Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Uploaded by
i232029Copyright:
Available Formats
Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Uploaded by
i232029Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Brain Gain Network A Proposal Egovernance Model To Convert The B
Uploaded by
i232029Copyright:
Available Formats
Brain Gain Network: A proposal e-govemance model to
convert the brain drain into brain gain
Md. Muntasir Mamun Joarder
Software Engineer, Dohatec New Media,
House # 60, Road SA, Dhanmondi WA, Dhaka-1209. Bangladesh
Email: svo97-12@hotmail.com
Abstract: It is observed that, the scientisfs. engineers and are described. Here in this section definition, causes ~
the highly educated and qualified scholars of the problems etc of brain drain are described. Section 3
developing countries are migrating in the developed describes the model and the govemance policy of
countries from their motherland. They appear as human proposed brain gain network in detail. In section 4 the
resources educated. trained through profissional pracfice positive effects of the proposed brain gain network are
and employed in much better conditions thon those the described.
country af their origin could have provided to them. If
such a counfry were able to use these resources largely 2. BRAIN DRAIN
shaped through others investments. it would gain a lor. In
this paper an e-governance model is presented to conven 2.1. What is brain drsin ?
fhis brain drain info gain by tracking and maintaining
these diversified brains of a developing country so that the Brain drain is the important species of the entire
migrated scholars get the oppor!uni@ to serve their genus of brain migration from LDCs (Low Developed
motherland remaining in remote from their counrry of Countries). The term “Brain Drain” is a loaded and
origin. A governance palicy is also proposed, in this paper, pejorative, suggestive of loss of vital resources, without
so that the government of a L D C (Low Developed compensation (Adaars, 1968). It is one way permanent
Country) can successfully and efficiently maintain this migration of skilled-people mostly from LDCs to DCs. In
netkwork to achieve maximum gain. easy words, brain drain is the process of intellectual or
professional resource of a country through immigration.
Keywordp: Brain drain. e-government. brain gain network
2.2. Causes of brain drain
1. INTRODUCTION
The causes:of brain drain are oflen seen in a bi-
The SESTAT database of the National Science polar model of “@lis" exerted by the immigration
Foundation (NSF) shows that in 1995, 1.434 million countries and “push” exerted factors operating in the
people (12%) out of the 12 million people who have emigration countries, in which differentials between the
science and engineering degrees or who work in science two determine the docision of the individual who migrates.
and engineering occupations in the U.S.A., are of foreign The pushes are depressing characteristics in the country of
origin[l]. Over 72% of these were originally born in a the origin, which produces emigration. O n the other hand,
developing country. When looking at the level of pull factors are the.’attracting feaNres in the country of
qualifications, it appears. that the higher the diploma the destination, which induce immigration. The push-pull
bigger -the propoltion of the foreign-born population[ I]. approach can give an important insight into the analysis of
These figures focus one thing that the highly educated brain migration [Z].Some of the important push and pull
scholars of developing countries are consuming their factors (as listed in Economics of Brain Migration’ by
brains for developed countries. And in most of the cases Ghosh and Ghosh, 1982). involved in brain migration
they are not renvning back to their motherland. They have from LDCs are given below:
often settled abroad and built their professional as well as
their personal life there. If such a low developed country Pushfactors:
were able to use these brains IargeJy shaped through 1) Under employment,
others’ investments, it would then gain a lot. There are two 2 ) Economic under development;
ways to implement the brain gain: either through the ntum 3) Low wagdsalary,
of thi expatriates to the country of origin or through their 4) political instability;
remote mobilization and association to its development. 5 ) Over production and under utilization or HQM;
The main objective focused throughout this paper is to 6) Lack of research and other facilities;
create the links through which they could effectively and 7) Lack of freedom;
8) Discrimination in appointment and promotion;
productively be connected to its development, without any
physical temporary or permanent r e m . An e-governance 9) Poor working facilities; .
model is proposed in this paper to maintain the links IO) Lack of scientific tradition and culture;
among these brains effectively so that they can participate 1 I) Unsuitable institution;
and contribute easily for their motherland. 12) Desire for a better urban life;
The remaining portion of this paper is organized in the 13) Desire for higher qualification and recognition;
following way. In section 2. the basics of the brain drain 14) Better career expectation;
424 Proceedings IEEE INMIC 2003
I S ) Lack of satisfactory working conditions, among the migrated brains so that they may contribute for
the betterment of their country of origin. The goal of this
Pullfactors: network is to make a common place of migrated scholars
I ) Better economic prospects; so that they may carry benefit for their govemment. These
2) Higher salary and income; migrated scholars will find a common place to gather.
