K50T60 Infineon
K50T60 Infineon
Uploaded by
Emerson Müller Juarez AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
K50T60 Infineon
K50T60 Infineon
Uploaded by
Emerson Müller Juarez AvilaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
K50T60 Infineon
K50T60 Infineon
Uploaded by
Emerson Müller Juarez AvilaCopyright:
Available Formats
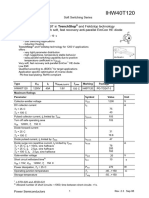
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
Low Loss DuoPack : IGBT in TRENCHSTOP™ and Fieldstop technology with soft,
fast recovery anti-parallel Emitter Controlled HE diode
Features:
C
Very low VCE(sat) 1.5V (typ.)
Maximum Junction Temperature 175°C
Short circuit withstand time 5s
Designed for : G
- Frequency Converters E
- Uninterrupted Power Supply
TRENCHSTOP™ and Fieldstop technology for 600V applications offers :
- very tight parameter distribution
- high ruggedness, temperature stable behavior
- very high switching speed
Positive temperature coefficient in VCE(sat)
Low EMI PG-TO247-3
Low Gate Charge
Very soft, fast recovery anti-parallel Emitter Controlled HE diode
Qualified according to JEDEC1 for target applications
Pb-free lead plating; RoHS compliant
Complete product spectrum and PSpice Models : http://www.infineon.com/igbt/
Type VCE IC VCE(sat),Tj=25°C Tj,max Marking Package
IKW50N60T 600V 50A 1.5V 175C K50T60 PG-TO247-3
Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Collector-emitter voltage, Tj ≥ 25C VCE 600 V
DC collector current, limited by Tjmax
2)
TC = 25C IC 80
TC = 100C 50
Pulsed collector current, tp limited by Tjmax ICpuls 150
A
Turn off safe operating area, VCE = 600V, Tj = 175C, tp = 1µs - 150
Diode forward current, limited by Tjmax
TC = 25C IF 100
TC = 100C 50
Diode pulsed current, tp limited by Tjmax IFpuls 150
Gate-emitter voltage VGE 20 V
3)
Short circuit withstand time
tSC 5 s
VGE = 15V, VCC 400V, Tj 150C
Power dissipation TC = 25C Ptot 333 W
Operating junction temperature Tj -40...+175
Storage temperature Tstg -55...+150 C
Soldering temperature, 1.6mm (0.063 in.) from case for 10s - 260
1
J-STD-020 and JESD-022
2)
Value limited by bond wire
3)
Allowed number of short circuits: <1000; time between short circuits: >1s.
IFAG IPC TD VLS 1 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
Thermal Resistance
Parameter Symbol Conditions Max. Value Unit
Characteristic
IGBT thermal resistance, RthJC 0.45 K/W
junction – case
Diode thermal resistance, RthJCD 0.8
junction – case
Thermal resistance, RthJA 40
junction – ambient
Electrical Characteristic, at Tj = 25 C, unless otherwise specified
Value
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
min. Typ. max.
Static Characteristic
Collector-emitter breakdown voltage V ( B R ) C E S V G E = 0V , I C = 0 .2m A 600 - - V
Collector-emitter saturation voltage VCE(sat) V G E = 15 V , I C = 50 A
T j =2 5 C - 1.5 2
T j =1 7 5 C - 1.9 -
Diode forward voltage VF V G E = 0V , I F = 5 0 A
T j =2 5 C - 1.65 2.05
T j =1 7 5 C - 1.6 -
Gate-emitter threshold voltage VGE(th) I C = 0. 8m A, V C E = V G E 4.1 4.9 5.7
Zero gate voltage collector current ICES V C E = 60 0 V , µA
V G E = 0V
T j =2 5 C - - 40
T j =1 7 5 C - - 3500
Gate-emitter leakage current IGES V C E = 0V , V G E =2 0 V - - 100 nA
Transconductance gfs V C E = 20 V , I C = 50 A - 31 - S
Integrated gate resistor RGint - Ω
Dynamic Characteristic
Input capacitance Ciss V C E = 25 V , - 3140 - pF
Output capacitance Coss V G E = 0V , - 200 -
Reverse transfer capacitance Crss f= 1 MH z - 93 -
Gate charge QGate V C C = 48 0 V, I C =5 0 A - 310 - nC
V G E = 15 V
Internal emitter inductance LE - 13 - nH
measured 5mm (0.197 in.) from case
1)
Short circuit collector current IC(SC) V G E = 15 V ,t S C 5 s - 458.3 - A
V C C = 4 0 0 V,
T j 1 50 C
1)
Allowed number of short circuits: <1000; time between short circuits: >1s.
