Section 3: Radians: AQA Core 2 Trigonometry
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsSection 3: Radians: AQA Core 2 Trigonometry
Uploaded by
wolfretonmathsAQA Core 2 Trigonometry
1 of 1 15/01/13 MEI
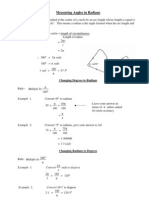
Section 3: Radians
Crucial points
1. Where possible, leave your answer in terms of
When an angle is a simple multiple or fraction of 180, then leave your
answers in terms of .
2. You must know the notation for angles in radians
When an angle is given as a multiple or fraction of you can assume it is
in radians.
Otherwise you write, say, 0.7 rads.
In some older textbooks 0.7 rads might be written as 0.7
c
.
3. Make sure that your calculator is in the right mode
Remember when you want to work out, say, sin
3
, make sure your
calculator is in rad mode.
4. Make sure that angles are in radians before using sector formulae
The formulae for arc length ( r ) and sector area (
2
1
2
r ) can only be used
when the angle, , is in radians.
To change degrees to radians multiply by
180
.
5. Make sure that your solutions lie in the required range
When you are solving a trigonometric equation make sure you check what
range the solutions are to lie in and give all the solutions within that range.
If the range is given in radians, e.g. 0 2 , then give your answers in
radians. If the range is given in degrees, e.g. 0 360 , then give your
answers in degrees.
6. You must know the relationship between the radius and tangent of a
circle
Remember that the radius of a circle and the tangent to a circle meet at
right angles.
You might also like
- Using Parametric Equations - Solutions PDFNo ratings yetUsing Parametric Equations - Solutions PDF4 pages
- All LESSON Handouts - Chapter 6 RevisedNo ratings yetAll LESSON Handouts - Chapter 6 Revised19 pages
- Trigonometric Functions: A Mathematician Knows How To Solve A Problem, He Can Not Solve It. - MILNE100% (2)Trigonometric Functions: A Mathematician Knows How To Solve A Problem, He Can Not Solve It. - MILNE37 pages
- Jee Mains Maths Notes Available in Word FormatNo ratings yetJee Mains Maths Notes Available in Word Format47 pages
- Pre Calculus Q4 Week 1 2 Angles in A Unit CircleNo ratings yetPre Calculus Q4 Week 1 2 Angles in A Unit Circle24 pages
- Obj. 17 Radian Measure: Unit 5 Trigonometric and Circular FunctionsNo ratings yetObj. 17 Radian Measure: Unit 5 Trigonometric and Circular Functions12 pages
- MathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14From EverandMathsTraks: Geometry: A Collection of Blackline Masters for ages 11-14No ratings yet
- Using Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDFNo ratings yetUsing Partial Fractions in Integration Exercise PDF1 page
- Vectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDFNo ratings yetVectors in Two & Three Dimensions Exercise PDF2 pages