3 ) Better level of living and way of life; They will be able to discuss on some constructive
4 ) Bener research facilities; planning, to arrange online meetings, conferences etc.
5 ) Modem educational system and bener opportunity for They also will be benefited through this gain network. One
higher qualifications: can help other and can ask for help to others. They can
6) Prestige of foreign training; share their knowledge and experiences among them and
7) Intellectual freedom. help their country providing valuable information,
8) Better working condition and better employment proposals etc.
opportunities;
9) Relative political stability; 3.1. Governance policy of Brain Gain Network
IO) Presence of a rich, scientific and cultural tradition;
1 I ) Attraction of urban centres; Throughout this section I will try to clarify the
12) Availability of experiencelsupponing staff; concept and policy to successfully maintain the gain
13) Frequent chances o f a lucky break in life; network.
14) Technological gap;
15) Allocation of substantial funds for research. 1. The government ofLDC have to create a new sector
for the maintenance of Gain network.
2.3. Problems for brain drain 2. There must be a office and a set of paid employees to
successfully maintain of the scholar database and to
The governments of LDCs expends lots of their do the related tasks inside the country. This may be
money for education and training purpose. They take called the main domestic branch of the gain network.
several initiatives to make their generation educated and 3. The first and the main task for this office will be to
skilled. People of these countries take education and collect the full data of the scholars who are already
training and prepare themselves as skilled personnel. migrated and to maintain a database to hold these
These skilled persons migrate to another developed records. This may be collected informing the
country in search for better life. They finally become embassies of LDCs in DCs. It is assumed that most
permanent citizen of those developed countries and of the migrated scholars can be tracked by this way.
consumes their brain and skill for the betterment of those These scholars will be informed about this
countries. So finally all the initiatives taken by the govemment initiative and will be provided their Gain
govemment become fruitless. Thus for the lack of network unique IDS.
management lots of LDCs are paying this loss. These 4. This gain network ofice have to set up a policy to
govemments prepare their people as skilled but in the long collect data of the outgoing scholars whether they are
tun these skilled people are seen of no work for their going out for education or job. They are also be given
motherland. their personal network IDS.
5. This network will maintain a website as a common
2.4. Probability in reducing brain drain gathering place. Through this website the registered
members will be able to log into and to update their
The probability to reduce skilled migration is status. The gain network domestic office will be
more or less impossible. There are several causes for that. responsible to provide the helping documents to the
Most of the points are provided as “push-pull” factors in network members for appropriately using that
section 1.l.b. So it is not possible to totally stop the website.
migration of scholars from LDCs to DCs. The DCs also 6. The domestic office will conduct a statistical research
require the brains from LDCs. Becaues the companies of and divide the total network in some effective work
DCs have to pay more wages to their citizens than that to zones. This will be the main work of this domestic
the foreign (migrated) workers. But from the viewpoint of office.
LDCs these low wage carry huge currency. So the The strategy of the research may be to collect
employer and the employee both remain satisfied. This is country wise migration statistics and then to divide
one of the major reasons that makes it impossible to stop the work zones analyzing that statistical report. While
the skilled migration from the LDCs to the DCs. creating zones some factors like communication
among the zone members, number of scholars in that
zone etc must be considered
3. BRAIN GAIN NETWORK 7. Then this office have to assign registered members
into their nearest zone and let them be informed. If in
A country whose main resource is the human the future any member shift hidher place he may
resource, faces brain drain [3]. The main theme behind this have to be re-assigned in another zone by the
proposed brain gain network is to trace and to make links administrators.