IFAG IPC TD VLS 2 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
Switching Characteristic, Inductive Load, at Tj=25 C
Value
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
min. Typ. max.
IGBT Characteristic
Turn-on delay time td(on) T j=25 C, - 26 - ns
VCC=400V,IC=50A,
Rise time tr VGE=0/15V,rG=7, - 29 -
Turn-off delay time td(off) L =103nH,C=39pF - 299 -
L , C f rom Fig. E
Fall time tf Energy losses include - 29 -
Turn-on energy Eon “tail” and diode reverse - 1.2 - mJ
recovery.
Turn-off energy Eoff - 1.4 -
Total switching energy Ets - 2.6 -
Anti-Parallel Diode Characteristic
Diode reverse recovery time trr T j =2 5 C , - 143 - ns
Diode reverse recovery charge Qrr V R = 4 00 V , I F = 5 0 A, - 1.8 - µC
Diode peak reverse recovery current Irrm d i F / d t =1 2 80 A / s - 27.7 - A
Diode peak rate of fall of reverse d i r r /d t - 671 - A/s
recovery current during t b
Switching Characteristic, Inductive Load, at Tj=175 C
Value
Parameter Symbol Conditions Unit
min. Typ. max.
IGBT Characteristic
Turn-on delay time td(on) T j=175 C, - 27 - ns
VCC=400V,IC=50A,
Rise time tr VGE=0/15V,rG=7, - 33 -
Turn-off delay time td(off) L =103nH,C=39pF - 341 -
L , C f rom Fig. E
Fall time tf Energy losses include - 55 -
Turn-on energy Eon “tail” and diode reverse - 1.8 - mJ
recovery.
Turn-off energy Eoff - 1.8 -
Total switching energy Ets - 3.6 -
Anti-Parallel Diode Characteristic
Diode reverse recovery time trr T j =1 7 5 C - 205 - ns
Diode reverse recovery charge Qrr V R = 4 00 V , I F = 5 0 A, - 4.3 - µC
Diode peak reverse recovery current Irrm d i F / d t =1 2 80 A / s - 40.7 - A
Diode peak rate of fall of reverse d i r r /d t - 449 - A/s
recovery current during t b
IFAG IPC TD VLS 3 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
t p=2µs
140A 100A
120A
10µs
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
100A
T C =80°C
80A 10A 50µs
T C =110°C
60A
40A Ic
1ms
20A Ic 1A DC 10ms
0A
100H z 1kH z 10kHz 100kH z
1V 10V 100V 1000V
f, SWITCHING FREQUENCY VCE, COLLECTOR-EMITTER VOLTAGE
Figure 1. Collector current as a function of Figure 2. Safe operating area
switching frequency (D = 0, TC = 25C, Tj 175C;
(Tj 175C, D = 0.5, VCE = 400V, VGE=0/15V)
VGE = 0/15V, rG = 7)
300W
80A
Ptot, POWER DISSIPATION
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
250W
60A
200W
150W 40A
100W
20A
50W
0A
0W
25°C 50°C 75°C 100°C 125°C 150°C 25°C 75°C 125°C
TC, CASE TEMPERATURE TC, CASE TEMPERATURE
Figure 3. Power dissipation as a function of Figure 4. Collector current as a function of
case temperature case temperature
(Tj 175C) (VGE 15V, Tj 175C)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 4 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
120A 120A
V G E =20V V G E =20V
100A 100A
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
15V 15V
80A 13V 13V
80A
11V 11V
60A 9V 60A 9V
7V 7V
40A 40A
20A 20A
0A 0A
0V 1V 2V 3V 0V 1V 2V 3V 4V
VCE, COLLECTOR-EMITTER VOLTAGE VCE, COLLECTOR-EMITTER VOLTAGE
Figure 5. Typical output characteristic Figure 6. Typical output characteristic
(Tj = 25°C) (Tj = 175°C)
VCE(sat), COLLECTOR-EMITT SATURATION VOLTAGE
2.5V IC =100A
80 A
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT
2.0V
60 A
IC =50A
1.5V
40 A
1.0V IC =25A
20 A T J = 17 5 °C
0.5V
2 5 °C
0A 0.0V
0V 2V 4V 6V 8V 0°C 50°C 100°C 150°C
VGE, GATE-EMITTER VOLTAGE TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
Figure 7. Typical transfer characteristic Figure 8. Typical collector-emitter
