Foliation and lineation
A fabric describes the spatial and geometric relationships that make up a rock at the microscopic to centimeter scale. It includes planar structures like bedding and cleavage, as well as the preferred orientation of minerals. Fabrics can be primary, forming during rock formation processes, or secondary and resulting from deformation. Foliation refers specifically to planar fabric and can develop through processes like cleavage, schistosity, and mylonitic foliation under increasing metamorphic conditions and deformation. Lineations describe linear fabric elements oriented in rocks, such as intersection lineations between planar features or mineral lineations showing preferred mineral alignments. Together, foliations and lineations define the tectonite class of a rock.
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Similar to Foliation and lineation
Similar to Foliation and lineation (20)
More from Md Asif Hasan
More from Md Asif Hasan (20)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Foliation and lineation
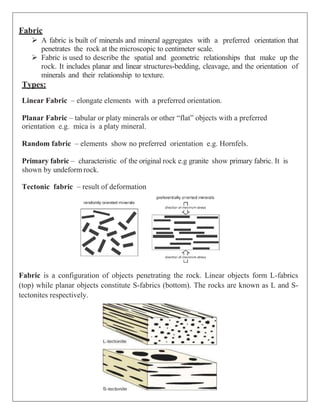
- 1. Fabric A fabric is built of minerals and mineral aggregates with a preferred orientation that penetrates the rock at the microscopic to centimeter scale. Fabric is used to describe the spatial and geometric relationships that make up the rock. It includes planar and linear structures-bedding, cleavage, and the orientation of minerals and their relationship to texture. Types: Linear Fabric – elongate elements with a preferred orientation. Planar Fabric – tabular or platy minerals or other “flat” objects with a preferred orientation e.g. mica is a platy mineral. Random fabric – elements show no preferred orientation e.g. Hornfels. Primary fabric – characteristic of the original rock e.g granite show primary fabric. It is shown by undeform rock. Tectonic fabric – result of deformation Fabric is a configuration of objects penetrating the rock. Linear objects form L-fabrics (top) while planar objects constitute S-fabrics (bottom). The rocks are known as L and S- tectonites respectively.
- 2. Foliation (planar textural elements): Folios = page or leaf-like. Fabric-forming planar structure is called foliation. Foliation is broadly defined as any planar arrangement of mineral grains /structural features in a rock. Structural geologist's definition: Planar fabric is secondary and due to mineral recrystallization and/or plastic behavior during deformation at elevated temperatures
- 3. Foliation is easily recognized if there is an alternate of quartz and feldspars with mica and amphibole. Types of foliation Primary foliation: Primary – forms during deposition of sediments and formation of magmatic rocks. In granite there is primary foliation. Flow banding in rhyolite or granite Flow foliation in dikes or other intrusives OR Structuresrelated to theoriginal rock-forming process. Originated by sedimentary processes such as transportanddeposition: Bedding (So) Preferred orientation of sedimentaryclasts Originated by primary igneous processes suchas lava flowandcrystallization: Magmatic layering inigneous rocks(cumulates Preferredorientation of bubblesandpumice fragments
- 4. Recognition of primary foliation Recognitionof primary foliationis importantfor the reconstruction of the structural evolution after sedimentation crystallization (So, S1, S2, etc.) SecondaryFoliation: Forms after lithification and/or crystallization of rocks Secondary foliation is the product of stress and strain (tectonic foliation). Examples are cleavage, schistosity, and mylonitic foliations. OR Secondary foliation—the result of microscopically penetrative deformation and distortion of sedimentary, volcanic, or intrusive igneous rocks, usually under metamorphic condition. Cleavage: Cleavage refers to the ability of a rock to split or cleave into more or less parallel surfaces
- 5. Cleavage Development Compaction cleavage develops due to reorientation of mineral grains and collapse of pore space. Some dissolution. Pencil cleavage develops due to tectonic stress and development of a secondary cleavage. Pressure solution important in it. In case of pencil cleavage clay minerals oriented in two planes. Slaty cleavage develops due to tectonic shortening, reorientation of clay grains, and solution of quartz. QF- and M-domains.
- 6. Slaty cleavage is used to describe rocks that split into thin, planar slabs when hit with a hammer. Slaty cleavage commonly occurs under low-grade metamorphic conditions Phyllitic Cleavage : (thin wavy foliation) In phyllitic cleavage QF- and M-domains become more pronounced because of increasing of grain size as temperature increase with depth.
- 7. Schistosity: Higher metamorphic grades lead to schistosity. Schistosity describes rocks with foliated mineral grains that are large enough to see without magnification Schistosity tends to affect all the different mineral components. Rocks with schistosity are generally referred to as schist. Gneissic foliation: Gneissic textures occur when the silicate minerals in the rock separate and recrystallized into alternating bands of light (quartz and feldspar) and dark (biotite, amphibole, or hornblende) grains of silicate minerals.
- 8. Crenulation cleavage develops when the principal stress direction changes. Symmetric versus asymmetric depends on the orientation of the original cleavage compared to that of the secondary cleavage. Cleavage develops perpendicular to the direction of shortening. Axial plane cleavage parallels the axial surface. Cleavage refraction occurs when cleavage crosses layers of varying viscosity or competency.
- 9. Styolitic Cleavage: Styolite is dissolution feature. This feature is found mostly in carbonate rocks e.g. limestone Mylonite foliation formed by shear-related plastic grain size reduction of a coarse-grained granitic rock. This fabric forms because of high non-coaxial strain and it is found in shear zones or thrust zones that involve large (kilometer scale or more) displacements. OR Mylonitic foliation: Forms due to grain-size reduction by a mix of brittle and plastic deformation in shear zones. Migmatite: Compositional banding due to in-situ partial melting. Swirly appearance. Flattening Fabric: In a conglomerate, flattened pebbles may define a foliation.
- 10. Tectonites • Rocks that are PERVADED by foliation, lineation and/or cleavage. S: Schistosity (foliation) only due to flattening- no lineation L: Lineation only, due to unidirectional stretching/ constriction LS: Foliation and Lineation, related to non coaxial strain- shearing OR L -tectonites Rocks that show a marked linear fabric (INDICATE CONSTRICTIONAL STRAIN) S tectonites Rocks showing pronounced planar fabric (FLATTENING STRAIN) LS tectonites Deformed rocks that contain both linear and planar fabric (PLANE STRAIN)
- 11. S-Surfaces All planar and some curved structures in deformed rocks i.e. Cleavage, foliations, and bedding S0 – Oldest surface, S1 – next oldest, etc. Fold Sets – F1, F2, etc. Linear Structures – L1, L2, etc. Deformation Structures – D1, D2, etc RELATIVE AGE TERMINOLOGY Lineation (linear textural elements) Fabric forming linear structure is called lineation. Parallelism or alignment of linear elements in the rock Types of lineations: We will focus on those that are related to deformation 1) Intersection 2) Crenulation 3) Mineral 4) Stretching
- 12. Intersection lineation (the most common): Intersection of two planar features- an "apparent" lineation in that there is no fabric that is linear OR Intersection lineations—formed by the intersection of any two foliations Bedding and cleavage (parallel to the fold axis) Cleavage and a second cleavage e.g.intersection between cleavage and planar surface
- 13. Crenulation lineation (best seen in hand specimen): Intersection between fold hinges and foliation Mineral lineation: preferred alignment of minerals due to deformation and/or recrystallization during deformation Aligned needle shaped grains (hornblende) Streaked or smeared mineral fibers Long axes of platy minerals like micas Stretching lineation: elongation of minerals due to "stretching" deformation Prepared By Md. Asif Hasan Geo 47