Proceedings IEEE INMlC 2003 425
8. The office will have to now develop two planning meeting, conduct short research on any
committees. that is the governing bodies. One will be project/problem. In one sentence, he will
for the domestic office and another will for remote communicate and discuss with his members, come to
scholars. I am discussing only the nature of the a final conclusion, prepare a documentation and
activities of the remote planning committee. This submit that to zone Co-ordinator. Any proposal, any
planning committee will be consisted of some posts: desire for contribution from any individual member
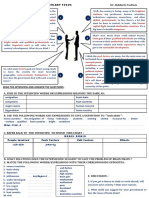
President, Zone Co-ordinator, Zonal President and will be known to zonal president. If this proposal be
zone members. an effective one zone co-ordinator will request the
president to propose that to the govemment.
President : When govemment of LDC will take any
development initiative "President" of the gain Zone Member: Zone member is a unit of the brain
network will be informed. Heishe will be requested gain network.
from the domestic office (actually from the
govemment) to submit a report within some due time 3.1. Plus points of Gain network over the LDCs
analyzing the problem so that the final plan be a rigid
one. President will inform the zone Co-ordinator and 1. Communication : Communication and tracking
request hidher to submit a summary report is the main advantage of the brain gain network.
consulting with the zonal presidents. On the other Through this network the govemment will get
hand, any proposal from the zone co-ordinator will the actual figure and the status for her scholars in
also be submitted to the domestic office by the abroad. Through this network there will create a
president. Chain of command is the major factor for straight communication between the
running gain network successfully. governments of LDCs and their migrated
scholars.
Zone CO-Ordinator: The brain gain network will be 2. Conrribution : By this network the migrated
divided into some zones. Each zone must have a scholars of LDCs will get the opportunity to
zonal president who will be selectedlelected among contribute for their country. They may desire to
the zone members. Zone co-ordinator will be the do something positive for their country by giving
controller of all the zonal presidents. Zone co- donation, technology and information.
ordinator will be liable to convey the order from the 3. Investment :There may be a lot of scholars of
network president to the zonal presidents. Zone Co- LDCs who are in several good companies with
ordinator will collect the final reports from the zonal good reputation, who can request those
presidents, compile them. prepare the summary companies to invest in their country of origin. If
reportlsolution and submit that to the president. On they have any desire to do something they will
the other hand, he/she will also submit any find the actual place to present their proposals.
development proposal from any zonal president to 4. Technolam' Tran$er : Government of LDC
the network president. may he informed about the current technology
through gain network. And thus can incorporate
those technologies in their country.
5. Accuracy : As the government will take
decisions from a bunch of scholars while
incorporating any major development so the
1
'1
Zanc to-Ordinator
accuracy in planning will be high.
6. Knowledge share: Sharing of knowledge will be
the main advantage through this network.
Covemment and the local citizens will get
advanced information. This will help the nation
to develop remaining synchronized with the
current world. Thus the gain network will play
role in development by reducing the digital gap.
7. Patriotism : This network will help forming
patriotism inside the migrated scholars.
4.CONCLUSION
Figure I : Organizational Communication Chart Thus the diversified gain network can be a great initiative
to successfully utilize the migrated brains of LDCs. In one
ZonaI Presiden/: Zonal president will pfay the main sense, it may be said that,,the more the skilled persons will
role to utilize hidher zone members to discuss the be in the DCs the more will be the country resources in
problem and to prepare a possible solution report and abroad and the country will be benefited. Thus the gain
submit it to the zone co-ordinator. He may arrange
426 Proceedings IEEE INMlC 2003
I
network will be a focus point to reduce the digital gap 1999, http:ilwww.unesco.orglmostlmeyer.htm
between the LDCs and the DCs.