(VCE=10V) saturation voltage as a function of
junction temperature
(VGE = 15V)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 5 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
t d(off)
t d(off)
t, SWITCHING TIMES
t, SWITCHING TIMES
100ns tr
tf
100ns
tf
t d(on)
tr
10ns t d(on )
10ns
0A 20A 40 A 60A 80 A
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT RG, GATE RESISTOR
Figure 9. Typical switching times as a Figure 10. Typical switching times as a
function of collector current function of gate resistor
(inductive load, TJ=175°C, (inductive load, TJ = 175°C,
VCE = 400V, VGE = 0/15V, rG = 7Ω, VCE= 400V, VGE = 0/15V, IC = 50A,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E) Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
7V
t d (off) 6V
VGE(th), GATE-EMITT TRSHOLD VOLTAGE
m ax.
typ.
5V
t, SWITCHING TIMES
100n s
4V m in.
tf
3V
tr
2V
t d(on)
1V
10 ns 0V
25°C 50 °C 75°C 100°C 12 5°C 150°C -50°C 0°C 50°C 100°C 150°C
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
Figure 11. Typical switching times as a Figure 12. Gate-emitter threshold voltage as
function of junction temperature a function of junction temperature
(inductive load, VCE = 400V, (IC = 0.8mA)
VGE = 0/15V, IC = 50A, rG=7Ω,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 6 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
*) Eon and Ets include losses *) E on a nd E ts in clu d e lo ss e s
Ets*
due to diode recovery
6 .0m J d u e to d io d e rec o v e ry
8.0mJ
E ts *
E, SWITCHING ENERGY LOSSES
E, SWITCHING ENERGY LOSSES
5 .0m J
6.0mJ
Eon* 4 .0m J
4.0mJ 3 .0m J
Eoff E off
2 .0m J
2.0mJ
E on *
1 .0m J
0.0mJ 0 .0m J
0A 20A 40A 60A 80A
IC, COLLECTOR CURRENT RG, GATE RESISTOR
Figure 13. Typical switching energy losses Figure 14. Typical switching energy losses
as a function of collector current as a function of gate resistor
(inductive load, TJ = 175°C, (inductive load, TJ = 175°C,
VCE = 400V, VGE = 0/15V, rG = 7Ω, VCE = 400V, VGE = 0/15V, IC = 50A,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E) Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
*) Eon and Ets include losses *) E on and E ts include losses
due to diode recovery due to diode recovery
Ets* 4m J
E, SWITCHING ENERGY LOSSES
E, SWITCHING ENERGY LOSSES
3.0mJ
3m J E on *
E ts *
2.0mJ
Eoff
2m J
E off
1.0mJ
Eon*
1m J
0.0mJ 0m J
25°C 50°C 75°C 100°C 125°C 150°C 300V 350V 400V 450V 500V 550V
TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE VCE, COLLECTOR-EMITTER VOLTAGE
Figure 15. Typical switching energy losses Figure 16. Typical switching energy losses
as a function of junction as a function of collector emitter
temperature voltage
(inductive load, VCE = 400V, (inductive load, TJ = 175°C,
VGE = 0/15V, IC = 50A, rG = 7Ω, VGE = 0/15V, IC = 50A, rG = 7Ω,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E) Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 7 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
C iss
VGE, GATE-EMITTER VOLTAGE
15V 1nF
c, CAPACITANCE
120V
480V
10V
C oss
5V 100pF
C rss
0V 0V 10V 20V 30V 40V
0nC 100nC 200nC 300nC
QGE, GATE CHARGE VCE, COLLECTOR-EMITTER VOLTAGE
Figure 17. Typical gate charge Figure 18. Typical capacitance as a function
(IC=50 A) of collector-emitter voltage
(VGE=0V, f = 1 MHz)
12µs
800A
IC(sc), short circuit COLLECTOR CURRENT
tSC, SHORT CIRCUIT WITHSTAND TIME
700A 10µs
600A
8µs
500A
6µs
400A
300A 4µs
200A
2µs
100A
0µs
0A 10V 11V 12V 13V 14V
12V 14V 16V 18V
