yetClient Name: Prepared By: Date: A Project Name: Location: Description1 page
- Sectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)No ratings yetSectional Properties of Rolled Steel Joists (Ref: Is: 808 - 1989 & Is: 12778 - 2004)49 pages
- Anchor Bolt + Base Plate Design Joint 8 - v2No ratings yetAnchor Bolt + Base Plate Design Joint 8 - v24 pages
- Rectangular Pad Footing Design: (Provied)No ratings yetRectangular Pad Footing Design: (Provied)6 pages
- Design of Members For Flexure Using The Steel Construction Manual (13th Ed.)No ratings yetDesign of Members For Flexure Using The Steel Construction Manual (13th Ed.)4 pages
- Beam-Column Hunch-End Plate Moment Conn PDFNo ratings yetBeam-Column Hunch-End Plate Moment Conn PDF11 pages
- Steel Overhead Ground Wire and Stranded Steel Guy Wire: Overhead Conductors Electric UtilityNo ratings yetSteel Overhead Ground Wire and Stranded Steel Guy Wire: Overhead Conductors Electric Utility1 page
- Steel Overhead Ground Wire and Steel Guy Wire: Overhead Conductors Electric UtilityNo ratings yetSteel Overhead Ground Wire and Steel Guy Wire: Overhead Conductors Electric Utility1 page
- Torque-Tension Chart For A307 Gr5 Gr8 Gr9 PDFNo ratings yetTorque-Tension Chart For A307 Gr5 Gr8 Gr9 PDF1 page
- ACI 421.1R-99: Reported by Joint ACI-ASCE Committee 421No ratings yetACI 421.1R-99: Reported by Joint ACI-ASCE Committee 42115 pages
- Torque-Tension Chart For A307 Gr5 Gr8 Gr9 PDFNo ratings yetTorque-Tension Chart For A307 Gr5 Gr8 Gr9 PDF1 page
- Mobile Elevated Work Platforms (MEWP) Program: Provo, UtahNo ratings yetMobile Elevated Work Platforms (MEWP) Program: Provo, Utah14 pages
- Key - Section: Advanced Building ConstructionNo ratings yetKey - Section: Advanced Building Construction8 pages
- Design of Bracing Connections in Concentrically Braced Frames100% (1)Design of Bracing Connections in Concentrically Braced Frames43 pages
- 10.2 Bridge Loading Test 10.2.1 GeneralNo ratings yet10.2 Bridge Loading Test 10.2.1 General69 pages
- Behaviour of Block Shear Failure in Different Connections: Jagdish R. Dhanuskar & Laxmikant M. GuptaNo ratings yetBehaviour of Block Shear Failure in Different Connections: Jagdish R. Dhanuskar & Laxmikant M. Gupta15 pages