121 Study of concepfs and causes of Brain Drain -A UN
'I
REFERENCES Reporl ",http:Nshikshanic.nic.in/cdSOyearsl~ST/H3
18TH301O2.htm
[ I ] Jean-Baptisre Meyer and Mercy Brown. "Scienfi/ic
DiasporaxA New Approach lo the Brain Drain", 131 Karim Kawar,Chairman,lnformationTechnology
Prepared for the World Conference on Science Association ,Jordan. " h u eNorex",
UNESCO. ICSU Budapest, Hungary, 26 June-l July http:/lwww.dse.de/eficVkawar.htm
Proceedings IEEE INMIC 2003 427
You might also like
- RGUHS BAMS Transcript Certificate FormatDocument3 pagesRGUHS BAMS Transcript Certificate Formatreseachinhealth100% (9)
- Brain Drain in PakistanDocument14 pagesBrain Drain in Pakistani232029No ratings yet
- A Study On The Impact of Brain Drain in Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesA Study On The Impact of Brain Drain in Indian Economyidharma1947No ratings yet
- (Forum 3) E-BookletDocument47 pages(Forum 3) E-BookletĐoàn Phương LinhNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain - Position Paper EssayDocument6 pagesBrain Drain - Position Paper EssayLizel GumadlasNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain DissertationDocument8 pagesBrain Drain DissertationPaperWritingServiceCanada100% (1)
- ldcr2012 ch4 en PDFDocument37 pagesldcr2012 ch4 en PDFAuuhotelarNo ratings yet
- 1 AnatomyofBrainDrain-APainfulReality1Document13 pages1 AnatomyofBrainDrain-APainfulReality1Ruthlyn LindorNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background of Studies: Individuals ("Human Capital") To Other Nations or JurisdictionsDocument18 pages1.1 Background of Studies: Individuals ("Human Capital") To Other Nations or JurisdictionssatyaNo ratings yet
- Ldcr2012 Ch4 enDocument37 pagesLdcr2012 Ch4 enAndrei PostelnicuNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain From PakistanDocument6 pagesBrain Drain From PakistanSajid Munir KalyarNo ratings yet
- PHD Literature ReviewDocument31 pagesPHD Literature ReviewAbdu KontaNo ratings yet
- Aferro Brain DrainDocument30 pagesAferro Brain DrainDan VNo ratings yet
- University Press of Florida Journal of Third World StudiesDocument25 pagesUniversity Press of Florida Journal of Third World StudiesbabawaleifeoluwaNo ratings yet
- Brain DrainDocument4 pagesBrain DrainankurNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Brain Drain in IndiaDocument5 pagesThesis On Brain Drain in Indiafjmzktm7100% (1)
- B 1Document25 pagesB 1Sabin SadafNo ratings yet
- Pak EconomyDocument22 pagesPak EconomyCh Arslan BashirNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain in NepalDocument4 pagesBrain Drain in NepalHimal SigdelNo ratings yet
- Brain DrainDocument2 pagesBrain DrainybreghtanNo ratings yet
- The Economic Consequences of 'Brain Drain' of The Best and Brightest - Microeconomic Evidence From Five CountriesDocument38 pagesThe Economic Consequences of 'Brain Drain' of The Best and Brightest - Microeconomic Evidence From Five CountriesselureinahpetsNo ratings yet
- cst462s Term Research ProjectDocument26 pagescst462s Term Research Projectapi-526073737No ratings yet
- Thesis On Brain DrainDocument6 pagesThesis On Brain DrainChristina Bauer100% (1)
- Thesis Statement On Brain DrainDocument8 pagesThesis Statement On Brain Drainmelissahewittpalmbay100% (2)
- Information TechnologDocument4 pagesInformation Technologmanazar hussainNo ratings yet
- TalkingPoints B4UDocument3 pagesTalkingPoints B4UDr. Priyanka JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document22 pagesChapter 10krupamayekarNo ratings yet
- Junior SeniorDocument4 pagesJunior SeniorferlynjoybayanNo ratings yet
- Brain DrainDocument3 pagesBrain DrainEzra AtëbeNo ratings yet
- 2 Bac - Brain Drain Reading An VocabDocument2 pages2 Bac - Brain Drain Reading An VocabSadiki Flta0% (1)
- Brain Drain-EditedDocument2 pagesBrain Drain-EditedChaimae SweetNo ratings yet
- Journal On The Brain Drain Effect To High EducationDocument6 pagesJournal On The Brain Drain Effect To High Educations_dyahNo ratings yet