VGE, GATE-EMITTETR VOLTAGE VGE, GATE-EMITETR VOLTAGE
Figure 19. Typical short circuit collector Figure 20. Short circuit withstand time as a
current as a function of gate- function of gate-emitter voltage
emitter voltage (VCE=400V, start at TJ=25°C,
(VCE 400V, Tj 150C) TJmax<150°C)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 8 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
10 K/W
D=0.5 D=0.5
ZthJC, TRANSIENT THERMAL IMPEDANCE
ZthJC, TRANSIENT THERMAL IMPEDANCE
-1 0.2 0.2
10 K/W
0.1 -1 0.1
10 K/W
R,(K/W) , (s)
0.18355 7.425*10-2 R,(K/W) , (s)
0.05
0.12996 8.34*10-3 0.2441 7.037*10-2 6.53*10
0.05
0.09205 7.235*10-4 0.2007 7.312*10-3
0.03736 1.035*10-4 0.1673 6.431*10-4
0.00703 4.45*10-5 0.02 0.1879 4.79*10-5
-2 0.02 R1 R2 R1 R2
10 K/W
0.01
0.01 -2
10 K/W
C 1 = 1 /R 1 C 2 = 2 /R 2 C1= 1/ R1 C 2 = 2 /R 2
single pulse single pulse
1µs 10µs 100µs 1ms 10ms 100ms 1µs 10µs 100µs 1ms 10ms 100ms
tP, PULSE WIDTH tP, PULSE WIDTH
Figure 21. IGBT transient thermal Figure 22. Diode transient thermal
impedance impedance as a function of pulse
(D = tp / T) width
(D=tP/T)
300ns 4.0µC
TJ=175°C T J =175°C
Qrr, REVERSE RECOVERY CHARGE
3.5µC
trr, REVERSE RECOVERY TIME
250ns
3.0µC
200ns 2.5µC
2.0µC
150ns
TJ=25°C 1.5µC
100ns T J=25°C
1.0µC
50ns 0.5µC
0.0µC
0ns 700A/µs 800A/µs 900A/µs 1000A/µs
700A/µs 800A/µs 900A/µs 1000A/µs
diF/dt, DIODE CURRENT SLOPE diF/dt, DIODE CURRENT SLOPE
Figure 23. Typical reverse recovery time as Figure 24. Typical reverse recovery charge
a function of diode current slope as a function of diode current
(VR=400V, IF=50A, slope
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E) (VR = 400V, IF = 50A,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
IFAG IPC TD VLS 9 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
40A T J =175°C
-750A/µs
Irr, REVERSE RECOVERY CURRENT
OF REVERSE RECOVERY CURRENT
T J=25°C
dirr/dt, DIODE PEAK RATE OF FALL
30A -600A/µs
T J =25°C
-450A/µs
20A T J=175°C
-300A/µs
10A
-150A/µs
0A/µs
0A 700A/µs 800A/µs 900A/µs 1000A/µs
700A/µs 800A/µs 900A/µs 1000A/µs
diF/dt, DIODE CURRENT SLOPE diF/dt, DIODE CURRENT SLOPE
Figure 25. Typical reverse recovery current Figure 26. Typical diode peak rate of fall of
as a function of diode current reverse recovery current as a
slope function of diode current slope
(VR = 400V, IF = 50A, (VR=400V, IF=50A,
Dynamic test circuit in Figure E) Dynamic test circuit in Figure E)
120A I F =100A
2.0V
100A
VF, FORWARD VOLTAGE
IF, FORWARD CURRENT
T J =25°C
1.5V 50A
80A 175°C
25A
60A 1.0V
40A
0.5V
20A
0A 0.0V
0V 1V 2V 0°C 50°C 100°C 150°C
VF, FORWARD VOLTAGE TJ, JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
Figure 27. Typical diode forward current as Figure 28. Typical diode forward voltage as a
a function of forward voltage function of junction temperature
IFAG IPC TD VLS 10 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
IFAG IPC TD VLS 11 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
i,v
diF /dt tr r =tS +tF
Qr r =QS +QF
tr r
IF tS tF
QS 10% Ir r m t
QF
Ir r m
dir r /dt VR
90% Ir r m
Figure C. Definition of diodes
switching characteristics
1 2 n
r1 r2 rn
Tj (t)
p(t)
r1 r2 rn
Figure A. Definition of switching times
TC
Figure D. Thermal equivalent
circuit
Figure B. Definition of switching losses
IFAG IPC TD VLS 12 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
IKW50N60T
TRENCHSTOP™ Series q
Published by
Infineon Technologies AG
81726 Munich, Germany
© 2013 Infineon Technologies AG
All Rights Reserved.
Legal Disclaimer
The information given in this document shall in no event be regarded as a guarantee of conditions or
characteristics. With respect to any examples or hints given herein, any typical values stated herein and/or
any information regarding the application of the device, Infineon Technologies hereby disclaims any and all
warranties and liabilities of any kind, including without limitation, warranties of non-infringement of intellectual
property rights of any third party.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices, please contact the nearest
Infineon Technologies Office (www.infineon.com).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements, components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the
types in question, please contact the nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
The Infineon Technologies component described in this Data Sheet may be used in life-support devices or
systems and/or automotive, aviation and aerospace applications or systems only with the express written
approval of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the
failure of that life-support, automotive, aviation and aerospace device or system or to affect the safety or
effectiveness of that device or system. Life support devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the
human body or to support and/or maintain and sustain and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable
to assume that the health of the user or other persons may be endangered.
IFAG IPC TD VLS 13 Rev. 2.6 20.09.2013
You might also like
- CRG40T60AN3HDocument9 pagesCRG40T60AN3HVadim PopovichNo ratings yet
- "Air Control 2": 1. GeneralDocument32 pages"Air Control 2": 1. GeneralmadiNo ratings yet
- Ahf Maintenance GuidelinesDocument3 pagesAhf Maintenance GuidelinesSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Infineon Ikw50n60t Ds v02 06 EnDocument13 pagesInfineon Ikw50n60t Ds v02 06 Enmjesion1No ratings yet
- IKW50N60TDocument13 pagesIKW50N60TTspi RitzelNo ratings yet
- Infineon IKP - W20N60T DS v02 - 08 ENDocument13 pagesInfineon IKP - W20N60T DS v02 - 08 ENshivguptaNo ratings yet
- K30T60 InfineonTechnologiesDocument13 pagesK30T60 InfineonTechnologieskhawar mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Ikw75n60t TeslaDocument14 pagesIkw75n60t TeslaRaduNo ratings yet
- Ikw30n60t - Igbt K30T60Document13 pagesIkw30n60t - Igbt K30T60Arya WijanarkaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 9Document14 pagesDatasheet 9surya.ach57No ratings yet
- H40T60 InfineonDocument12 pagesH40T60 InfineonSutirtha MaitiNo ratings yet
- Ikw25N120T2: Low Loss DuopackDocument15 pagesIkw25N120T2: Low Loss DuopackJesus CotrinaNo ratings yet
- SKW25N120: Fast IGBT in NPT-technology With Soft, Fast Recovery Anti-Parallel Emitter Controlled DiodeDocument13 pagesSKW25N120: Fast IGBT in NPT-technology With Soft, Fast Recovery Anti-Parallel Emitter Controlled DiodeDhanil PattaliNo ratings yet
- K20N60 Infineon PDFDocument13 pagesK20N60 Infineon PDFranduNo ratings yet
- IKW75N60TDocument13 pagesIKW75N60TY Automation (Jean)No ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument13 pagesDatasheetMundo GGNo ratings yet
- SKB06N60 Rev2 3G-48108Document14 pagesSKB06N60 Rev2 3G-48108charlydigitalNo ratings yet
- H40T120 InfineonDocument14 pagesH40T120 InfineonTharanga Kumara PriyadarshanaNo ratings yet