- A012 Drishti Bhatia EconomicsDocument22 pagesA012 Drishti Bhatia EconomicsDrishti BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Consequences of Intellectual Migration of Human Capital in The Context of National SecurityDocument12 pagesCauses and Consequences of Intellectual Migration of Human Capital in The Context of National SecurityCat DeluxeNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain of Agriculture and Veterinary Graduates To Abroad: Evidence From NepalDocument9 pagesBrain Drain of Agriculture and Veterinary Graduates To Abroad: Evidence From NepalindrajitNo ratings yet
- Paper 5 TSPSCDocument133 pagesPaper 5 TSPSCsrihasNo ratings yet
- Brain Drain Causes and Implications (CSS Essay)Document7 pagesBrain Drain Causes and Implications (CSS Essay)Optimistic Pashteen100% (1)
- Brain DrainDocument2 pagesBrain DrainPedro ThunderNo ratings yet
- Problem of Brain Drain in IndiaDocument3 pagesProblem of Brain Drain in IndiaHardik PatelNo ratings yet
- Brain DrainDocument12 pagesBrain DrainCHEIKH TALEB ELEMINENo ratings yet
- Human Capital-Arresting The Brain - Drain PDFDocument13 pagesHuman Capital-Arresting The Brain - Drain PDFAlireza Shabani ShojaeiNo ratings yet
- Final Informatics Practices Class XiDocument348 pagesFinal Informatics Practices Class XisanyaNo ratings yet
- Test - 03 - GS - II - Dhyeya IAS PDFDocument63 pagesTest - 03 - GS - II - Dhyeya IAS PDFGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- National Knowledge Commission of India An OverviewDocument55 pagesNational Knowledge Commission of India An OverviewVishalNo ratings yet
- Thesis Knowledge TransferDocument4 pagesThesis Knowledge Transferpatricemillertulsa100% (2)
- Name:Spandan Banerjee Mobile:9474490581 Institution Name:Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math, Howrah-711202 Year of Study:2ndDocument6 pagesName:Spandan Banerjee Mobile:9474490581 Institution Name:Ramakrishna Mission Vidyamandira, Belur Math, Howrah-711202 Year of Study:2ndSpandan BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- TalkingPoints B4UDocument3 pagesTalkingPoints B4UDr. Priyanka JainNo ratings yet
- Brain DrainDocument5 pagesBrain DrainvikasbumcaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Brain DrainDocument8 pagesIntroduction of Brain Drainkrupamayekar0% (1)
- Ejiofor NyffDocument7 pagesEjiofor Nyffclark philip100% (1)
- Ch.4 Notes 12 Ied RisDocument3 pagesCh.4 Notes 12 Ied Risaryaharshit222No ratings yet
- The Presentation On "BRAIN-DRAIN": - Submitted by Udai Bagga DFMRM-03ADocument14 pagesThe Presentation On "BRAIN-DRAIN": - Submitted by Udai Bagga DFMRM-03AUdai BaggaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: BRAIN DRAIN 1Document13 pagesRunning Head: BRAIN DRAIN 1Prateekṣhyā PraneethaNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Knowledge Gap in Developing SocietiesDocument38 pagesBridging The Knowledge Gap in Developing SocietiesAung win tunNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 5global Labor MarketDocument31 pagesLesson 4 5global Labor MarketAndrea May PolvorosaNo ratings yet
- Young People - Coping With An Unpredictable Future: Reading ExerciseDocument3 pagesYoung People - Coping With An Unpredictable Future: Reading ExerciseNhân Lê100% (1)
- SAMPLE - Brain DrainDocument9 pagesSAMPLE - Brain Drainnyeinhtwehtwe96No ratings yet
- DSPGBROCHURES v3Document2 pagesDSPGBROCHURES v3Jillian DraughonNo ratings yet
- Presentation OnDocument15 pagesPresentation OnguptaankkurNo ratings yet
- The Smart Mission: NASA’s Lessons for Managing Knowledge, People, and ProjectsFrom EverandThe Smart Mission: NASA’s Lessons for Managing Knowledge, People, and ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationi232029No ratings yet
- 23I-2016 B Assignment#2Document10 pages23I-2016 B Assignment#2i232029No ratings yet
- Ayyub Khan EraDocument6 pagesAyyub Khan Erai232029No ratings yet
- Making DecisionsDocument22 pagesMaking Decisionsi232029No ratings yet
- Hydrology Lesson 2 Return Period, CDF and PDF: Stefania TameaDocument11 pagesHydrology Lesson 2 Return Period, CDF and PDF: Stefania TameaYuritza Velandia CastroNo ratings yet
- Thin Lenses: Prepared By: Jenno S. Lantaya, OdDocument31 pagesThin Lenses: Prepared By: Jenno S. Lantaya, OdKwenzie FortalezaNo ratings yet