- SGW50N60HS: High Speed IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument11 pagesSGW50N60HS: High Speed IGBT in NPT-technologyPIKO MOBNo ratings yet
- SGW25N120: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument11 pagesSGW25N120: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyaffes electroniqueNo ratings yet
- SGW25N120Document11 pagesSGW25N120yayayalyayayaNo ratings yet
- IHW20N120R2Document12 pagesIHW20N120R2yayayalyayayaNo ratings yet
- SGW15N60Document14 pagesSGW15N60ZekoNo ratings yet
- S, D - 100A, 600v, Igp50n60t, 333w, 150v (Max) PDFDocument14 pagesS, D - 100A, 600v, Igp50n60t, 333w, 150v (Max) PDFManuel SierraNo ratings yet
- K40T120 InfineonDocument16 pagesK40T120 InfineonSyed Danish ShahNo ratings yet
- MBQ50T65FESCDocument8 pagesMBQ50T65FESCAlanWeissNo ratings yet
- IHW20N120R2: Reverse Conducting IGBT With Monolithic Body DiodeDocument12 pagesIHW20N120R2: Reverse Conducting IGBT With Monolithic Body Diodees9857No ratings yet
- IHW15N120R2: Reverse Conducting IGBT With Monolithic Body DiodeDocument12 pagesIHW15N120R2: Reverse Conducting IGBT With Monolithic Body DiodehoaNo ratings yet
- TGH80N65F2DS Finaldatasheet Rev0.1.0Document9 pagesTGH80N65F2DS Finaldatasheet Rev0.1.0Candra ErwinantoNo ratings yet
- TGH80N65F2D2 Finaldatasheet Rev0.0.0Document9 pagesTGH80N65F2D2 Finaldatasheet Rev0.0.0Candra ErwinantoNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor KGT25N120NDH: Technical DataDocument8 pagesSemiconductor KGT25N120NDH: Technical DataAnonymous oyUAtpKNo ratings yet
- SGP30N60 SGW30N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument12 pagesSGP30N60 SGW30N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyNikethana RamanayakaNo ratings yet
- MSG40T65FHDocument5 pagesMSG40T65FHisaiasvaNo ratings yet
- MBQ 50 T 65 FDSCDocument10 pagesMBQ 50 T 65 FDSCisaiasvaNo ratings yet
- MBQ25T120FESC: High Speed Fieldstop Trench IGBTDocument10 pagesMBQ25T120FESC: High Speed Fieldstop Trench IGBTToli ToliNo ratings yet
- SGP15N60 SGW15N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument11 pagesSGP15N60 SGW15N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyMuhammad ZamanNo ratings yet
- Igbt 030a, 600v, SGP - w30n60hs-Ds, Alto Vel.Document12 pagesIgbt 030a, 600v, SGP - w30n60hs-Ds, Alto Vel.Manuel SierraNo ratings yet
- SGP30N60HS SGW30N60HS: High Speed IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument12 pagesSGP30N60HS SGW30N60HS: High Speed IGBT in NPT-technologyGaby FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Mbq40T120Fes: High Speed Fieldstop Trench IgbtDocument8 pagesMbq40T120Fes: High Speed Fieldstop Trench IgbtgilamadaNo ratings yet
- MBQ50T65FESC MagnaChipDocument8 pagesMBQ50T65FESC MagnaChipFREDDY CHACON BOTELLONo ratings yet
- Ihw30N160R2: Trenchstop Reverse Conducting (RC-) Igbt With Monolithic Body DiodeDocument12 pagesIhw30N160R2: Trenchstop Reverse Conducting (RC-) Igbt With Monolithic Body DiodeuripdwNo ratings yet
- SRE60 N065 FSUD6 Datasheet V1Document12 pagesSRE60 N065 FSUD6 Datasheet V1sh msNo ratings yet
- GD50PIY120C6SDocument13 pagesGD50PIY120C6Sbwska3219424No ratings yet
- SGT40N60NPFDPN - Datasheet: 40A, 600V Field Stop IgbtDocument6 pagesSGT40N60NPFDPN - Datasheet: 40A, 600V Field Stop IgbtAnonymous nC9gpUWPNo ratings yet
- 40T65FDSCDocument10 pages40T65FDSCVladimir Gavuka100% (1)
- SGT40N60NPFDPN SilanDocument6 pagesSGT40N60NPFDPN SilanJonathan DutánNo ratings yet
- YGW60N65T1 Rev3Document8 pagesYGW60N65T1 Rev3Gregory FilonovNo ratings yet
- TGAN80N65F2DS Final Datasheet Rev3.0.0Document9 pagesTGAN80N65F2DS Final Datasheet Rev3.0.0Candra ErwinantoNo ratings yet
- tgan40n60f2dsDocument9 pagestgan40n60f2dshs31264579No ratings yet
- MBQ60T65PESTHDocument8 pagesMBQ60T65PESTHJuan Sebastian Arenas100% (1)
- SGP04N60, SGB04N60 SGD04N60, SGU04N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologyDocument12 pagesSGP04N60, SGB04N60 SGD04N60, SGU04N60: Fast IGBT in NPT-technologymhorfNo ratings yet
- IGBTDocument13 pagesIGBTEddy SanchezNo ratings yet
- Not Recommended: TSG60N100CEDocument9 pagesNot Recommended: TSG60N100CETERASAT SANo ratings yet
- MBQ40T65FESC: 650V Field Stop IGBTDocument8 pagesMBQ40T65FESC: 650V Field Stop IGBTJuan FerchoNo ratings yet
- GD50PJX65L3SDocument13 pagesGD50PJX65L3Stulio enrique leon ayalaNo ratings yet
- Afghl50t65sqdc 650v 50a 1,6v SicDocument11 pagesAfghl50t65sqdc 650v 50a 1,6v SicRaduNo ratings yet
- 40N60FL IgbtDocument9 pages40N60FL IgbtSius TécnicaNo ratings yet
- SGT 40 N 60 NPFDPNDocument5 pagesSGT 40 N 60 NPFDPNEzequiel HayesNo ratings yet
- Igbt DatasheetDocument8 pagesIgbt Datasheetkemal100% (1)
- TGAN80N60F2DSDocument9 pagesTGAN80N60F2DSJuan Carlos Vega HernandezNo ratings yet
- FGH4L50T65MQDC50 D-3225044Document10 pagesFGH4L50T65MQDC50 D-3225044cementsaimNo ratings yet
- xP270 e PDFDocument276 pagesxP270 e PDFEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- General Specifications: Axfa11G Magnetic Flowmeter Remote ConverterDocument10 pagesGeneral Specifications: Axfa11G Magnetic Flowmeter Remote ConverterEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Semipont 4: Power Bridge RectifiersDocument3 pagesSemipont 4: Power Bridge RectifiersEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Liebert Gxt4 230V, 5000-10,000VA: User ManualDocument56 pagesLiebert Gxt4 230V, 5000-10,000VA: User ManualEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKD 160 07913230 PDFDocument3 pagesSEMIKRON DataSheet SKD 160 07913230 PDFEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Semikron DatasheetDocument3 pagesSemikron DatasheetEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Delta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: e H T U B ADocument52 pagesDelta Programmable Logic Controller DVP Series: e H T U B AEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- K2611Document6 pagesK2611Emerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Bobina RogowskiDocument3 pagesBobina RogowskiEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ES7314-6CH04-0AB0: General InformationDocument16 pagesData Sheet 6ES7314-6CH04-0AB0: General InformationEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Description and Operating Instructions Industrial Ethernet Rail Switch Spider XTX (/XFX)Document8 pagesDescription and Operating Instructions Industrial Ethernet Rail Switch Spider XTX (/XFX)Emerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Commercial Accelerometers of Different TechnologiesDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of Commercial Accelerometers of Different TechnologiesEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Multimetro Rishab 18 PDFDocument7 pagesMultimetro Rishab 18 PDFEmerson Müller Juarez Avila100% (1)