- Solid in Air DiffusionDocument5 pagesSolid in Air DiffusionMicrosoft GamingNo ratings yet
- Limestone Object Cleaning - Local Museum Guide - Version 2.0Document30 pagesLimestone Object Cleaning - Local Museum Guide - Version 2.0Bhavana ChavanNo ratings yet
- ME 2204 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery TEST (I Unit) QNDocument2 pagesME 2204 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery TEST (I Unit) QNVignesh VickyNo ratings yet
- Enabling Natural Zero-Shot Prompting On Encoder Models Via Statement-TuningDocument16 pagesEnabling Natural Zero-Shot Prompting On Encoder Models Via Statement-TuningKayky RamosNo ratings yet
- List - Ipynb - ColabDocument6 pagesList - Ipynb - Colabvaishnaviware005No ratings yet
- Module 1 LangCulSocDocument25 pagesModule 1 LangCulSocdesiree viernesNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 (NS) September 2023 Test 3Document8 pagesGrade 8 (NS) September 2023 Test 3hlsetlalentoasecNo ratings yet
- Journal of Business Research: Maria Elena Baltazar HerreraDocument7 pagesJournal of Business Research: Maria Elena Baltazar HerreraYOMARY MORALESNo ratings yet
- Group no.8.RUPD AnalysisDocument82 pagesGroup no.8.RUPD AnalysisSantosh BansodeNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Date Sheet 2022 Fall Foc IubDocument53 pagesMid Term Date Sheet 2022 Fall Foc IubHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument15 pagesPumpJonathan Guzmán Mendoza100% (1)
- Ideas of Caring in Nursing PracticeDocument5 pagesIdeas of Caring in Nursing PracticeNoor AfifahNo ratings yet
- State Vs Shashi Tharoor Sec 91 Application PDF 1 1Document21 pagesState Vs Shashi Tharoor Sec 91 Application PDF 1 1Prakhar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/52Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/52Gaming Core.No ratings yet
- DWITIYA SOPAN LogDocument76 pagesDWITIYA SOPAN Logasmiyaaslam062007No ratings yet
- Research Methodology Lecture 2Document30 pagesResearch Methodology Lecture 2AyushNo ratings yet
- SHS - Annex F - Performance Evaluation Form - Jarapan ResthouseDocument57 pagesSHS - Annex F - Performance Evaluation Form - Jarapan ResthouseLovelie Wagas100% (1)
- Joao Capistrano de Abreu - Chapters of Brazil's Colonial History 1500-1800 (Library of Latin America) - Oxford University Press, USA (1998)Document271 pagesJoao Capistrano de Abreu - Chapters of Brazil's Colonial History 1500-1800 (Library of Latin America) - Oxford University Press, USA (1998)Israel Leite100% (1)
- DC Voltage Balancing and Current Sharing Control of Parallel Multiple Modules Static Var Generator Based On CPS SPWMDocument7 pagesDC Voltage Balancing and Current Sharing Control of Parallel Multiple Modules Static Var Generator Based On CPS SPWMFrancois DillingerNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Green Purchase Behavior A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument15 pagesFactors Affecting Green Purchase Behavior A Systematic Literature ReviewNgọc TrầnNo ratings yet
- QUALITIES FOR JOBS (Adjectives) : Join The Adjectives With Their DefinitionDocument4 pagesQUALITIES FOR JOBS (Adjectives) : Join The Adjectives With Their DefinitionZahariuc AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Morocco Ducted Inverter - FA SeriesDocument34 pagesMorocco Ducted Inverter - FA SeriesAbdellahJrhaidarNo ratings yet
- The Writing Process: Steps in Writing An EssayDocument17 pagesThe Writing Process: Steps in Writing An EssayNataļja BronfmaneNo ratings yet
- Michael Gane - Forest Strategy - Strategic Management and Sustainable Development For The Forest Sector (2007)Document422 pagesMichael Gane - Forest Strategy - Strategic Management and Sustainable Development For The Forest Sector (2007)Yanny ManggugubatNo ratings yet
- NCM 100j - ReviewerDocument5 pagesNCM 100j - ReviewerRAIANA MANIPOLNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Method: Name: - DateDocument1 pageThe Scientific Method: Name: - DateElleKaye MercadoNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Episode 1Document10 pagesFS 1 Episode 1Princess Ann PelandasNo ratings yet