- K300 ML1400 Indexing Example v1 0 PDFDocument7 pagesK300 ML1400 Indexing Example v1 0 PDFEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications: Absolute Maximum RatingsDocument5 pagesPower Amplifier Applications Power Switching Applications: Absolute Maximum RatingsEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- 120 X 120 X 38 MM SERIES: Dimensions DrawingDocument2 pages120 X 120 X 38 MM SERIES: Dimensions DrawingEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- SunonDocument4 pagesSunonEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Product Overview: BD682: 4.0 A, 100 V PNP Darlington Bipolar Power TransistorDocument1 pageProduct Overview: BD682: 4.0 A, 100 V PNP Darlington Bipolar Power TransistorEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- 3AUA0000002547 Ip21 3 Phase PhaseDocument2 pages3AUA0000002547 Ip21 3 Phase PhaseEmerson Müller Juarez AvilaNo ratings yet
- Jallib Tutorial BookDocument164 pagesJallib Tutorial Bookjesito2010No ratings yet
- Quizizz: CC221-QUIZ3Document107 pagesQuizizz: CC221-QUIZ3Darwin VargasNo ratings yet
- JBL Flip 6 ManualDocument11 pagesJBL Flip 6 Manualjev_ssNo ratings yet
- Model 1Document124 pagesModel 1shilpasusanNo ratings yet
- Hog-163 Encoder BAUMER PDFDocument4 pagesHog-163 Encoder BAUMER PDFthanggimme.phanNo ratings yet
- Prosoft MVI56E-MCMRDocument3 pagesProsoft MVI56E-MCMRiedmondNo ratings yet
- Phone CircuitsDocument24 pagesPhone CircuitsMike White100% (1)
- Choosing A Projector For Your DIY Multi-Touch Table - Multi-Touch InterfacesDocument5 pagesChoosing A Projector For Your DIY Multi-Touch Table - Multi-Touch Interfacesrares_draganNo ratings yet
- DEBUGDocument11 pagesDEBUGria ramadhiyaniNo ratings yet
- 21ECL305Document3 pages21ECL305jjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 SelcalDocument10 pagesChapter 7 SelcalDesti RakalNo ratings yet
- WIFIDocument8 pagesWIFIswathiNo ratings yet
- DriverDocument5 pagesDriverHanks ZetaNo ratings yet
- SamyangDocument3 pagesSamyangMahfooz AliNo ratings yet
- Transistor Rca Sa 5010 - Recherche Google Web 1Document3 pagesTransistor Rca Sa 5010 - Recherche Google Web 1rosaire lessardNo ratings yet
- Urban Antenna DesignDocument214 pagesUrban Antenna Designcalinkgb78% (9)
- Basic DC DC Converter CalculatorDocument2 pagesBasic DC DC Converter CalculatorLukmanLoekmanNo ratings yet
- Hilti Tcu-7-36Document7 pagesHilti Tcu-7-36ManuelNo ratings yet
- Optical Networking: Synchronous Optical Network (Sonet)Document16 pagesOptical Networking: Synchronous Optical Network (Sonet)api-26172869No ratings yet
- Kxns 500Document92 pagesKxns 500محمد الأمينNo ratings yet
- Fourier MathcadDocument11 pagesFourier MathcadAlberto OlveraNo ratings yet
- Bub323z DDocument8 pagesBub323z Dtomoyo2009No ratings yet
- Novel Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter With Reduced Components For Low-And High-Voltage ApplicationsDocument10 pagesNovel Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter With Reduced Components For Low-And High-Voltage ApplicationsLawiii KkkNo ratings yet
- Toshiba Portege R830Document13 pagesToshiba Portege R830Juswadji SudionoNo ratings yet
- 328Document22 pages328raom_2No ratings yet
- Calibration TablesDocument24 pagesCalibration TablesNatthaphon NaosookNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet (DOP-107EV)Document8 pagesInstruction Sheet (DOP-107EV)vefonseca24No ratings yet
- Mims, Forrest M. - Introduction To Transistors & Transistor Projects-Radio Shack (1972)Document116 pagesMims, Forrest M. - Introduction To Transistors & Transistor Projects-Radio Shack (1972)Polimeras Dimitris100% (1)